Patents
Literature
168 results about "Current crowding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
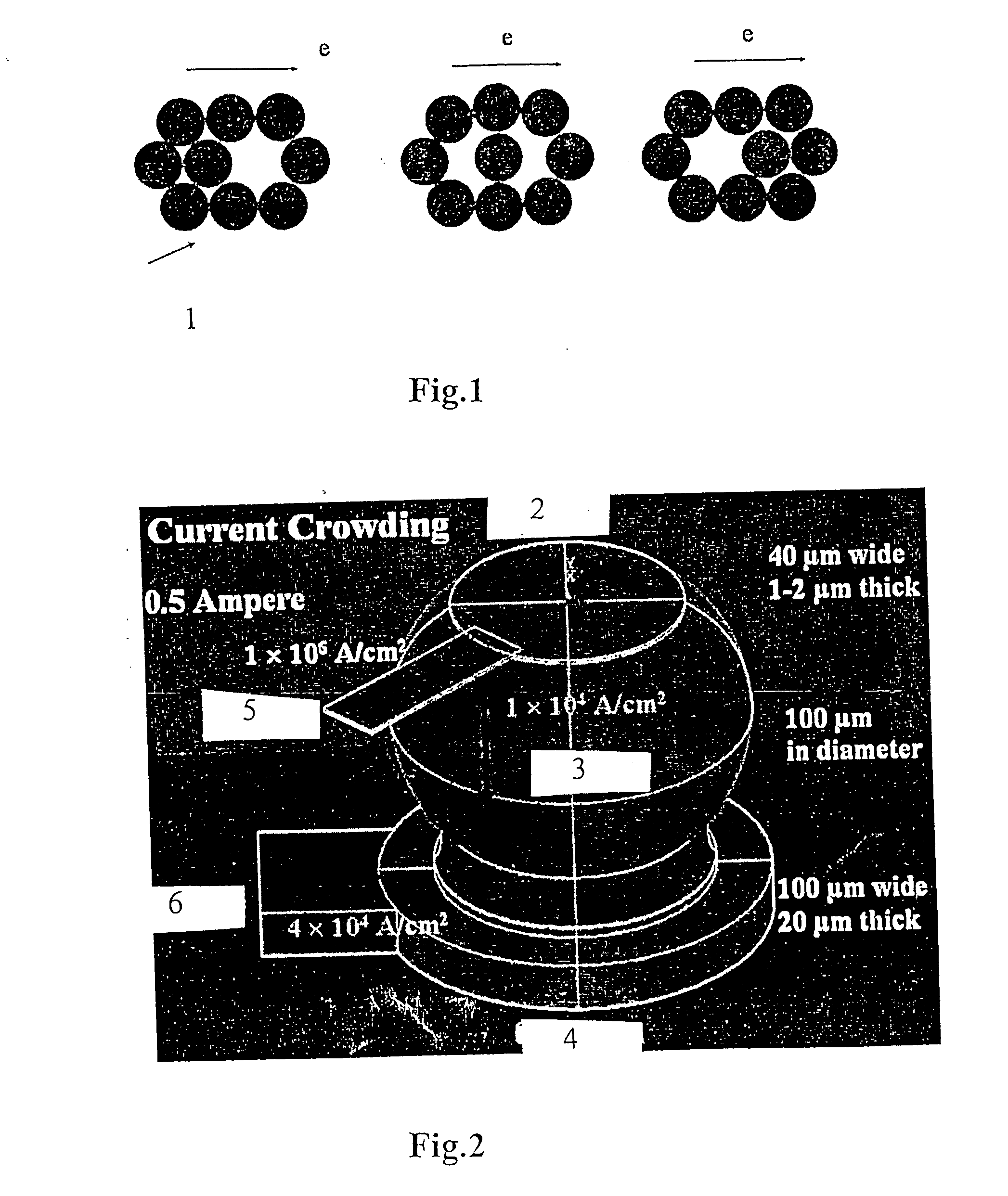
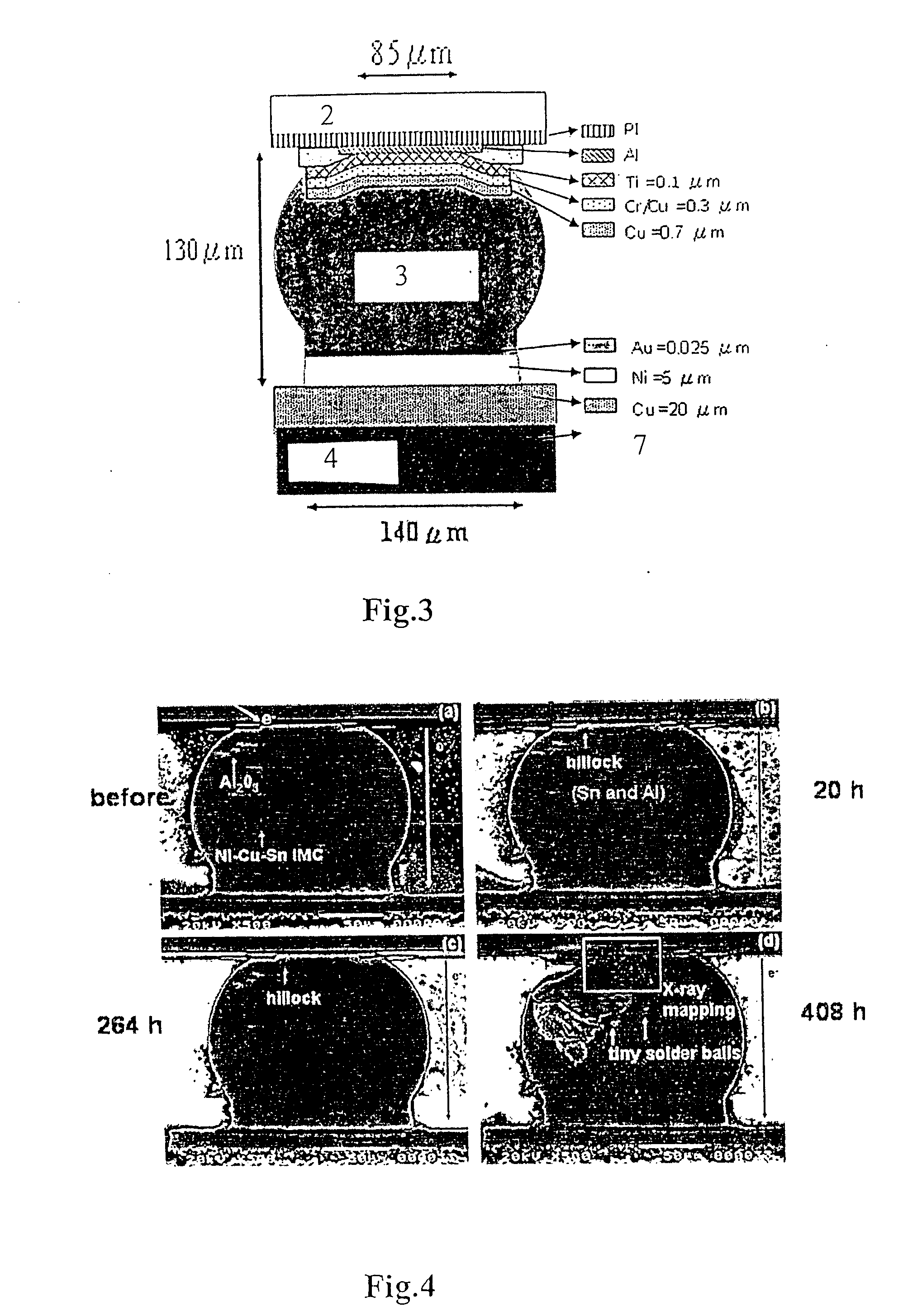
Current crowding (also current crowding effect, or CCE) is a nonhomogenous distribution of current density through a conductor or semiconductor, especially at the vicinity of the contacts and over the PN junctions.
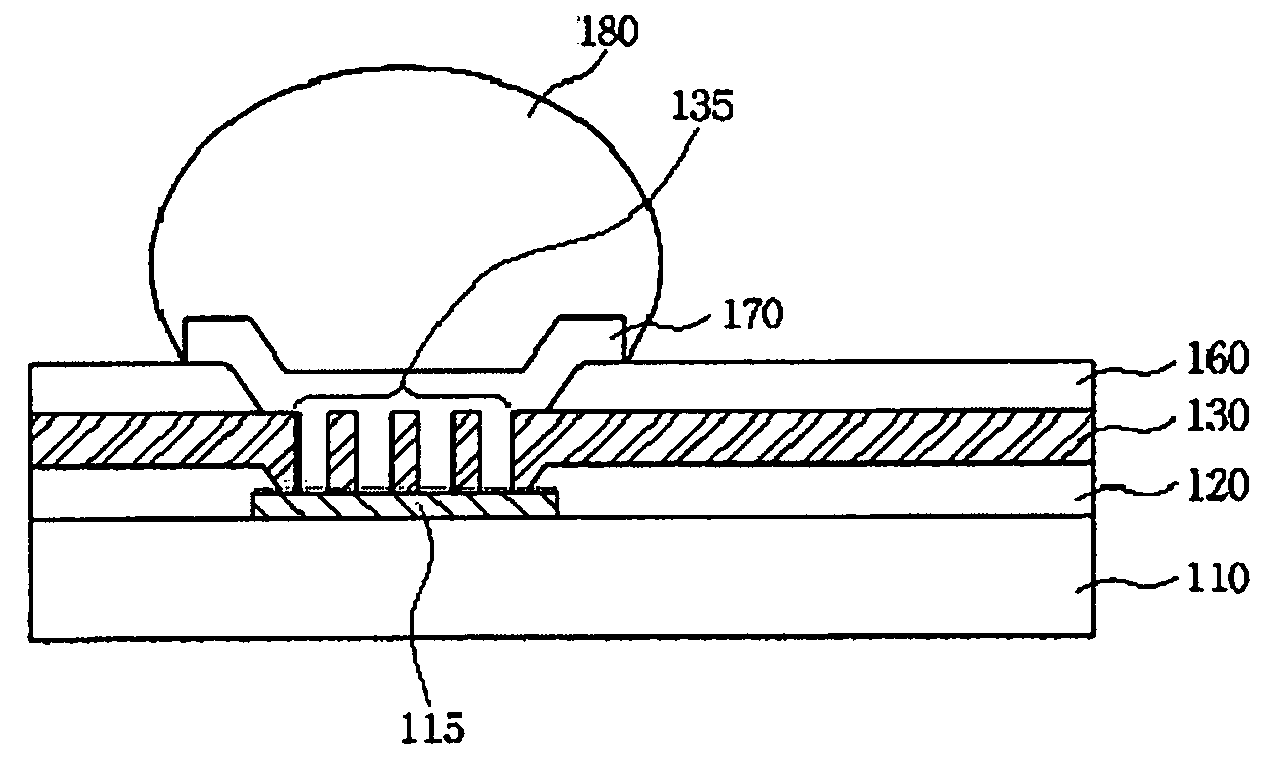
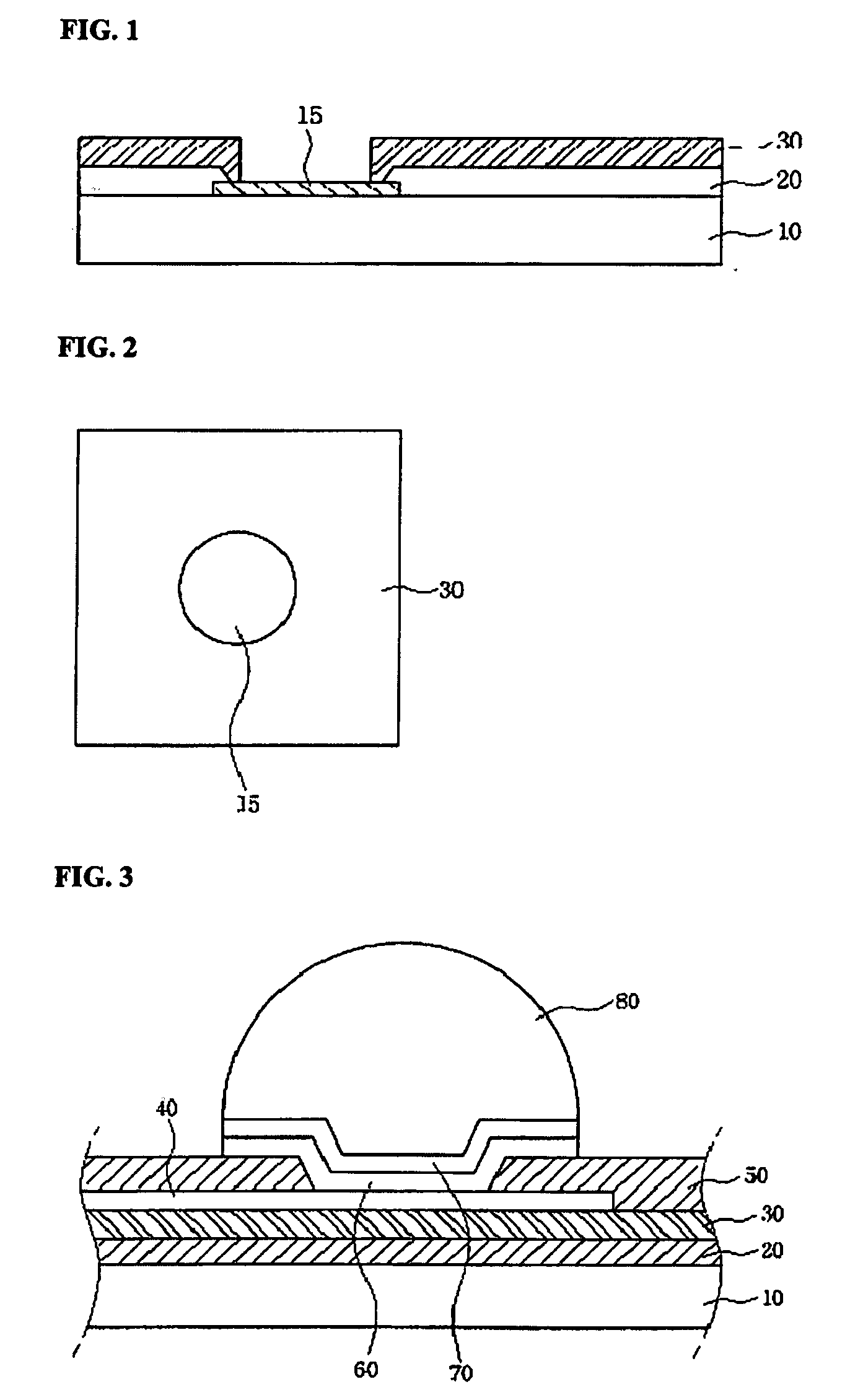
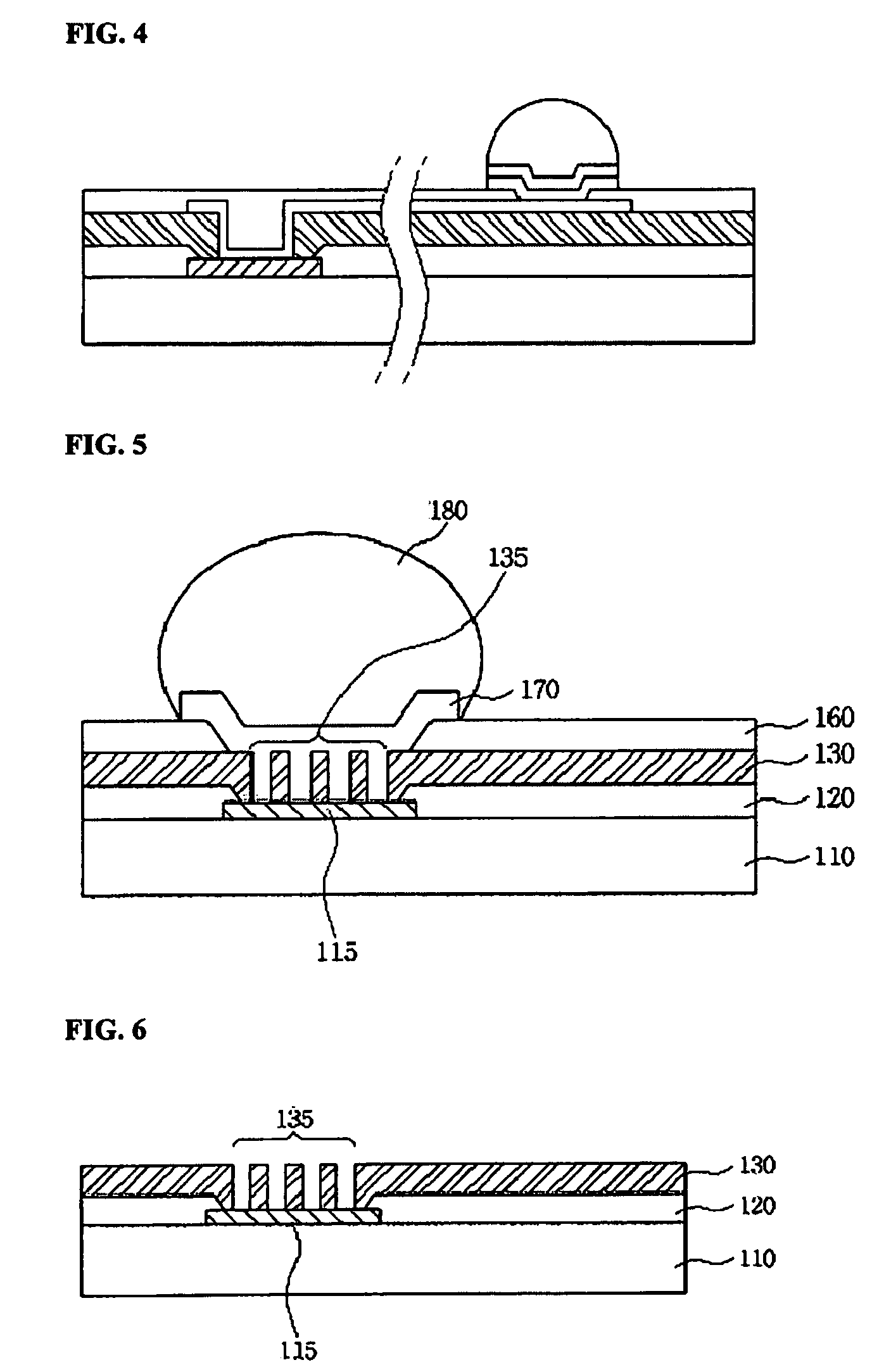
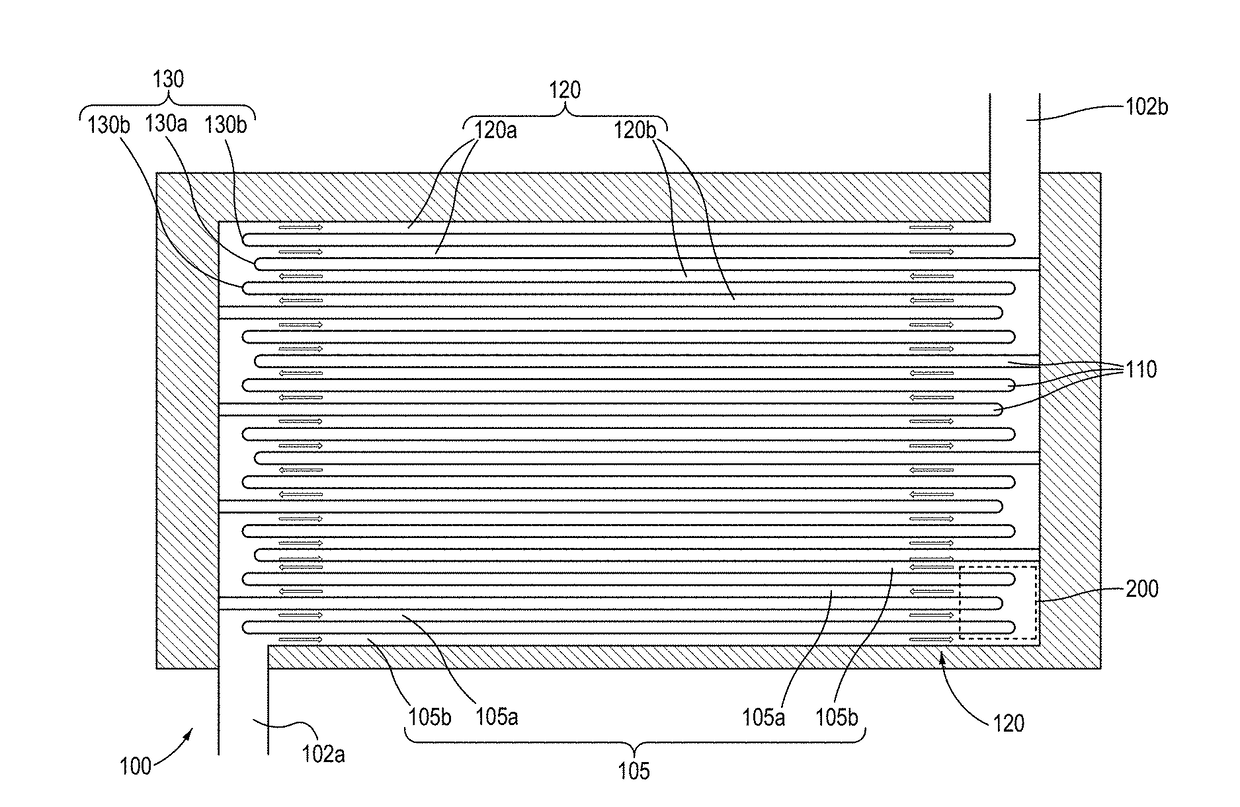
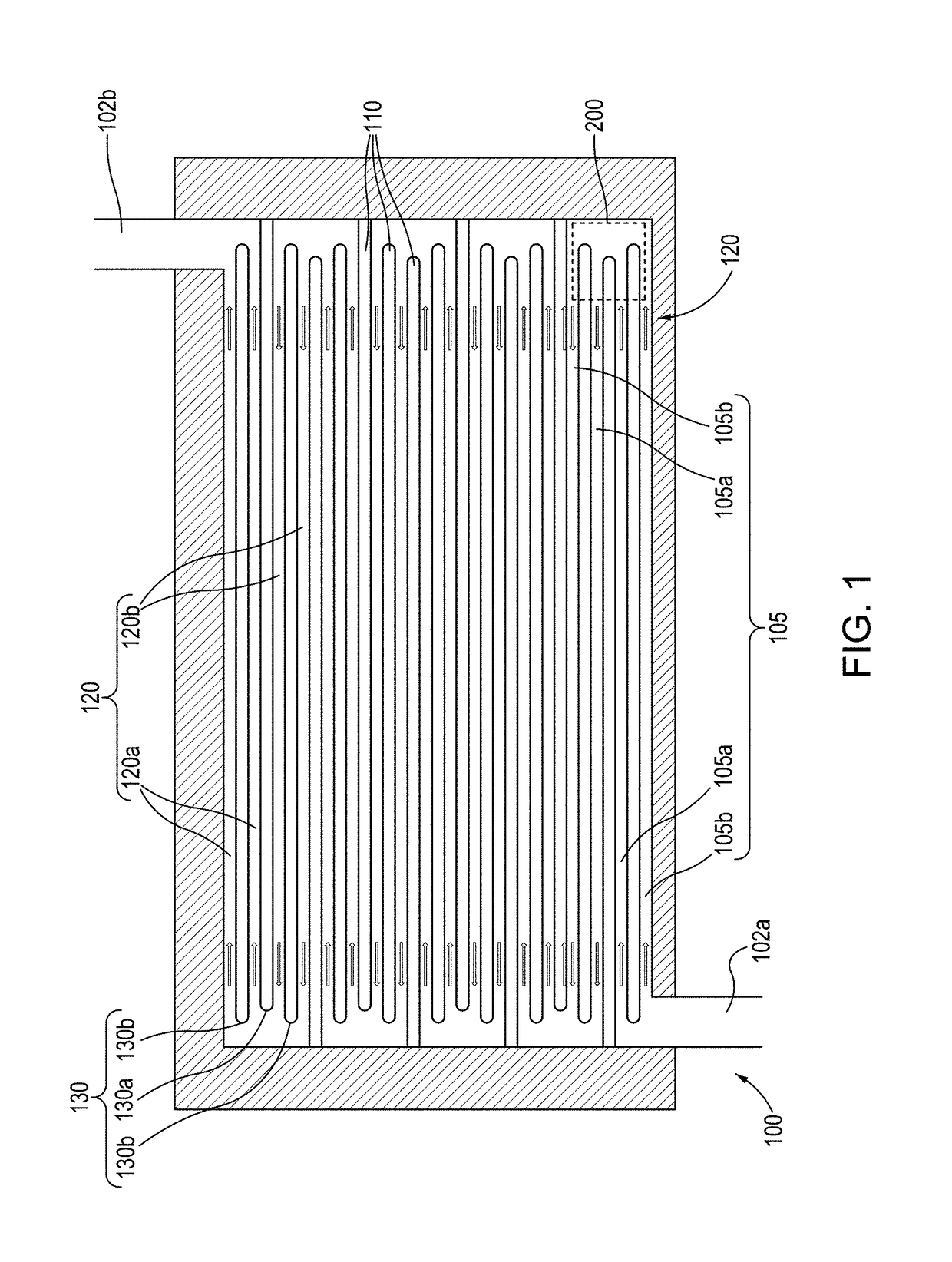
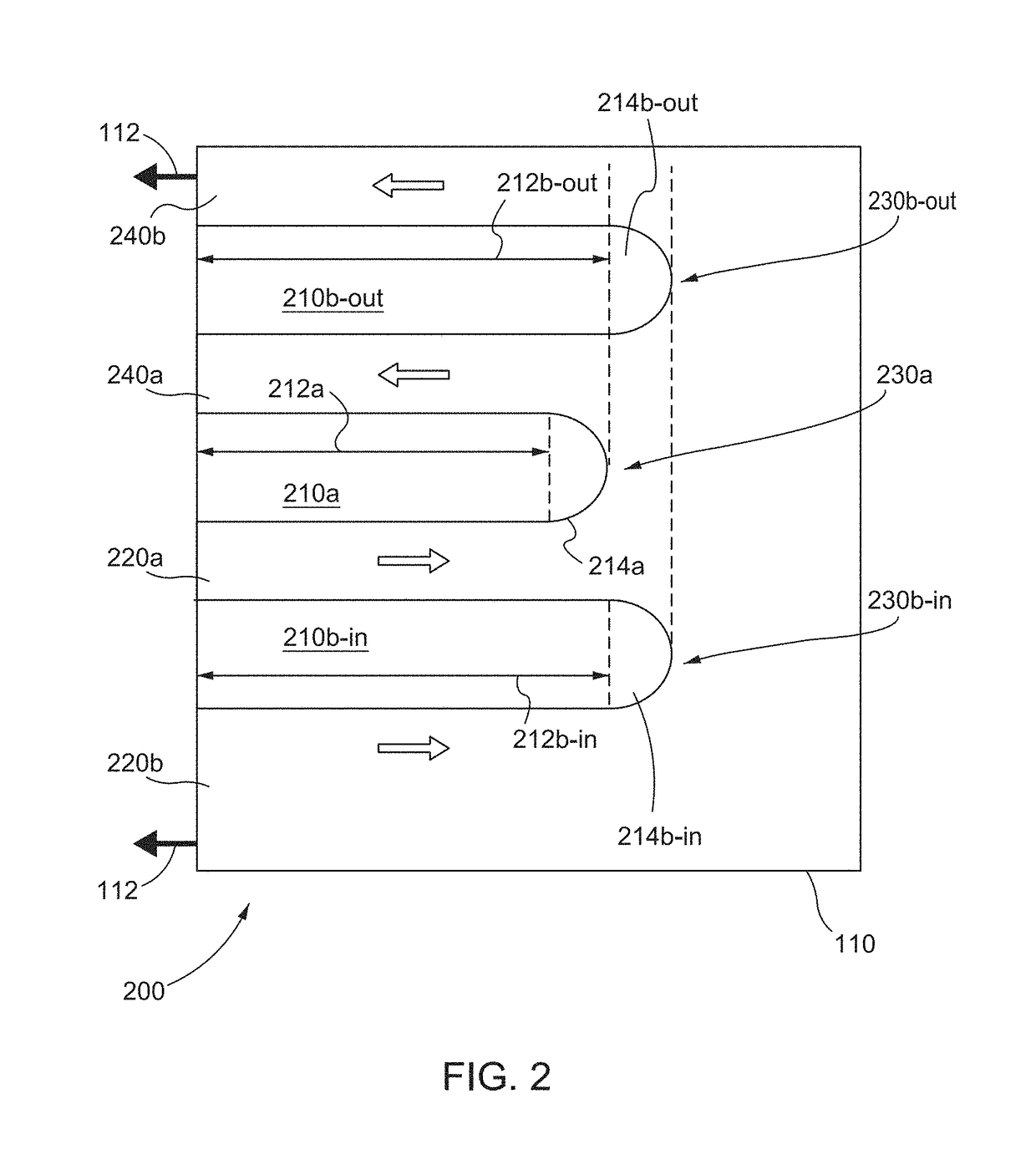
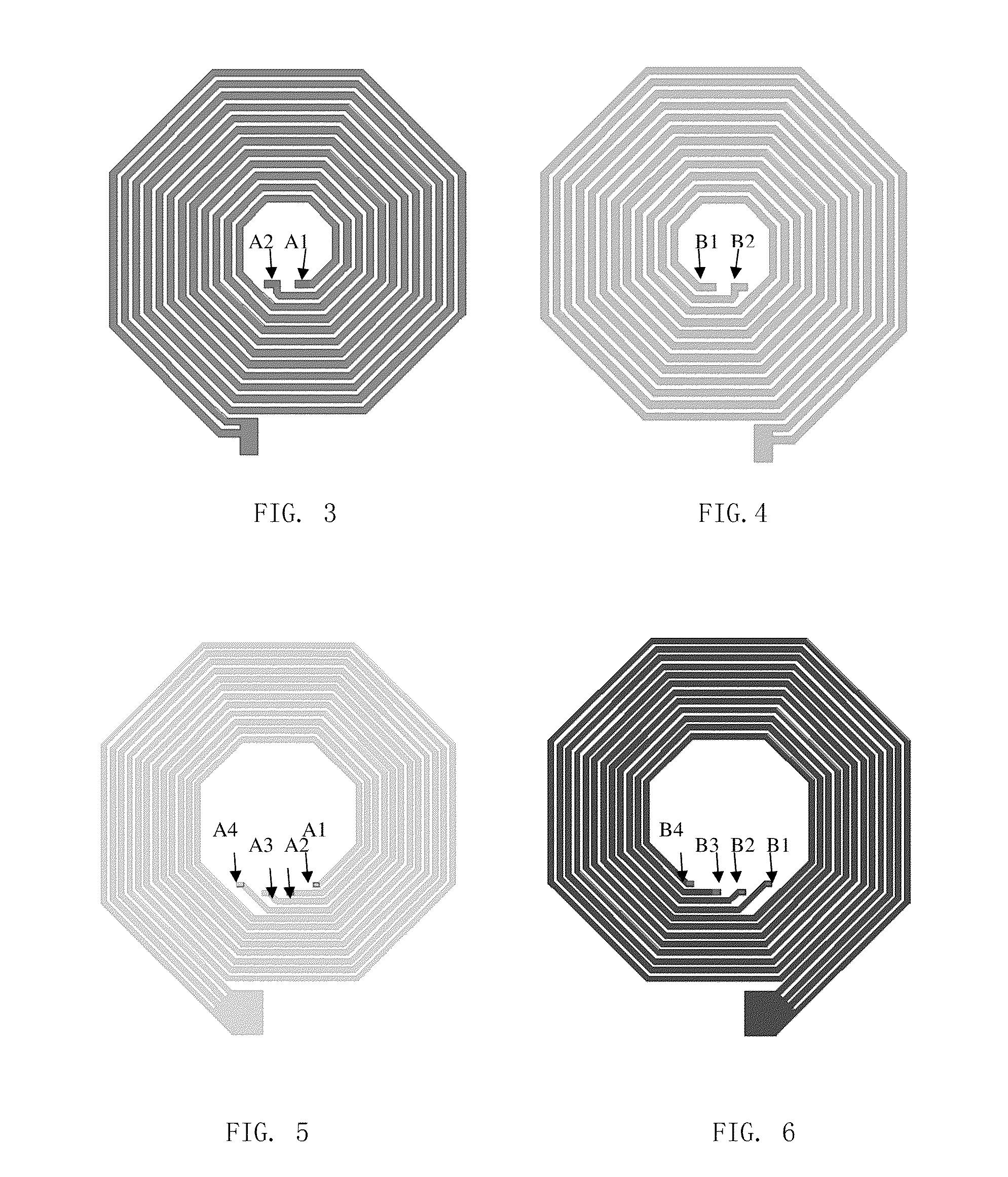
Bump with multiple vias for semiconductor package and fabrication method thereof, and semiconductor package utilizing the same
ActiveUS20090283903A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageSemiconductor chip
A bump for a semiconductor package forms a polymer layer having multiple vias on an electrode pad above a semiconductor chip to increase an electrical contact area between the electrode pad and a metal bump. Further, the bump forms a polymer layer having multiple vias on a redistribution electrode pad to increase a surface area of an electrode interconnection. The multiple vias increase electrical and mechanical contact areas, thereby preventing current crowding and improving joint reliability. The bump for a semiconductor package may further comprise a stress relaxation layer at the lower portion of the bump.
