Method for preparing polymer in situ alloy by alkene monomer polymerization initiated by plasma surface
A technology of surface initiation and monomer polymerization, applied in the field of preparation of polymer alloys, can solve the problems of less research on polymer/polymerizable monomer reaction processing system, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Validation of In Situ Initiated Polymerization of Olefinic Monomers
[0028] Take 10g of pure polypropylene pellets, place them in the plasma generator, turn on the power, adjust the power to 20W, the gas medium is carbon dioxide, the flow rate is 50ml / min, discharge for 10 minutes, then take out the polypropylene pellets, Let stand in the atmosphere for 5 minutes. Then the pellets were transferred to a 100 ml three-neck flask, and 20 ml of styrene monomer distilled under reduced pressure was poured into it. The reaction temperature was set at 100° C., and the whole reaction was carried out under argon protection and condensed reflux. After reacting for one hour, take out the three-neck bottle, place it in an ice-water mixture and cool it to room temperature, take out the product, and place it in a beaker filled with 500 ml of ethyl acetate to take out the homopolymerized polystyrene, take it out after 2-3 days , put the remaining material back into a beaker containing...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Validation of In Situ Initiated Polymerization of Olefinic Monomers
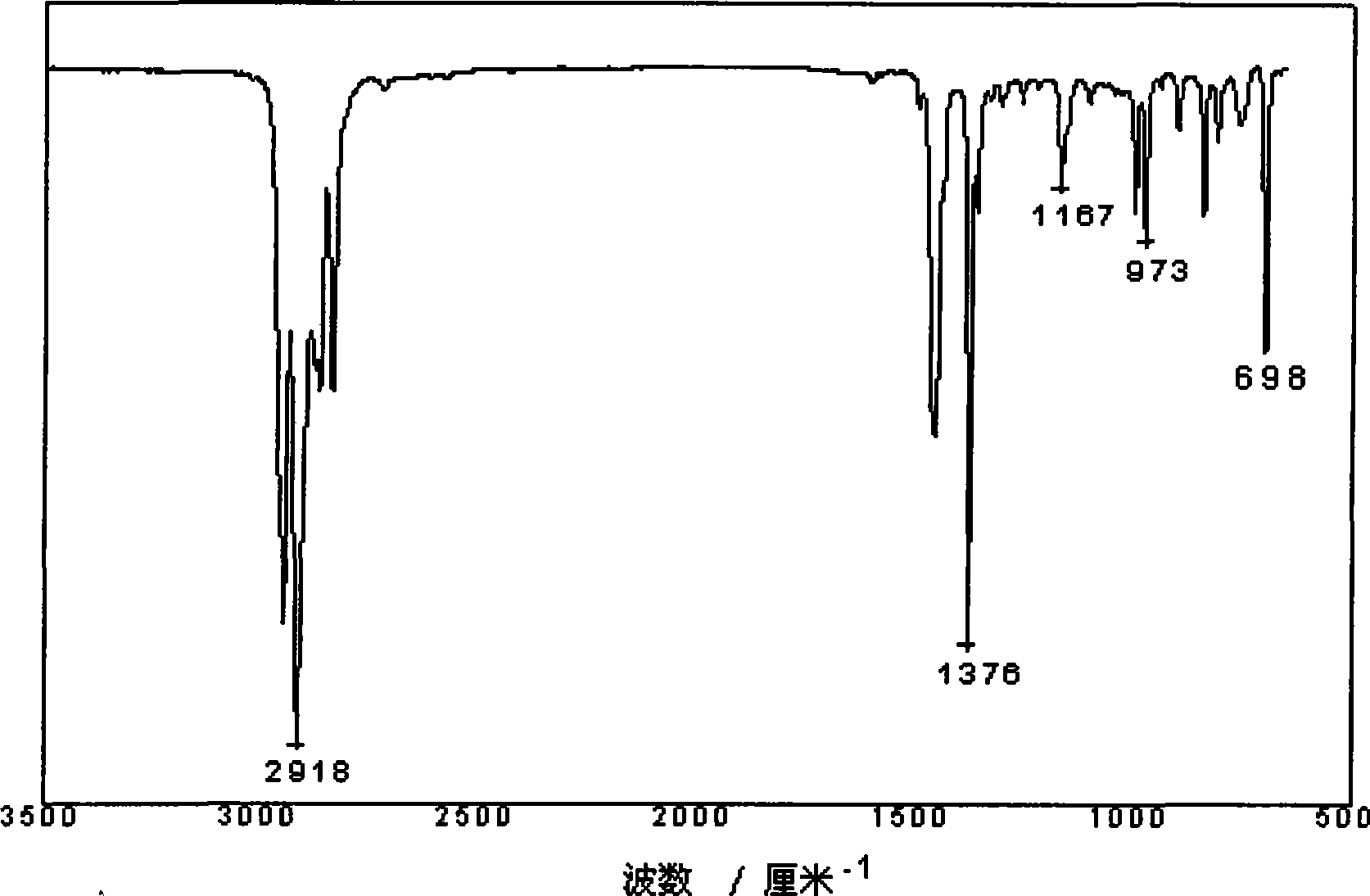
[0033] Take 8g of pure polystyrene pellets, put them in the plasma generator, turn on the power, adjust the power to 20W, the gas medium is nitrogen, the flow rate is 50ml / min, discharge for 20 minutes, and then take out the polystyrene pellets , let stand in the atmosphere for 5 minutes. Then the pellets were transferred to a 100 ml three-neck flask, and 30 ml of styrene monomer distilled under reduced pressure was poured into it. The reaction temperature was set at 100° C., and the whole reaction was carried out under the protection of argon and condensed reflux. After reacting for five hours, the three-neck flask was taken out, placed in an ice-water mixture and cooled to room temperature, the product was taken out, placed in a beaker containing 100 ml of ethyl acetate, and fully dissolved. In order to measure the molecular weight of polystyrene initiated in situ, ethyl acetate solution was carrie...
