Lithium ion battery, evaluation method of lithium ion battery, battery module and whole vehicle
A lithium-ion battery and battery module technology, which is applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc., can solve problems such as increased heat generation of batteries, decreased battery performance, and decreased output voltage, and achieve ease of design Pressure, improved power performance and discharge efficiency, and the effect of reasonable matching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0068] The preparation method of the positive pole piece:
[0069] The positive electrode active material, the conductive agent carbon black, the conductive agent carbon nanotube, and the binder polyvinylidene fluoride are mixed in a certain mass ratio, and the positive electrode slurry is prepared by stirring with N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent by a planetary mixer; The positive electrode slurry is uniformly coated on both surfaces of the positive electrode current collector aluminum foil, and after drying, rolling and slitting are performed to obtain positive electrode pole pieces.
[0070] The preparation method of the negative pole piece:
[0071] Mix the negative electrode active material, conductive agent carbon black, thickener sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and binder styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) in a certain mass ratio, use deionized water solvent, and stir to prepare negative electrode slurry by planetary mixer ; Coat the negative electrode slurry evenly on the...
Embodiment 1-3
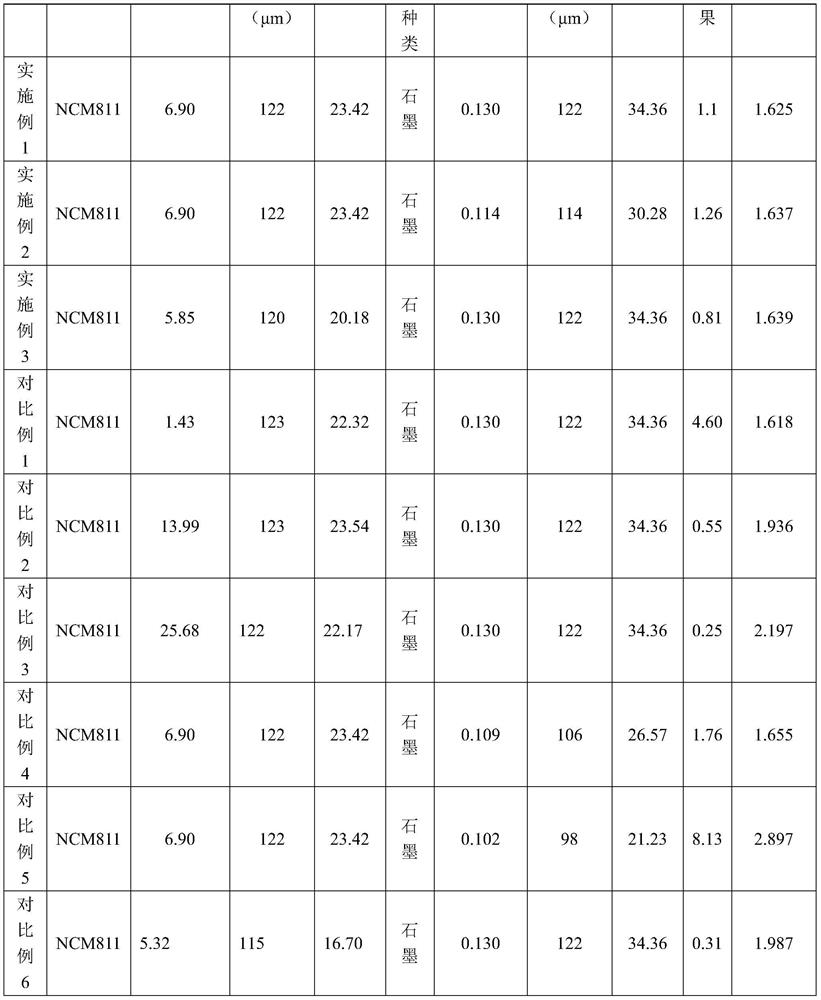
[0080] The lithium ion batteries provided in Examples 1-3 are designed (including the preparation method) based on the above-mentioned specific embodiments, wherein the coordination relationship between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the lithium ion battery is: The specific values of each parameter and the data results of the final coordination relationship are shown in Table 1;
[0081] where R c is the resistivity of the positive electrode, T c is the thickness of the positive electrode, P c is the porosity of the positive electrode, R a is the resistivity of the negative electrode, T a is the thickness of the negative pole piece, P a is the porosity of the negative pole piece.
Embodiment 4-7
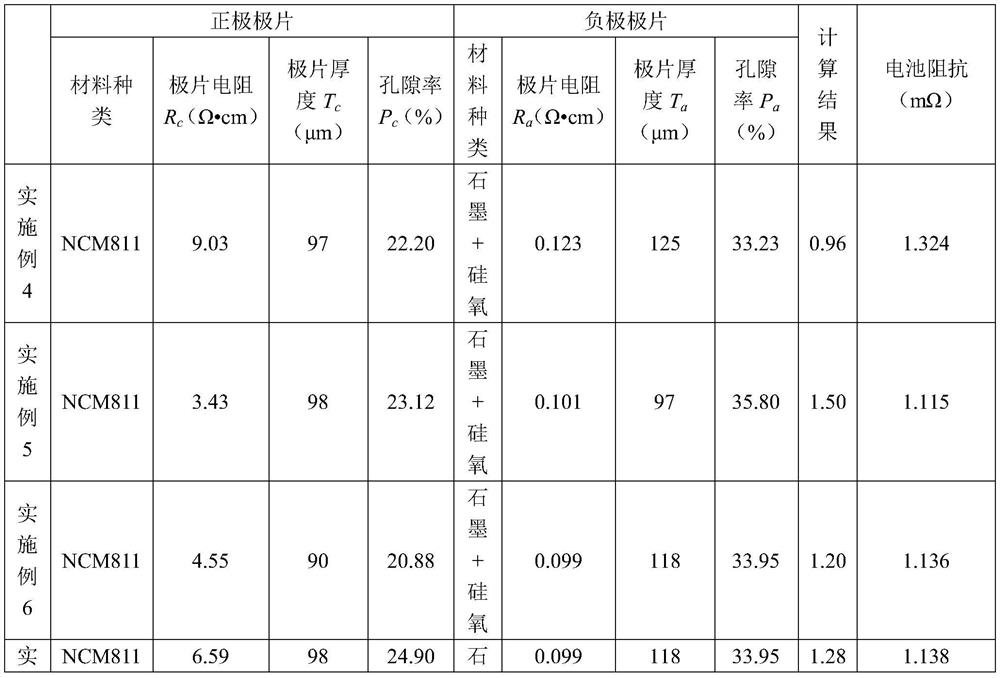
[0094] The lithium ion batteries provided in Examples 4-7 are designed based on the above-mentioned specific embodiments (including the preparation method), wherein the coordination relationship between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the lithium ion battery is: The specific value of each parameter and the data result of the final coordination relationship are shown in Table 2;
[0095] where R c is the resistivity of the positive electrode, T c is the thickness of the positive electrode, P c is the porosity of the positive electrode, R a is the resistivity of the negative electrode, T a is the thickness of the negative pole piece, P a is the porosity of the negative pole piece.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com