Method for screening potential biomarker of prostate cancer and application thereof
A technology for biomarkers and prostate cancer, which is applied in the field of screening potential biomarkers of prostate cancer, and can solve problems such as the unclear mechanism of prostate cancer research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
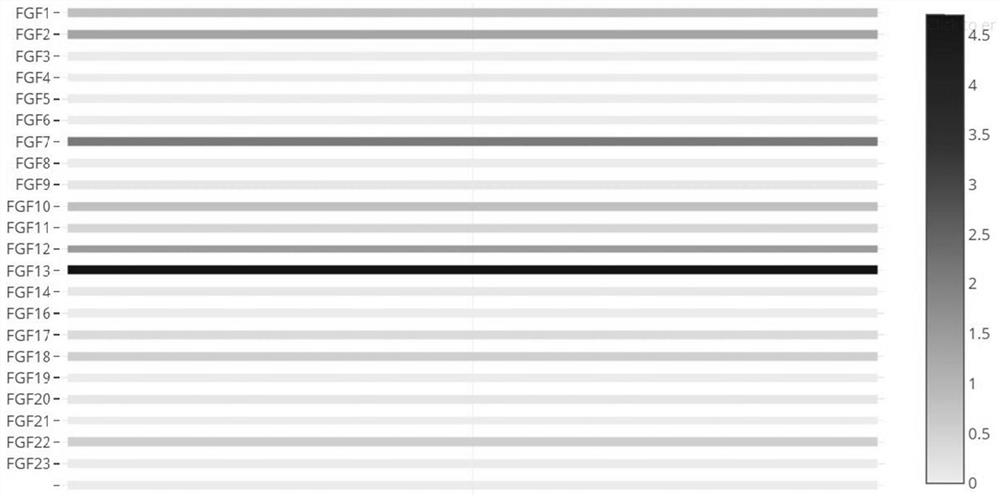
[0078] Previous studies have determined the general expression profile and function of some FGF family factors in prostate cancer. Based on this, the present invention selects FGF family genes as an example to carry out the method for screening potential biomarkers of prostate cancer mentioned in the present invention. Detailed description. It should be noted that the following content about FGF family genes and their upstream miRNAs, software versions used, etc., should only be understood as a convenience for those skilled in the art to more comprehensively grasp the analysis method of the present invention, rather than for the screening method of the present invention limitations.
[0079] A method for screening potential biomarkers of prostate cancer, comprising the steps of:
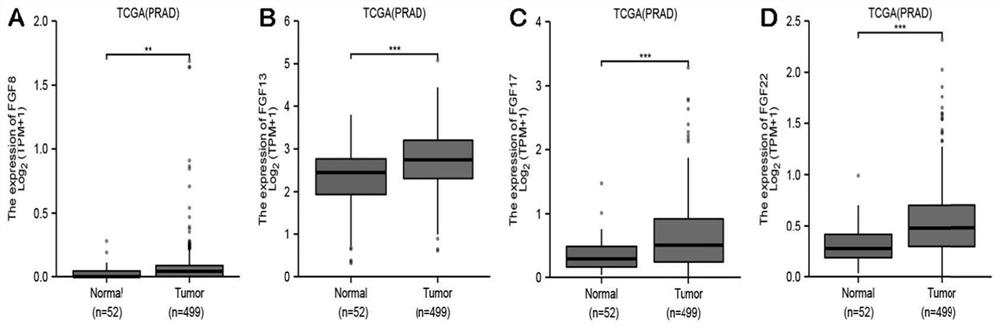
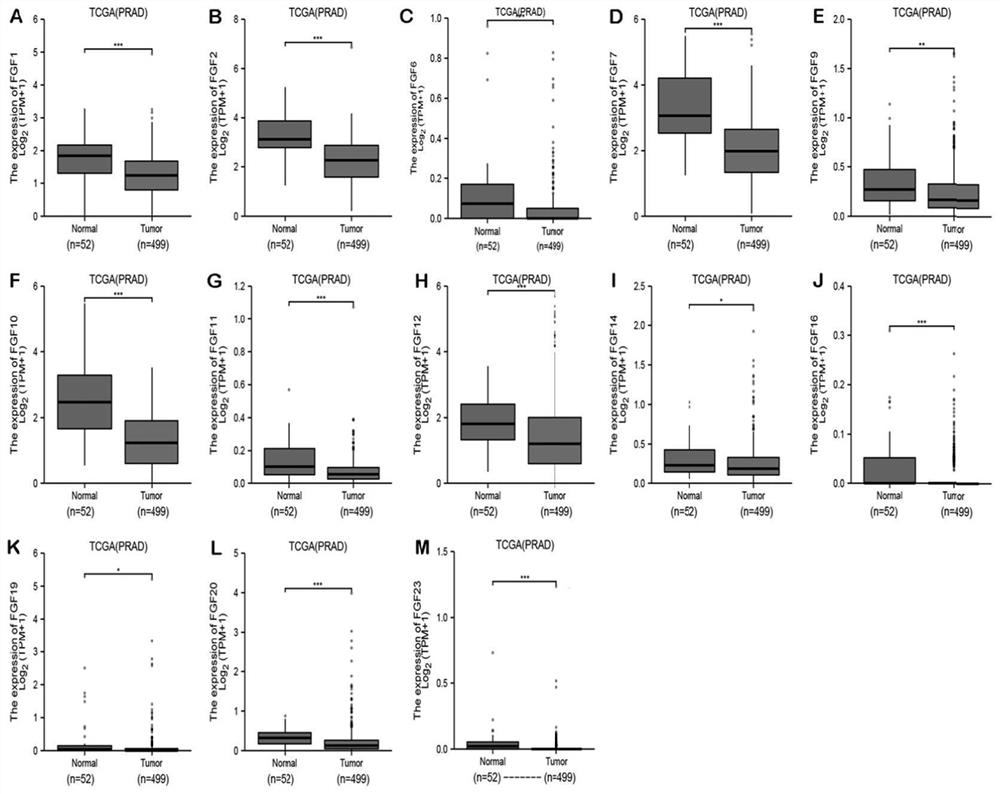
[0080] (1) The prostate cancer data in the TCGA database were used to evaluate the expression levels of FGF family genes in prostate cancer and normal tissues. FGF family factors (FGF8, FGF13, FGF1...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Example 2 Analysis of FGF17 and FGF22 Expression in Prostate Cancer and Adjacent Cells
[0099] (1) Collect surgically resected prostate cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues from 46 prostate cancer patients, and sign informed consent with the patients;
