Polymerizable thioxanthone water-based photoinitiator as well as preparation method and application thereof
A thioxanthone water-based and xanthone-based water-based technology is applied in the field of thioxanthone water-based photoinitiators and their preparation, which can solve the problems of low curing efficiency and high cost of raw materials, achieve high curing degree and overcome oxygen inhibition of polymerization. , the effect of high light-induced efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
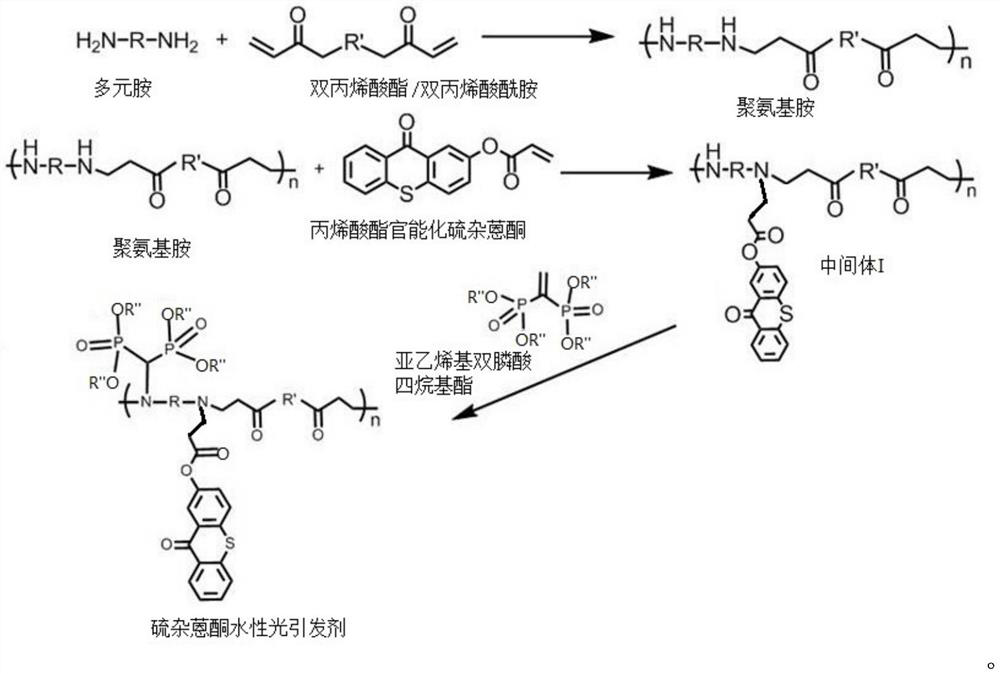
[0062] A kind of preparation method of thioxanthone aqueous photoinitiator comprises the steps:
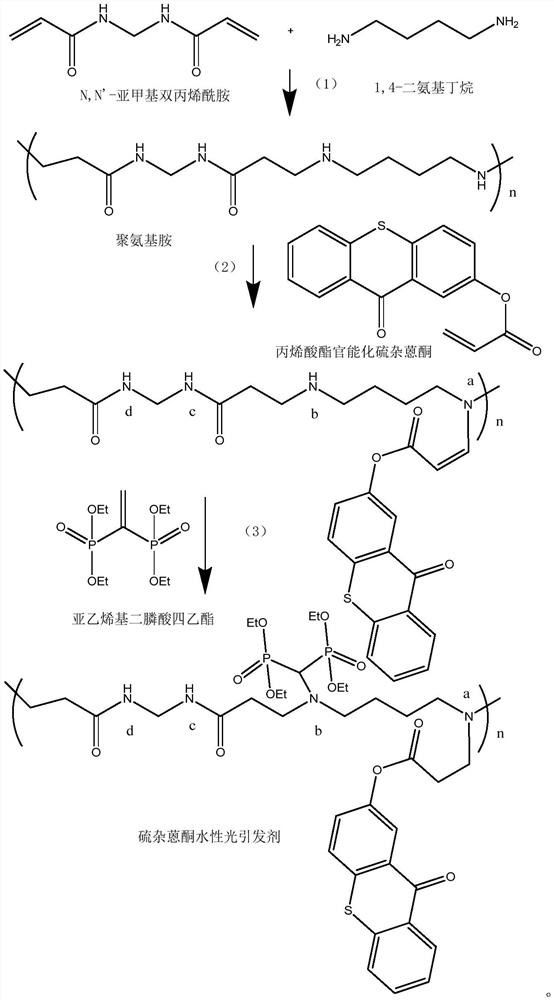
[0063] (1) Mix N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (2.6mmol) and 1,4-diaminobutane (2.9mmol), N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide and 1,4-bisacrylamide The molar ratio of aminobutane was 1:1.1, dissolved in methanol (1.5 mL), and stirred at 40°C for 12 hours. The pure polymer is then isolated by precipitation into diethyl ether and filtered and dried under vacuum to yield the polyaminoamine.
