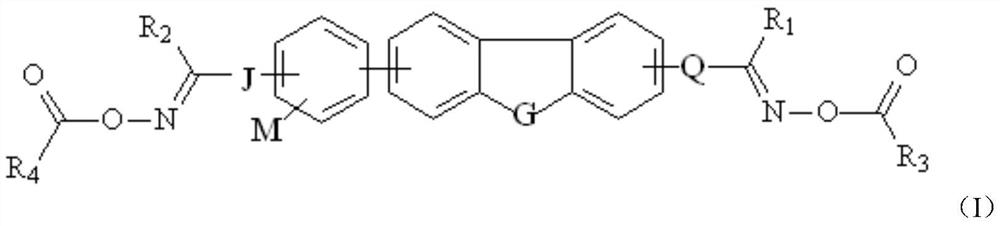
Bis-oxime ester photoinitiator, preparation method, photosensitive resin composition and application
A photoinitiator and ester technology, applied in the field of photocuring, can solve the problem of easy migration of photoinitiators, and achieve the effect of reducing migration and high initiation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0056] The present application also provides a kind of preparation method of above-mentioned double oxime ester photoinitiator on the other hand, and this preparation method comprises:
[0057] S1, under the action of the first catalyst, use raw material a to react with raw material b to obtain intermediate a, the synthetic route is as follows:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, X 1 means halogen, A means -CH 2 -or-NH-, G' means R 5 or R 6 group, G means group, R 5 and R 6 represent independently of each other a polymerizable group;
[0060] S2, under the action of the second catalyst, intermediate a is subjected to Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction with raw material c and raw material d to obtain intermediate b. The synthetic route is as follows:
[0061]
[0062] Among them, X 2 and x 3 are independently selected from halogen;
[0063] J and Q represent linking bonds or carbonyl groups,
[0064] R 1 ’ for R 1 or R 1 -CH 2 -, R 2 ’ means R 2 or R 2 -CH 2 ...
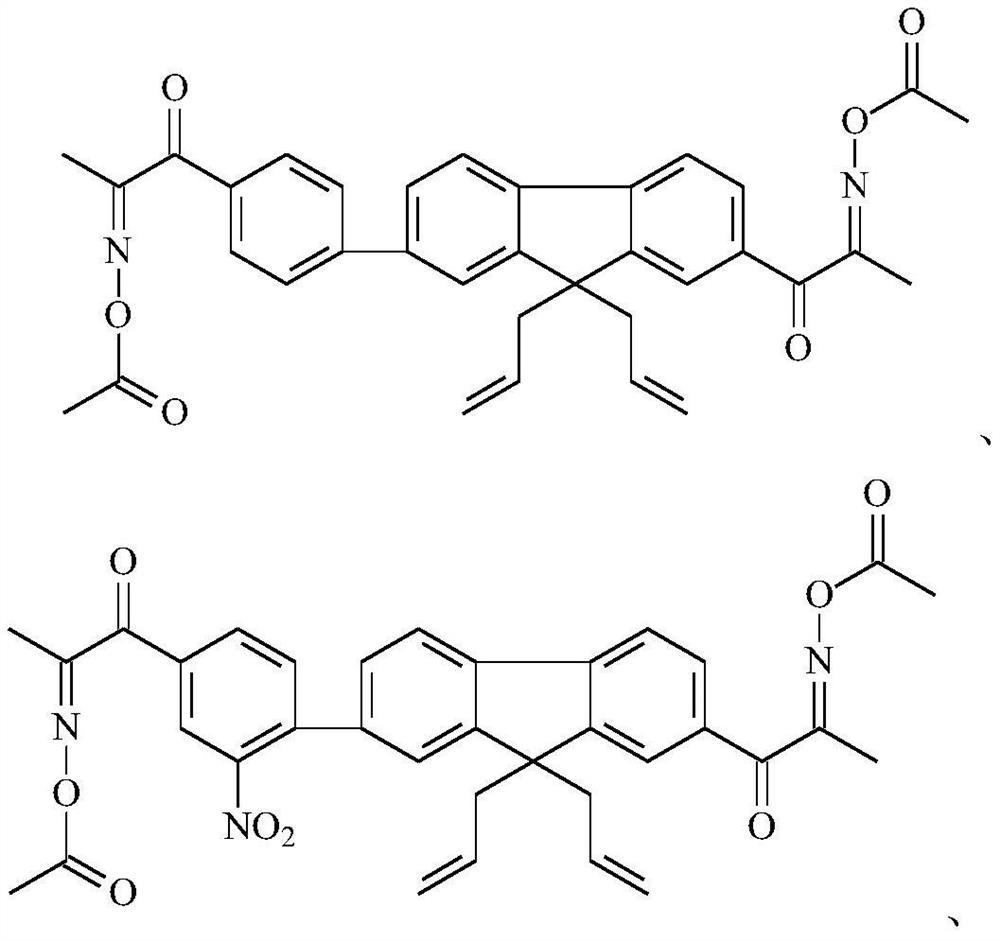
Embodiment 1
[0118] (1) Synthesis of Intermediate 1a
[0119] Add 24.2g of raw material 1a, 10.8g of sodium methoxide, and 50mL of thionyl chloride (DMSO) into a 250mL four-necked flask, blow nitrogen into the above-mentioned four-necked flask, and stir at room temperature for 0.5h. Then, 21.3 g of the raw material 1b was slowly added dropwise to the