Multi-stage preparation process of carbonyl synthesizing aldehyde and/or alcohol
A technology of hydroformylation and reaction, applied in the field of multi-stage preparation of oxo aldehyde and/or alcohol, and can solve problems such as ineffective conversion and unfavorable energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
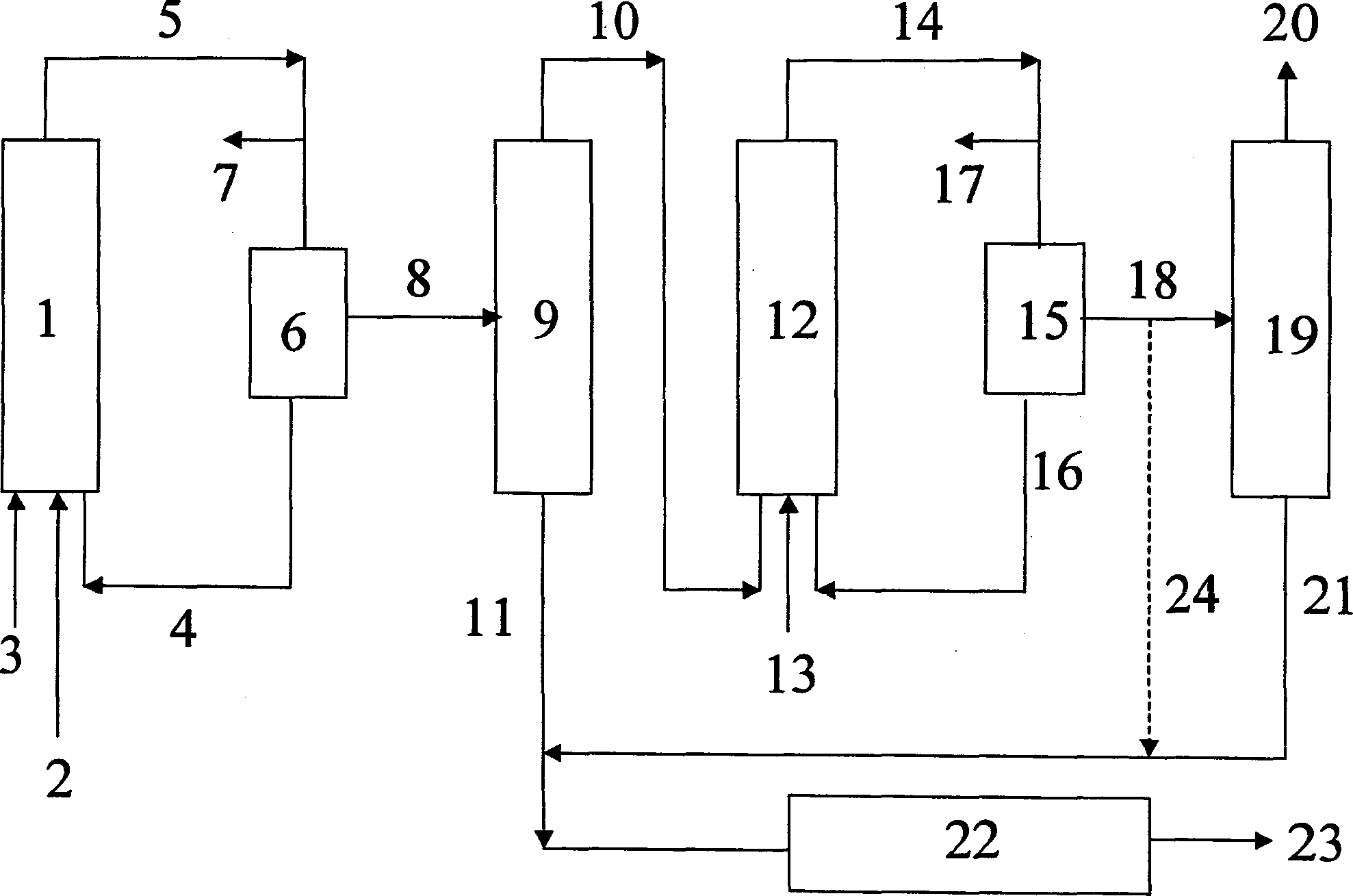
[0025] The method of embodiment 1 is as block flow process figure 1shown. The olefin mixture 3 , the synthesis gas 2 (carbon monoxide and hydrogen) and the catalyst solution or catalyst precursor 4 are fed into the first hydroformylation reactor 1 . The resulting hydroformylation mixture 5 is depressurized, the depressurized gas 7 (unconsumed synthesis gas) is vented, and the catalyst 4 is removed from the depressurized hydroformylation mixture in a first catalyst removal step 6, The catalyst is then returned to the first hydroformylation reactor 1 after optionally removing a small portion of the catalyst stream and making up with fresh catalyst. Catalyst here also refers to a catalyst precursor, for example, a cobalt(II) salt solution. In a distillation column 9 , the catalyst-free hydroformylation mixture 8 is separated into a low-boiling component 10 mainly composed of unreacted olefins and a crude aldehyde 11 . Low boiling point components 10 , synthesis gas 13 and cata...
