Testing method for skin inflammation or irritation and kit
A kit, skin technology, applied in the field of skin inflammation or irritation detection and kit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] Example 1 - Method of Measuring the Irritant Effect of Water on the Skin
[0095] As a means of determining the sensitivity of the method for measuring subclinical effects, we selected two bland fluids to determine the inflammatory potential following exposure. Some of the mildest liquids that come to mind are the different types of water that are present during cleansing of the skin, and it is also a major ingredient in many topical skin care products. In this example, we use PGE 2 Inflammatory responses after skin exposure to deionized water and tap water were measured as markers.
[0096] The determination follows the following method:
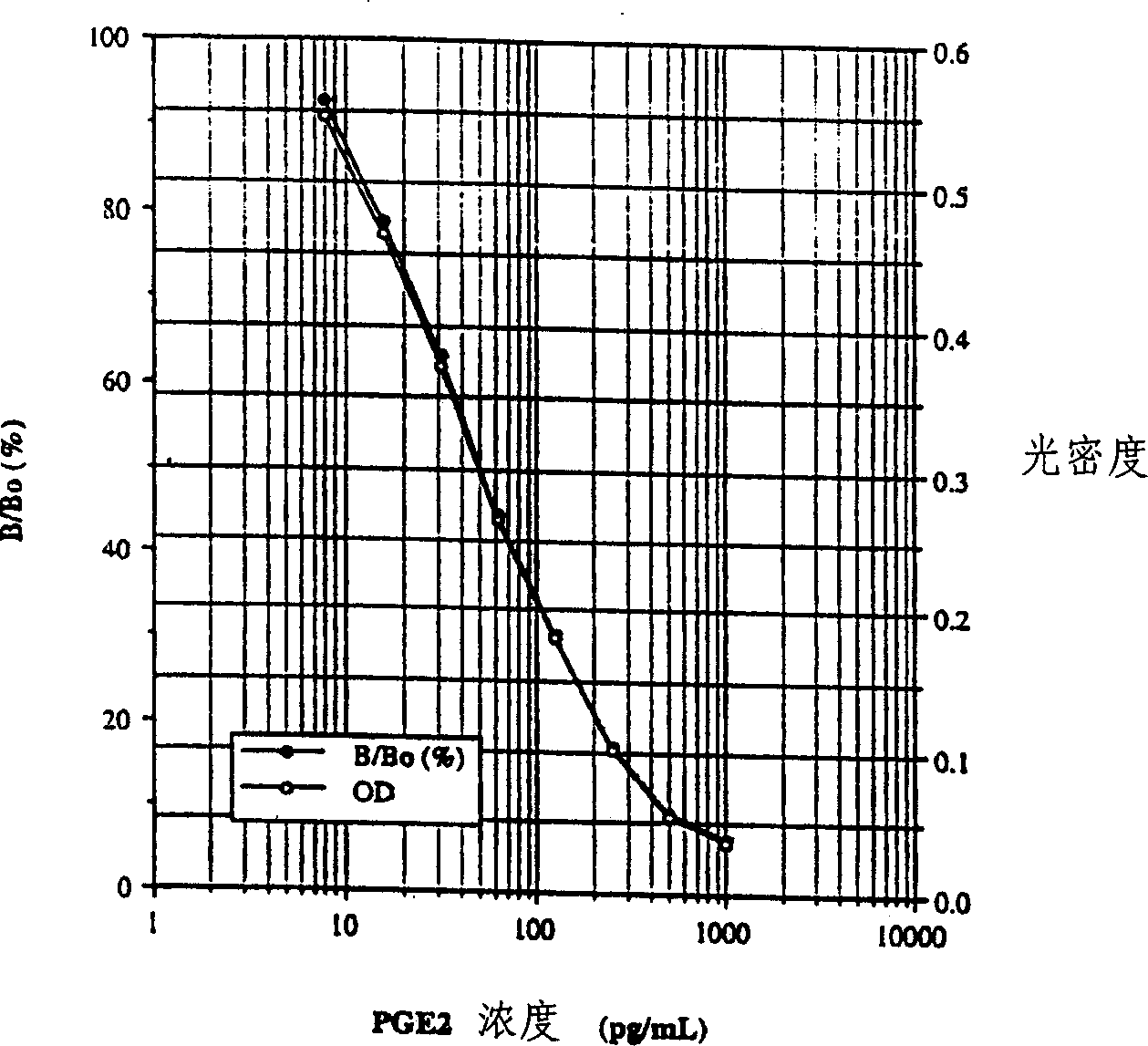
[0097] 1. Determination of PGE contained in secretions present on the skin surface along the volar forearm of the subject 2 (Cuderm Corporation, Dallas, Texas) by placing a mild adhesive-coated microporous plastic film, Sebutape(R) (Cuderm Corporation, Dallas, Texas) on the skin in direct contact with the skin. After 1 minute the...
