Electrode bar for grounding
A technology of grounding electrodes and rods, applied in the direction of connecting contact materials, etc., can solve the problems of difficult quality control of copper layer thickness, pinhole corrosion, insufficient mechanical strength, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
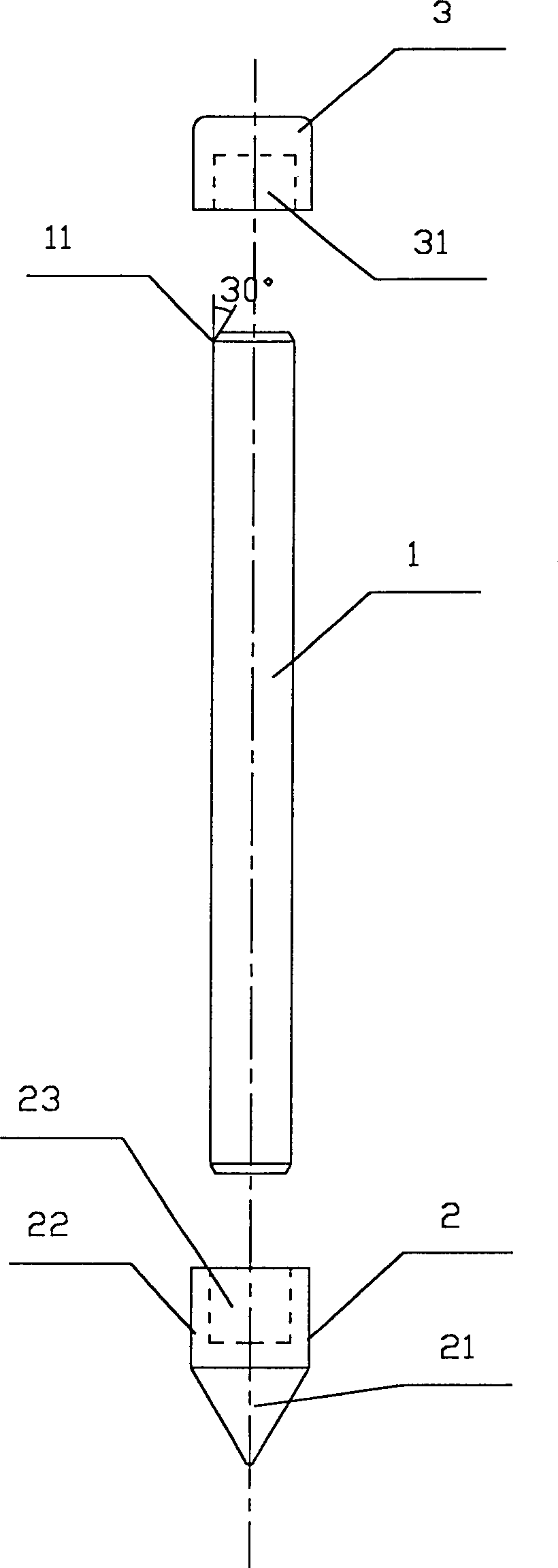
[0039] Example 1, see figure 1 , the figure shows a grounding electrode rod, which includes a cylindrical rod body 1, the rod body is a copper-plated steel rod, copper-clad steel rod or other metal rod body, at one end of the rod body 1 is set There is a ground drilling safety cone 2, and a hammering condom 3 is arranged at the other end. The hammering condom 3 is cylindrical, and one end of the hammering condom 3 is provided with a cylindrical cavity A31 adapted to the end of the rod 1; The inner diameter of the cavity A31 and the outer diameter of the end of the rod body 1 are a transition fit, and the gap is 0.05-0.10 mm. The described ground drilling safety cone 2 includes a tapered head 21 and a columnar tail 22 for connecting with the rod 1, and a hole suitable for the other end of the rod 1 is provided on the end face of the columnar tail 22. Cavity B23; the conical head 21 is solid, and its shape is conical, and the end face of columnar tail 22 has the cavity B23 tha...