Owner:NEPES CO LTD
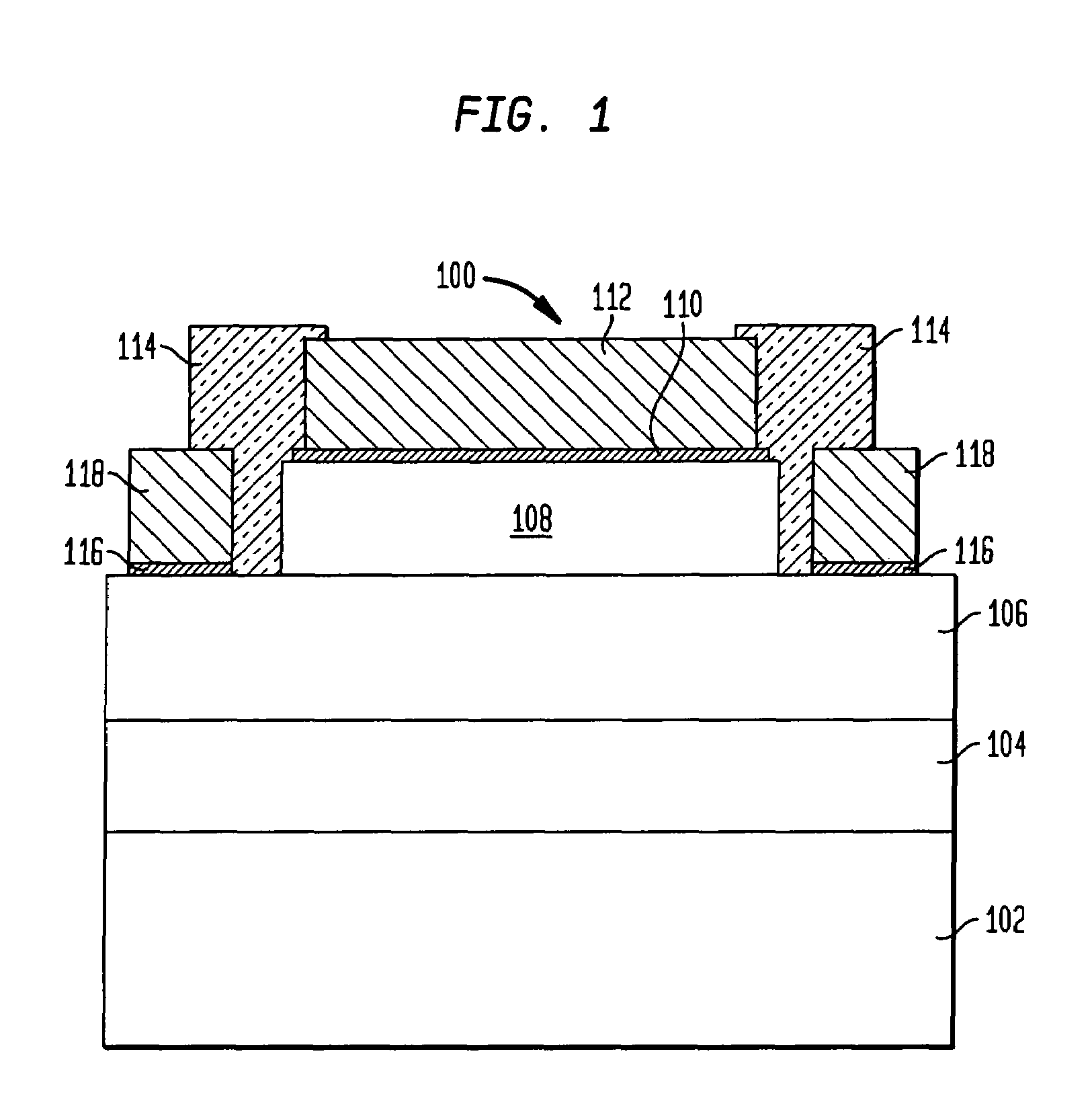
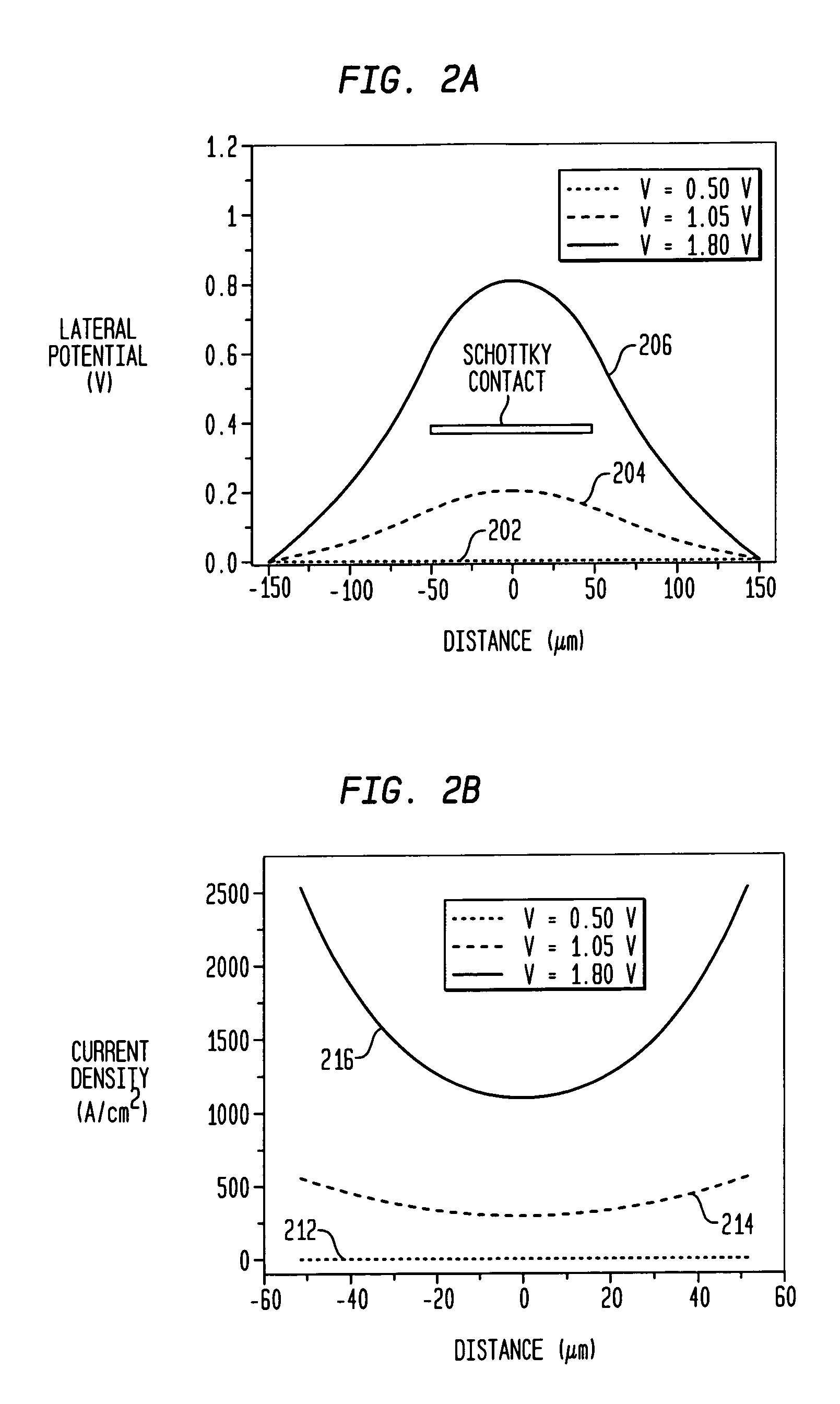
Lateral conduction Schottky diode with plural mesas
ActiveUS7084475B2Reduce heat buildupSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPath lengthOhmic contact
A lateral conduction Schottky diode includes multiple mesa regions upon which Schottky contacts are formed and which are at least separated by ohmic contacts to reduce the current path length and reduce current crowding in the Schottky contact, thereby reducing the forward resistance of a device. The multiple mesas may be isolated from one another and have sizes and shapes optimized for reducing the forward resistance. Alternatively, some of the mesas may be finger-shaped and intersect with a central mesa or a bridge mesa, and some or all of the ohmic contacts are interdigitated with the finger-shaped mesas. The dimensions of the finger-shaped mesas and the perimeter of the intersecting structure may be optimized to reduce the forward resistance. The Schottky diodes may be mounted to a submount in a flip chip arrangement that further reduces the forward voltage as well as improves power dissertation and reduces heat generation.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Multiple-gate MOS transistor and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050263821A1Improve reliabilityImprove rendering capabilitiesTransistorGrinding drivesCrystal orientationGate voltage
Provided is a multiple-gate metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor and a method for manufacturing the same, in which a channel is implemented in a streamline shape, an expansion region is implemented in a gradually increased form, and source and drain regions is implemented in an elevated structure by using a difference of a thermal oxidation rate depending on a crystal orientation of silicon and a geographical shape of the single-crystal silicon pattern. As the channel is formed in a streamline shape, it is possible to prevent the degradation of reliability due to concentration of an electric field and current driving capability by the gate voltage is improved because the upper portion and both sides of the channel are surrounded by the gate electrodes. In addition, a current crowding effect is prevented due to the expansion region increased in size and source and drain series resistance is reduced by elevated source and drain structures, thereby increasing the current driving capability.
Owner:III HLDG 2
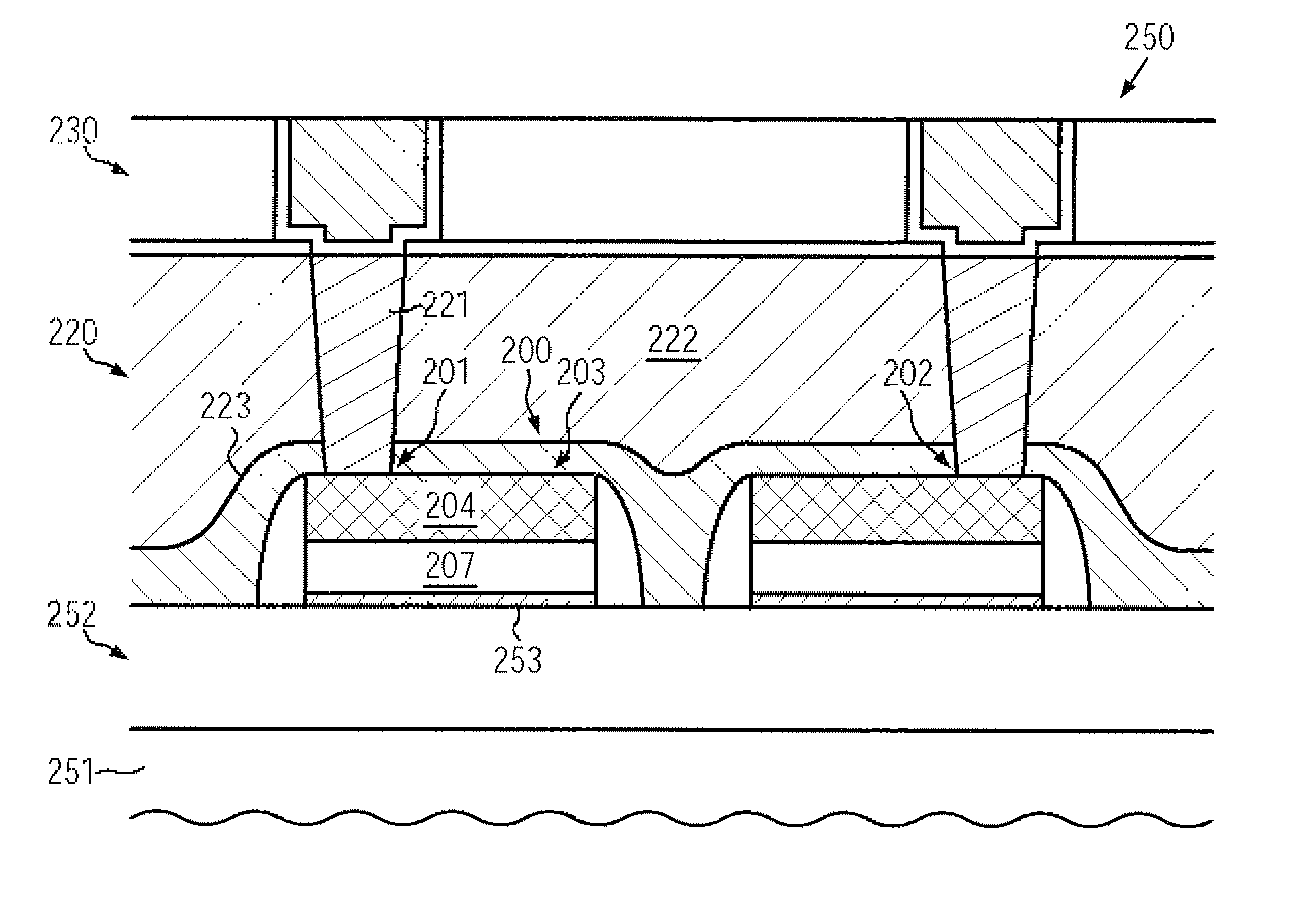
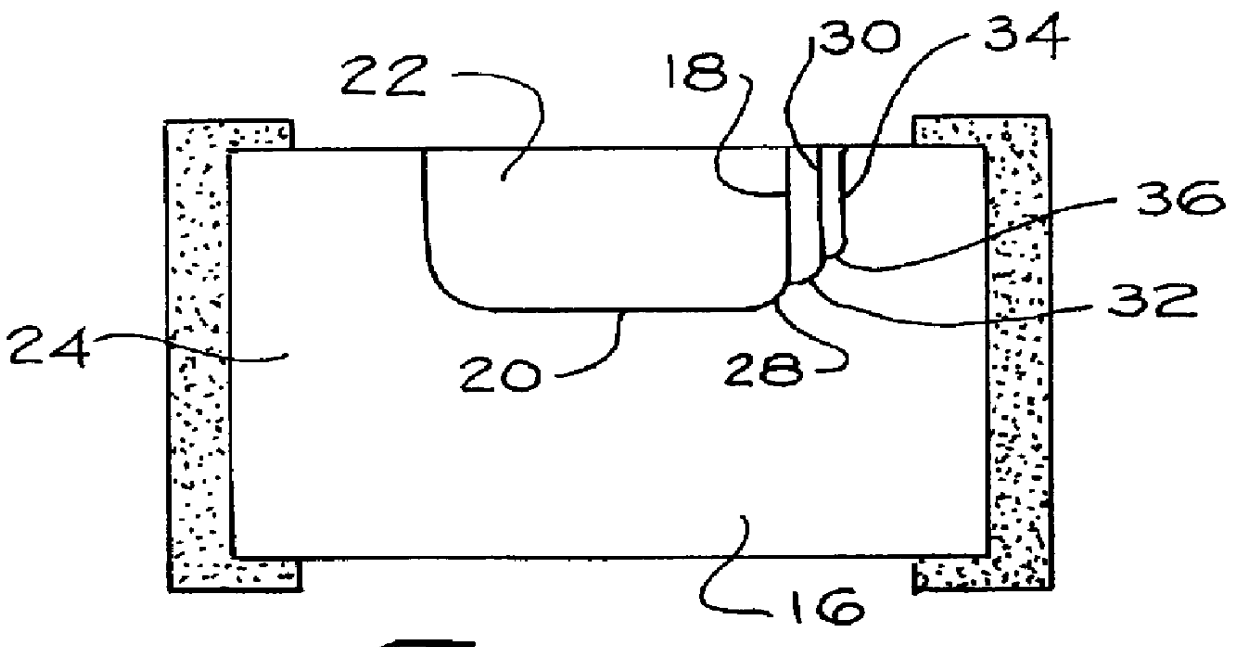
Electromigration-Resistant Flip-Chip Solder Joints
InactiveUS20080251927A1Enhance formation of voidLow reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCopper interconnect
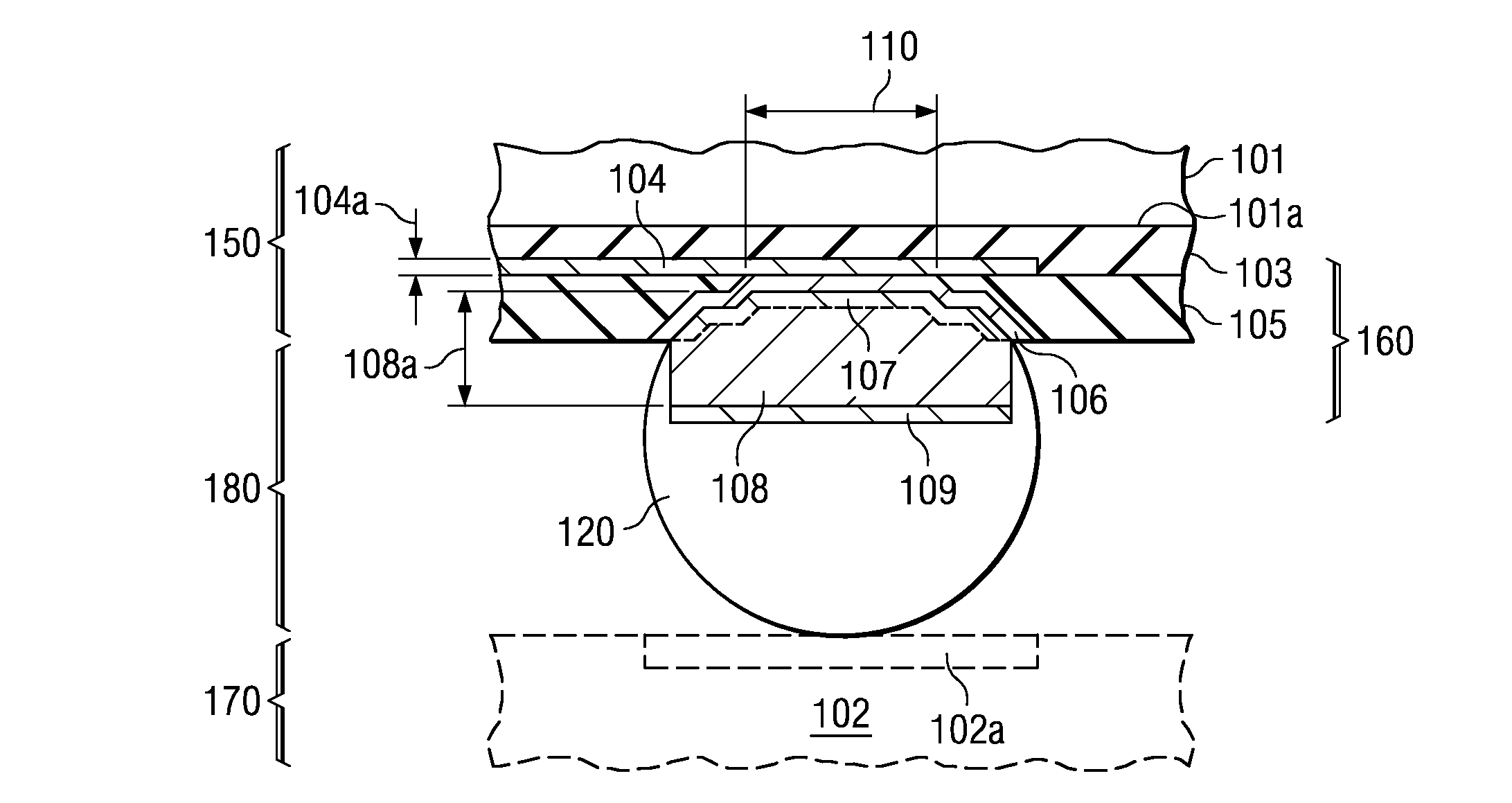
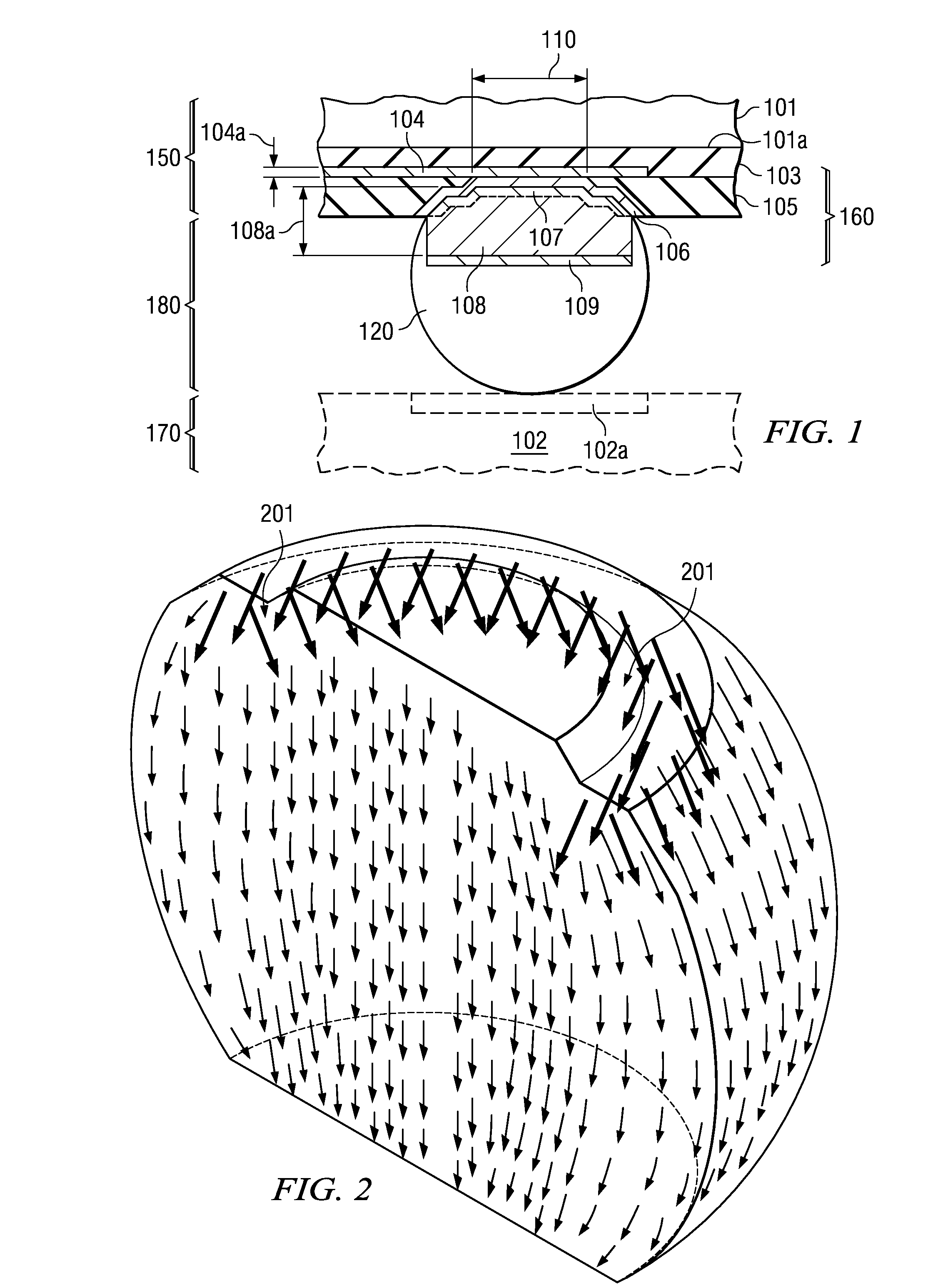
A semiconductor device contact structure practically eliminating the copper diffusion into the solder as well as the current crowding at the contact with the subsequent electromigration in the solder. A column-like electroplated copper stud (108) is on each contact pad. The stud is sized to provide low, uniform electrical resistance in order to spread the current from the contact to an approximately uniform, low density. Preferably, the stud height (108a) is at least ten times the thickness of the copper interconnect layer (104). Stud (108) is capped by an electroplated nickel layer (109) thick enough (preferably about 2 μm) to suppress copper diffusion from stud (108) into solder body (120), thus practically inhibiting intermetallic compound formation and Kirkendall voiding.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Superconducting nanowire avalanche photodetectors with reduced current crowding
