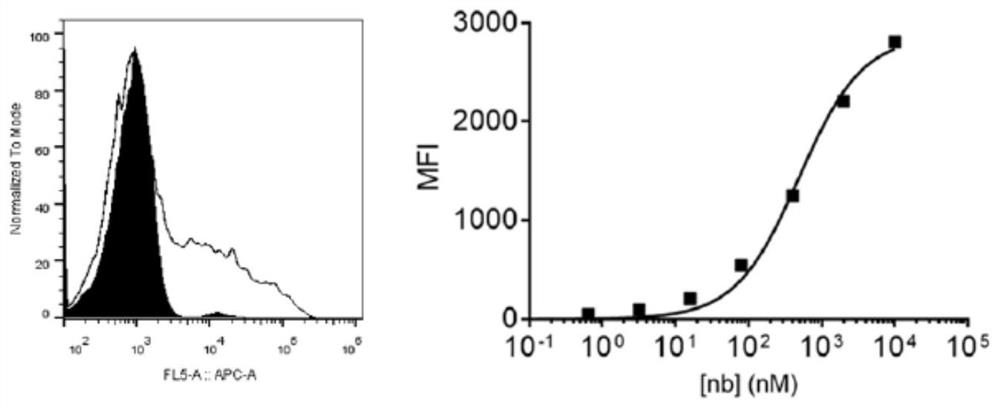
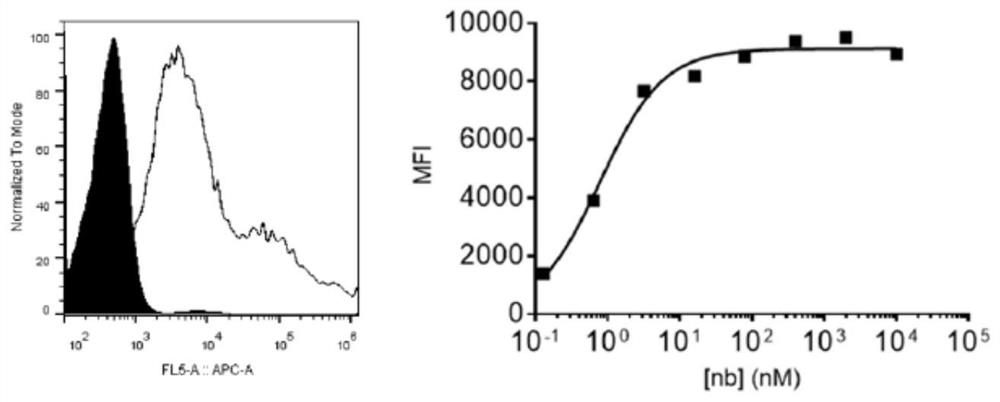
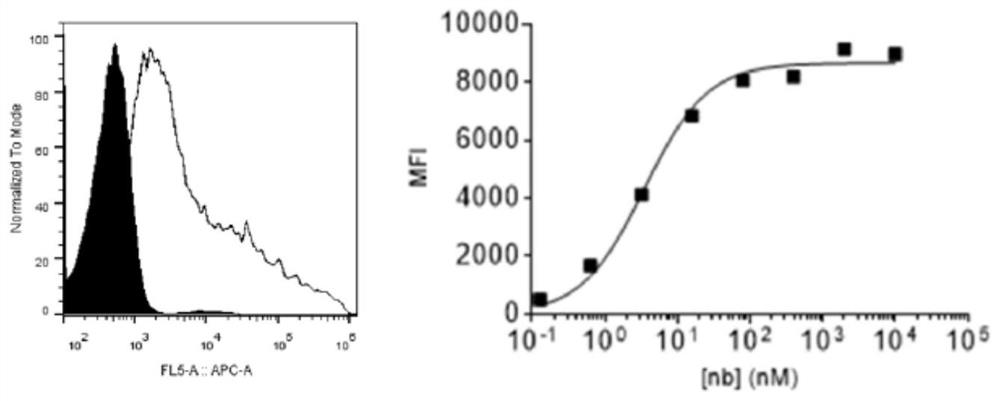
Specific antibody of new coronavirus S protein NTD region as well as preparation method and application of specific antibody
A specific, protein-based technology, applied in the direction of viruses/bacteriophages, microbial-based methods, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of large-scale mass production of high finished products, unfavorable large-scale mass production, and limited antibody specificity. Low production cost, conducive to large-scale popularization and application, and high antibody stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0131] Example 1: Preparation of antigens
[0132] The conventional method for preparing antigens in the prior art is to recombinantly express and purify the NTD region of the S protein as an antigen, and then immunize animals such as mice, rabbits, and monkeys. However, the above-mentioned prior art has the following disadvantages: the immune systems in animals such as mice, rabbits, and monkeys have limited ability to generate specific spatial structures for recognizing antigens; The NTD region of recombinantly expressed and purified S protein is not a membrane protein, and its existing state is not as good as the natural state, so the obtained antibody may not be able to correctly recognize the antigen.
[0133] For the NTD domain of the new coronavirus S protein, the antigen preparation method of the present invention is specifically:
[0134] (1)串联、构建编码S蛋白NTD区域(即第1-304位氨基酸,具体为: MFVFLVLLPLVSSQCVNLTTRTQLPPAYTNSFTRGVYYPDKVFRSSVLHSTQDLFLPFFSNVTWFHAIH VSGTNGTKRFDNPVLPFNDGVYFA...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2: Alpaca immunization injection
[0140] In this example, alpacas were immunized with the antigen prepared in Example 1. Specific steps are as follows:
[0141] (1) The antigens prepared in Example 1 were equally divided into 4 parts;
[0142] (2) The alpacas were immunized 4 times in total, and the antigens were subcutaneously injected into the animals. The first immunization was recorded as the first day, and the subsequent immunizations were on the 10th, 19th, and 28th days respectively; On the 28th day, before the fourth immunization injection, about 200 mL of alpaca venous peripheral blood was collected, and on the 42nd day, that is, 14 days after the fourth immunization, about 300 mL of alpaca venous peripheral blood was collected.
[0143] Compared with the traditional immunization technical solutions for animal antibodies such as mice and rabbits, the method provided in this example collects a large amount of alpaca venous peripheral blood, which is c...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3: Construction of Antibody Libraries
[0145] Using the two batches of alpaca venous peripheral blood collected in Example 2 as raw materials, a high diversity Nanobody library was constructed. The two batches of alpaca venous peripheral blood were treated in the same way, specifically:
[0146] (1) Using density gradient centrifugation to separate lymphocytes from the peripheral blood of alpaca veins;
[0147] (2) Extracting the total mRNA of lymphocytes and reverse transcribing into cDNA;
[0148] (3) Using appropriate DNA primers, the above-mentioned cDNA is used as a template, and the VHH fragments of alpaca immunoglobulin IgG2 and IgG3 are obtained by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, that is, the DNA fragments of Nanobodies;
[0149] (4) connecting the DNA of VHH to the phage surface display screening vector to form a VHH-pIII fusion protein expression vector plasmid library; wherein, pIII is a protein present on the phage surface flagella;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com