[0003] There are two problems in the existing ocean profiler
observation system: one is that the working mode of the profiler adopts single-point observation, and the
observation data is directly transmitted to the control center through cables or radios. Poor performance and expandability; Second, there is no information interaction between profilers, which makes it impossible to perform high-resolution, three-dimensional observations in a certain area of the ocean
[0006] Second, the uplink and downlink rates are asymmetric: the limited network environment cannot be predicted, the uplink and downlink rates are determined by the specific environment, and the propagation speed of
sonar will be affected by the
temperature and pressure of
seawater [0009] Fifth,
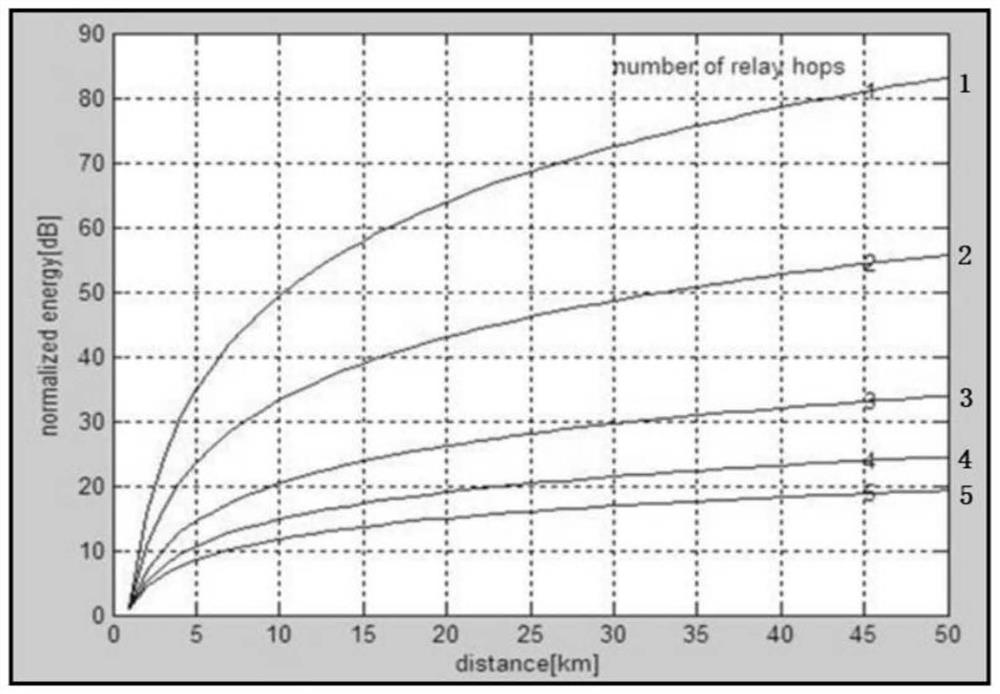
limited resources: resources mainly include memory, energy, and bandwidth. Due to process limitations, the memory space and energy of nodes are limited, and the available bandwidth of underwater acoustic
waves is limited. There are only 5KHz in long-distance transmission systems exceeding ten kilometers. bandwidth
[0012] First, there are two main aspects in the construction of the underwater acoustic communication
network on the
seabed at this stage: one is that the observation node collects data independently and transmits it directly to the control center through cables or radios. The mobility of such working methods and poor
scalability; second, there is no information interaction between the observation nodes, and they cannot work together. In view of the problems existing in the existing technology, there is a demand for real-time high-resolution continuous three-dimensional
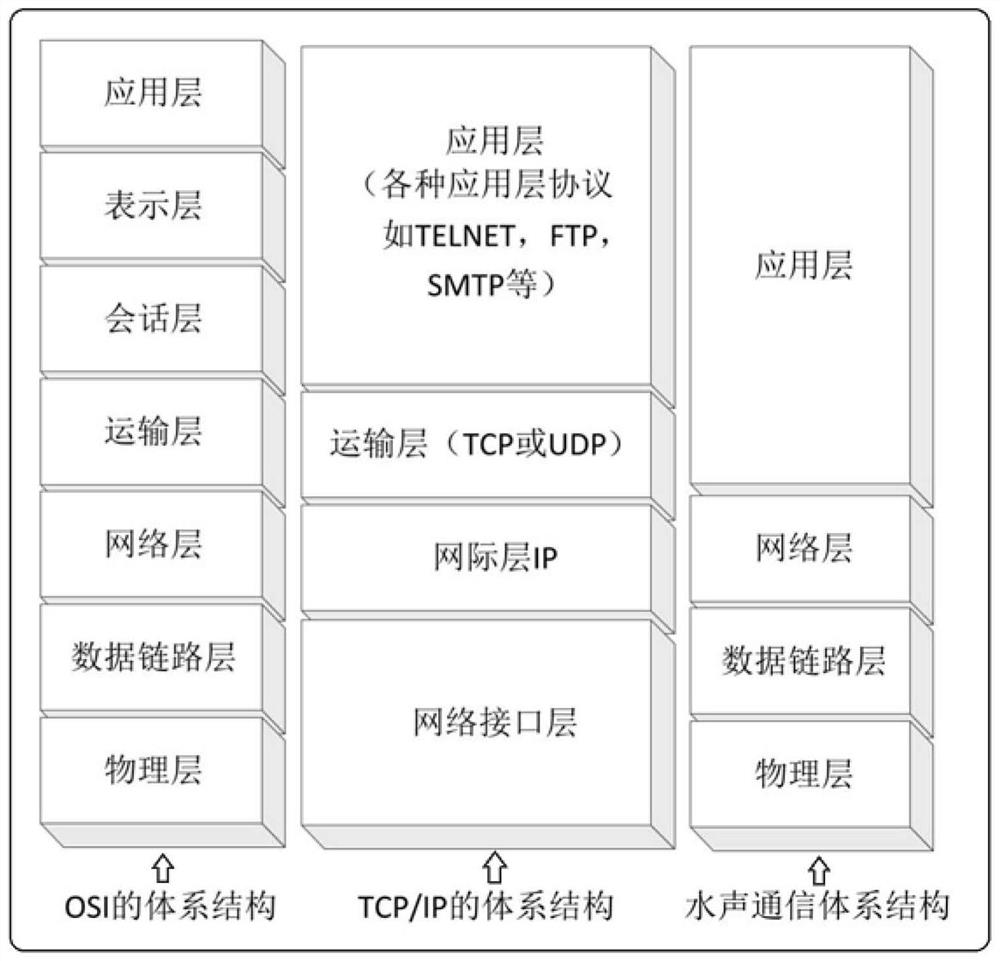
ocean observation technology, so there is an urgent need to use marine environment observation As a background, the network protocol part of the underwater acoustic communication network
system in
ocean observation technology is designed and implemented;