ActiveUS20170186933A1Current crowdingImprove signal-to-noise ratioSuperconductor detailsPhotometry electrical circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceSwitched current
Superconducting nanowire avalanche photodetectors (SNAPs) have using meandering nanowires to detect incident photons. When a superconducting nanowire absorbs a photon, it switches from a superconducting state to a resistive state, producing a change in voltage that can be measured across the nanowire. A SNAP may include multiple nanowires in order to increase the fill factor of the SNAP's active area and the SNAP's detection efficiency. But using multiple meandering nanowires to achieve high fill-factor in SNAPs can lead to current crowding at bends in the nanowires. This current crowding degrades SNAP performance by decreasing the switching current, which the current at which the nanowire transitions from a superconducting state to a resistive state. Fortunately, staggering the bends in the nanowires reduces current crowding, increasing the nanowire switching current, which in turn increases the SNAP dynamic range.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Integrated circuit structure and formation method thereof
ActiveCN102074582AReduce current crowdingReduce tensionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
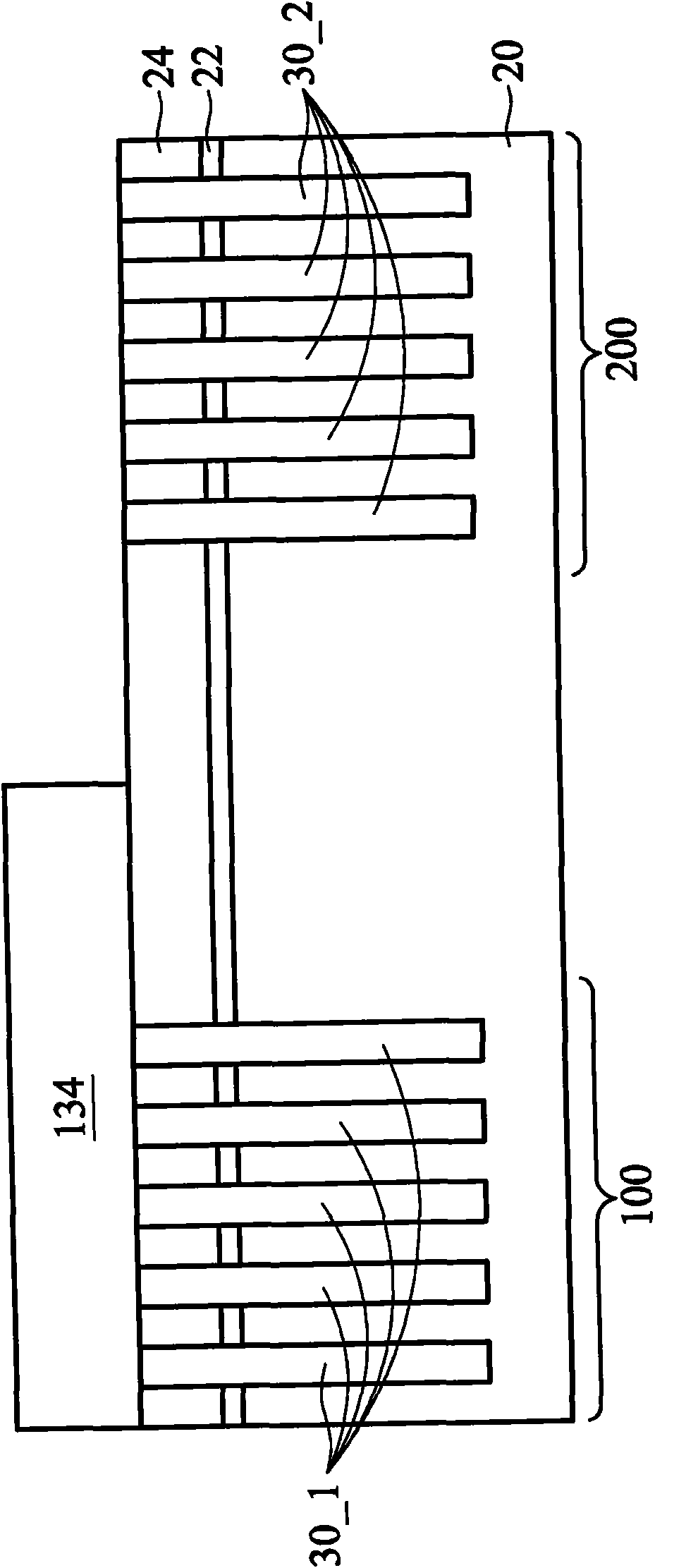
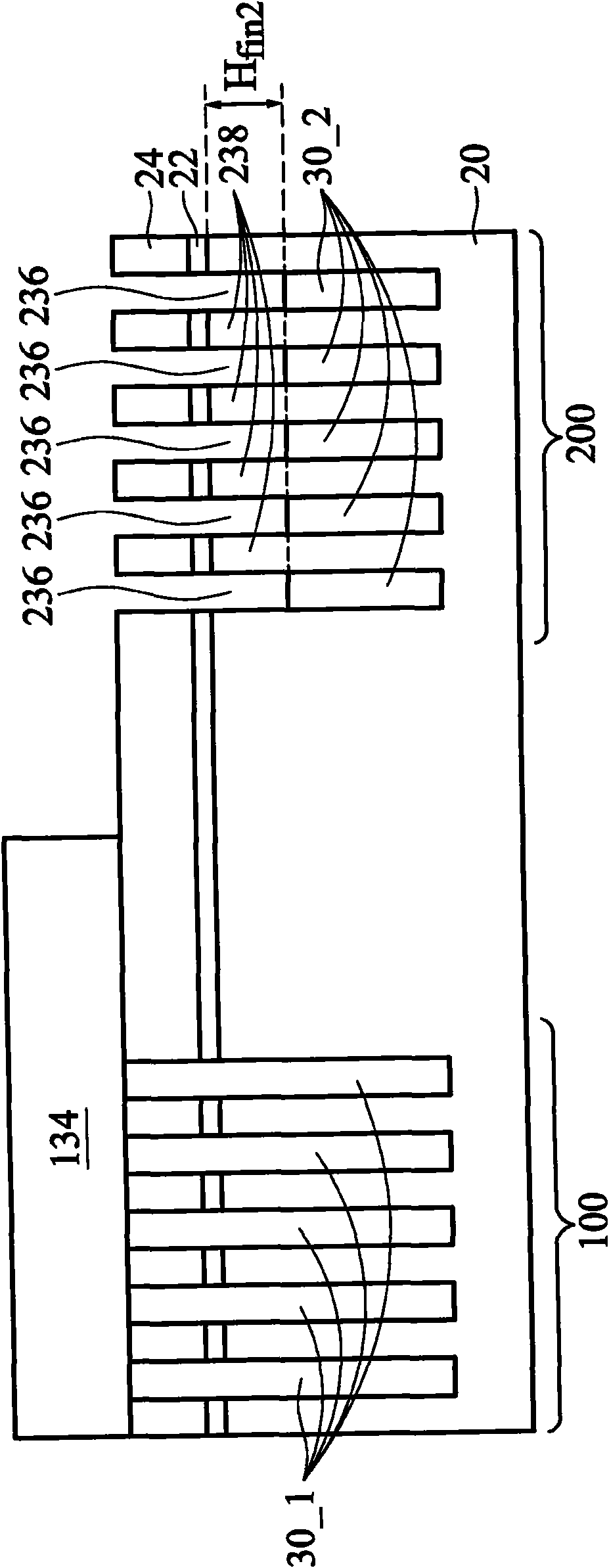
The invention provides an integrated circuit structure and a formation method thereof, and the structure comprises a first portion in which a semiconductor substrate is contained in a first element region, and a second portion in which a semiconductor substrate is contained in a second element region. A first semiconductor fin is over the semiconductor substrate and has a first fin height. A second semiconductor fin is over the semiconductor substrate and has a second fin height. The first fin height is greater than the second fin height. The invention has a positive effect on the reduction of the current crowding at the source electrode and the drain electrode regions. Because of the volume increase of the stress source electrode and the drain electrode regions, the tension and the compression strain on the channel region of a fin-type field effect transistor are increased.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Bump with multiple vias for semiconductor package and fabrication method thereof, and semiconductor package utilizing the same
ActiveUS7977789B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower flowSemiconductor chip
A bump for a semiconductor package forms a polymer layer having multiple vias on an electrode pad above a semiconductor chip to increase an electrical contact area between the electrode pad and a metal bump. Further, the bump forms a polymer layer having multiple vias on a redistribution electrode pad to increase a surface area of an electrode interconnection. The multiple vias increase electrical and mechanical contact areas, thereby preventing current crowding and improving joint reliability. The bump for a semiconductor package may further comprise a stress relaxation layer at the lower portion of the bump.
