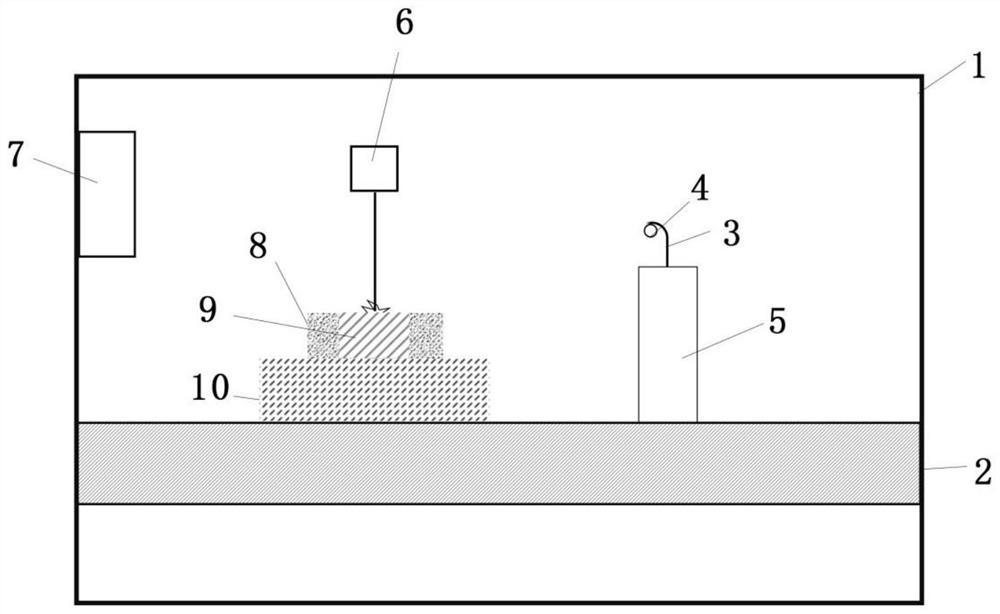
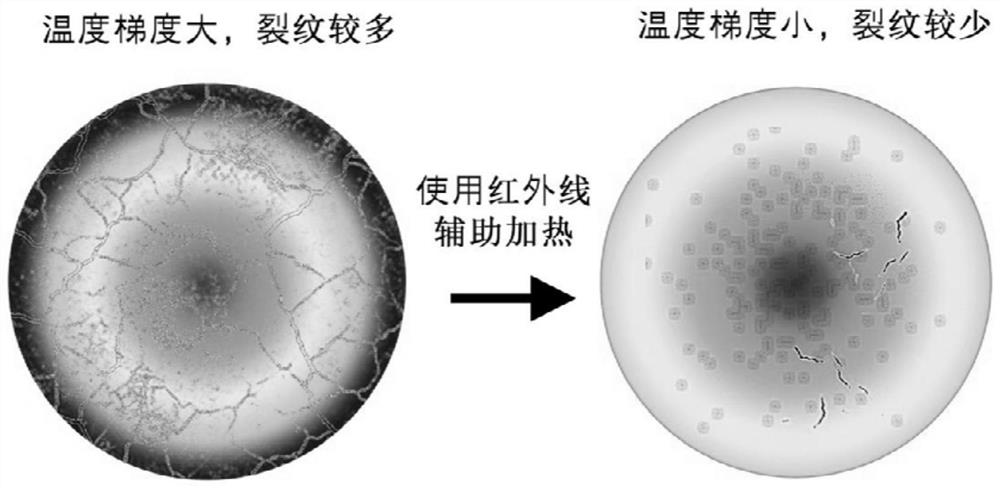
Preparation method of laser additive manufacturing hot crack sensitive material based on infrared auxiliary preheating
A laser additive and infrared technology, applied in the directions of additive manufacturing, additive processing, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the mechanical properties of formed parts, uneven temperature distribution of the molten pool, material deformation and cracking, etc., to save equipment. The effect of retrofit cost, simple installation, and improved design freedom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] (1) The composition of the aluminum-based alloy is that the Cu content is 3.6-4.5wt.%, the Li content is 0.7-1.1wt.%, the Mg content is 0.3-1.0wt.%, the Ag content is 0.3-0.8wt.%, and the Zr content is It is 0.1-0.2wt.%, the balance is Al, and the particle size of the powder is 25-53 μm.
[0043] (2) Use computer-aided design software to build a 3D solid geometric model of the target part and export it as an STL file, then use Materialise Magics software to slice the model in layers, and set the laser scanning path and laser process parameters. The laser process parameters are set as follows: the laser power is 250-350W, the laser scanning speed is 600-1000mm / s, the scanning spacing is 50μm, and the powder thickness is 30μm. The laser filling direction is rotated 37°.
[0044] (3) The slice file obtained in step (2) is imported into the computer control system of the transformed selective laser melting and forming equipment, and the aluminum-based alloy powder in step ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) The composition of the tungsten-based alloy is that the Ni content is 5.8-7.2wt.%, the Fe content is 2.0-3.5wt.%, the Co content is 0.5-1.0wt.%, the balance is W, and the powder particle size is 15-45μm .
[0049] (2) Use computer-aided design software to build a 3D solid geometric model of the target part and export it as an STL file, then use Materialise Magics software to slice the model in layers, and set the laser scanning path and laser process parameters. The laser process parameters are set as follows: the laser power is 375-475W, the laser scanning speed is 400-600mm / s, the scanning distance is 50μm, and the powder thickness is 50μm. The partition scanning strategy is adopted, and the partition size is 5mm. The laser filling direction is rotated 37°.
[0050] (3) The slice file obtained in step (2) is imported into the computer control system of the transformed selective laser melting and forming equipment, and the aluminum-based alloy powder in step (1) i...
Embodiment 3
[0054] (1) The composition of nickel-based alloy is Cr content of 21.3-22.5wt.%, Fe content of 17.8-18.6wt.%, Mo content of 8.4-9.2wt.%, W content of 5.6-6.2wt.%, Co content It is 1.0-1.6 wt.%, the balance is Ni, and the particle size of the powder is 20-47 μm.
[0055] (2) Use computer-aided design software to build a 3D solid geometric model of the target part and export it as an STL file, then use Materialise Magics software to slice the model in layers, and set the laser scanning path and laser process parameters. The laser process parameters are set as follows: the laser power is 300-450W, the laser scanning speed is 1000-1400mm / s, the scanning distance is 50μm, and the powder thickness is 50μm. The laser filling direction is rotated 37°.
[0056] (3) The slice file obtained in step (2) is imported into the computer control system of the transformed selective laser melting and forming equipment, and the aluminum-based alloy powder in step (1) is placed in the laser addit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com