Multi-mode microwave detection system and method based on fast frequency hopping technology
A microwave detection and frequency hopping technology, used in mode conversion, automatic power control, transmission of sensing components using wave/particle radiation devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
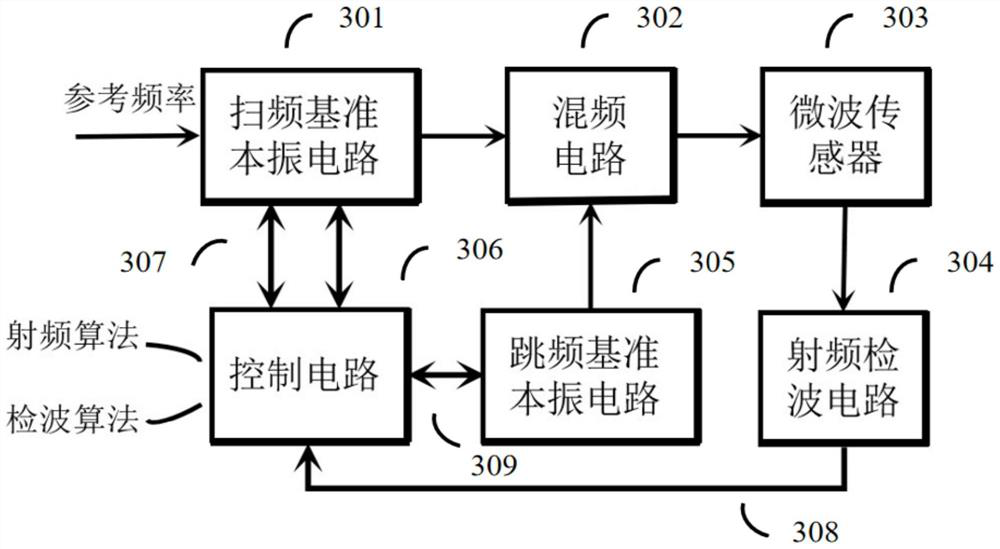
[0034] This embodiment provides a multi-mode microwave detection circuit based on fast frequency hopping technology, such as figure 1 As shown, the circuit includes: frequency sweeping local oscillator circuit (LO1) 301, frequency hopping reference local oscillator circuit (LO2) 305, frequency mixing circuit 302, microwave sensor 303, radio frequency detection circuit 304 and corresponding control circuit 306.
[0035] The control circuit 306 is connected with the frequency sweeping local oscillator reference circuit (LO1) 301 through the control line 307, and connected with the frequency hopping reference local oscillator circuit (LO2) 305 through the control line 309; the radio frequency detection circuit 304 is connected with the control circuit 306 through the data transmission line 308 .
[0036]Among them, the frequency-sweeping local oscillator reference circuit LO1 adopts a wideband fractional frequency-division phase-locked loop (PLL) containing a Sigma-Delta modulati...
Embodiment 2
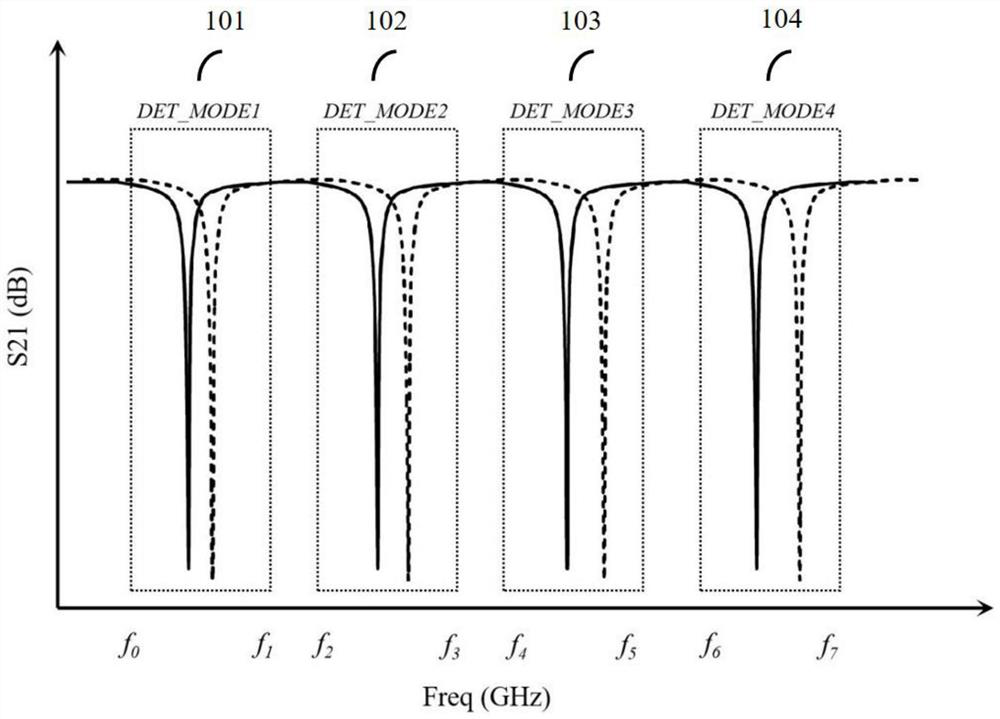
[0041] This embodiment provides a method for multi-mode microwave detection based on fast frequency hopping technology. The microwave detection of a 4-resonant mode is used as an example to introduce the following, see figure 2 , figure 2 Among them, 101, 102, 103 and 104 respectively correspond to the resonant modes in four different operating frequency ranges.
