USY type molecular sieve modification method and application thereof
A molecular sieve and modification technology, which is applied in the direction of molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems affecting the spatial structure of molecular sieves, affecting the stability of molecular sieves, and destroying molecular sieve crystals. It achieves good water solubility, The effect of enriching the secondary pore structure and improving the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
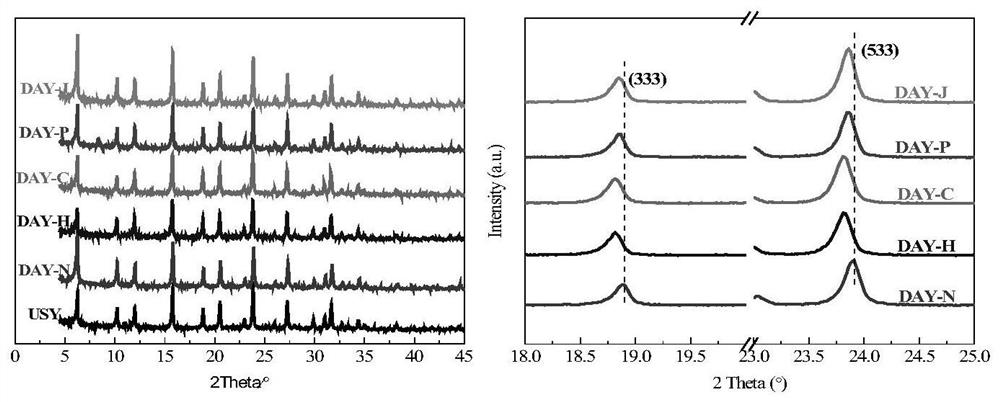
[0047] This example mainly investigates the selection of organic acid components in the organic acid-chelating agent composite dealumination modifier. Five common organic acids, tartaric acid, citric acid, oxalic acid, succinic acid and malic acid, were used to treat the same commercial USY molecular sieve at a concentration of 0.3 mol / L. "USY" stands for commercial ultra-stable Y molecular sieve, "DAY-N", "DAY-H", "DAY-C", "DAY-P", "DAY-J" stand for citric acid, succinic acid, The samples prepared by treating Y molecular sieves with oxalic acid, malic acid and tartaric acid, the specific surface area and pore structure data of each sample are shown in Table 1 below:
[0048] Table 1Y Specific surface area and pore structure data of molecular sieves
[0049]
[0050] figure 1 In this example, the XRD patterns and partial enlarged spectra of Y molecular sieves treated with different organic acids are shown. like figure 1 As can be seen from the results shown in Table 1 a...
Embodiment 2
[0055] This example investigates the effect of the composite modifier and compares the structural properties of the samples modified with citric acid, chelating agent and industrial USY molecular sieve.
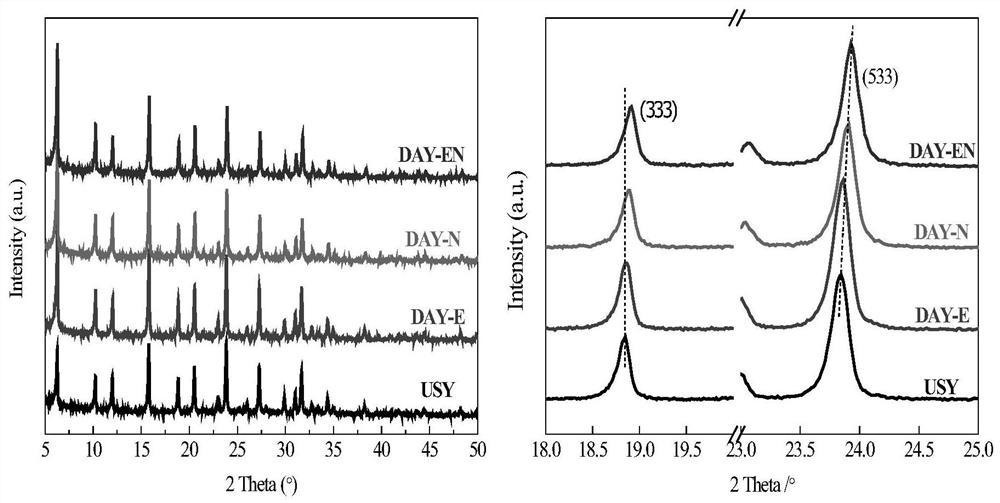
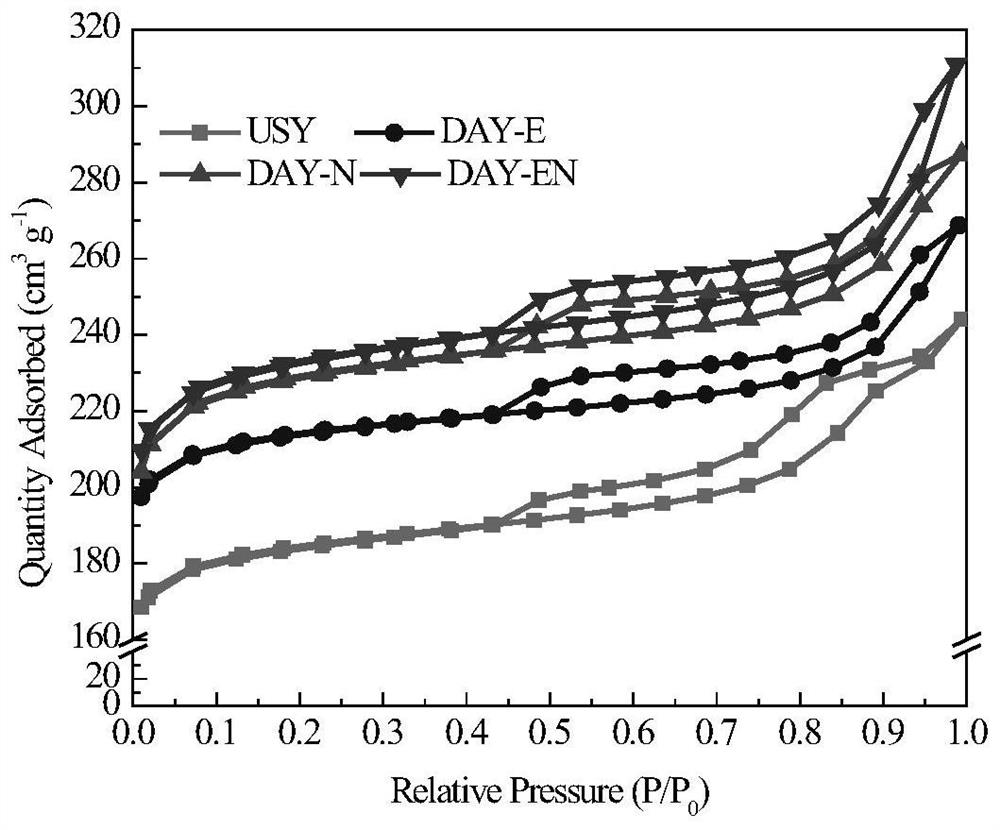
