Sintered composite main phase permanent magnet and preparation method thereof
A composite main phase and permanent magnet technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductors/transformers/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve problems such as inability to maintain high remanence Br, inconsistent distribution of magnetic properties, limited diffusion depth, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
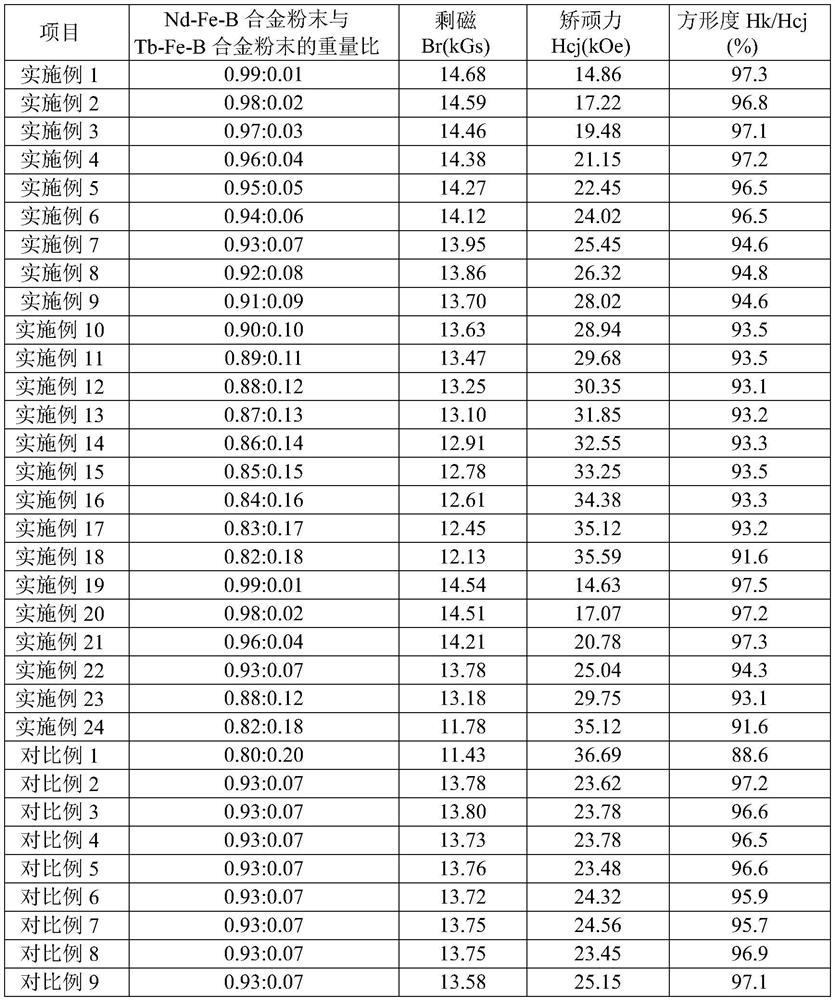
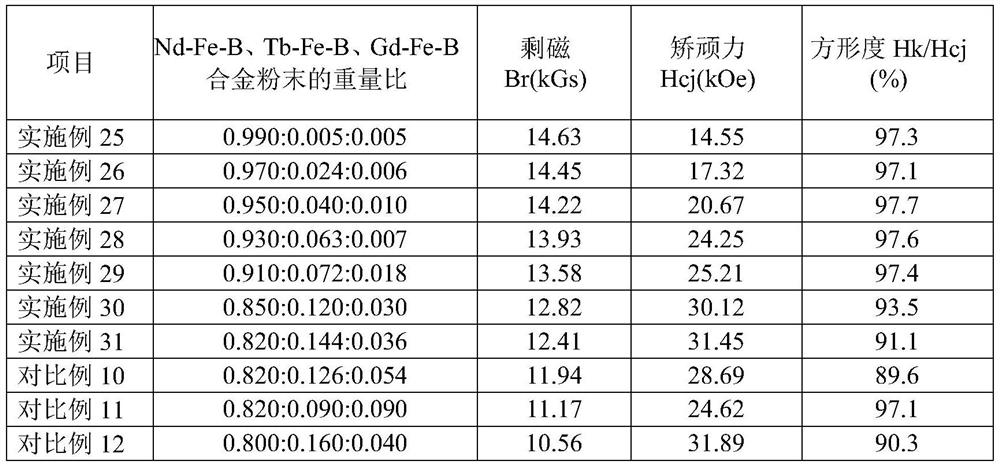
Embodiment 1~18
[0067] The chemical formula of the R-Fe-B alloy in the sintered R-Fe-B and HR-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets of Examples 1 to 18 of the present invention is Nd by atomic percentage 13.90 B5.75 co 1.00 Cu 0.30 Ga 0.20 Zn 0.10 Zr 0.05 Ti 0.10 Fe 余量 , and satisfy n 2Cu +n 2Zn ≥n 1Ga ; The chemical formula of HR-Fe-B alloy is Tb by atomic percentage 18.50 B 5.35 Cu 0.20 Ga 0.20 Zn 0.20 Fe 余量 , and satisfy n 2Ga +n 2Zr ≤n 2Cu +n 2Zn ≤2.0×n 2Ga ;
[0068] The sintered Nd-Fe-B and Tb-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets are made by the following steps:
[0069] Smelting: Nd-Fe-B alloy flakes are obtained after melting the raw materials of Nd-Fe-B alloy, with an average thickness of 0.358mm; Tb-Fe-B alloy flakes are obtained after melting the raw materials of Tb-Fe-B alloy, The average thickness is 0.347mm;
[0070] Crushing: Nd-Fe-B alloy flakes and Tb-Fe-B alloy flakes are hydrogen broken to form coarse powder;
[0071] Mixing: Nd-Fe-B allo...
Embodiment 19~24
[0076] The chemical formula of the R-Fe-B alloy in the sintered R-Fe-B and HR-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets of Examples 19 to 24 in the present invention is Nd by atomic percentage 13.75 B 5.80 co 1.20 Cu 0.20 Ga 0.10 Zn 0.10 Zr 0.15 Fe 余量 , and satisfy n 2Cu +n 2Zn ≥n 1Ga ; The chemical formula of HR-Fe-B is Tb by atomic percentage 17.50 B 5.45 Cu 0.20 Ga 0.20 Zn 0.10 Zr 0.10 Fe 余量 , and satisfy n 2Ga +n 2Zr ≤n 2Cu +n 2Zn ≤2.0×n 2Ga ;