above-mentioned four-neck flask, and the addition was controlled within 3 hours, and the liquid phase followed the reaction until the raw material no longer changed. The material obtained after the reaction was poured into deionized water, stirred, and the product was extracted with n-hexane, and the n-hexane product solution was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the n-hexane was removed by rotary evaporation, and then recrystallized with methanol as a solvent to obtain 28.7g of yellow solid product, ie intermediate 1a, the yield is 75wt%, and the purity is 98wt%.
[0120] The synthetic route is:
[0121]
[0122] Intermediate 1...
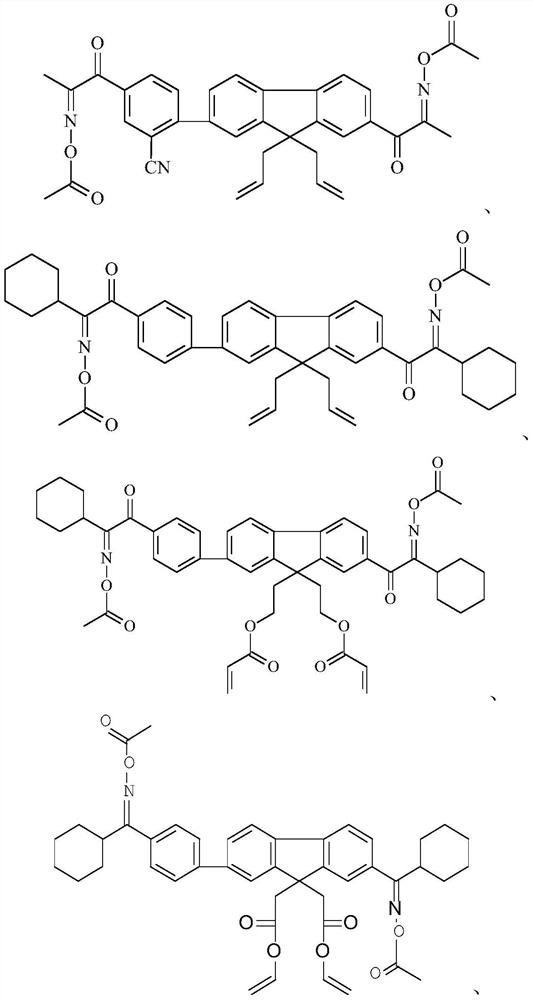
Embodiment 2
[0141] (1) Synthesis of Intermediate 2a.
[0142] Add 24.3g of raw material 2a, 10.8g of sodium methoxide, and 50mL of thionyl chloride (DMSO) into a 250mL four-neck flask, blow in nitrogen gas, stir at room temperature for 0.5h, then slowly add 10.6g of epichlorobutane dropwise, and control the drop for 3h. After the addition, the liquid phase followed the reaction until the raw materials no longer changed. Pour the material obtained after the reaction into deionized water, stir, extract the product with n-hexane, dry the n-hexane product solution with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, remove the n-hexane by rotary evaporation, and recrystallize with methanol as a solvent to obtain 28.2 g of a white solid product , namely intermediate 2a, with a yield of 90wt% and a purity of 98wt%.
[0143] The synthetic route is:
[0144]
[0145] The structure of intermediate 2a was confirmed by H NMR and mass spectrometry:
[0146] 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 , 500MHz): 1.8936-1.9451 (2H, m), 2.49...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com