[0056] At room temperature, add 5g of industrial USY molecular sieve into a 250mL three-necked flask, and then add 25mL of 0.3mol L -1 Add 0.3mol L of citric acid solution at the same time -1 25 mL of disodium EDTA solution, vigorously stirred at 80 °C for 4 h. After the reaction was completed, the resulting milky white suspension was filtered, washed until neutral, and dried at 110° C. for 12 h. The sample number "USY" stands for industrial USY molecular sieve, "DAY-E" for disodium EDTA modification, "DAY-N" for citric acid modification, and "DAY-EN" for compound modification. The characterization results of the effect comparison of the composite modifier are shown in Table 3 below:
[0057] Table 3 Effects of different modifiers on the crystal structure of USY molecular ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] In this example, the influence of experimental conditions on the modification effect was investigated, and the parameters such as modifier concentration, reaction time and reaction temperature were mainly investigated. 2 / Al 2 O 3 The higher the value, the more suitable it is to prepare the modified Y molecular sieve with small unit cell and high stability.
[0067] At room temperature, adjust the concentration of citric acid solution and the concentration of disodium EDTA solution, using 0.2mol·L respectively. -1 , 0.3mol·L -1 , 0.4mol·L -1 and 0.5mol·L -1 ; Adjust the reaction time and use 3h, 4h, 5h and 6h respectively; adjust the reaction temperature and use 70°C, 80°C, 90°C and 100°C respectively.
[0068] Influence of reaction conditions on modification effect
[0069]Table 5 shows the effect of different modifiers in Example 3 on the crystal structure of USY molecular sieve. From the weighting factor of the experimental conditions, the concentration of cit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com