Embodiment approach 2
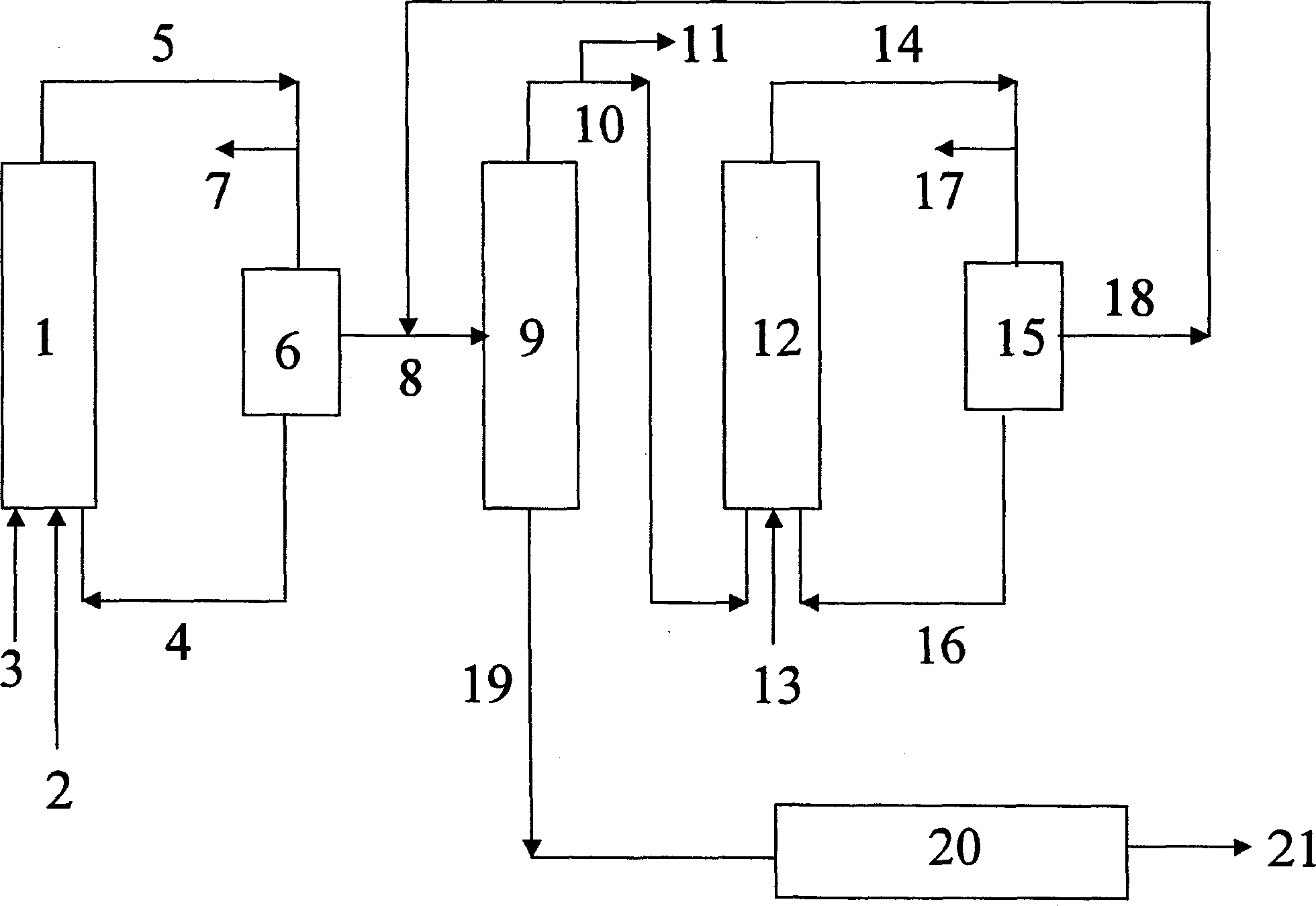
[0030] A block flow diagram of another embodiment of the method of the present invention is as figure 2 shown. The olefin mixture 3 , the synthesis gas 2 (carbon monoxide and hydrogen) and the catalyst 4 or its precursor are fed into the first hydroformylation reactor 1 . The hydroformylation mixture 5 thus obtained is depressurized, the depressurized gas 7 (unconsumed synthesis gas) is vented off, and the catalyst 4 is removed from the depressurized hydroformylation mixture in a first catalyst removal step 6 , optionally removing a small portion of the catalyst stream and making up with fresh catalyst, the catalyst is then returned to the first hydroformylation reactor 1 . The catalyst-free hydroformylation mixture 8 is fed to a distillation column 9, where the hydroformylation mixture 8 is combined with the catalyst-free hydroformylation mixture from the second hydroformylation reactor 12 Together, the mixture 18 is separated into a low boiling fraction 10 containing unre...