Owner:NEPES CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor devices having ESD protection
InactiveUS20020076876A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
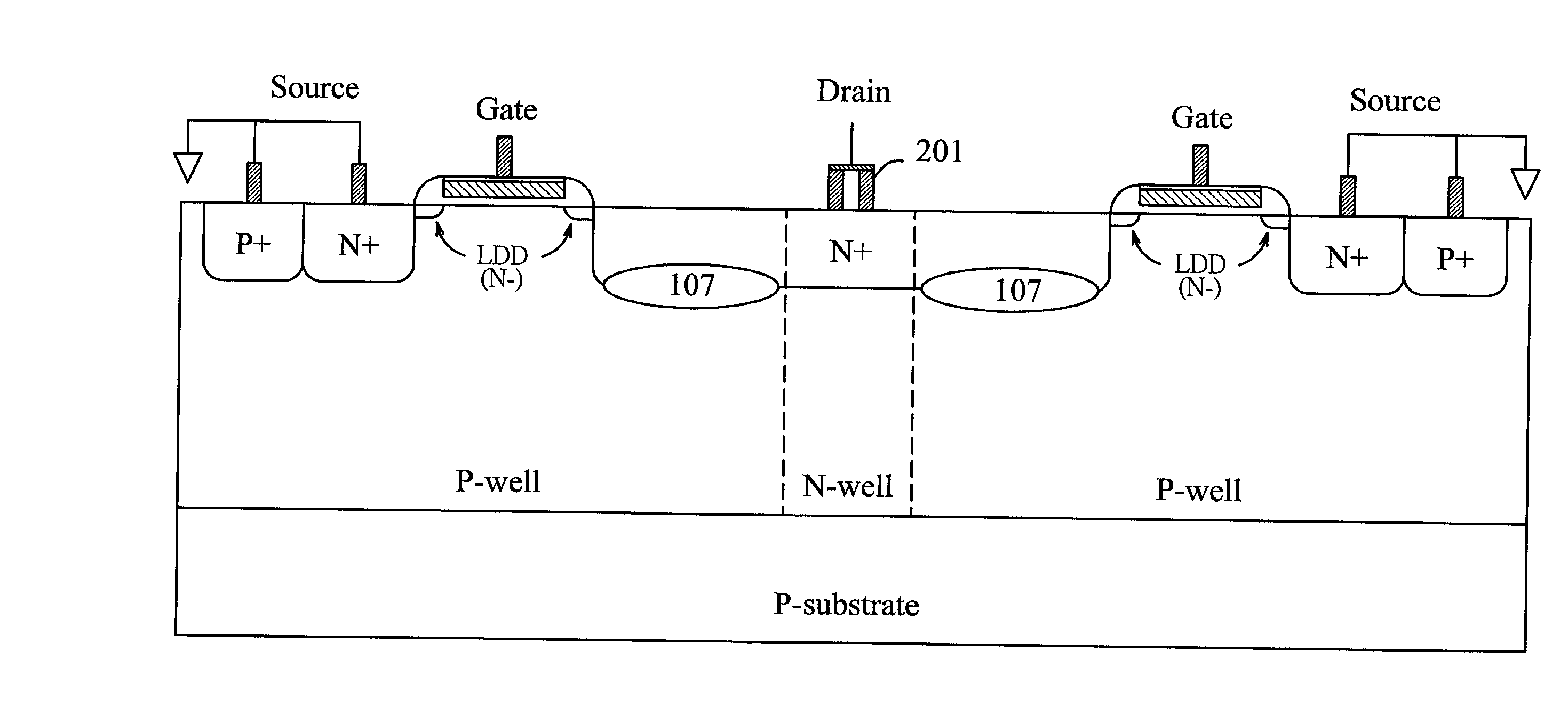
A Method for manufacturing semiconductor devices having ESD protection. The method includes the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate having a well region, forming a gate structure on the semiconductor substrate, the gate structure including an oxide layer, a gate electrode on said oxide layer, and two spacer sidewalls, forming a source region within the well region at one side of the gate structure, forming a drain region within the well region at the other side of the gate structure, forming lightly doped source / drain regions in the well region and beneath the spacer walls of the gate structure wherein the lightly doped source / drain regions have the same conductivity type as the drain region and, and performing an implant with the same conductivity type as the well region as to form an ESD implantation region. The ESD implantation region is located under the diffusion region that is between the drain contact and the poly gate of output NMOS, but without covering the region right under the drain contact. Therefore, the ESD current is discharged through the ESD-implanted region to the substrate without causing current crowding under the drain contact as to burn out the drain contact.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
P and N contact pad layout designs of GaN based LEDs for flip chip packaging
InactiveUS20050133806A1Efficient use ofIncrease current densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact padSemiconductor materials
Based on the unique properties of the flip chip packaging process and GaN based LEDs with transparent substrates, new principles and methods for designing the layout of P contact pads and N contact pads are disclosed. The new designs of the present invention drastically increase the light extraction efficiency of LEDs by reducing the current crowding effect, increasing the uniformity of the spreading current in the active layer, and utilizing most of the available light emitting semiconductor material of the active layer. The present invention combined with the flip chip packaging process significantly improves the LEDs' heat dissipation.
Owner:PENG HUI +1
Process for protecting solder joints and structure for alleviating electromigration and joule heating in solder joints
InactiveUS20060027933A1Relieve electromigration damageAlleviate current crowding effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyCurrent distribution
This invention provides a process for protecting solder joints, comprising forming an UBM or pad metallurgy in solder joints and then further forming a small solder bump on UBM or pad metallurgy between substrate and chip. Wherein a material of high electric resistance is coated at the ends of UBM or pad metallurgy where substrate is connected to chip, as to equalize the current distribution of solder bump, therefore the electromigration resistance of solder joints is improved by suppressing the current crowding and joule heating phenomenon.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE COMPRISING eFUSES OF ENHANCED PROGRAMMING EFFICIENCY
ActiveUS20100107403A1Increase current densityImprove toleranceFuse device manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLinear configurationSemiconductor
In sophisticated integrated circuits, an electronic fuse may be formed such that an increased sensitivity to electromigration may be accomplished by including at least one region of increased current density. This may be accomplished by forming a corresponding fuse region as a non-linear configuration, wherein at corresponding connection portions of linear segments, the desired enhanced current crowding may occur during the application of the programming voltage. Hence, increased reliability and more space-efficient layout of the electronic fuses may be accomplished.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Electrically programmable fuse structures with narrowed width regions configured to enhance current crowding and methods of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20070210413A1Enhance current crowdingIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Electrically programmable fuse structures and methods of fabrication thereof are presented, wherein a fuse includes first and second terminal portions interconnected by an elongate fuse element. The first terminal portion has a maximum width greater than a maximum width of the fuse element, and the fuse includes a narrowed width region where the first terminal portion and fuse element interface. The narrowed width region extends at least partially into and includes part of the first terminal portion. The width of the first terminal portion in the narrowed region is less than the maximum width of the first terminal portion to enhance current crowding therein. In another implementation, the fuse element includes a restricted width region wherein width of the fuse element is less than the maximum width thereof to enhance current crowding therein, and length of the restricted width region is less than a total length of the fuse element.
Owner:IBM CORP
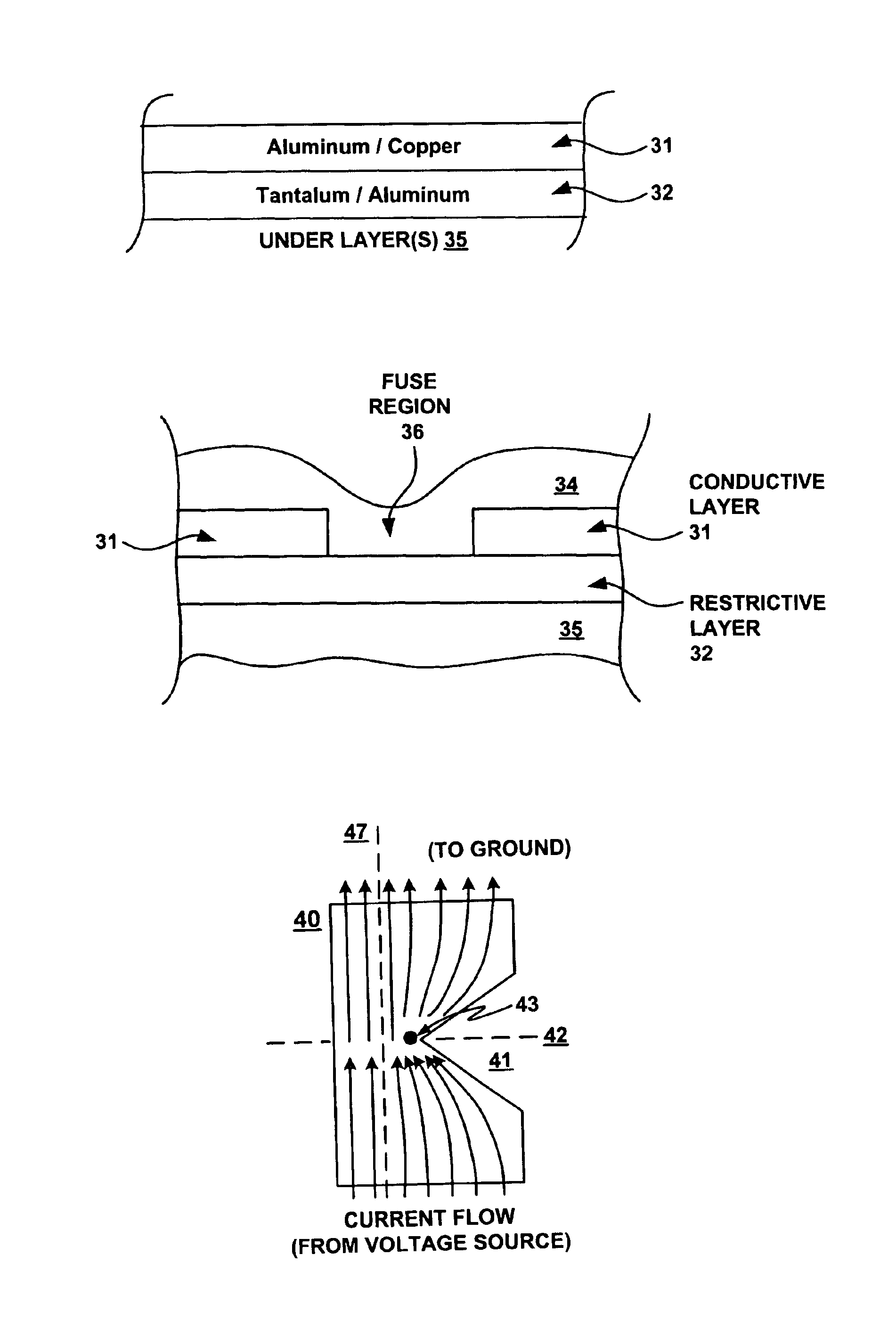
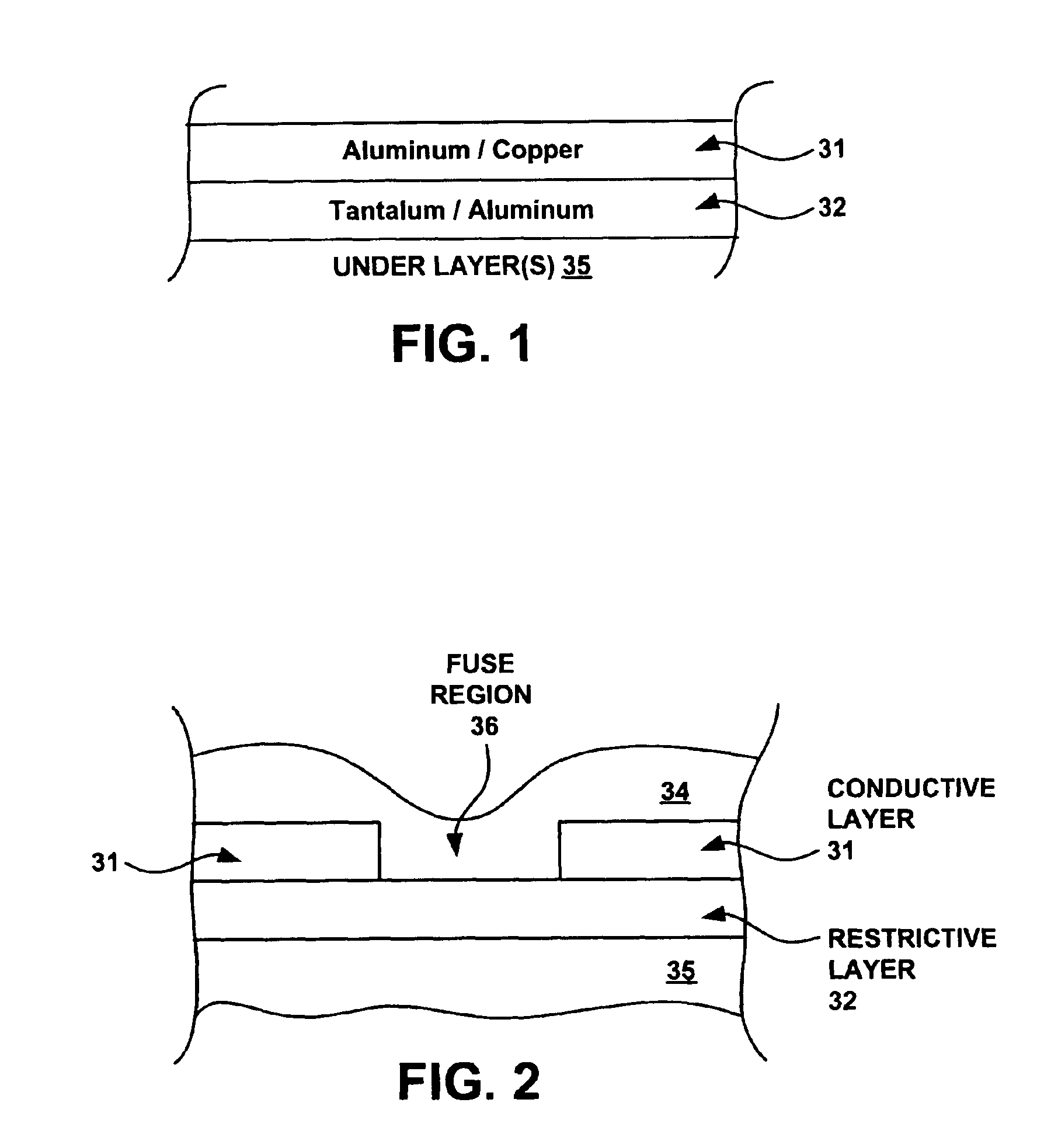
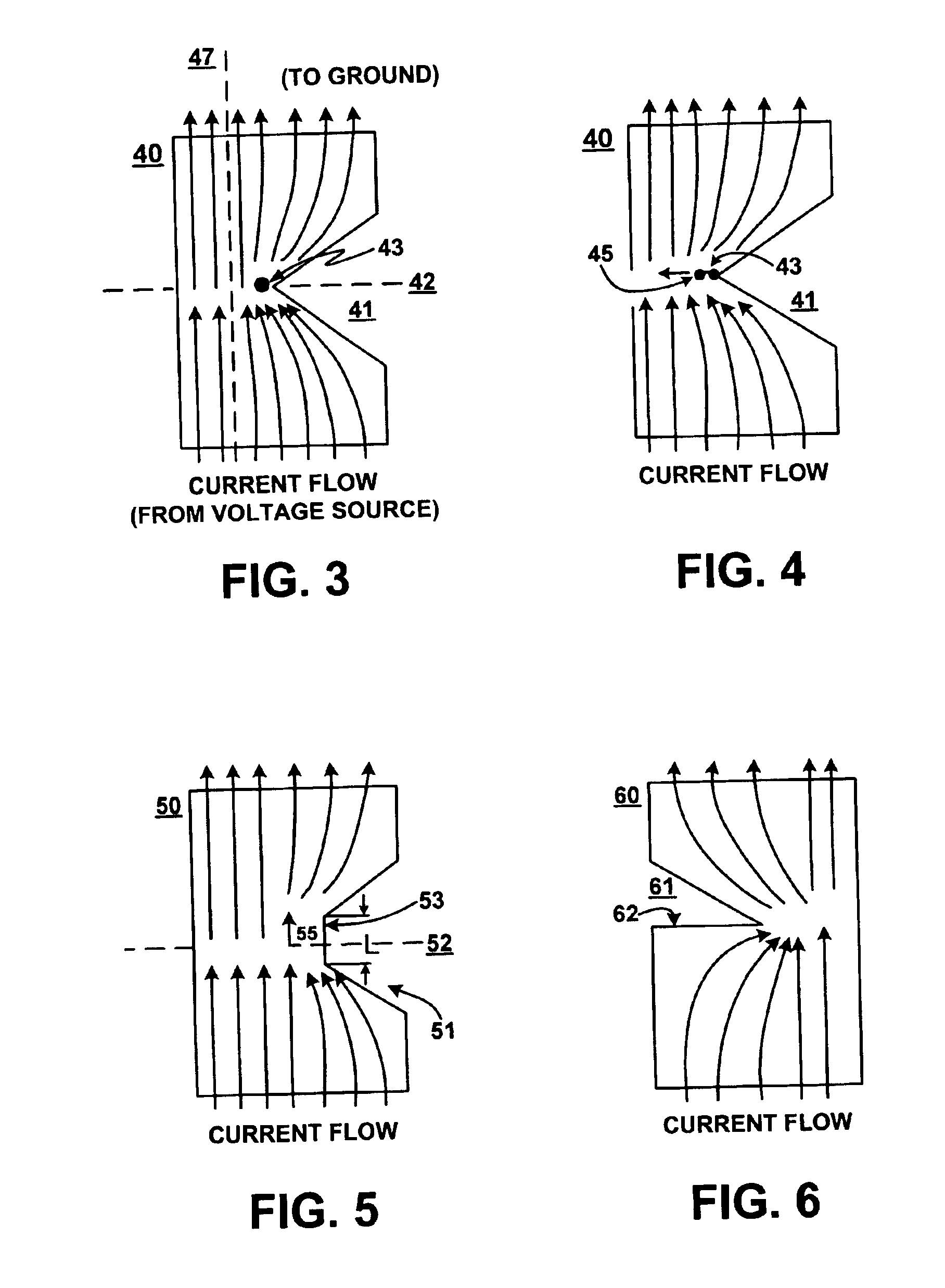
Fuse structure
InactiveUS6960978B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringVoltage source
A fuse structure is described. The fuse structure includes a first region adapted to be coupled to a voltage source, a second region adapted to be coupled to a ground, and a current flow region disposed between the first and second regions. The current flow region has a configuration that causes a void to be opened at a point of localized heating due to current crowding within the current flow region and that causes the void to propagate across the current flow region.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Nitride light emitting diode having composite double current spreading layer
ActiveCN102097560AImprove luminous efficiencyAvoid current crowdingSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a nitride light emitting diode having a composite double current spreading layer. The composite double current spreading layer is a composite semiconductor layer which consists of a first current spreading layer and a second current spreading layer in a sequentially superposed manner; the first current spreading layer is formed on a distribution insulated layer of an n-type nitride semiconductor layer and the second current spreading layer is formed by mutually superposing u-type nitride semiconductor layers and n-type nitride semiconductor layers; and the composite double current spreading layer is connected with the n-type nitride semiconductor layers and an active layer respectively. In the composite double current spreading layer arranged on the nitride light emitting diode, the current can be distributed over the entire light emitting area quite evenly to avoid current crowding, therefore, both the light emitting efficiency of a nitride light emitting diode assembly and the electrostatic breakdown voltage can be raised effectively.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Graded vias for LED chip P- and N- contacts
ActiveUS9412907B1Improve light emission efficiencyImprove uniformitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact padCurrent crowding
The present disclosure provides various embodiments of light emitting chips and packages with improved current spreading structures, such as non-uniform via structures or varied via structures. In some embodiments, these structures may be used to regulate current flow and current crowding in order to improve emitter efficiency and uniformity. Some embodiments of this disclosure may also refer to contact pad placement to improve current flow. In some embodiments of non-uniform via structures, the size of the vias may vary, whereas in other embodiments, the shape or spacing between the vias may vary.
