Marker and probe composition for screening bladder cancer and application of marker and probe composition
A technology of markers and compositions, applied in the field of probe compositions and markers for bladder cancer screening, can solve the problems of lack of non-invasive diagnostic methods and achieve high sensitivity and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0117] The preparation of the chip is mainly based on a glass sheet or a silicon sheet as a carrier, and oligonucleotide fragments or cDNAs are arranged on the carrier in sequence as probes by means of in situ synthesis and micro-array.
[0118] The chip described in this application is based on the signal detection of DNA sequence hybridization after bisulfite treatment. Bisulfite treatment is to change unmethylated cytosine into uracil, while methylated cytosine remains unchanged. Change, then convert uracil to thymine, and finally carry out chip hybridization; finally judge the type of base added according to the fluorescent color, and then determine whether the site is methylated.
[0119] The present application provides a method for bladder cancer screening, which includes:
[0120] detect the methylation level of the marker, and
[0121] The risk of the subject suffering from bladder cancer is judged based on the methylation level, and the marker is selected from one o...
Embodiment 1
[0125] Example 1. Screening markers
[0126] 1) Sample collection: Download the 450k methylation microarray cancer tissue data in TCGA, involving a total of 7,769 cancer tissue samples of 26 types of tumors, including adrenocortical carcinoma (80), bladder urothelial carcinoma (409), acute myeloid Leukemia (140), brain low-grade glioma (654), breast cancer (740), cervical cancer (286), colorectal cancer (348), esophageal cancer (183), uveal melanoma (80), head and neck squamous Stem cell carcinoma (527), bladder tissue carcinoma (660), liver cancer (377), lung adenocarcinoma (425), lung squamous cell carcinoma (372), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (29), ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (10), pancreatic cancer (184), mesothelioma (116), prostate cancer (488), skin melanoma (104), sarcoma (117), gastric cancer (397), testicular cancer (134), thymus cancer (94) ), thyroid cancer (506), endometrial cancer (309). For healthy people, Boercheng collected the plasma of 38 healthy pe...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2. Sample preparation, library building and verification methods
[0140] A marker that can distinguish bladder cancer from healthy people obtained in Example 1 was verified in a plasma sample, and the specific detection method was as follows:
[0141] 1.1.cfDNA extraction and purification
[0142] 1.1.1. Plasma sample preparation:
[0143] Centrifuge the blood sample at 2000 g for 10 min at 4°C and transfer the plasma to a new centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the plasma sample at 16,000g at 4°C for 10 minutes, and proceed to the next step according to the type of collection tube used. The type of collection tube used in this experiment is other.
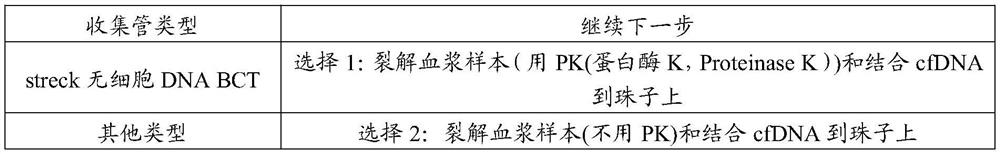
[0144] Table 1
[0145]
[0146] 1.1.2. Lysis and conjugation
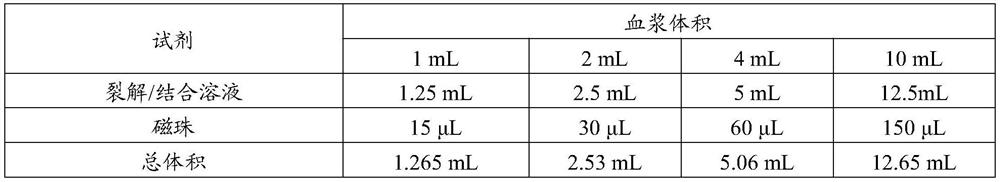
[0147] 1.1.2.1. Prepare the binding solution / bead mixture according to the table below and mix thoroughly.
[0148] Table 2
[0149]
[0150] Add an appropriate volume of plasma sample.
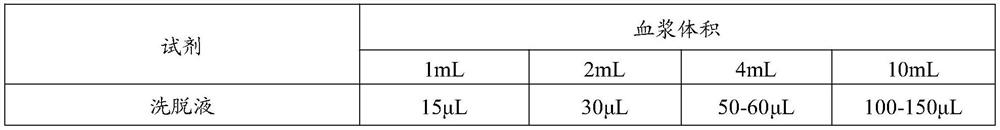
[0151] 1.1.2.2. Thoroughly mix the plasma sample and bindin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com