[0064] (2) Polyaminoamine (0.1g, 0.02mmol) and acrylate-functionalized thioxanthone (TXA) (0.028g, 0.01mmol) were dissolved in methanol (2.5mL), stirred at 70°C under nitrogen for 48 Hour. When the reacted solution was added to 10 mL of diethyl ether, the pure polymer was isolated as an orange solid with a yield of 50%.
[0065] (3) The product of step (2) (0.015 g, 0.055 mmol) and tetraethyl vinylidene diphosphonate (0.05 g, 0.166 mmol) were stirred in chloroform (0.5 mL) for 48 h at room temperature. ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] A preparation method of thioxanthone aqueous photoinitiator, the difference from Example 1 is: increase the molar weight of 1,4-diaminobutane to 3.4mmol, so that N,N'-methylene bis The molar ratio of acrylamide and 1,4-diaminobutane becomes 1:1.3.
[0071] Specifically include the following steps:
[0072] (1) N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (2.6 mmol) and 1,4-diaminobutane (3.4 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (1.5 mL), and stirred at 40° C. for 12 hours. The pure polymer is then isolated by precipitation into diethyl ether and filtered and dried under vacuum to yield the polyaminoamine.
[0073] (2) Polyaminoamine (0.1g, 0.02mmol) and acrylate-functionalized thioxanthone (TXA) (0.028g, 0.01mmol) were dissolved in methanol (2.5mL), stirred at 70°C under nitrogen for 48 Hour. When this solution was added to excess diethyl ether, the pure polymer was isolated as an orange solid in 50% yield.
[0074] (3) The product of step (2) (0.015 g, 0.055 mmol) and tetraethyl vinyli...
Embodiment 3
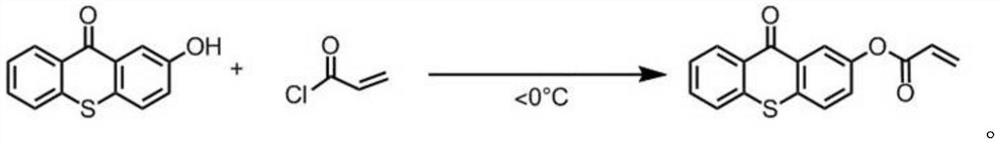
[0076] A preparation method of a thioxanthone aqueous photoinitiator, the difference from Example 1 is: N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide is replaced by 1,6-hexanediol diol in an equimolar amount Acrylate.
[0077] Specifically include the following steps:
[0078] (1) 1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate (2.6 mmol) and 1,4-diaminobutane (2.9 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (1.5 mL), and stirred at 40° C. for 12 hours. The pure polymer is then isolated by precipitation into diethyl ether and filtered and dried under vacuum to yield the polyaminoamine.
[0079] (2) Polyaminoamine (0.1g, 0.02mmol) and acrylate-functionalized thioxanthone (TXA) (0.028g, 0.01mmol) were dissolved in methanol (2.5mL), stirred at 70°C under nitrogen for 48 Hour. When this solution was added to excess diethyl ether, the pure polymer was isolated as an orange solid in 50% yield.
[0080] (3) The product of step (2) (0.015 g, 0.055 mmol) and tetraethyl vinylidene diphosphonate (0.05 g, 0.166 mmol) were stirred in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com