Callicarpa nudiflora as fish vaccine adjuvant and application thereof
The technology of naked flower purple pearl and fish is applied in the field of naked flower purple pearl as an adjuvant for fish vaccine, which can solve the problems of large consumption of vaccine, high cost, difficult to handle, etc., and achieves improvement of immune protection rate, low residue and price. low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
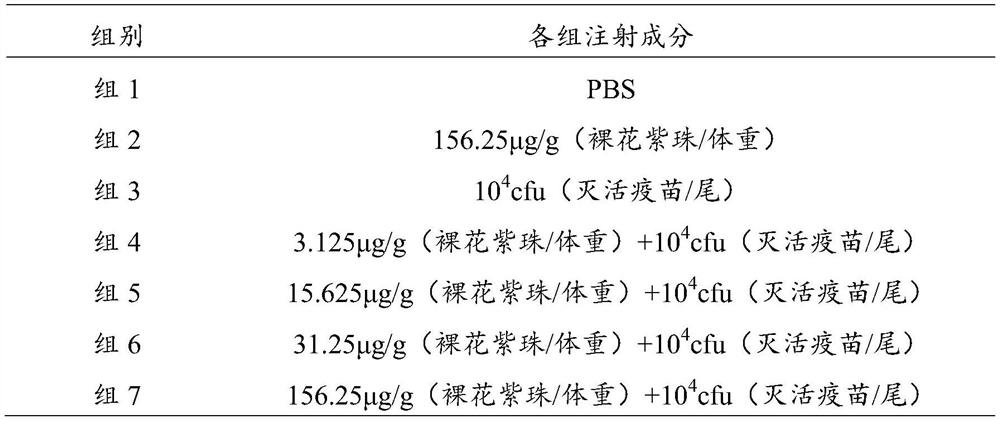
[0023] (3) Preparation and use of inactivated vaccine: Put Edwardella lentus in 1% concentration formalin, and let stand overnight in a 4°C refrigerator. The next day, the cells were washed three times with PBS and centrifuged, and PBS was added to prepare inactivated vaccines of different concentrations. The zebrafish were inoculated by intraperitoneal injection after mixing different concentrations of the violet pearl adjuvant and the inactivated vaccine in proportion, and then the zebrafish were fed and observed according to the aforementioned method.
[0024] (4) Determination of the optimal concentration of S. japonica as an adjuvant for zebrafish / herring: different concentrations of S. japonica adjuvant (0mg / mL, 0.1mg / mL, 0.5mg / mL, 1mg / mL, 2.5mg / mL, 5mg / mL) and vaccine (10 4 / 10 5 cfu) immunized with zebrafish / herring after mixing in proportion, 30 days later, live Edward lentus challenge test was performed at a challenge concentration of 10 4 / 10 5 cfu, zebrafish / he...
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Test of safe injection dose of Violet nudica to zebrafish
[0027] 1. Materials and methods
[0028] (1) Test materials and breeding conditions: Five-month-old healthy TU strain zebrafish with a body weight of about 0.32 g were selected. During the test, each group was placed in a separate water tank, and the zebrafish were fed with Artemia twice a day, and the water temperature was controlled at 21 Between ℃-25℃, 14 hours of light and 10 hours of darkness per day;
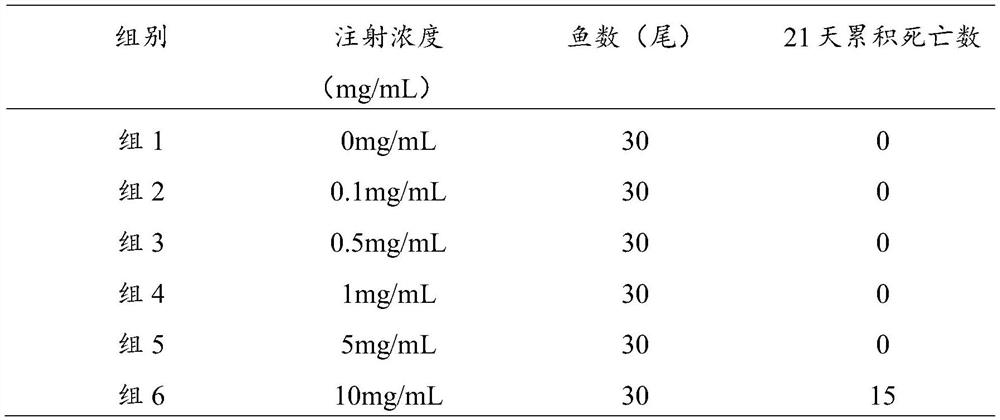
[0029] (2) Determination of the safe dose for zebrafish injection with S. japonica: The zebrafish were injected intraperitoneally with S. japonica at the aforementioned concentration, 30 animals in each group, 10 μL per tail, and observed for 21 days.
[0030] 2. Test results
[0031] The death situation of zebrafish in the control group and the experimental group in 21 days is shown in Table 1. It can be seen that the maximum safe injection dose of zebrafish to zebrafish is 50 μg / tail, that is...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Lethal concentration test of Edwardsiella lentus to zebrafish
[0035] 1. Materials and methods
[0036] (1) test material and breeding conditions: the same as in Example 1;
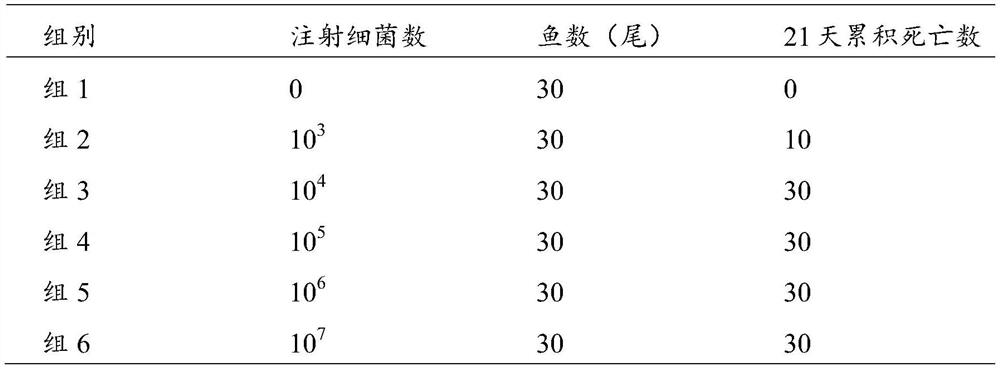
[0037] (2) Determination of lethal concentration of Edwardsiella lentus to zebrafish: 0 and 10 were used respectively. 3 , 10 4 , 10 5 , 10 6 , 107 The number of Edwardsiella lentus was intraperitoneally injected into zebrafish, 30 tails per group, 10 μL per tail, and observed for 21 days.
[0038] 2. Test results
[0039] The mortality of the zebrafish in the control group and the experimental group in 21 days is shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the injection of Edwardella lentus to the zebrafish has a lethal concentration of 10 4 / tail.
[0040] Table 2 Lethal concentration test of Edwardella lentus to zebrafish injection
[0041]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com