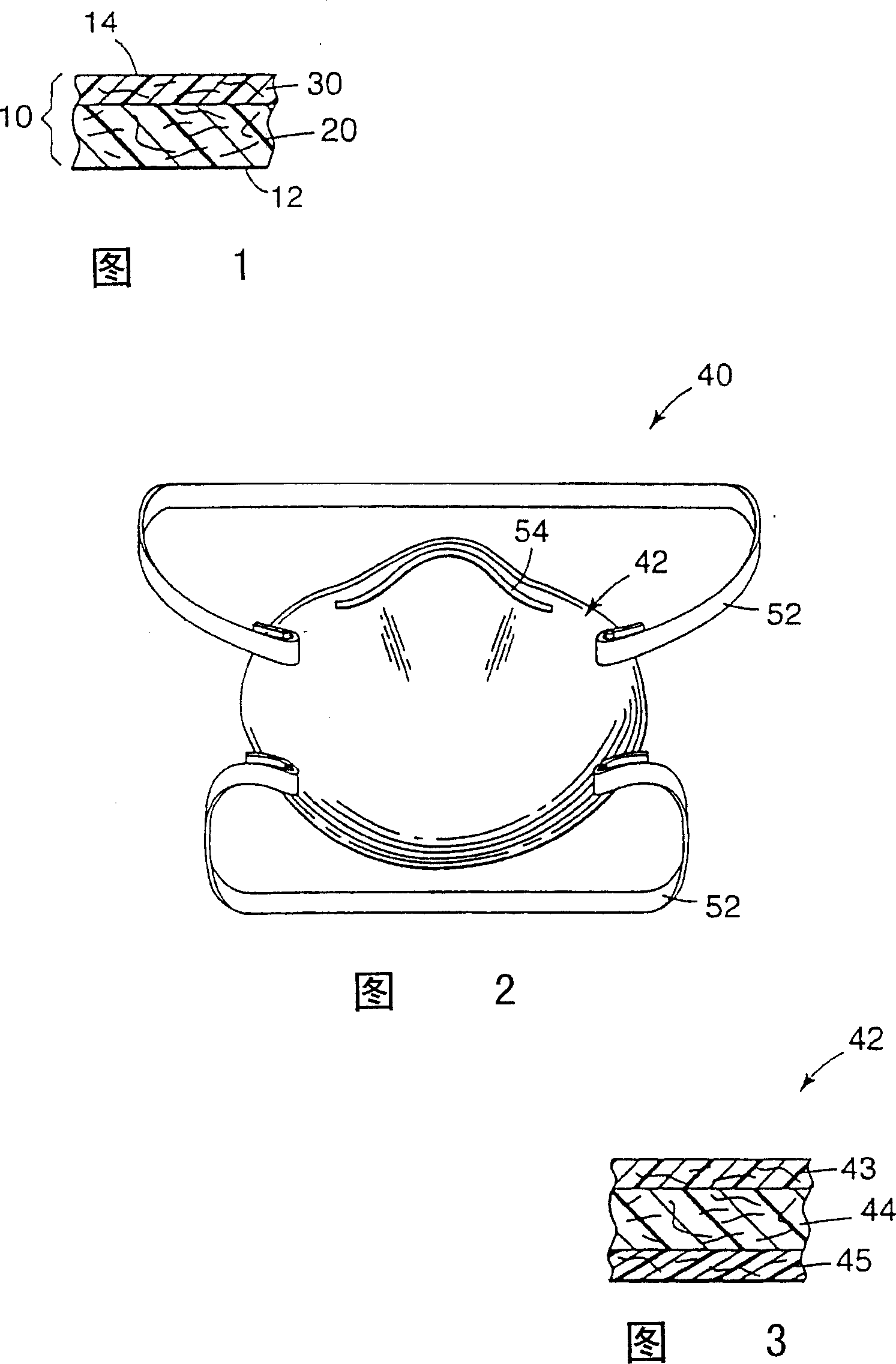
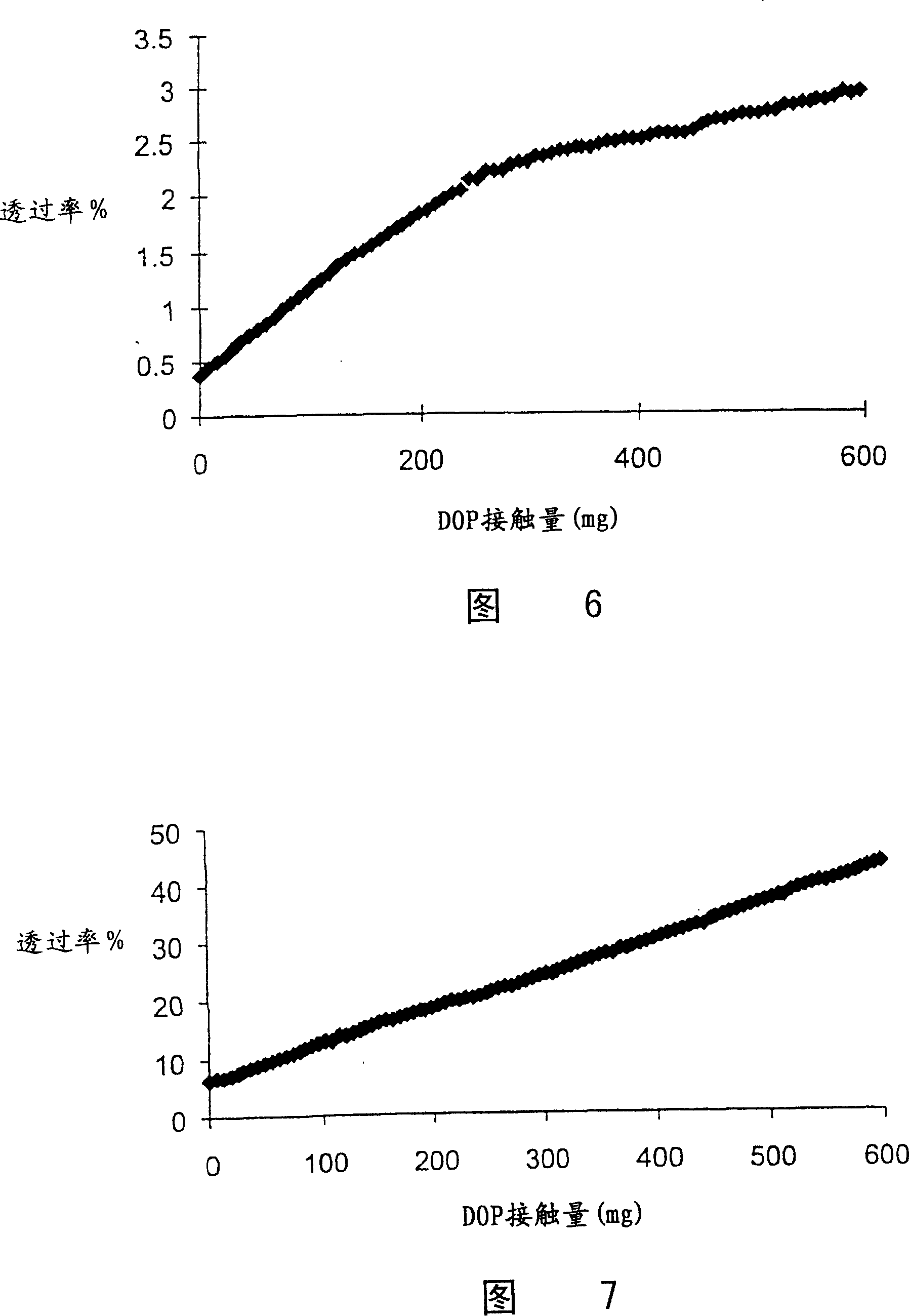
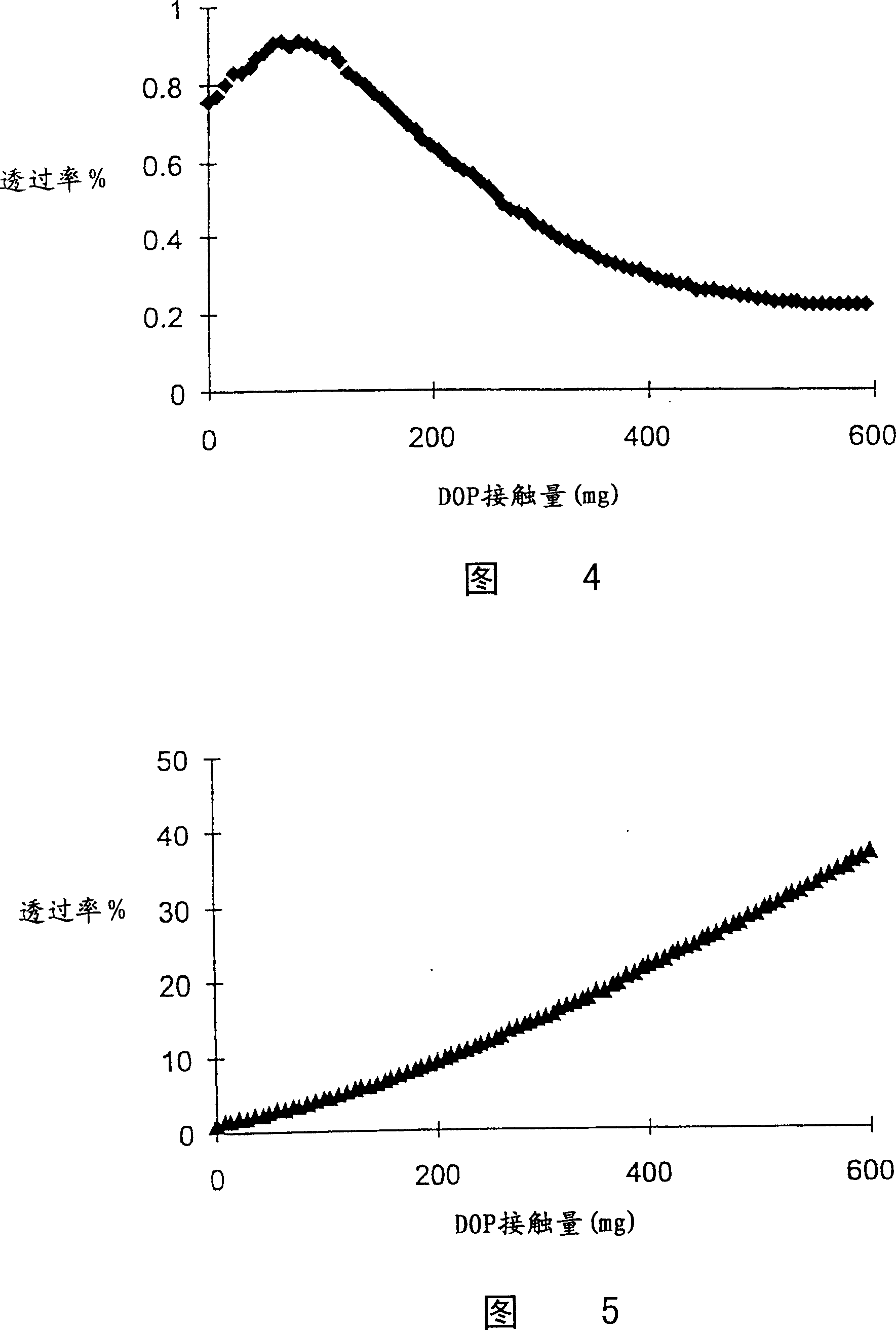Oily-mist resistant filter, breathing apparatus comprising same, and method for removing granule solid and liquid aerosol from gas
A filter and aerosol technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, respiratory protection containers, respiratory filters, etc., can solve problems such as improving the filter system, and achieve a safe breathing environment, pressure drop, and small pressure drop Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
test approach 1
[0124] The discharge current of the unpolarized sample was measured starting from 25°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min. Two samples from the same fabric were subjected to the same test except that they were placed in opposite directions when the samples were placed between the electrodes. For cases where the sample is placed in an orientation that produces a positive discharge current at temperatures above about 110°C, the peak position of the sample is measured.