[0077] The sintered Nd-Fe-B and Tb-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets are made by the following steps:
[0078] Melting: Smelting the Nd-Fe-B alloy raw materials to obtain Nd-Fe-B alloy flakes with an average thickness of 0.353mm; melting the Tb-Fe-B alloy raw materials to obtain Tb-Fe-B alloy ingots , with an average thickness of 1.95cm;
[0079] Crushing: Nd-Fe-B alloy flakes and Tb-Fe-B alloy ingots are respectively hydrogen broken to form Nd-Fe-B alloy coarse powder and Tb-Fe-B alloy coarse pow...
Embodiment 7、22
[0110] Compared with Comparative Examples 6, 7, and 8 in Examples 7 and 22, when the content of Cu, Zn, Ga, and Zr elements in the Tb-Fe-B alloy does not satisfy n 2Ga +n 2Zr ≤n 2Cu +n 2Zn ≤2.0×n 2Ga , the remanence Br and coercive force Hcj of sintered Nd-Fe-B and Tb-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets are lower, the main reason is that some Nd is formed in the Tb-Fe-B alloy 6 Fe 13 Cu and Nd 6 Fe 13 Ga-type compounds, Tb 2 Fe 17 Phase, TbFe 2 equal. These substances are magnetic, the saturation magnetization Js is low, and cannot effectively remove Nd 2 Fe 14 B.Tb 2 Fe 14 The inter-grain coupling effect of B main phase leads to low remanence Br and coercive force Hcj of sintered Nd-Fe-B and Tb-Fe-B composite main phase permanent magnets.
[0111] Compared with Comparative Example 9 in Examples 7 and 22, when the content of heavy rare earth HR elements in the Tb-Fe-B alloy increases to 23, the coercivity of the sintered Nd-Fe-B and Tb-Fe-B composite main...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com