Owner:CREELED INC
Lateral conduction schottky diode with plural mesas
ActiveUS20050179104A1High dopingReduce heat buildupSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePath length
A lateral conduction Schottky diode includes multiple mesa regions upon which Schottky contacts are formed and which are at least separated by ohmic contacts to reduce the current path length and reduce current crowding in the Schottky contact, thereby reducing the forward resistance of a device. The multiple mesas may be isolated from one another and have sizes and shapes optimized for reducing the forward resistance. Alternatively, some of the mesas may be finger-shaped and intersect with a central mesa or a bridge mesa, and some or all of the ohmic contacts are interdigitated with the finger-shaped mesas. The dimensions of the finger-shaped mesas and the perimeter of the intersecting structure may be optimized to reduce the forward resistance. The Schottky diodes may be mounted to a submount in a flip chip arrangement that further reduces the forward voltage as well as improves power dissertation and reduces heat generation.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Partial inter-locking metal contact structure for semiconductor devices and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050112957A1Improves Structural IntegrityHigh wiring densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A structure and method of fabricating a “Lego”-like interlocking contact for high wiring density semiconductors is characterized in that the barrier liner formed in the contact via extends only partially upwards into the adjacent wire level. As a consequence, current crowding and related reliability problems associated with conventional prior art interconnect structures is avoided and structural integrity of the contact via (metal stud) structure is enhanced. The novel “crown” shape of the Lego-like interlocking contact structure that is fabricated to extend in an upward direction may be employed for other integrated circuit applications including forming capacitor (e.g., MIMCAP) and heat sink structures due to its increased surface area.
Owner:IBM CORP
High performance MOS device with graded silicide
ActiveUS20070013010A1Alleviate current crowding effectIncrease currentTransistorSolid-state devicesCondensed matter physicsSemiconductor
A semiconductor device suffering fewer current crowding effects and a method of forming the same are provided. The semiconductor device includes a substrate, a gate over the substrate, a gate spacer along an edge of the gate and overlying a portion of the substrate, a diffusion region in the substrate wherein the diffusion region comprises a first portion and a second portion between the first portion and the gate spacer. The first portion of the diffusion region has a recessed top surface. The semiconductor device further includes a silicide layer on the diffusion region, and a cap layer over at least the silicide layer. The cap layer provides a strain to the channel region of the semiconductor device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Stacked inductor with multi paths for current compensation
InactiveUS20110133877A1Reduce the impactIncrease inductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSpiral inductorSkin effect
A multi-path stacked inductor for current compensation is represented in this invention. This structure includes top and bottom metal trace, which are aligned with each other. Each metal trace consists of multi paths. The inner path in top metal flips over to the outer path in the bottom metal, while the outer path in top metal flips over to the inner path in the bottom metal. These paths join together at the end of the metal trace with via holes. Skin effect and current crowding effect are reduced by means of this method. This stacked inductor possesses larger inductance than single layer spiral inductor, with relatively higher Q factor.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
Light-emitting semiconductor device having enhanced brightness
InactiveUS20050082555A1Increase brightnessImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCurrent distribution
This invention this invention provides a light-emitting semiconductor device having enhanced brightness, to ensure even current distribution emitted by a front contact of the light emitting diodes so as to improve the light-emitting efficiency of the active layer. This invention adopts the method to manufacture the light-emitting device, comprising the steps of: forming an active layer on a substrate; forming a capping layer on the active layer to enhance current distribution, where a back contact is located on another side of the substrate and a front contact is located above the capping layer. This invention is characterized by: re-designing the front contact, by reducing the width of a metallic pattern constructing fingers or Mesh lines and increasing the number of the fingers or Mesh lines, so as to resolve the current crowding problem.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Manufacturing method of top-gate oxide thin-film transistor
ActiveCN103000530AHeating fastReduced series resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumLow voltage