Embodiment 2
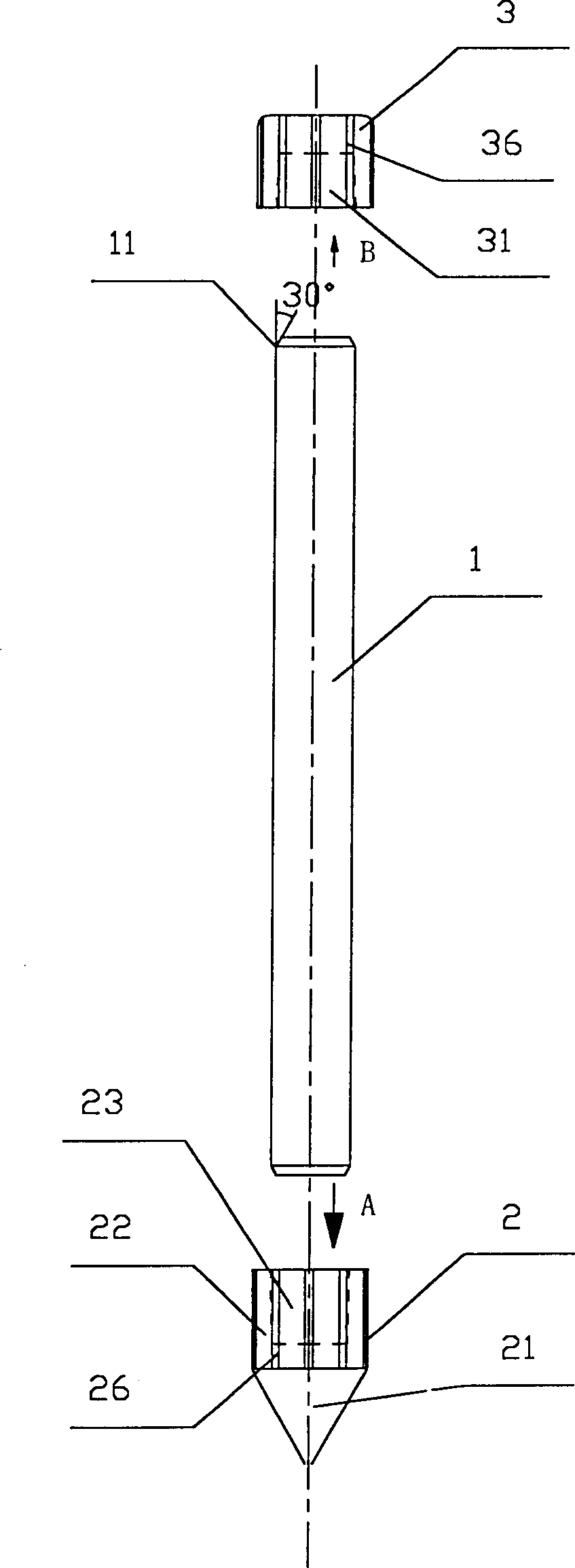
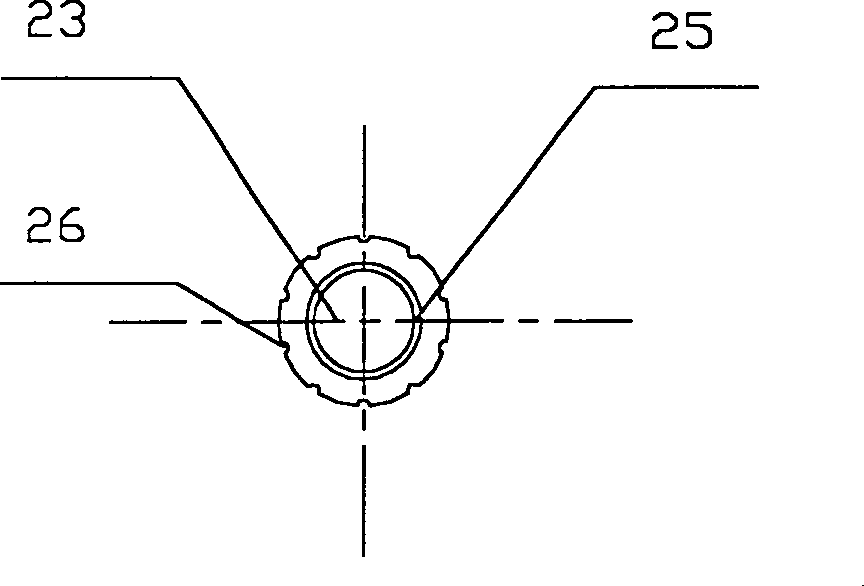
[0040] Example 2, see figure 2 , 2A And 2B, a kind of grounding electrode rod is shown in the figure, and difference with last embodiment is: the cavity B23 of described earth-boring safety cone 2 is the tapered hole with taper slightly, and its taper is 1: 30, the connection between the tapered hole 23 and the end of the cylindrical rod body 1 is tighter. Similarly, in order to make the connection between the hammering condom 3 and the rod body 1 tight, the cavity A31 of the hammering condom can be a slightly tapered tapered hole with a taper of 1:30. Another point of difference is: the outer surface of the ground drilling safety cone 2 and the hammering condom 3 are respectively provided with several soil raising ditches B26 and soil raising ditches A36, and the distribution density is 1 to 25 per centimeter of circumference; There are 10 middle soil-raising ditch B26 and soil-raising ditch A36 respectively, and described soil-raising ditch B26 and soil-raising ditch A36 ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3, see image 3 , the figure shows a grounding electrode rod, which is different from Implementation 1 in that: the two ends of the safety cone 2 for drilling the ground, the hammering safety sleeve 3 and the rod body 1 can be threaded, and the column of the safety cone 2 The cavity B23 of the tail part 22 and the cavity A31 of the hammering condom are screw holes 25 and screw holes 32, and the two ends of the rod body 1 are provided with external threads 14 and 12; The hammering condoms 3 are in the shape of a hexagonal prism, that is, a hexagonal nut with one end closed. The columnar tail 22 of the ground drilling safety cone 2 is in the shape of a hexagonal prism, and its conical head 21 is in the shape of a hexagonal prism. See Figure 3A and 3 b.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com