Epoxy resin dechlorinating agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of epoxy resin and chlorine removal agent, which is applied in the field of chlorine removal agent to achieve the effects of large application value, reduction of chlorine content and cost of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
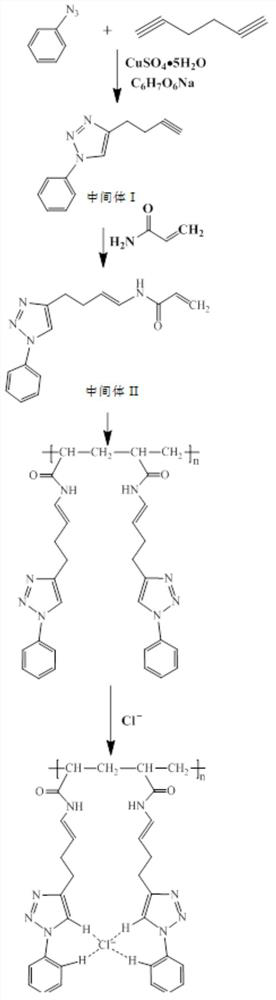
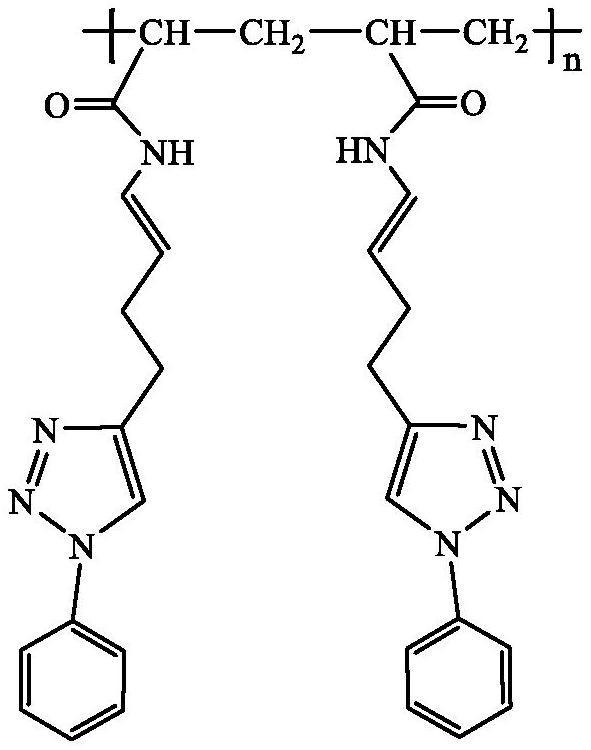
[0044] The preparation principle of the epoxy resin dechlorination agent of the present invention is: the epoxy resin dechlorination agent uses 1,5-hexadiyne and benzene azide as raw materials, copper sulfate pentahydrate and sodium ascorbate as catalysts, through azide and The click reaction of the alkyne can obtain the intermediate I, and then the addition reaction of the alkyne and the amino group can obtain the intermediate II, and finally, the epoxy resin dechlorination agent can be obtained through the polymerization reaction of the terminal double bond.
[0045] The epoxy resin dechlorination agent of the present invention has a ring structure, and there are 4 polarized C-H bonds on the 1,2,3-triazole ring and the benzene ring, which can realize - Captured, and the structure is stable. It captures Cl - The mechanism is as follows:
[0046]
[0047] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of epoxy resin chlorine removal agent, comprises the foll...
Embodiment 1
[0062] Add 44.35g of the first organic solvent (the mass ratio of water and tert-butanol is 1:1) in the there-necked flask equipped with stirrer, then add 7.88g catalyst (wherein the mol ratio of copper sulfate pentahydrate and sodium ascorbate is 1: 2), the temperature was raised to 60°C. Subsequently, 7.8g (0.1mol) of 1,5-hexadiyne and 11.9g (0.1mol) of benzene azide were dissolved in 20g of the first organic solvent, and slowly added dropwise to the three-necked flask, and the dropping time was kept at 4h. 12h, full argon protection. After completion of the reaction, cool to room temperature, extract with dichloromethane, separate the organic phase, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter and spin evaporate to remove the dichloromethane to obtain intermediate I.
[0063] 19.7g (0.1mol) of intermediate I and 7.1g (0.1mol) of acrylamide were dissolved in 40.2g of acetone and placed in a reactor, 0.67g of sodium hydroxide was added as a catalyst, and the pressure of the rea...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Add 107.8g of the first organic solvent (the mass ratio of water and tert-butanol is 1:1) in the there-necked flask equipped with stirrer, then add 10.65g catalyst (wherein the mol ratio of copper sulfate pentahydrate and sodium ascorbate is 1: 2), the temperature was raised to 60°C. Subsequently, 9.4g (0.12mol) of 1,5-hexadiyne and 11.9g (0.1mol) of benzene azide were dissolved in 20g of the first organic solvent, and slowly added dropwise to the three-necked flask, and the dropping time was maintained at 5h, and the reaction 14h, full argon protection. After completion of the reaction, cool to room temperature, extract with dichloromethane, separate the organic phase, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter and spin evaporate to remove the dichloromethane to obtain intermediate I.
[0067] 19.7g (0.1mol) of intermediate I and 8.5g (0.12mol) of acrylamide were dissolved in 65.8g of acetone and placed in the reactor, 0.94g of sodium hydroxide was added as a catalyst,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com