[0042] Among them, 101 corresponds to the DET_MODE1 working frequency range (f0, f1), 102 corresponds to the DET_MODE2 working frequency range (f2, f3), 103 corresponds to the DET_MODE3 working frequency range (f4, f5), 104 corresponds to the DET_MODE4 working frequency range is (f6, f7). In addition, a sufficient frequency interval needs to be reserved between adjacent resonant modes, and this interval is defined as an irrelevant frequency band, which is shown in figure 1 That is (f1, f2), (f3, f4) and (f5, f6).
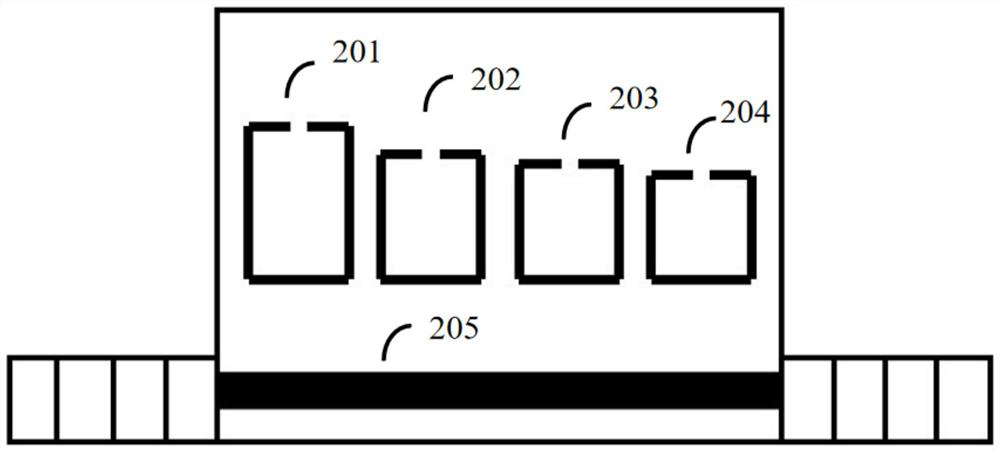
[0043] image 3 for correspondence figure 2 Schematic diagram of the basic structure of the mul...
Embodiment 3
[0090]This embodiment provides an n-mode microwave detection method based on fast frequency hopping technology, which introduces n resonant modes, and each resonant mode can independently respond to changes in the DUT, thereby obtaining n detections within one scan cycle. parameters (ie minimum insertion loss and resonant frequency offset).
[0091] f(DUT)=a 1 f(MODE1)+a 2 f(MODE2)+a 3 f(MODE3)+···+a n f(MODEn)
[0092] Among them, a 1 ,a 2 ,a 3 ...,a n are the fitting coefficients of the corresponding items of the multiple linear regression equation.
[0093] When the DUT changes, the n resonant modes will have different frequency shifts and insertion loss changes in their respective frequency ranges. After the deviation of the resonant frequency of different resonant modes and the change of the insertion loss are obtained by the multi-mode microwave detection system, the change amount of the DUT can be known through the corresponding calculation process.
[0094] A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com