Human motion intention recognition method and system for lower limb exoskeleton
A technology of human motion and recognition methods, applied in neural learning methods, character and pattern recognition, applications, etc., can solve the problems of difficult detection and recognition of human motion intentions, achieve convenient classification of human motion intentions, accurate classification effects, and reduce abnormal The effect of stationarity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
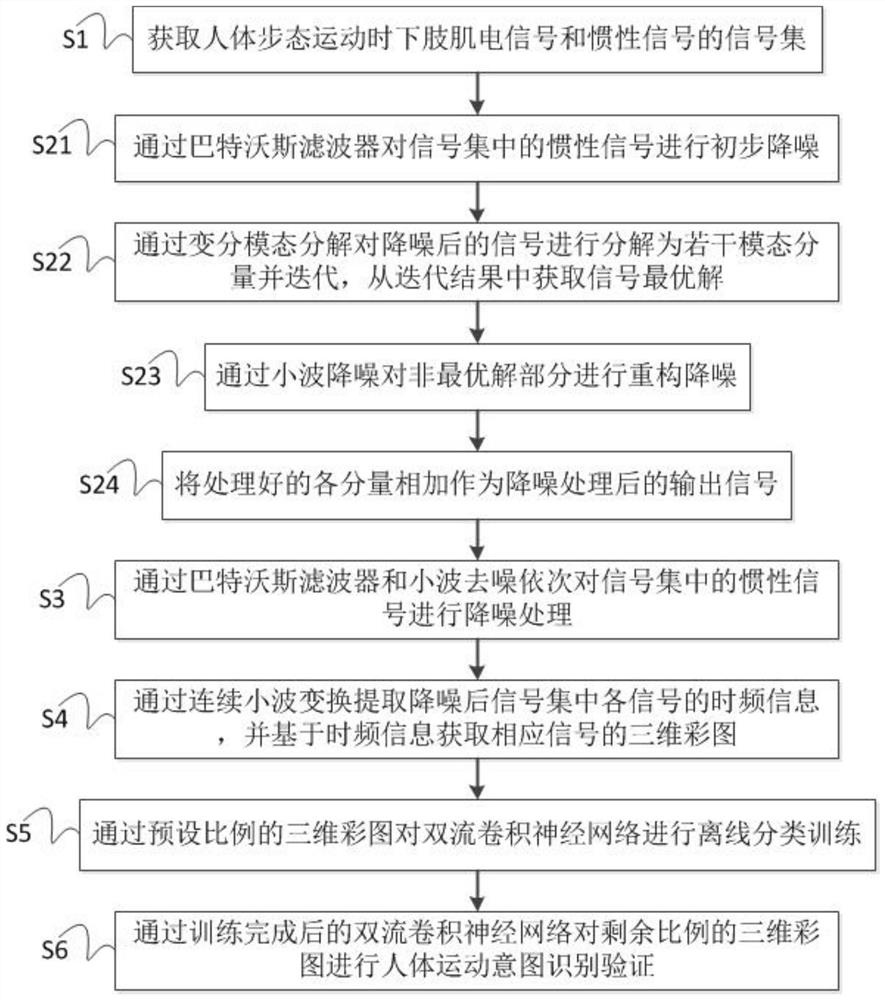
[0050] In order to enable the lower extremity exoskeleton robot to better recognize the user's movement intention during operation, so as to provide assistance to the user more accurately, such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention proposes a human body movement intention recognition method for lower extremity exoskeleton, including steps:
[0051] S1: Obtain the signal set of lower limb myoelectric signal and inertial signal during human gait movement;
[0052] S2: Through the Butterworth filter and variational mode decomposition, the EMG signals in the signal concentration are sequentially denoised;
[0053] S3: Through the Butterworth filter and wavelet denoising, the inertial signal in the signal set is denoised in turn;
[0054] S4: Extract the time-frequency information of each signal in the noise-reduced signal set through continuous wavelet transform, and obtain the three-dimensional color map of the corresponding signal based on the time-frequency information; ...