Embodiment approach 3
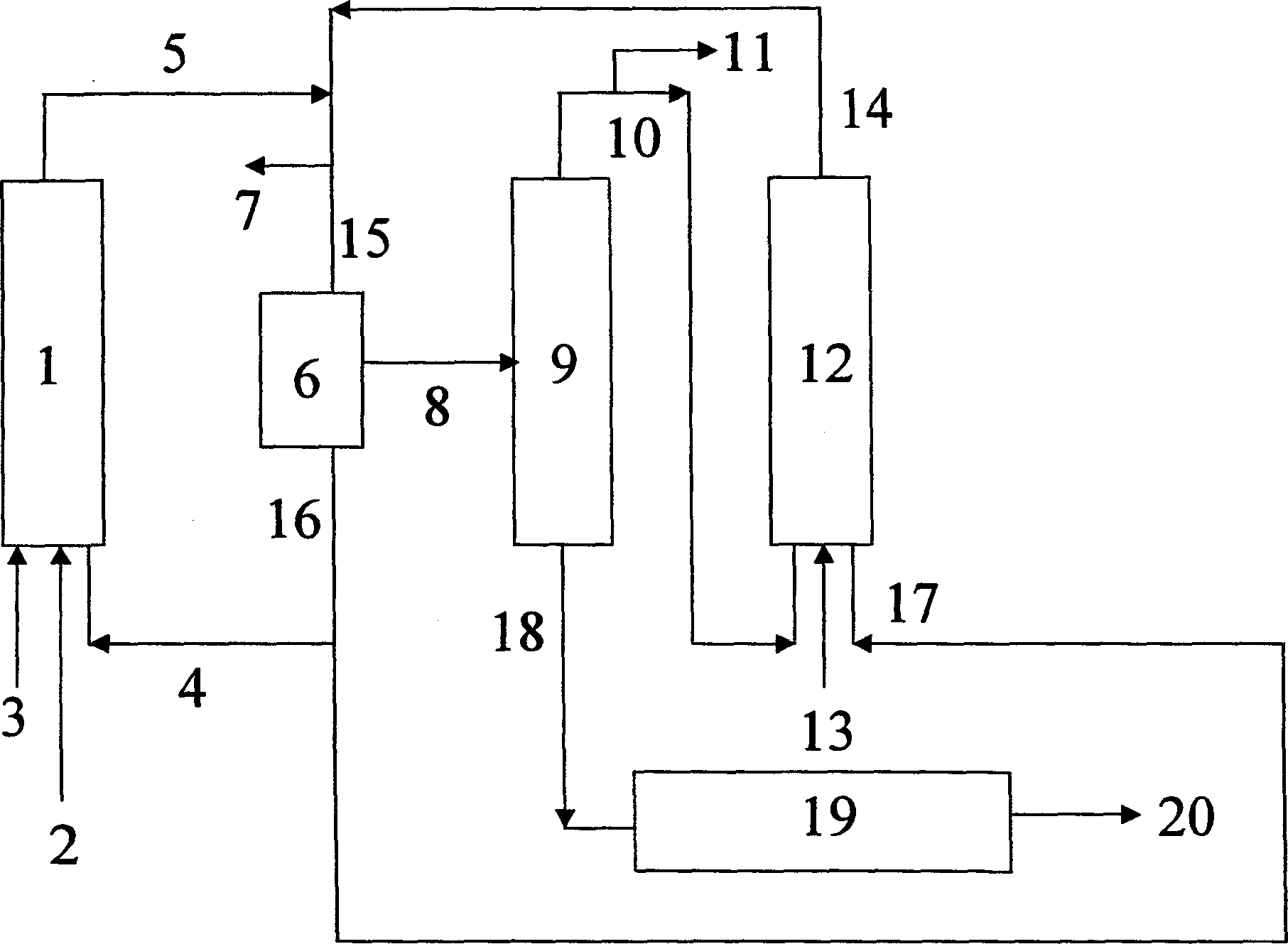
[0035] Yet another embodiment of the method of the present invention is as image 3 shown. The olefin mixture 3 , the synthesis gas 2 (carbon monoxide and hydrogen) and the catalyst solution or its precursor 4 are fed into the first hydroformylation reactor 1 . The hydroformylation mixture 5 thus obtained is depressurized together with the hydroformylation mixture 14 from the second hydroformylation reactor 12 to form a combined hydroformylation effluent 15 which is discharged under reduced pressure Gas 7 (unconsumed syngas). In catalyst removal step 6, catalyst 16 is removed from the combined hydroformylation reaction effluent to obtain a mixture 8 comprising formed aldehydes, alcohols and unreacted olefins. After optionally removing a portion of the catalyst stream and making up with fresh catalyst, the catalyst 16 is then again divided into two substreams 4 and 17 . Substream 4 is returned to the first hydroformylation reactor 1 and substream 17 is returned to the second...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com