Embodiment 2
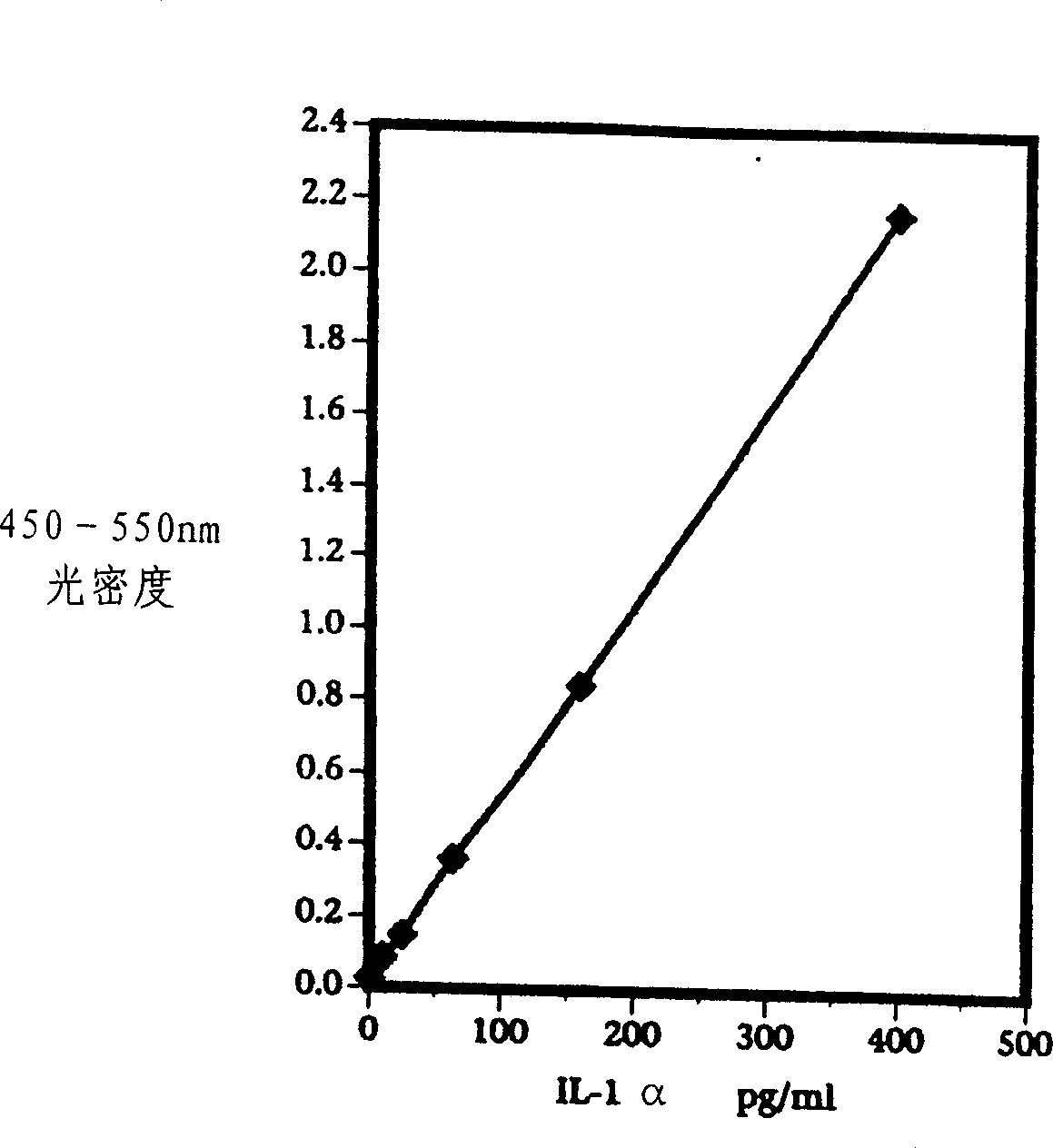
[0105] Example 2 - Possible Interaction of Anionic Surfactants with Interleukin-α (IL-1α)
[0106] One concern with using IL-la as a marker of inflammation or irritation is its potential interaction with surfactants often included in topical skin care compositions. This example illustrates this interaction by measuring the apparent level of IL-1α expressed on the skin as a function of the concentration of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS, Stepan Co., Northfield, IL) in the test fluid.
[0107] SLS concentration in deionized water
[0108] Table 2 shows the dose-dependent data for IL-la after exposing the skin to different concentrations of SLS. The amount or response of markers of inflammation is expected to increase with increasing levels of anionic surfactant. This was observed at low SLS levels, but not at the highest SLS concentration detected in the study, raising doubts about the feasibility of the method. We wish not to be bound by theory, and believe that high ...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3 Inflammation caused by mild face wash
[0110] pure water
Glycerin
Dodecyl Glucoside
Cocoamidopropyl betaine (cocomidopropyl
Glycereth-7
Ammonium dodecylsulfonate
Sodium cocoyl sarcosinate
PEG-120 Methyl Glucose Dioleate
Tetrasodium EDTA
spices
[0111] Table 4 shows the determination of PGE using the above method 2 The degree of irritation caused by the face wash compared to deionized water as indicated by the amount expressed.
[0112] subjects
Deionized water
facial cleanser
1
1.98
1.81
2
1.48
1.26
3
1.30
0.67
4
0.83
2.11
5
1.49
1.72
6
2.12
3.07
7
1.2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com