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a top-gate oxide thin-film transistor. The top-gate oxide thin-film transistor comprises an oxide semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode, the source electrode and the drain electrode respectively contact with the oxide semiconductor layer, and the oxide semiconductor layer is made of indium oxide, gallium oxide, zinc oxide or stannic oxide or binary or multibasic oxide of indium, gallium, zinc and stannum. The source electrode, the drain electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer are radiated by a variable magnetic field. Field effect migration rate of the top-gate thin-film transistor is high, and current crowding of the output characteristics is avoided when the drain electrode is at low voltage.
Owner:SHENZHEN DANBANG INVESTMENT GROUP
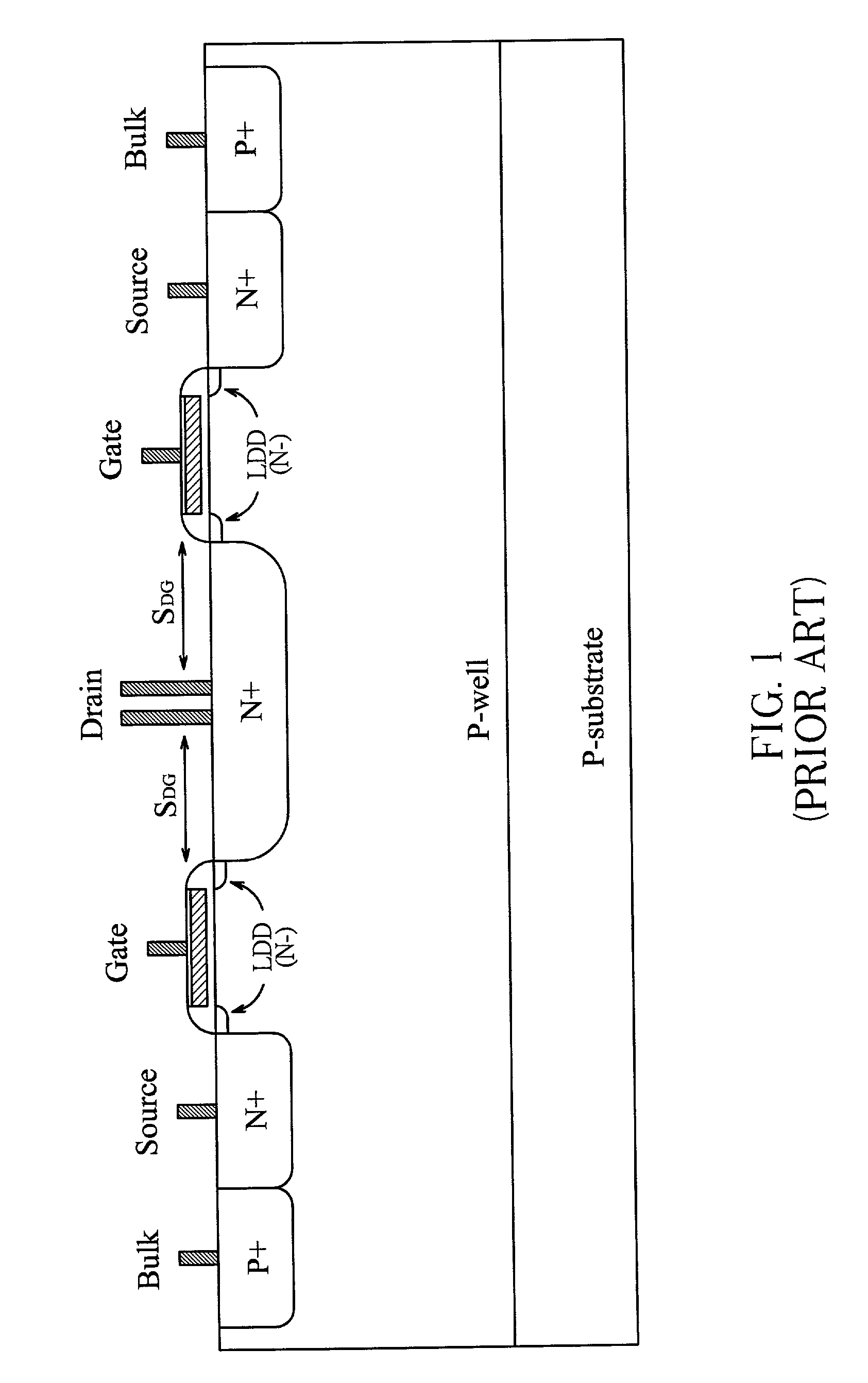
Trimmed surge resistors
InactiveUS6107909AFixed resistors with intervening connectorsCurrent responsive resistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An electrical resistor having a resistance value and capable of withstanding high power surges, utilizing a thick film deposited on a substrate and trimmed with one or more cuts configured to maintain a level of current crowding while increasing the resistance value of the resistor. A surge resistor can be modified in a similar fashion.
Owner:MMC BIDDING
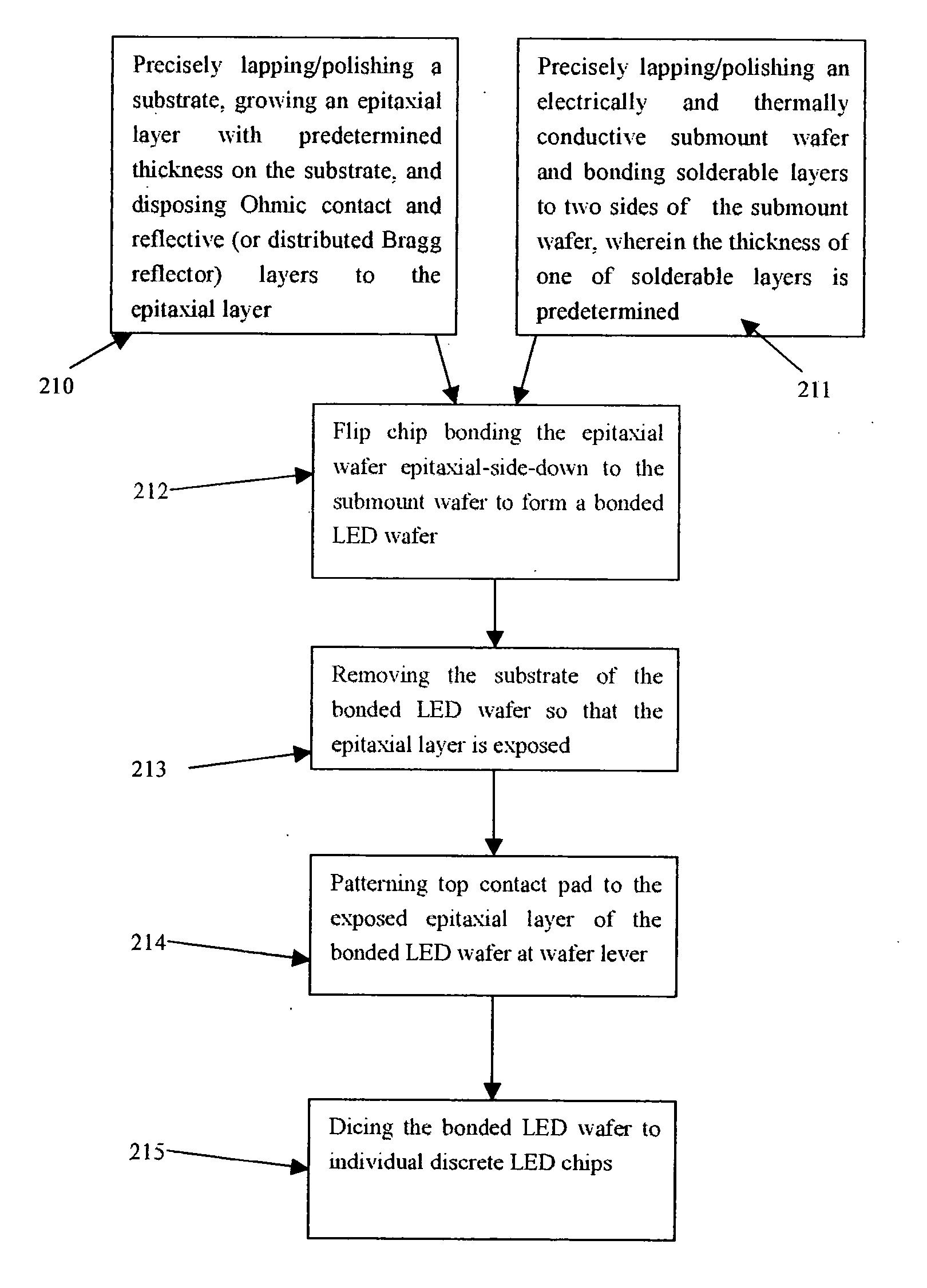
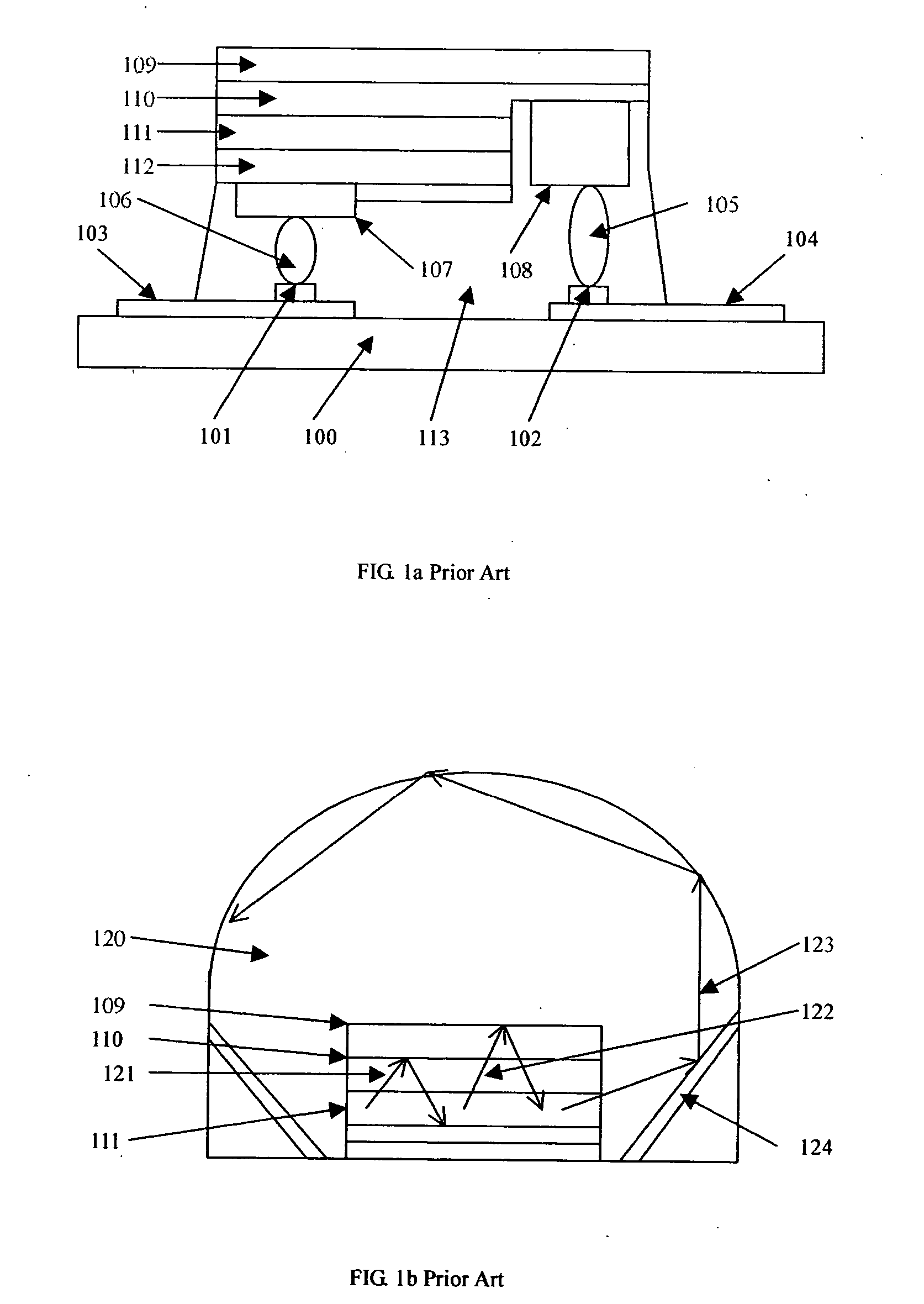
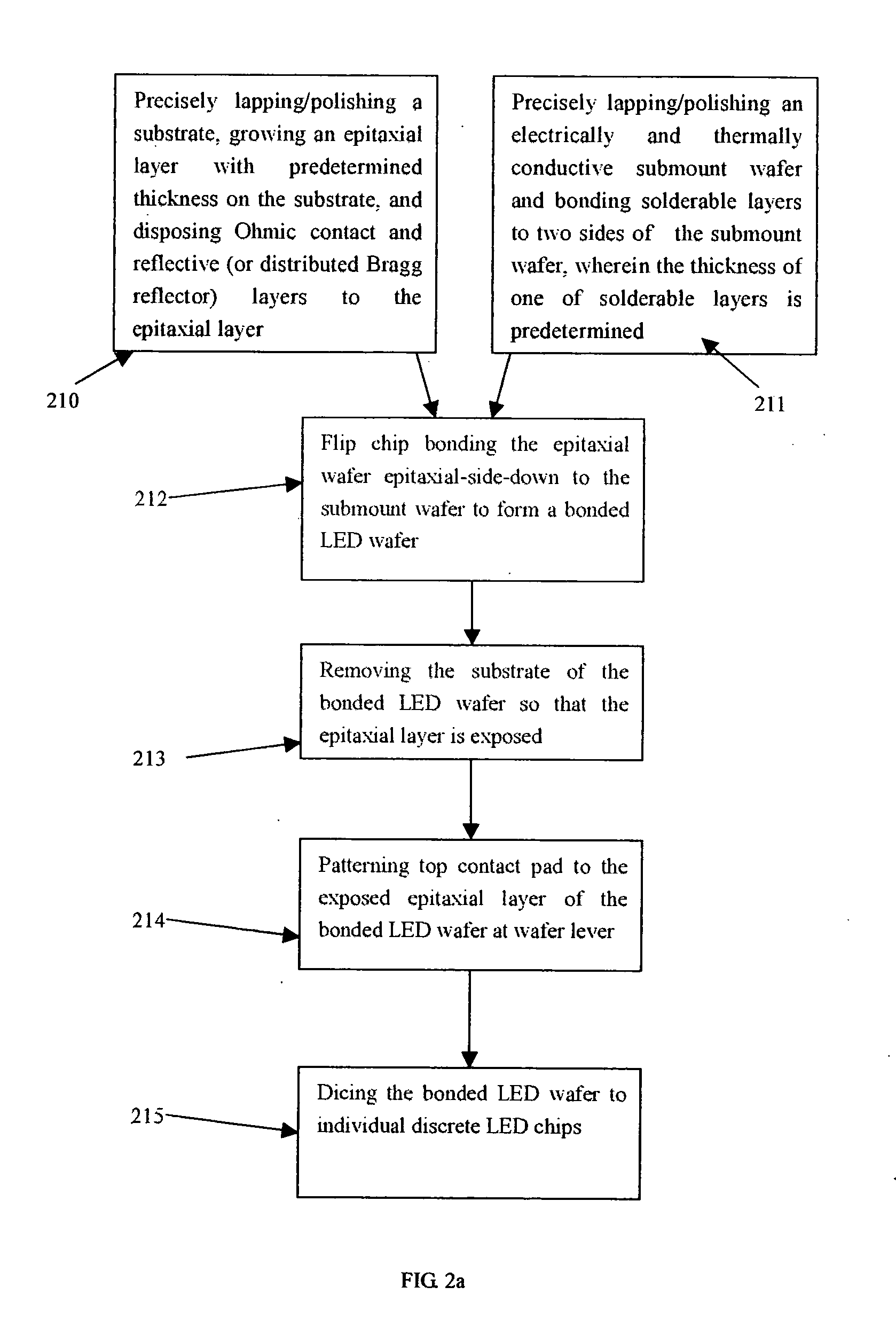
Flip chip assemblies and lamps of high power GaN LEDs, wafer level flip chip package process, and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050161779A1Heat dissipation fastImprove light extractionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh current densityTotal internal reflection
The present invention discloses new flip chip assemblies and lamps for high power semiconductor chips or devices including GaN LEDs and a new wafer level flip chip packaging process for cost effectively manufacturing the same. The advantages of the new flip chip assemblies, lamps, and the wafer level flip chip package process are: (1) the fabricating process is simpler; (2) no need for expensive flip chip equipments; (3) the throughput is higher; (4) eliminating lattice mismatch between the substrate and the epitaxial layer by removing the substrate; (5) better thermal dissipation; (6) reduced current crowding effect and higher current density; (7) higher light extraction efficiency; (8) eliminating the totally internal reflection; and (9) eliminating the Fresnel reflection at the dome-air interface.
Owner:PENG HUI +1
High performance transistor with a highly stressed channel
ActiveUS20070231999A1Improve performanceAlleviate current crowding effectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringGate stack
A MOS transistor having a highly stressed channel region and a method for forming the same are provided. The method includes forming a first semiconductor plate over a semiconductor substrate, forming a second semiconductor plate on the first semiconductor plate wherein the first semiconductor plate has a substantially greater lattice constant than the second semiconductor plate, and forming a gate stack over the first and the second semiconductor plates. The first and the second semiconductor plates include extensions extending substantially beyond side edges of the gate stack. The method further includes forming a silicon-containing layer on the semiconductor substrate, preferably spaced apart from the first and the second semiconductor plates, forming a spacer, a LDD region and a source / drain region, and forming a silicide region and a contact etch stop layer. A high stress is developed in the channel region. Current crowding effects are reduced due to the raised silicide region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High performance MOS device with graded silicide
ActiveUS7253481B2Few current crowding effectImproved drive currentTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorCondensed matter physics
A semiconductor device suffering fewer current crowding effects and a method of forming the same are provided. The semiconductor device includes a substrate, a gate over the substrate, a gate spacer along an edge of the gate and overlying a portion of the substrate, a diffusion region in the substrate wherein the diffusion region comprises a first portion and a second portion between the first portion and the gate spacer. The first portion of the diffusion region has a recessed top surface. The semiconductor device further includes a silicide layer on the diffusion region, and a cap layer over at least the silicide layer. The cap layer provides a strain to the channel region of the semiconductor device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveCN1770486AAvoid crowdingImproved current spreadSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
This invention discloses one semiconductor light element and its process method, which The device has upper and down electrode structure through device light layer both sides two ohm electrodes relative space upper shape compensation or etching block light down part of semiconductor to reduce upper and down light parts current crowding situations.
