Use of composite materials for absorbing and distributing liquids in actively and/or passively cooled current-carrying systems
A composite material, passive cooling technology, applied in separation methods, electric vehicles, gas treatment, etc., can solve the problems of gel blocking, low absorption capacity, low thermal stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073] Example 1: Preparation of a composite material that can be used according to the invention
[0074] Different composite materials and absorbent pads were prepared that could be used in accordance with the present invention.
[0075] The following materials were used:
[0076] Microfiber Spunbond Nonwoven: Microfiber Spunbond Nonwoven Polyamide / Polyester 200g / m 2 .
[0077] Superabsorbent particles 1: Partially neutralized and cross-linked polyacrylic acid, prepared by substance polymerization, particle size distribution d50 of 50 μm-1000 μm, coating weight 15 g / m 2 .
[0078] Superabsorbent Particles 2: Partially neutralized and cross-linked polyacrylic acid, prepared by reverse phase suspension polymerization, particle size distribution d50 is 50 μm-1000 μm, coating weight 15 g / m 2 .
[0079] Water-soluble distribution layer 1: water-soluble partially saponified polyvinyl alcohol, coating weight 20g / m 2
[0080] Water-soluble distribution layer 2: water-solubl...
example 2
[0092] Example 2: Testing the absorbent capacity of absorbent pads according to the invention
[0093] The absorbent capacity of the absorbent pad 7 was tested according to DIN 53923 with completely desalinated water. Absorbent Pad 7 was found to have a good water absorption of 8.7 kg / m 2 . In the test range according to DIN 53923, the absorbent pad 7 is suspended freely floating in the swollen state for 30 seconds. The water loss here is 550g / m 2 , so the retention is very good. The absorbent pad also dries easily without heating, suggesting that it is also capable of reversibly binding water. By being welded circumferentially swelling can be well controlled and blocking effects can be avoided by using a distribution layer. Dust formation can be avoided by immobilizing the superabsorbent particles.
example 3
[0094] Example 3: Testing the Water Vapor Absorption of Absorbent Pads According to the Invention
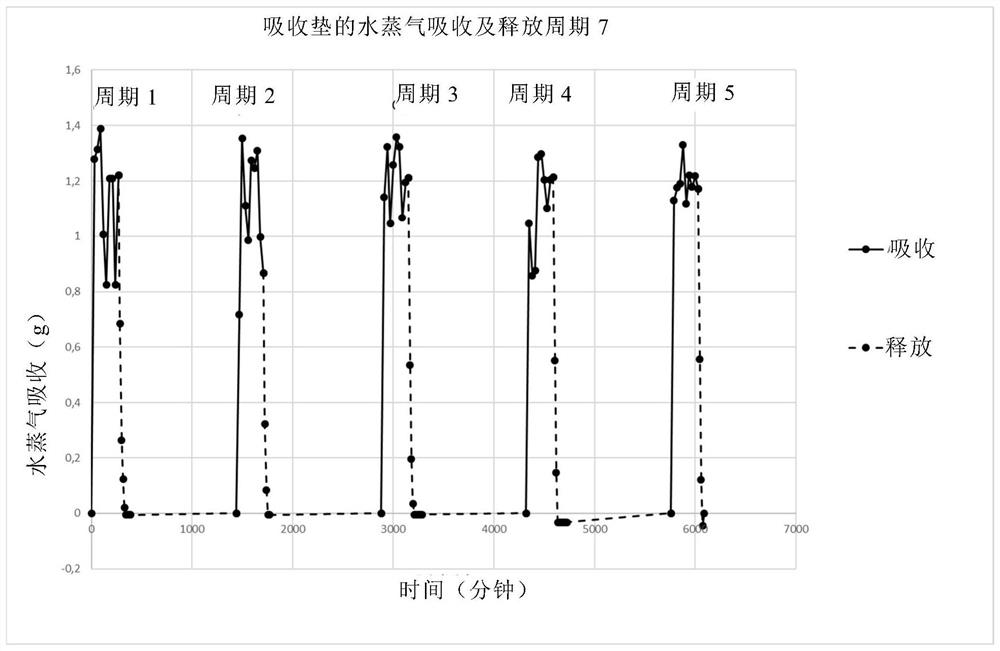
[0095] Absorbent Pad 7 was tested for water vapor absorption. For this purpose, the absorbent pads are stored in a climate chamber at 90% humidity and 30° C. for a period of 270 minutes. Weight gain was measured gravimetrically every 30 minutes over a period of 270 minutes. The absorbent pad 7 was then dried at room temperature and the weight loss was determined gravimetrically. This process is repeated 5 times and at figure 1 shown in .
[0096] The results show that water vapor absorption is very rapid. After 30 minutes the water vapor absorption has reached equilibrium. To this end, it is worth noting that re-drying also proceeds very quickly and is almost complete.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Basis weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com