Method for improving storage stability of solid electrolyte material, material and application
A solid electrolyte and storage stability technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of affecting battery performance, increasing the moisture content of solid electrolyte, and the specific surface area is easy to attach moisture, etc., to achieve the effect of extending the shelf life, low cost of use, and improving storage stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
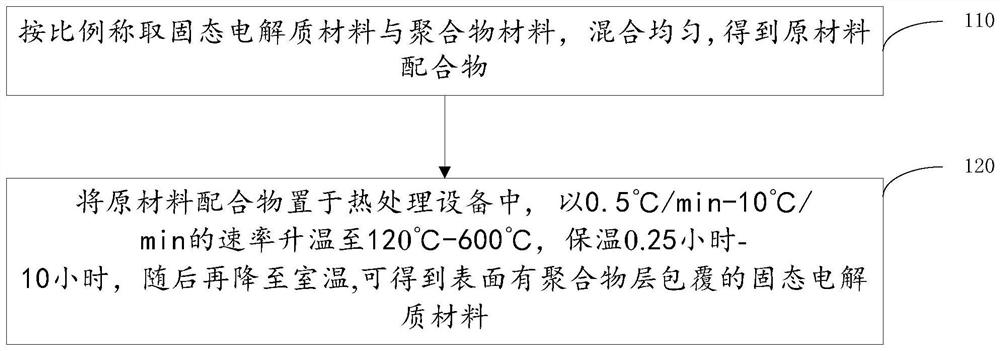
[0043] This example provides a method for preparing a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface, and the specific steps are:
[0044] Weigh the NASICON solid electrolyte material Li with a particle size of 2 μm at a mass ratio of 1:0.06 1.2 Al 0.2 Ti 1.8 (PO 4 ) 3 and polyvinylidene fluoride, added to a stirrer and thoroughly mixed for 1 hour, and mixed evenly to obtain a raw material complex.
[0045]The raw material complex was placed in a box furnace, heated to 200°C at a rate of 2°C / min, kept for 5 hours, and then naturally lowered to room temperature to obtain a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface.
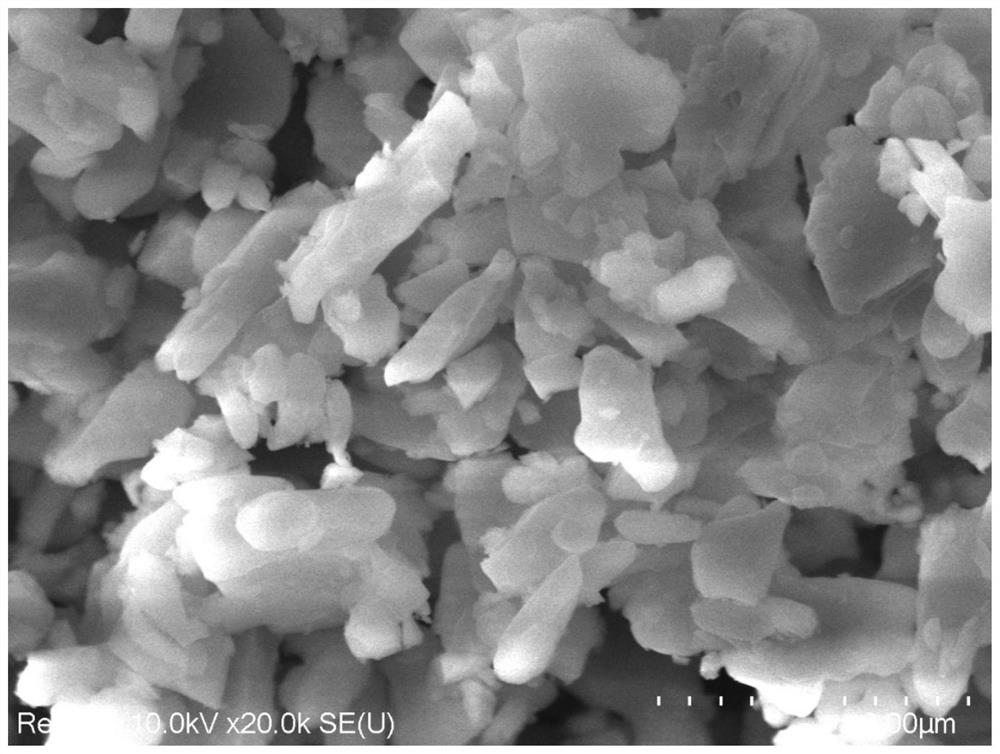
[0046] figure 2 The SEM of the solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer was prepared for this example. It can be seen that the surface of the solid electrolyte material has a lamellar structure, which is the polymer layer coated on the surface of the solid electrolyte material.
[0047] Water c...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface, and the specific steps are:
[0055] Weigh the garnet-type solid electrolyte material Li with a particle size of 5 μm at a mass ratio of 1:0.1 7 Ca 3 Ta 2 o 12 and polyvinylidene fluoride, added to a ball mill and mixed thoroughly for 1 hour, and mixed evenly to obtain a raw material complex.
[0056] The raw material complex was placed in a tube furnace, and the temperature was raised to 230°C at a rate of 2°C / min, kept for 4 hours, and then naturally lowered to room temperature to obtain a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface.
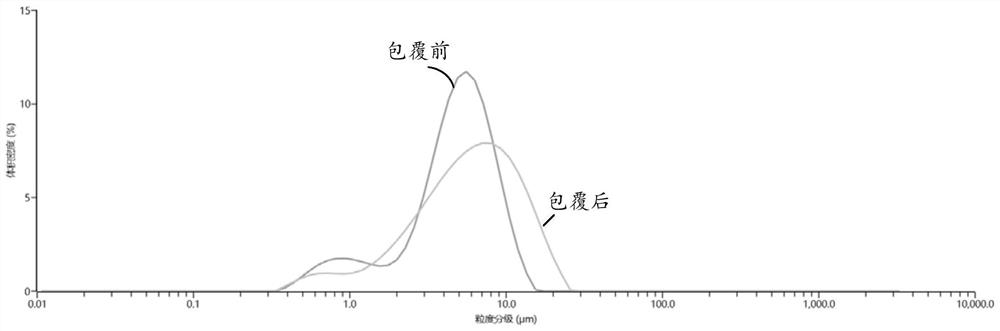
[0057] image 3 It is the volume particle size distribution curve of the solid electrolyte material in this example before and after coating the polymer. It can be seen from the figure that the average particle diameter D50 of the solid electrolyte after the polymer coating is 6 μm, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0065] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface, and the specific steps are:
[0066] Weigh the NASICON type solid electrolyte material Li with a particle size of 2 μm at a mass ratio of 1:0.05 1.5 Al 0.5 Ti 1.5 (PO 4 ) 3 and polytetrafluoroethylene, added into a ball mill and mixed thoroughly for 1 hour, and mixed evenly to obtain a raw material complex.
[0067] The raw material complexes were placed in a tube furnace, and the temperature was raised to 280°C at a rate of 2°C / min, kept for 2 hours, and then naturally lowered to room temperature to obtain a solid electrolyte material coated with a polymer layer on the surface.
[0068] Figure 4 The XRD patterns of the solid electrolyte material used in this example before and after polymer coating, from the comparison of the characteristic peaks in the figure, it can be seen that the polymer coating will not affect the structure of the origina...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com