Owner:晶能光電股份有限公司
Gallium nitride based light emitting diode chip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103346227AAchieving current extensionSolve the current crowding effectSemiconductor devicesDevice materialGallium nitride
The invention relates to a gallium nitride based light emitting diode chip and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a semiconductor device provided with at least one electric potential jumping barrier or a surface potential barrier and specially suitable for light emission. The gallium nitride based light emitting diode chip is structurally characterized in that an epitaxial wafer of a conventionally grown LED epitaxy structure in the industry of gallium nitride based light emitting diode chips serves as a substrate, the substrate comprises a sapphire substrate, a GaN buffer layer, a Si doped n type GaN layer, an InGaN / GaN multiple quantum well active area and a Mg doped p type GaN layer from bottom to top, then 1-6 layers of SiO2 / TiO2 distributed Bragg reflection structure layers are alternately deposited, then a composite metal Al film forms a reflected current barrier layer, and an ITO transparent conducting layer in the industry of the gallium nitride based light emitting diode chips is assembled at last. According to the gallium nitride based light emitting diode chip and the preparation method, the current crowding effect on a p metal electrode in the prior art is eliminated, and the problem of LED chip luminous efficiency reduction due to the fact that the metal electrode absorbs photons is resolved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
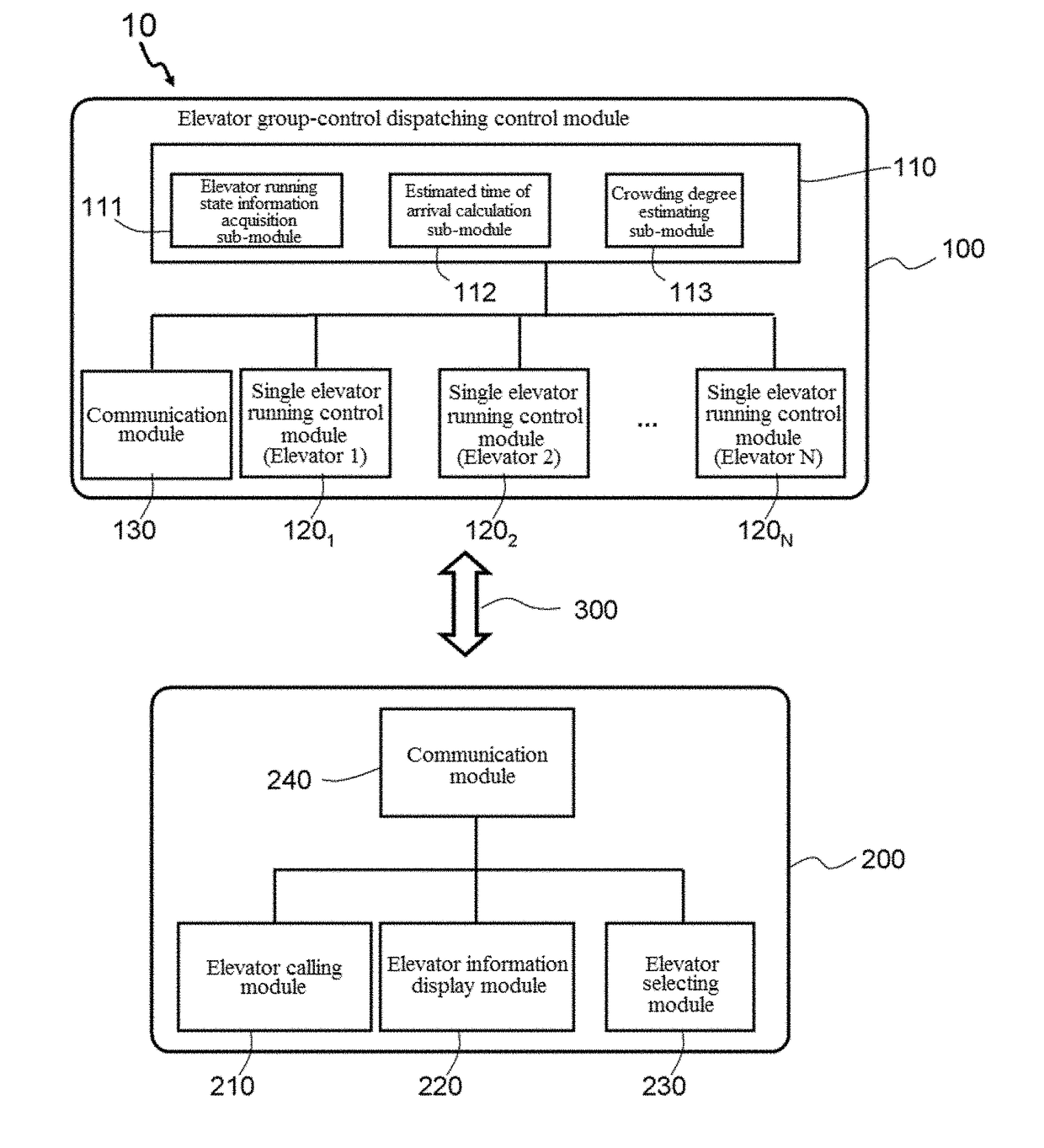
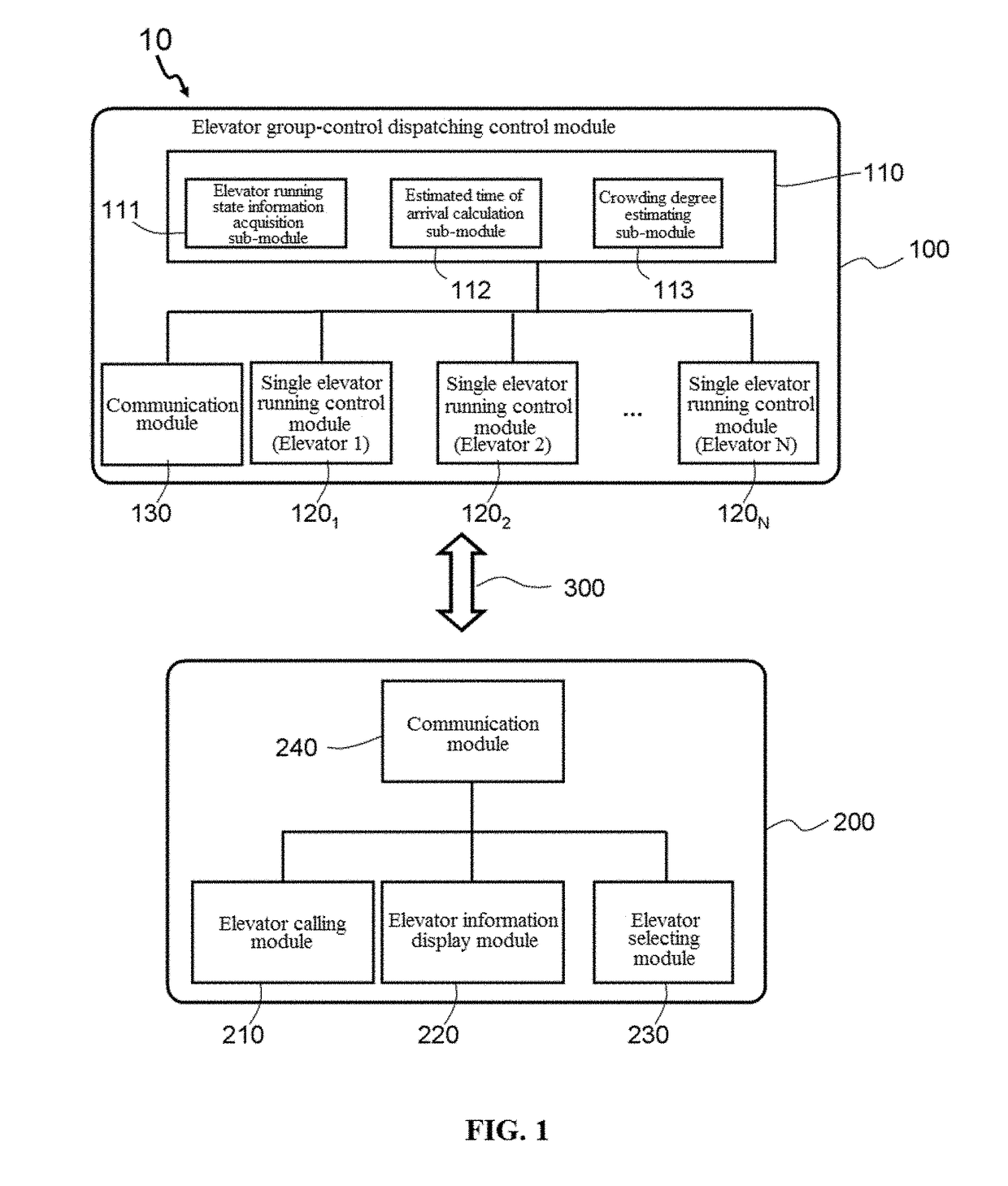
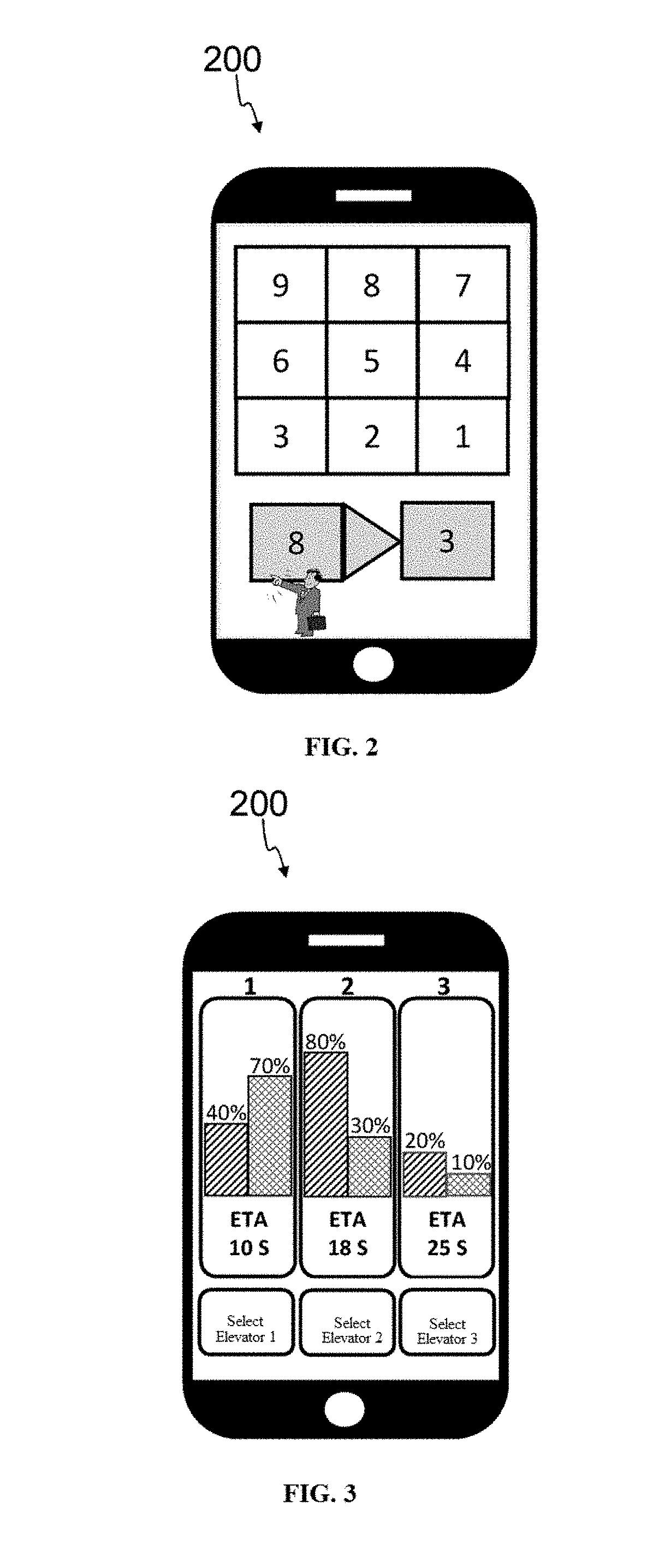
Preferred elevator selection with dispatching information using mobile phone app
ActiveUS20170260023A1Improve operational efficiencyIncrease experienceElevatorsControl systemSimulation
The present invention provides an elevator-calling control apparatus, an elevator-calling control system and an elevator-calling control method thereof, and belongs to the field of elevator control technologies. In an elevator-calling control process, the following steps are included: inputting an elevator-calling command; displaying elevator running state information and estimated time of arrival information of several elevators in a corresponding elevator group for a passenger to make reference, wherein the elevator running state information at least includes information that reflects a current crowding degree of the elevator; and selecting an elevator from the several elevators as the elevator that the passenger determines to take. The elevator-calling control of the present invention may facilitate a passenger to actively select an elevator that the passenger determines to take, which has good user elevator calling and taking experience and enhances the running efficiency of the elevator.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Preparation method for quasi-vertical-structured GaN-based schottky diode
InactiveCN107170680AIncrease working frequencySolve congestionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAir bridgeOhmic contact
The invention discloses a preparation method for a quasi-vertical-structured GaN-based schottky diode, and belongs to the technical field of a semiconductor device. A highly-doped N-type GaN layer is grown on a growth substrate in an epitaxial way; a highly-doped N+ GaN layer is grown on the N-type GaN layer in an epitaxial way; ohmic contact is formed on the N+ GaN layer; and schottky contact is formed on an N- layer, and schottky contact is led to a positive electrode through an air bridge. By virtue of the preparation method, the series resistance of the device can be lowered, working frequency can be improved, and the problem of current crowding can be solved.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
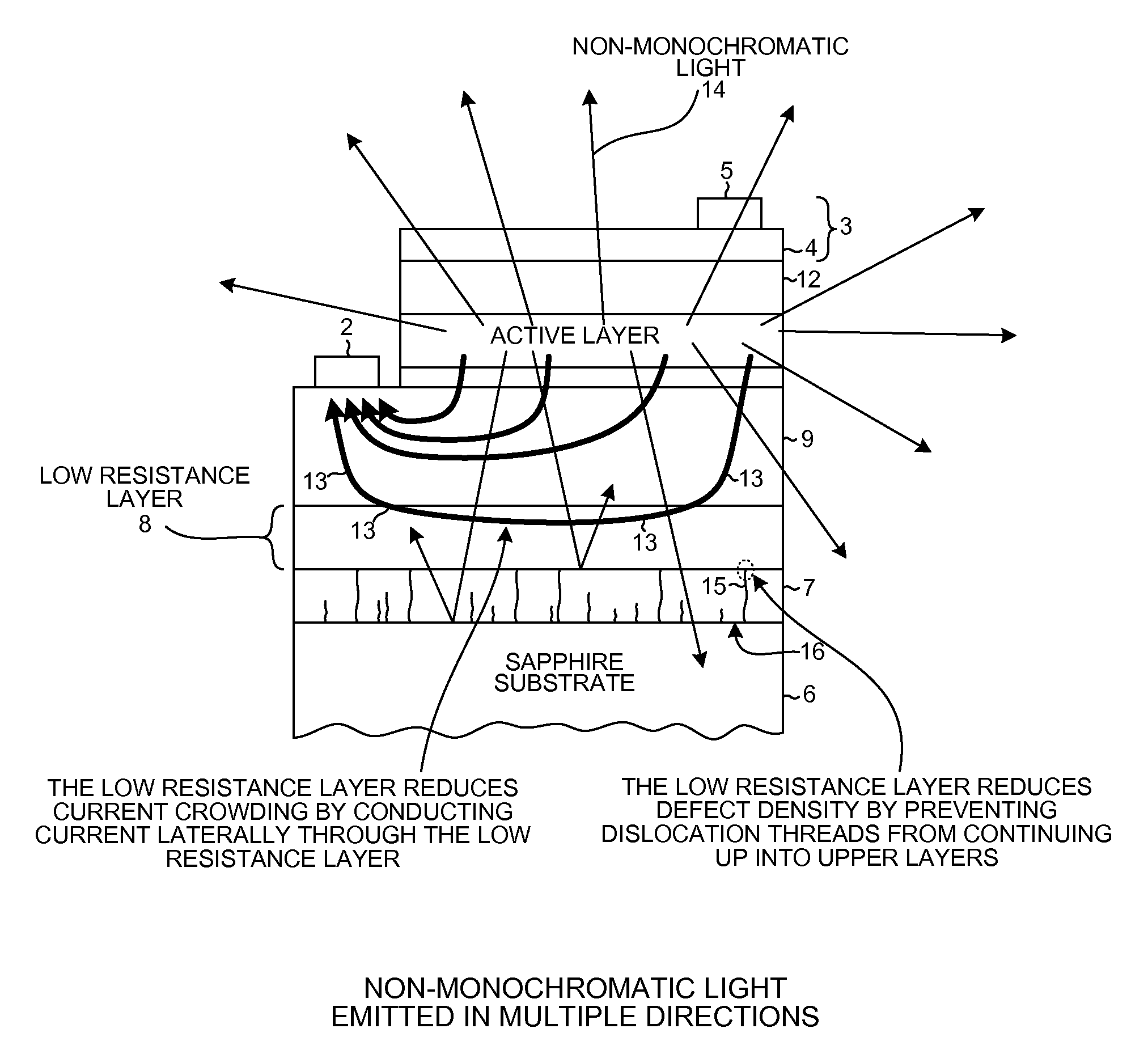
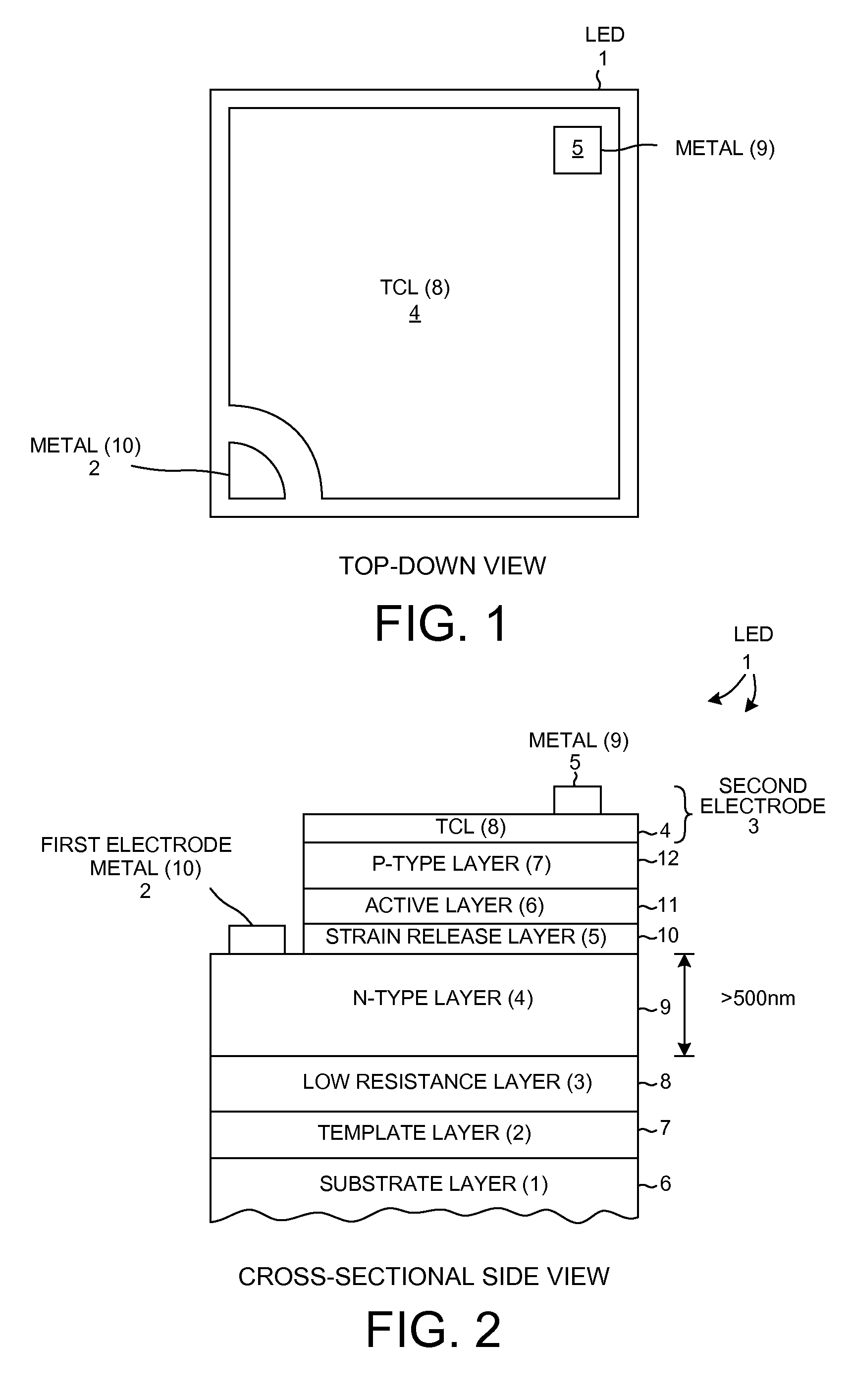
Laterally contacted blue LED with superlattice current spreading layer
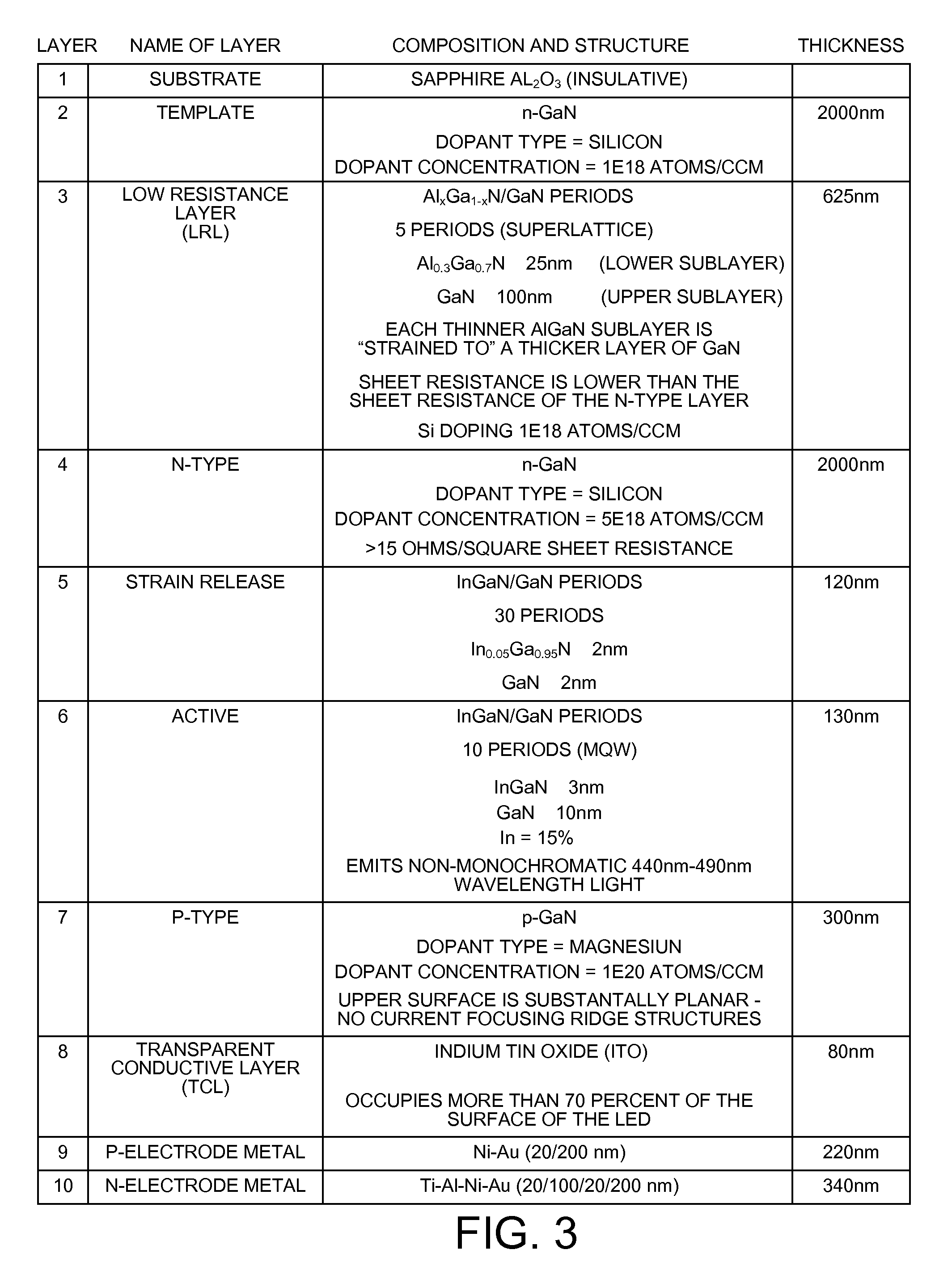
InactiveUS20130009130A1Facilitate lateral current flowFacilitates current spreadingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumActive layer
A laterally contacted blue LED device involves a PAN structure disposed over an insulating substrate. The substrate may be a sapphire substrate that has a template layer of GaN grown on it. The PAN structure includes an n-type GaN layer, a light-emitting active layer involving indium, and a p-type GaN layer. The n-type GaN layer has a thickness of at least 500 nm. A Low Resistance Layer (LRL) is disposed between the substrate and the PAN structure such that the LRL is in contact with the bottom of the n-layer. In one example, the LRL is an AlGaN / GaN superlattice structure whose sheet resistance is lower than the sheet resistance of the n-type GnA layer. The LRL reduces current crowding by conducting current laterally under the n-type GaN layer. The LRL reduces defect density by preventing dislocation threads in the underlying GaN template from extending up into the PAN structure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com