[0100] (2) Freeze the tissue samples in liquid nitrogen within 30 minutes of isolation, and then transfer to -80°C;
[0101] (3) Use samples at -80°C for protein extraction and qRT-PCR experiments.
[0102] The result is as Figure 13 shown. The results showed that, compared with adjacent normal tissues, the expressions of FGF17 and FGF22 in prostate cancer tissues were significantly increased, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.001).
[0103] Further, the prostate cancer cells C4-2, DU145, PC3 and normal prostate cells RWPE-1 were selected, and the expression levels of FGF17 and FGF22 were quantitatively detected by WB experiments, and the results were as follows: Figure 14 shown. The resul...
Embodiment 3
[0105]Example 3 Prostate cancer cell proliferation experiment
[0106] (1) RNA was extracted from PC3 and C4-2 cells and reverse transcribed, PCR amplified FGF17 cDNA and constructed into related vectors, sequenced and protein expression was verified, and the overexpression plasmid of FGF17 was obtained, and its effectiveness was verified by WB detection and specificity;
[0107] (2) Using the constructed FGF17 overexpression plasmid to transfect into PC3 and C4-2 cells, respectively, to construct and obtain PC3-FGF17 overexpression cells and C4-2-FGF17 overexpression cells;
[0108] (3) C4-2 cells, C4-2-FGF17 overexpression cells, PC3 cells and PC3-FGF17 overexpression cells were inoculated in 96 wells, each well was inoculated with 1×10 4 cells, three parallel wells for each cell;
[0109] (4) 24h, 48h, 72h and 96h after inoculation, the absorbance was detected by CCK-8 at 450nm to monitor the proliferation of cells.
[0110] The result is as Figure 15-16 shown. The re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com