Far-end true time delay beamforming implementation method based on few-mode fiber
A few-mode fiber, beamforming technology, applied in the field of microwave photonics, to achieve the effect of reducing demand, reducing cost, phase and delay jitter elimination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The solution of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
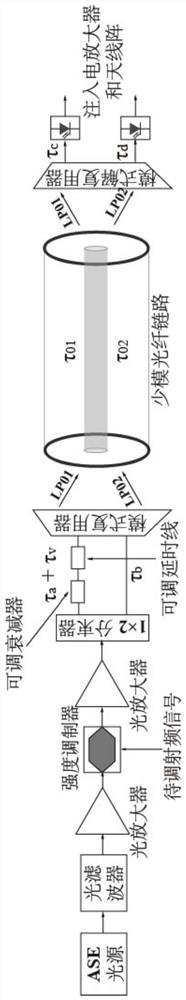
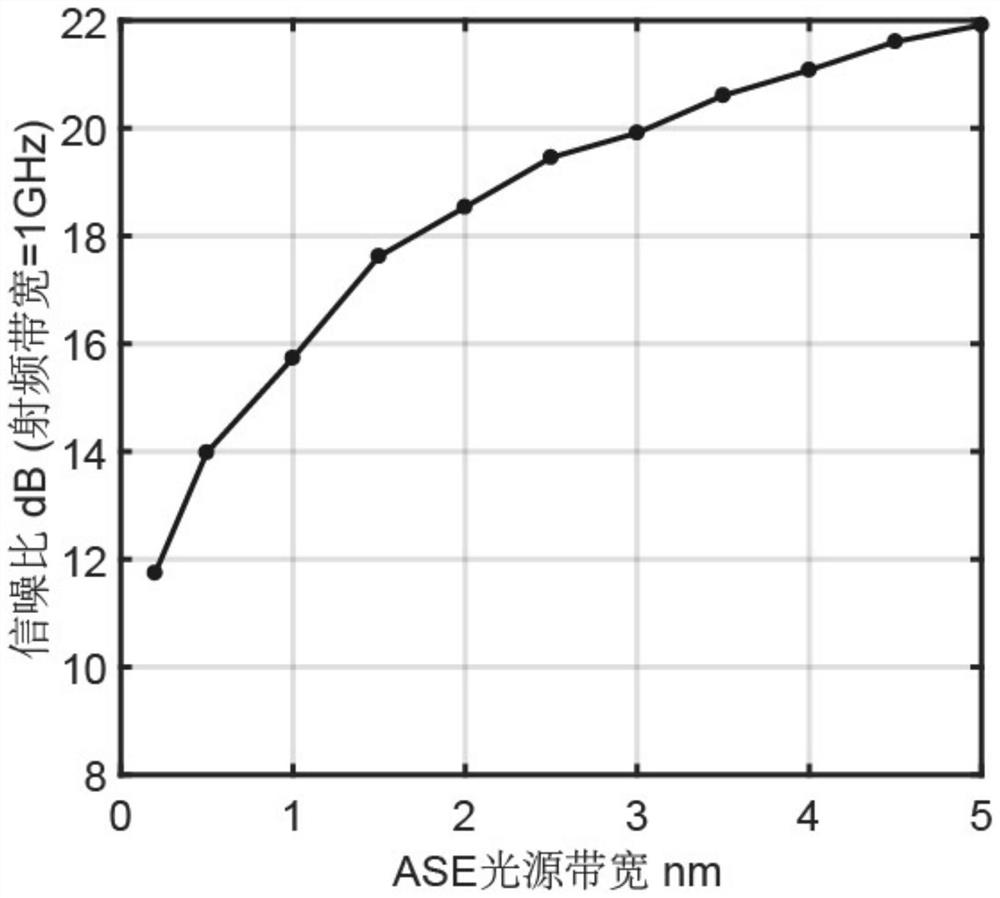
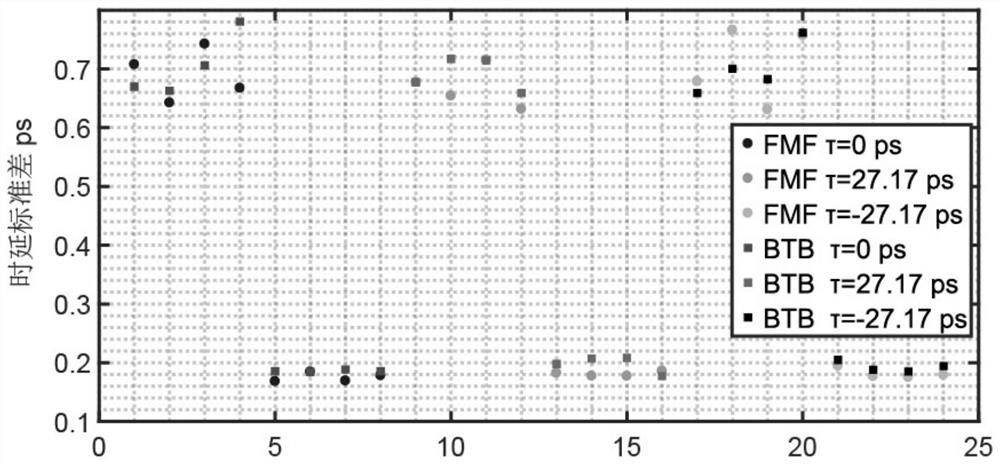
[0025] The scheme principle of the present invention is as follows figure 1 shown. The implementation here is exemplified by a two-element beamforming system using LP01 and LP02 modes of transmission. At the central office, the ASE light source is narrow-band filtered with an optical filter. The narrow-band filtered ASE light source is amplified by an optical amplifier and injected into the intensity modulator. The radio frequency signal to be modulated is modulated on the ASE optical carrier, amplified again by the optical amplifier, and split into a first delay copy signal and a second delay copy signal by a 1*2 coupler. After the first time-delayed copy signal passes through the adjustable optical attenuator and the adjustable optical delay line, the mode multiplexer is used to inject the LP01 mode of the few-mode fiber and transmit to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com