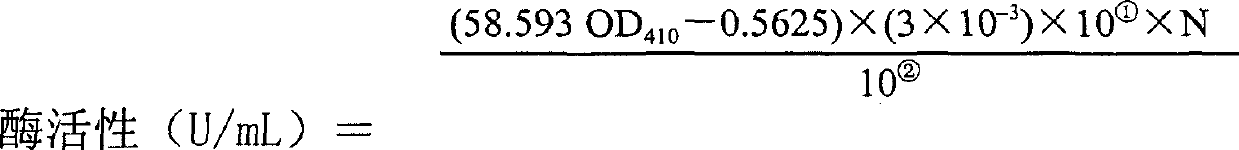Organophosphorus degradating enzyme and coding gene
A technology for organophosphorus pesticides and enzyme degradation, applied in the fields of enzymes, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This example illustrates the screening process of natural strain C2-1 that can degrade a variety of organophosphorus pesticides. The main steps are as follows:
[0037] 1. Take 0.5 g of soil sample in 100mL Burk inorganic salt liquid medium, shake culture overnight at 32°C.
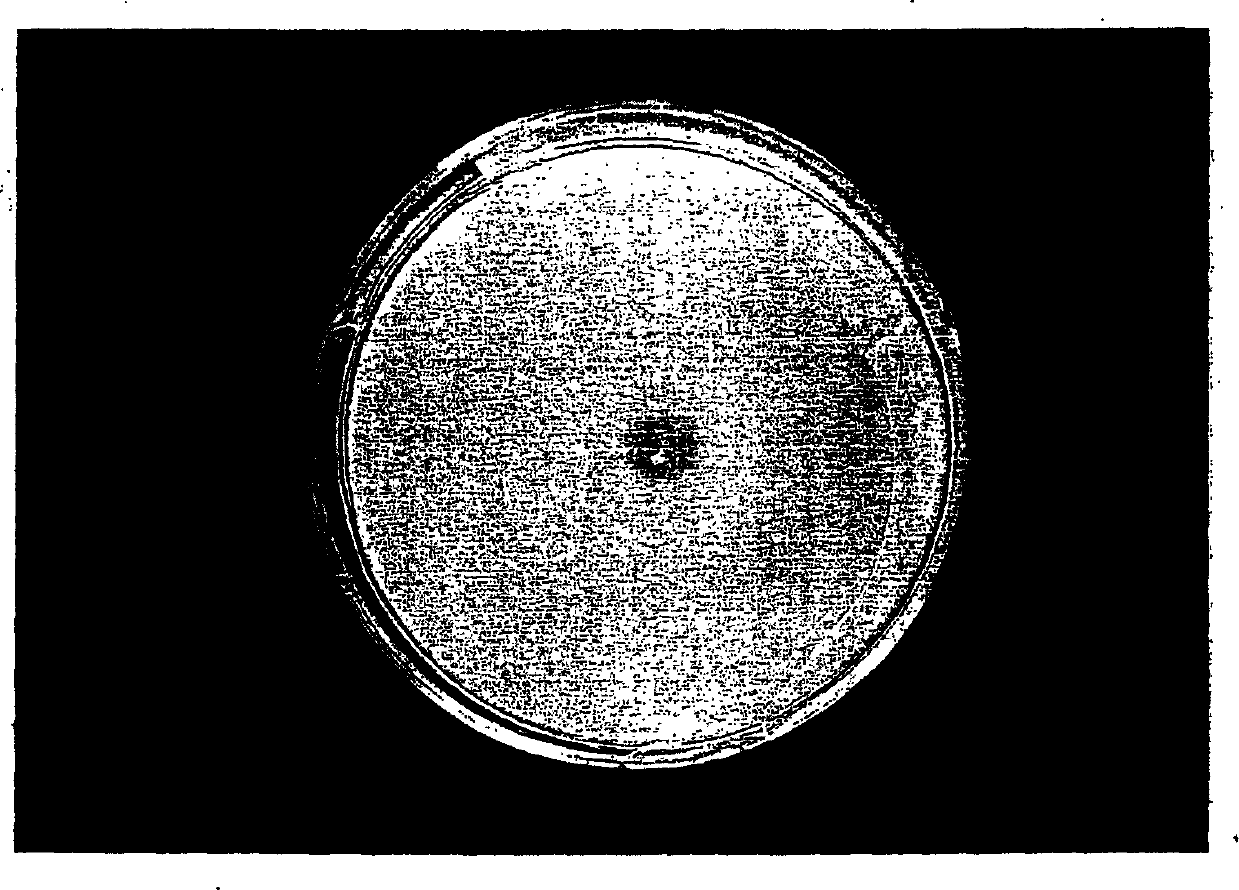
[0038] 2. Bacterial liquid is gradually diluted with sterile water, the dilution factor is 10, 10 2 , 10 3 , 10 4 , 10 5 , 10 6 , Respectively spread on the Burk inorganic salt solid medium plate supplemented with 0.2mg / mL dichlorvos (pure product) and 0.2mg / mL methyl parathion (pure product), cultured in a 32 ℃ incubator, pick A single colony was taken and purified by streaking on the plate.