Embodiment 3
[0035] In situ initiation versus thermal polymerization
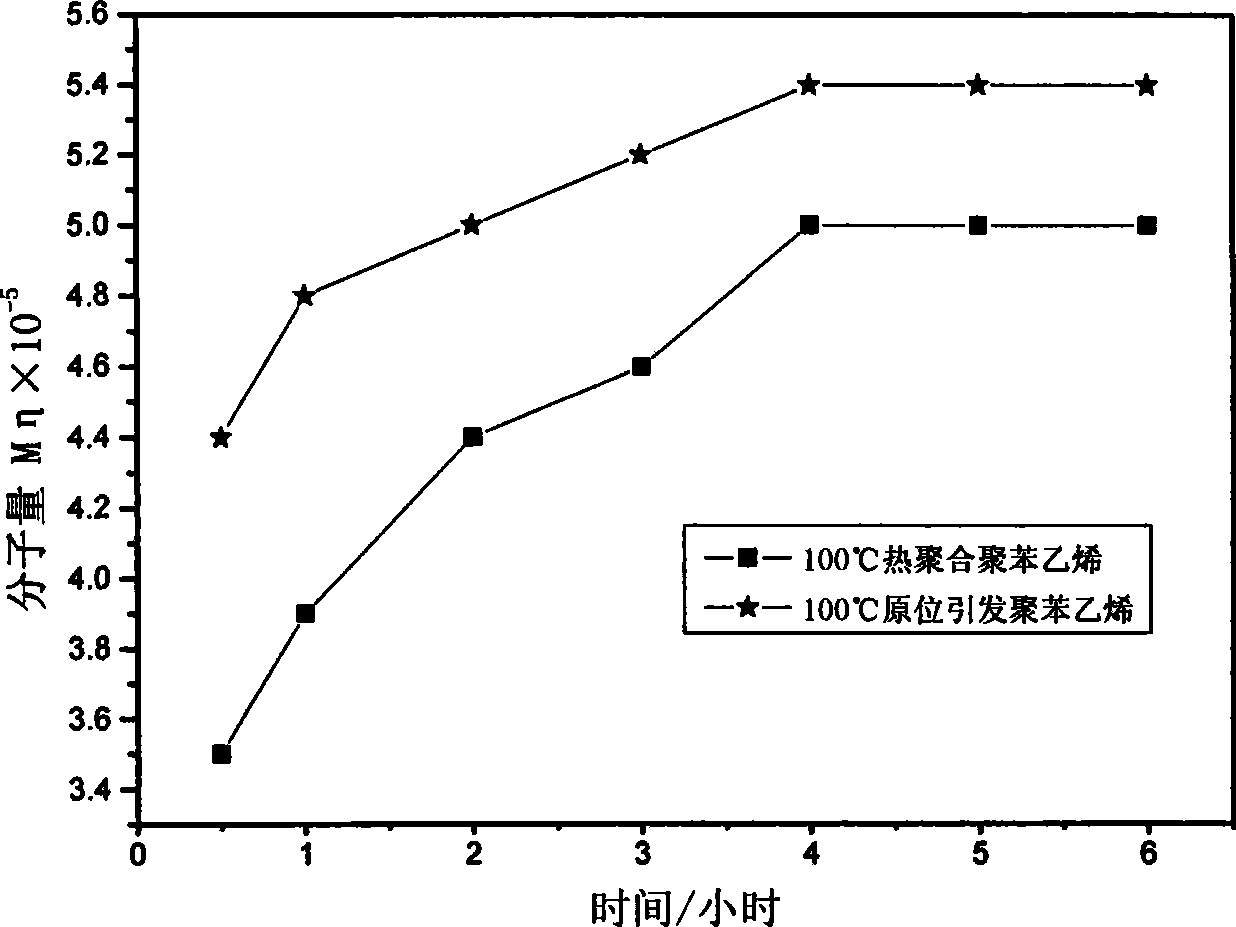
[0036] According to the method for embodiment 1, the polystyrene that the reaction time is respectively 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours, 4 hours, 5 hours and isolates measures the change of viscosity-average molecular weight along with the polymerization time;
[0037] Take 120 ml of styrene monomer that has been distilled under reduced pressure, and conduct thermal polymerization at 100°C. The reaction times are 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours, 4 hours, and 5 hours. Quantitative products are taken out, and polystyrene is separated. Ethylene, measure the change of its viscosity average molecular weight with the polymerization time.
[0038] The viscosity-average molecular weight of polystyrene initiated and thermally polymerized in situ with the change of polymerization time is shown in the appendix figure 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com