Bacillus martensii and application thereof
A technology of Bacillus and Martensis, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of losing oxygen-carrying capacity and achieve the effects of improving safety, growing fast, and reducing nitrite content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The present application provides a B. marcorestinctum YC-1, which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is: CCTCC No. M 20211678.
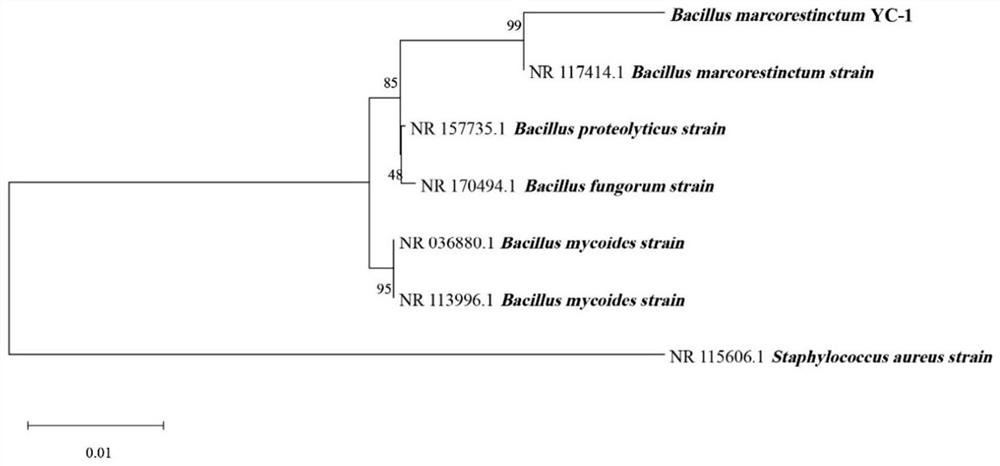
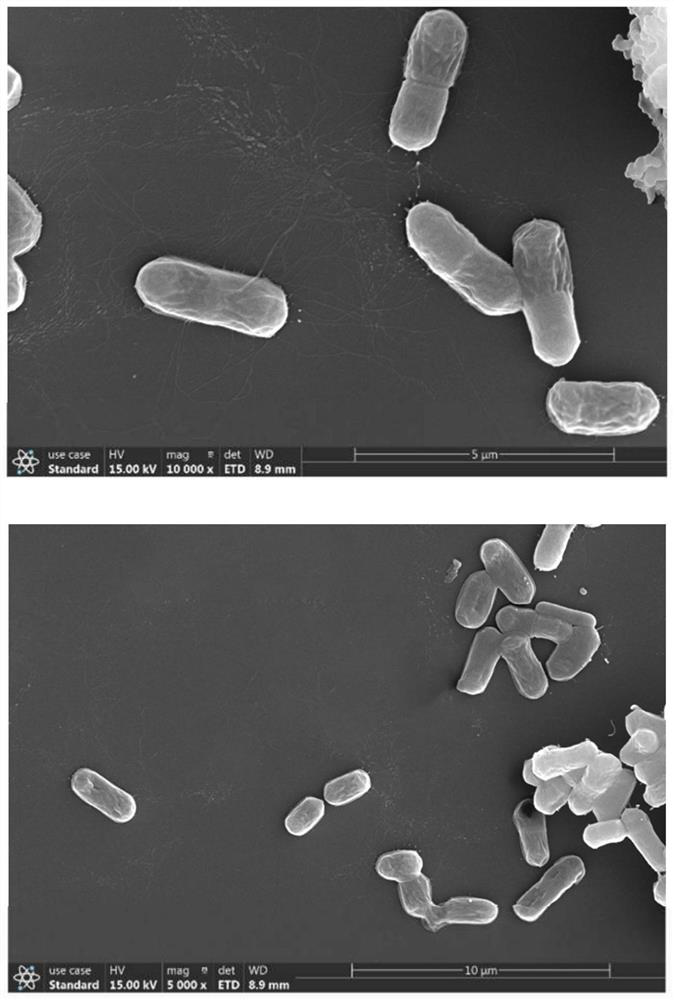
[0038] Specifically, the strain was isolated and screened from Sichuan traditional fermented sprouts, and its 16S rDNA sequencing was carried out to construct a 16S rDNA phylogenetic tree, and its morphological and physiological and biochemical characteristics were analyzed and identified.
[0039] The physiological and biochemical results of the strain are shown in Table 1. The strain can utilize glucose and glucose (gas production) and has nitrate reducing ability.
[0040] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical identification results table
[0041]
[0042] Remarks: "+" means use, "-" means not use
[0043] See figure 1 As shown, the 16S rDNA phylogenetic tree constructed by 16S rDNA sequencing of the strain showed that the strain was in the same branch as Bacillus mazenii.
[0044...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The application provides a method for preparing fermented sprouts, which uses the above-mentioned Bacillus martensii YC-1 to ferment to obtain fermented sprouts, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0049] Step S1. Cultivate Bacillus martensi YC-1 to obtain a bacterial suspension;
[0050] Step S2. Scribing the fresh and harmless mustard greens (two flat piles), air-drying and air-drying at room temperature for 20-30 hours;
[0051] Step S3. adding salt to the dried mustard greens, and marinating for 20-30 hours;
[0052] Step S4. After pickling, the mustard greens are washed, and after 20-30 hours of natural air drying, brown sugar water is added;
[0053] Step S5. Then add the auxiliary materials into the mustard greens, and stir evenly;
[0054] Step S6. The mustard is packed into a glass jar, and the Bacillus martensii YC-1 bacterial suspension is evenly sprayed on the surface of the mustard;
[0055] Step S7. Compress the mustard greens that have b...
experiment example 1
[0071] 1. Detection of volatile flavor compounds
[0072] The volatile flavor compounds were detected on the sprout samples stored and fermented for 3 months in Example 2 and Comparative Example 1, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0073] Table 2 Determination results of volatile flavor compounds
[0074]
[0075]
[0076] Through the analysis of flavor components, the sprouts of Example 2 have more types of volatile compounds. In Example 2, a total of 40 volatile compounds were detected, including acids (2 types), alcohols (6 types), aldehydes (7 types), esters (7 types), and olefins (18 types). A total of 30 volatile compounds were detected in Comparative Example 1, including acids (2 types), alcohols (3 types), aldehydes (5 types), esters (5 types), and olefins (15 types).
[0077] The content of volatile compounds measured in Example 2 is more abundant, with a total content of 24285.83 μg / 100g, much higher than the total content of volatile compounds measured...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com