[0039] 3. The isolated single colony strains were respectively inoculated to the organophosphorus pesticides methyl parathion (0.05%), parathion (0.05%), methamidophos (0.05%) and omethoate (0.05%). , Phoxim (0.05%) (both v / v) (the above-mentioned pesticides were purchased from China National Pesticide Quality Sup...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This experiment illustrates the purification process of OPHC2, the main steps of which are as follows:
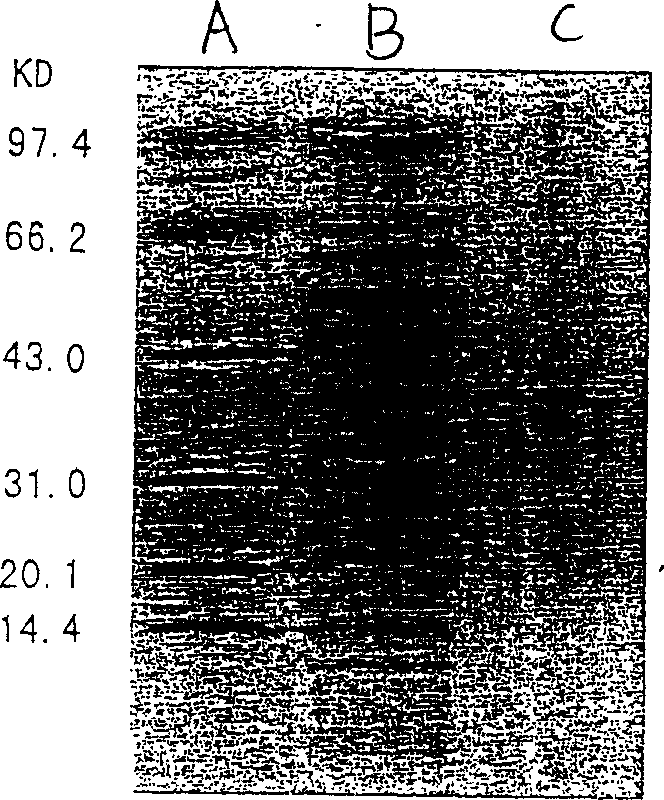
[0043] 1. Extraction of Pesticide Degrading Enzyme (OPHC2) Crude Enzyme Solution: Use 1000mL LB complete medium to culture C2-1 cells in large quantities, culture with shaking at 32℃ overnight, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and suspend the bacterial weight in In 100mL 50mmol / L Tris-Cl (pH8.0) buffer containing 0.1mmol / L protease inhibitor PMSF, crush the cells with an ultrasonic disruptor (Branson, USA), centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 20 minutes, collect the supernatant, and saturate it with The ammonium sulfate with a degree of 20%-90% precipitates the protein. The precipitate was resuspended in 20mL of 50mmol / L, pH8.0 Tris-HCl buffer, and dialyzed for desalting and concentration to obtain OPHC2 crude enzyme solution.
[0044] 2. Separation and purification of OPHC2: Separate the protein components in the crude enzyme solution by polyacryl...
Embodiment 3
[0046] This example illustrates the research on the enzymatic properties of the pesticide-degrading enzyme OPHC2. The main steps are as follows:
[0047] 1. Determination method of organophosphate degrading enzyme enzyme activity
[0048] The organophosphorus degrading enzyme can equally decompose methyl parathion into diethyl phosphorothioate and yellow p-nitrophenol. The activity of the enzyme can be determined by measuring the amount of the product p-nitrophenol.
[0049] The determination of the content of p-nitrophenol and the preparation of the standard curve are as follows: weigh 0.08346 g of p-nitrophenol, first dissolve it with a small amount of 95% ethanol, and then dilute to 100 mL with water, with a concentration of 6 mmol / L. Add different amounts of p-nitrophenol solution and 50mmol / L Tris-Cl (pH8.0) buffer solution according to the following table, the total volume is 1mL, then add 1mL 10% trichloroacetic acid to each tube, and then add 1mL 10% Na 2 CO 3 The total vo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com