Aromatic acid-based chlorine dioxide aqueous solution and preparation method thereof
A chlorine dioxide and aromatic acid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, botanical equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve the problems of low concentration of chlorine dioxide and the need to increase the concentration, and achieve improvement effect of concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
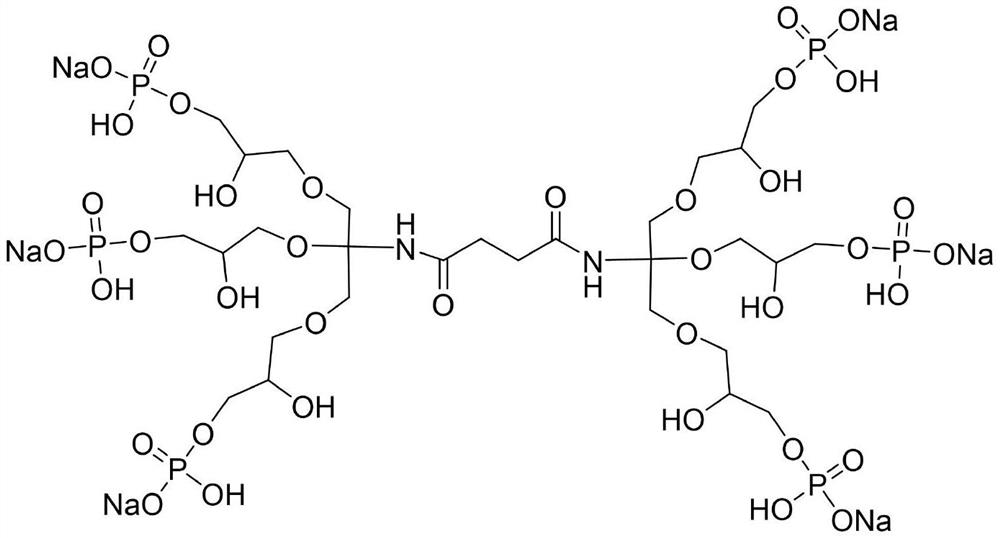
[0028] Preparation of phosphate sodium salt derivatives:
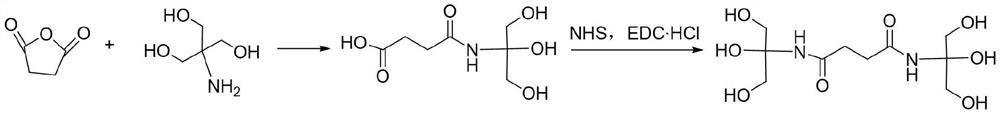
[0029] A. Add 0.1mol succinic anhydride and 0.105mol trishydroxymethylaminomethane into a four-neck flask, then add 60mL of ethanol to dissolve completely, under the protection of nitrogen, heat and reflux for 12h, then lower to room temperature, remove the nitrogen protection, Use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the solution to 6, then add a mixture of 1g NHS and EDC·HCl (the molar ratio of NHS and EDC·HCl is 2:1) under the protection of nitrogen, stir for 30min, and then add 0.105mol trimethylolamino Methane, then reflux reaction for 12h, stop the reaction, cool to room temperature, then use sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the solution to be neutral, spin dry, then dissolve with 60mL dichloromethane, wash several times with 60mL water, combine the organic phases, and rotate to evaporate, Dry at 50°C, polyhydric compounds;
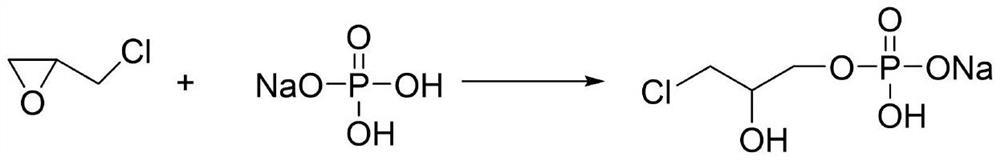
[0030] B. Add 0.1mol sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution into a four-necked ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Preparation of phosphate sodium salt derivatives:
[0034] A. Add 0.1mol succinic anhydride and 0.125mol trishydroxymethylaminomethane into a four-necked flask, then add 100mL ethanol to dissolve completely, under nitrogen protection, heat and reflux for 12h, then lower to room temperature, remove nitrogen protection, Use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 6, then add 2.5g of a mixture of NHS and EDC·HCl (the molar ratio of NHS to EDC·HCl is 2:1) under nitrogen protection, stir for 50min, and then add 0.125mol of trimethylol Aminomethane, then reflux reaction for 12h, stop the reaction, cool to room temperature, then adjust the solution to be neutral with sodium hydroxide solution, spin dry, then dissolve with 60mL dichloromethane, wash with 60mL water several times, combine the organic phases, and spin evaporate , dried at 50°C, polyhydroxyl compounds;
[0035] B. Add 0.1mol sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution into a four-necked flask, adjust the p...
Embodiment 6
[0045] The chlorine dioxide aqueous solution that embodiment 3-1, 3-2, 4-1, 4-2, 5-1, 5-2 and comparative example 1-comparative example 6 obtains carries out following performance test:
[0046] According to the 2002 edition of the disinfection specification and the provisions of GB / T38499-2020, the content and stability of the samples were tested.
[0047] The obtained data are shown in Table 2.
[0048] Table 2
[0049]
[0050] As can be seen from the above table, embodiment 3-1, 3-2, 4-1, 4-2, 5-1, 5-2 obtain chlorine dioxide aqueous solution and the loss of chlorine dioxide under 54 ℃ of conditions is obviously less than The loss of chlorine dioxide in the chlorine dioxide aqueous solution obtained in Comparative Example 1-Comparative Example 6, and Examples 5-1 and 5-2 illustrate that the high-concentration chlorine dioxide aqueous solution still has good stability.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com