Embodiment 2
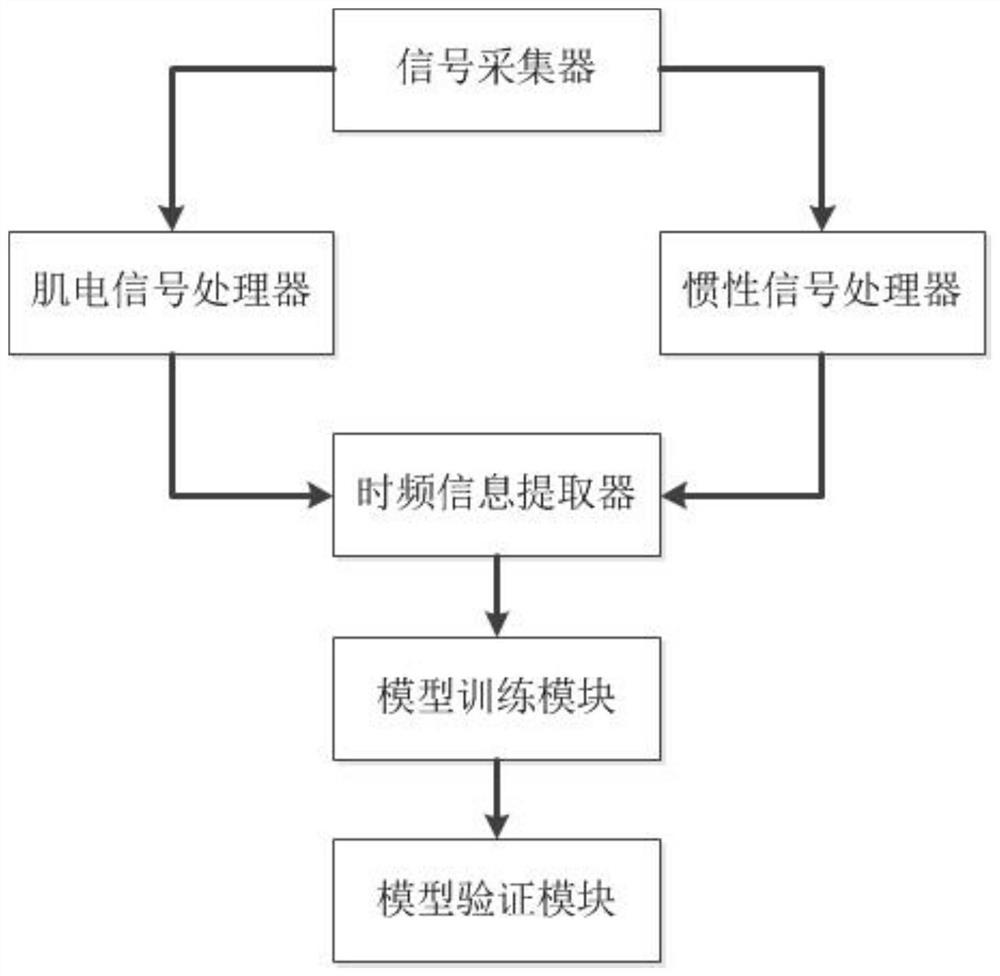
[0080] In order to better understand the technology of the present invention, this embodiment illustrates the present invention in the form of a system structure, such as figure 2 As shown, a human motion intention recognition system for lower extremity exoskeleton, including:
[0081] The signal collector is used to obtain the signal set of the lower limb myoelectric signal and inertial signal during human gait movement;
[0082] The myoelectric signal processor is used to sequentially perform noise reduction processing on the myoelectric signals in the signal concentration through the Butterworth filter and the variational mode decomposition;
[0083] The inertial signal processor is used to sequentially perform noise reduction processing on the inertial signals in the signal set through the Butterworth filter and wavelet denoising;
[0084] The time-frequency information extractor is used to extract the time-frequency information of each signal in the signal set after noi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com