[0013] Second, the existing underwater acoustic communication network cannot meet the assumptions of the TCP / IP protocol family. First, the delay is high and variable. Compared with the radio on land as a communication medium,
sonar as a communication medium obviously brings additional transmission. Time delay; the second is the
asymmetry of uplink and downlink rates, and the propagation speed of sonar will be affected by the
temperature and pressure of sea water; the third is intermittent connection, which is caused by factors such as node movement or node energy exhaustion, and
underwater acoustics The communication network saves
energy consumption through the way of node
dormancy, which prolongs the life of the network; the fourth is the low signal-to-noise ratio and high
bit error rate, channel attenuation,
multipath interference,
Doppler effect and other phenomena in the underwater acoustic communication network Both will cause problems of low signal-to-noise ratio and high bit error rate; fifth, resources are limited, limited by the process, the memory space and energy of the node are limited, and the available bandwidth of underwater acoustic
waves is limited. In the long-distance
transmission system exceeding ten kilometers There is only a bandwidth of 5KHz, which leads to the particularity of the underwater acoustic communication network protocol, and there is no corresponding solution in the existing technology;
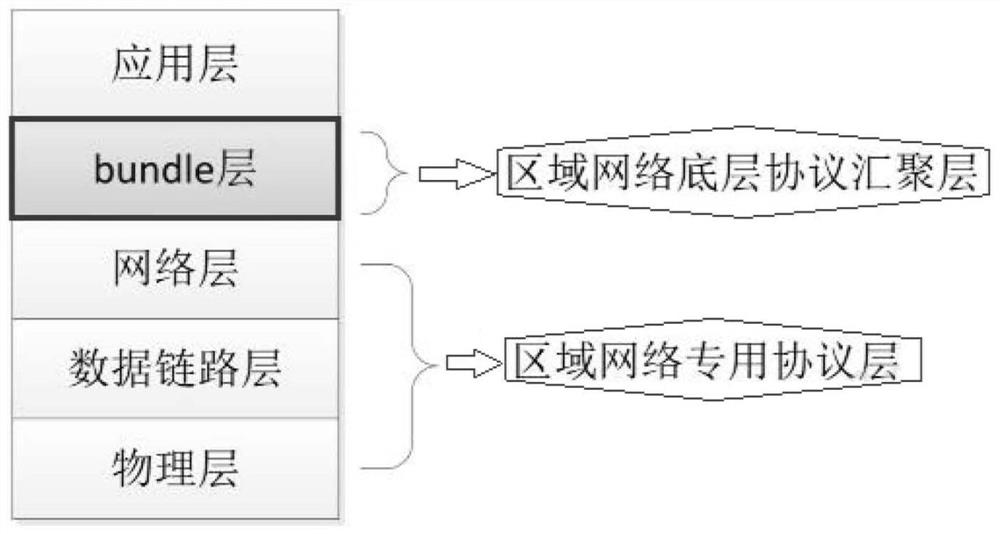
[0014] Third, limited by the technology level, the energy of underwater nodes is limited. In addition, the underwater acoustic communication has a long delay and is easy to be interrupted. The existing technology underwater communication has weak tolerance to interruption and delay. The underwater acoustic communication network is a typical restricted network. Using a fault-tolerant and delay-tolerant network protocol
system, in a traditional
wireless sensor network, communication requires at least one stable connection between the source and the sink.
In the underwater environment, the
