Method for identifying CNV microdeletion and microduplication syndrome diseased embryo and normal embryo
A syndrome and micro-repetition technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, genomics, etc., can solve the problem of inability to accurately detect CNV micro-deletions and micro-duplications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Reference sample collection of the patient and the patient's parents
[0037] Three patients with CNV micro-deletion micro-repetitive syndrome who will undergo assisted reproduction were recruited from Shanghai Ji'ai Genetics and Infertility Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Fudan University Affiliated Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital. Each family is required to sign written informed consent, and the research plan is approved by the Human Subject Ethics Committee of Shanghai Jiai Genetics and Infertility Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Fudan University Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital.
[0038] From September 2020 to June 2021, all families have a history of adverse pregnancies, and one couple with CNV micro-deletion micro-repetitive syndrome is referred to as "patient" and the other is referred to as "patient spouse" later, and the family chart is indicated Figure 1 。 At the same time as the recruitment, each patient couple and the patient's relatives (sa...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Example 2: in vitro fertilization, blastocyst biopsy and whole genome amplification (WGA)
[0134] 1. In vitro fertilization
[0135] In vitro fertilization (IVF) is performed in recruited families, where in vitro fertilization methods follow conventional methods in the art; maternal / paternal age, phenotype, ovulation outcome, number of fertilized eggs, and the number of blastocysts ultimately used for biopsy in these families are listed in Table 2. Through the above in vitro fertilization, a total of 16 blastocysts were obtained from 3 families for subsequent biopsy and haplotype analysis studies.
[0136] Table 2. Basic family information and in vitro fertilization situation of no. 1-2 family
[0137]
[0138] 2. Blastocyst biopsy and whole genome amplification
[0139]Take the above embryos in the blastocyst stage and remove 3 to 10 cells from the nourishing ectoderm on day 5 or 6 of embryonic development. Place the biopsy cells in a PCR tube filled with alkaline dena...
Embodiment 3
[0212] Example 3: SNP genotypic typing and haplotypes (haplotypes) analysis
[0213] 1. SNP genotype detection
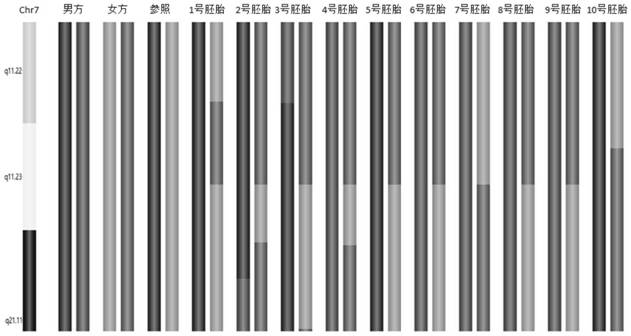
[0214]SNP genotype detection using Illumina SNP microarrays. Each chip contains nearly 300,000 or 700,000 SNPs, which can fully cover 23 pairs of human chromosomes. The 12 samples obtained by blastocyst biopsy and whole genome amplification in Example 2 were grouped according to family, and 3 whole genome amplification samples of the parent couple and the patient's relatives were grouped into a group, and the microarray SNP genotype detection and analysis were carried out, and the grouping situation was shown in Table 3. The specific experimental methods are carried out with reference to the instructions and will not be repeated here.
[0215] Table 3. Experimental grouping of SNP arrays of families 1-2
[0216]
[0217] Note: F stands for female and M stands for male
[0218] 2. Embryo chromosome aneuploidy detection
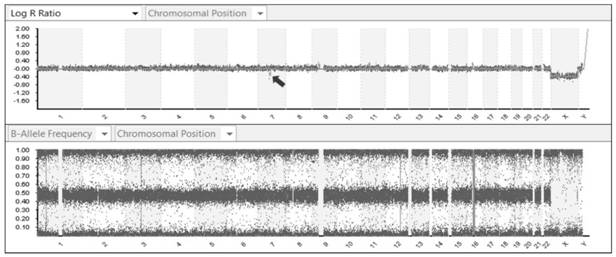
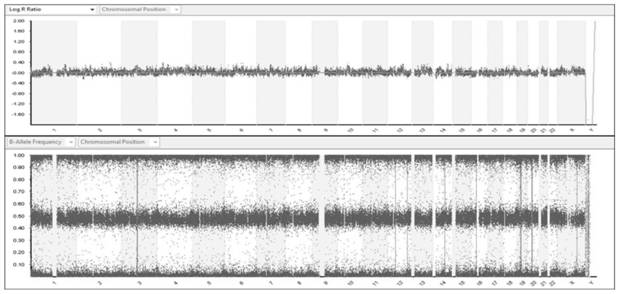
[0219] The principle and process of SNP gene ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com