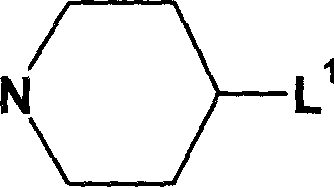
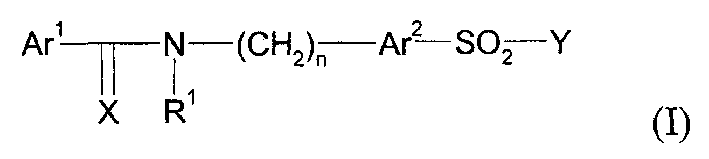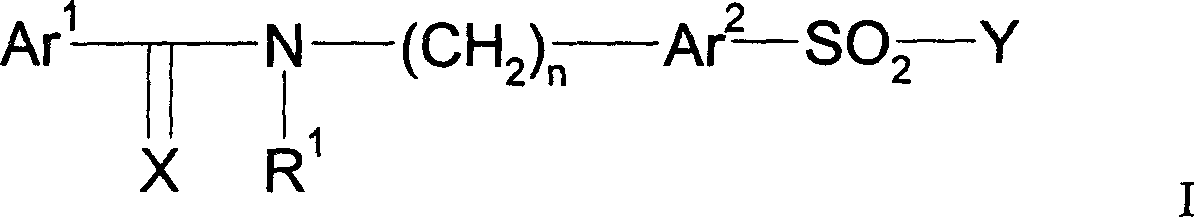Pharmaceutically active sulfonamide derivatives bearing both lipophilic and ionisable moieties as inhibitors of protein junkinases
A derivative, sulfonamide technology, applied in the field of sulfonamide derivatives, can solve the problems of impermeability of blood and meningeal membranes, low oral bioavailability, poor membrane permeability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0401] Example 1 (Protocole E; see Protocols 1, 3 and 6)
[0402] 3-Methoxy-N-{[5-({4-[(4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino]piperidin-1-yl}sulfonyl)thiophen-2-yl]methanol The preparation of base} benzamide (1)
[0403] {[(3-Methoxybenzoyl)amino]methyl}thiophene-2-sulfonyl chloride (1a)
[0404] To a solution of 2-aminomethylthiophene (10.6 mL, 103 mmol) and pyridine (9.1 mL, 104 mmol) in 100 mL of chloroform was added 3-methoxybenzoyl chloride (19.2 g, 103 mmol) in dichloromethane ( CH 2 Cl 2 ) solution. The reaction was warmed to room temperature over 1 hour and stirred for an additional 3 hours. Water was added when 3-methoxy-N-(thiophen-2-ylmethyl)benzamide (1b) (10.1 g) precipitated. The solid was filtered and washed with water. The remaining organic layer was washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated to give (1b) (15.2g). The overall yield was 25.3 g (99.9%). (1b) was used directly in the next step without further purification....
Embodiment 63
[0415] Example 63 (Protocole A; see Protocols 1, 3 and 7)
[0416] Preparation of 4-chloro-N-[(5-{[4-(hexylamino)piperidin-1-yl]sulfonyl}-thiophen-2-yl)methyl]benzamide 4-Chloro-N-thiophen-2-ylmethyl-benzamide (63a)
[0417] 2-Aminomethyl-thiophene (0.137 mol) and i PR 2 A solution of NEt (0.25 mol) in dichloromethane (200 mL) was added to a solution of 4-chlorobenzoyl chloride (0.114 mol) in 50 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane. A white solid formed and the reaction was warmed to room temperature over 1 hour. The mixture was diluted with 200 mL of dichloromethane, washed twice with aqueous hydrochloric acid (0.1 N), and dried over magnesium sulfate. After evaporation of the solvent, 28 g (98%) of a white solid, the title benzamide, was obtained: melting point 153-54°C, 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ7.9(d, J=8.67Hz, 2H), 7.58(d, J=8.67Hz, 2H), 7.44(dd, J=3.77, 1.13Hz, 1H), 7.22(d, J=5.27Hz, 1H), 7.16 (dd, J=3.39, 5.27Hz, 1H), 6.62 (brd, 1H), 4.98 (d, J=5.65Hz, 2H).
[0418] 5-(...
Embodiment 122
[0428] Example 122 (Protocole L; see Schemes 2 and 7)
[0429] 2-{[4-(Hexylamino)piperidin-1-yl]sulfonyl}-5-{[(3-methoxy-benzoyl)amino]methyl}thiophene-3- Preparation of Ethyl Carboxylate (122)
[0430] Diallyl-thiophen-2-ylmethylamine (122a)
[0431] 2-Aminomethyl-thiophene (51.4 g, 956 mmol) and i-Pr 2 NEt (140 g, 1081 mmol) in dichloromethane (1 L). Allyl bromide (115.7 g, 454 mmol) was added and reflux temperature was reached automatically after 2 hours of mildly exothermic reaction. The mixture was stirred overnight (16 hours), washed (saturated sodium bicarbonate solution; brine), dried (magnesium sulfate) and concentrated. The resulting oil was filtered through silica gel (ethyl acetate:hexane 1:4). The filtrate was concentrated and filtered repeatedly to obtain 70.3 g (80%) of brown oil, namely the title diallylamine. Determined by NMR: 1 H NMR (CDCl -3 )δ7.25 (br.d, J=5.9Hz, 1H), 6.98 (br.dd, J=5.1, 2.8Hz, 1H), 6.94-6.92 (m, 1H), 5.99-5.86 (m, 2H) , 5.29...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com