network topology changes dynamically, the nodes are sparsely distributed, the
transmission rate of the
acoustic wave is limited, and it is impossible to build a stable end-to-end connection with each other, which brings great challenges to the design of underwater acoustic-capacity-delay-tolerant
network routing protocols. great challenge;
[0015] Fourth, the nodes in the underwater acoustic-delay-tolerant network are sparsely distributed, and the link stability cannot be guaranteed. In order to improve the
message delivery rate, a multi-copy routing mechanism is usually used. However, the energy of underwater nodes Compared with the relatively limited memory, the multi-copy routing mechanism will inevitably bring additional
network overhead, thereby increasing memory usage and
energy consumption When the memory space is insufficient, the node will enter the congestion state, affecting the
normal delivery of the message; it is relatively difficult to build an end-to-end continuous and stable link in the underwater acoustic
fault tolerance network, the main reason is the high delay of the underwater acoustic link Moreover, the
transmission rate is easily affected by the external environment. The underwater node cannot obtain the congestion status of its communication node in real time and perform corresponding actions. The congestion problem is relatively severe; the divergent waiting protocol based on the contact probability overcomes the
blindness of the divergent waiting protocol. But at the same time, it also caused two problems. On the one hand, the node with a relatively high contact probability has a relatively heavy resource burden. It may receive a large number of copies in a short period of time and cause
network congestion; on the other hand, it has been successfully delivered. The redundant copy of the message cannot be deleted in time, which leads to
network congestion, and lacks a reasonable congestion control mechanism to ensure the performance of the CDK-SQ
routing protocol;
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More