Semiconductor light-emitting element
A light-emitting element and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as chip burn and aggravate current congestion, achieve the effects of reducing the impact of brightness, improving performance, and avoiding overall widening design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
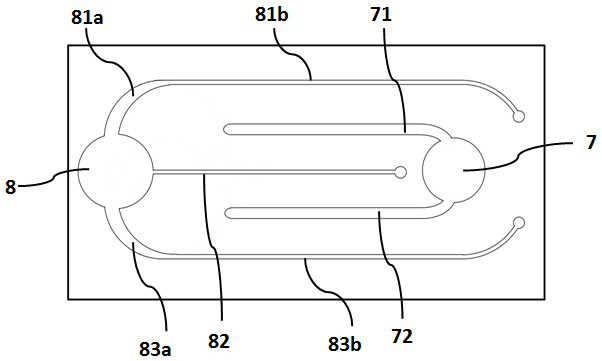
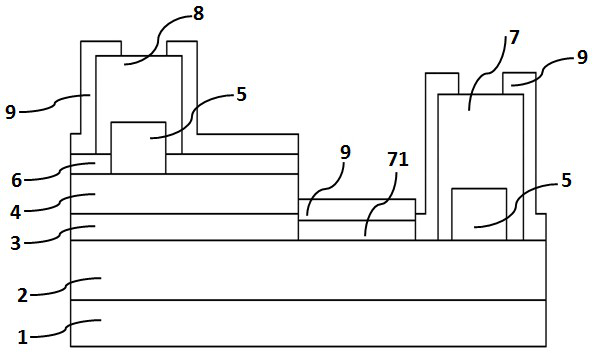
[0050] This embodiment provides the following semiconductor light-emitting element, figure 2 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of a semiconductor light-emitting element, which includes: 1: substrate; 2: first conductive type semiconductor layer; 3: active layer; 4: second conductive type semiconductor layer; 5: current blocking layer; 6: transparent conductive layer 7: first electrode; 71, 72: first electrode lead; 8: second electrode; 81, 82, 83: second electrode lead; 9: insulating protective layer.
[0051] The substrate 1 may be an insulating substrate or a conductive substrate. Substrate 1 is a growth substrate for epitaxial growth of semiconductor barrier crystal stacks, including sapphire (Al 2 O 3 ) or spinel (MgA1 2 O 4 ) insulating substrates; silicon carbide (SiC), ZnS, ZnO, Si, GaAs, diamond; and oxide substrates such as lithium niobate and niobium gallate that are lattice-matched with nitride semiconductors. The substrate 1 includes a first surface, a s...
Embodiment approach
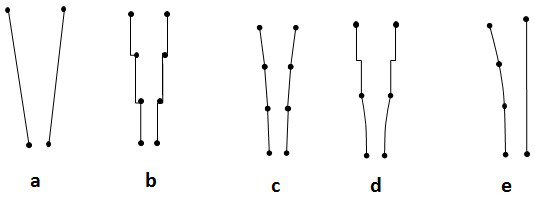
[0065] The second electrode 8 has a plurality of electrode leads, and at least one second electrode lead includes a connecting section connected to the second electrode, and an extension section extending from the connecting section to the first electrode; the second electrode lead extends The segment has a first portion extending from the second electrode lead connection segment to gradually approaching the first electrode and a second portion extending from the first portion and gradually approaching the first electrode, and the width of the first portion is gradually changed in the extending direction, so The width of the second part is fixed. As an embodiment of the present invention, the width of the first portion of the second electrode extension segment can be linearly narrowed at a fixed rate of change from the extension direction, such as image 3 As shown in a; as another embodiment of the present invention, the width of the first part of the second electrode extensi...
Embodiment 2
[0084] In this example, as Figure 9 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the two lead wires 81 and 83 of the p-electrode of this embodiment do not have the ends as in Embodiment 1, and other parts are the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com