[0125] Using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) at a heating rate of 10 °C / min, the melting temperature of the sample was determined, and the melting temperature was defined as the temperature in the second DSC heating cycle (that is, heating above the melting temperature, cooling and solidification sample, reheated) resulting in the largest peak observed for melting.
test approach 2
[0127] Test the sample according to TSDC Test Method 1 to determine the correct orientation of the sample. The sample is then placed in the Solomat TSC apparatus in an orientation that produces a positive discharge current at the lower peak temperature of TSDC Test Method 1.
[0128] The test was then conducted by polarizing the samples at 100° C. for 1, 5, 10 or 15 minutes in an electric field of 2.5 kilovolts / millimeter (kV / mm) in the apparatus described above. Still in the electric field, the sample was rapidly cooled (at the maximum cooling rate of the instrument) to -50°C. The electric field was removed and the sample was kept at -50°C for 5 minutes, then heated at a rate of 3°C / min while measuring the discharge current. A baseline was drawn based on the slope of the curve from 0 to about 30°C, and the half-peak width was measured to calculate the value of the half-peak width of each peak.
test approach 3
[0130] This method is the same as TSDC test method 2, except that a baseline is drawn between the minimum values on both sides of the selected peak, and the charge density of the sample is calculated at each polarization time. If there is no minimum on the high temperature side of the peak, a baseline is drawn between the minimum on the low temperature side of the peak and the crossing point of the curve on the high temperature side of the peak or extrapolated to the crossing zero current point. The area under the peak was integrated to calculate the charge density.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com