Module type tubular solid oxide fuel cell power generating system
A solid oxide, fuel cell technology, used in solid electrolyte fuel cells, fuel cells, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the heating efficiency of the combustion chamber to the battery body and fuel gas, affecting fuel transmission and reaction, and affecting power generation. System performance and other issues, to solve the high temperature oxidation problem, the reformation effect is good, and the battery performance is improved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1 Modular cell structure of the present invention
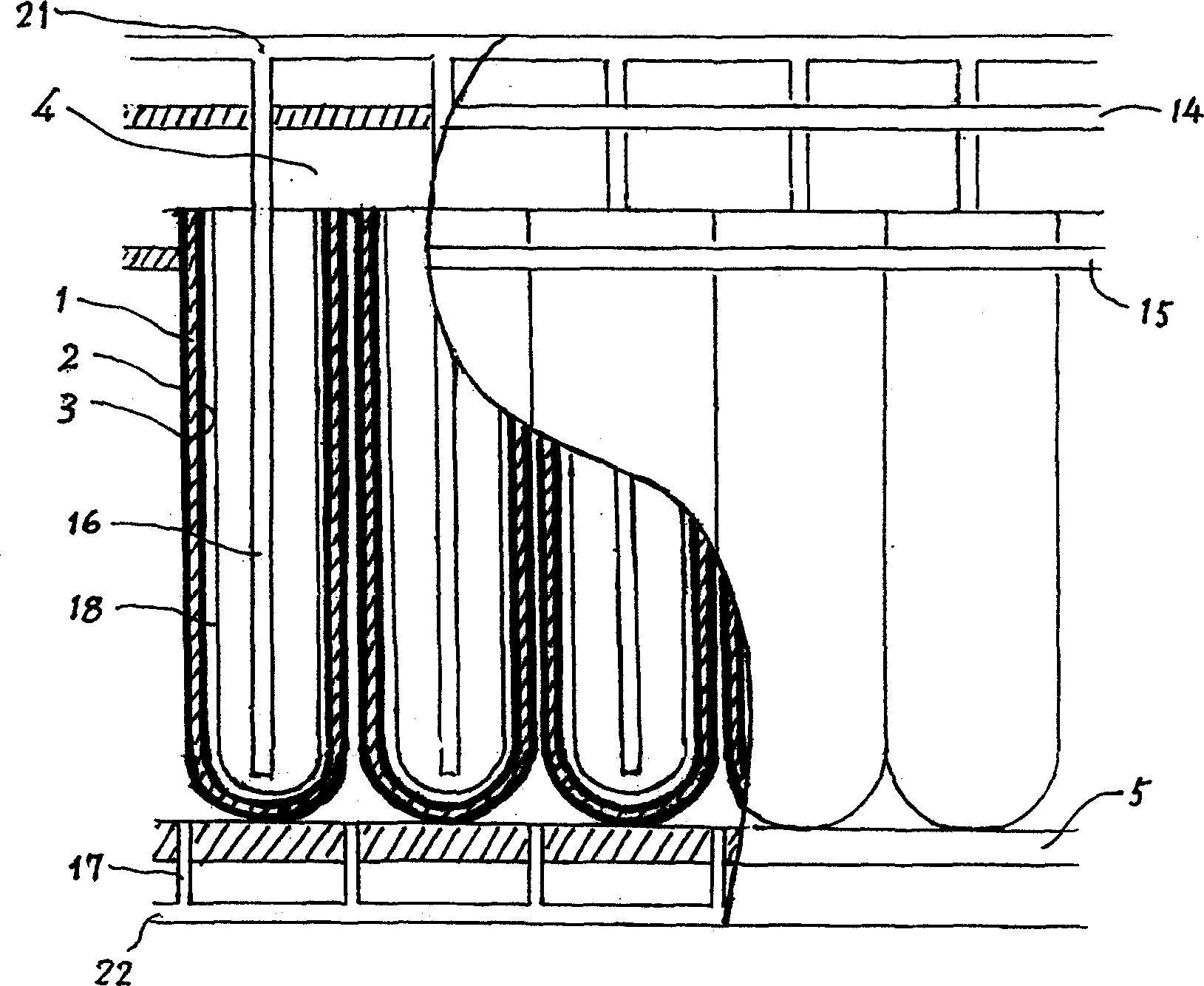
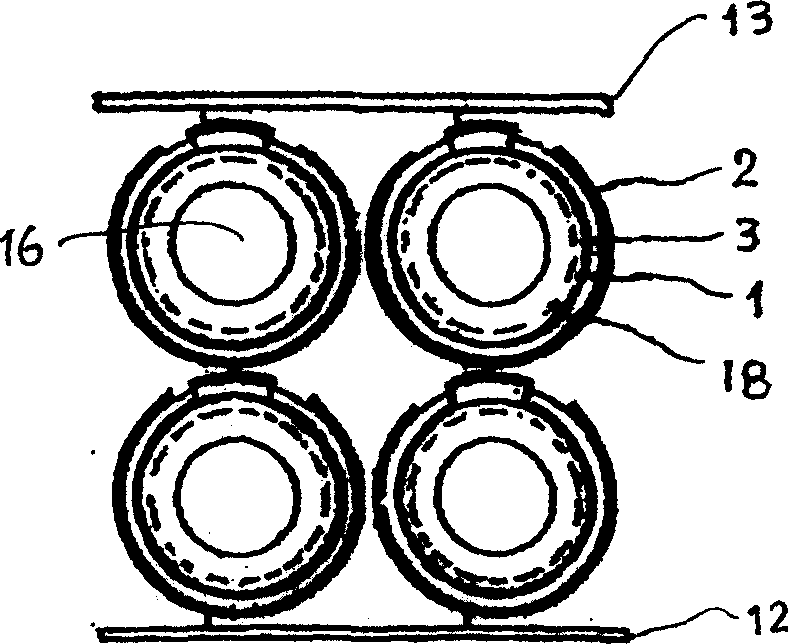
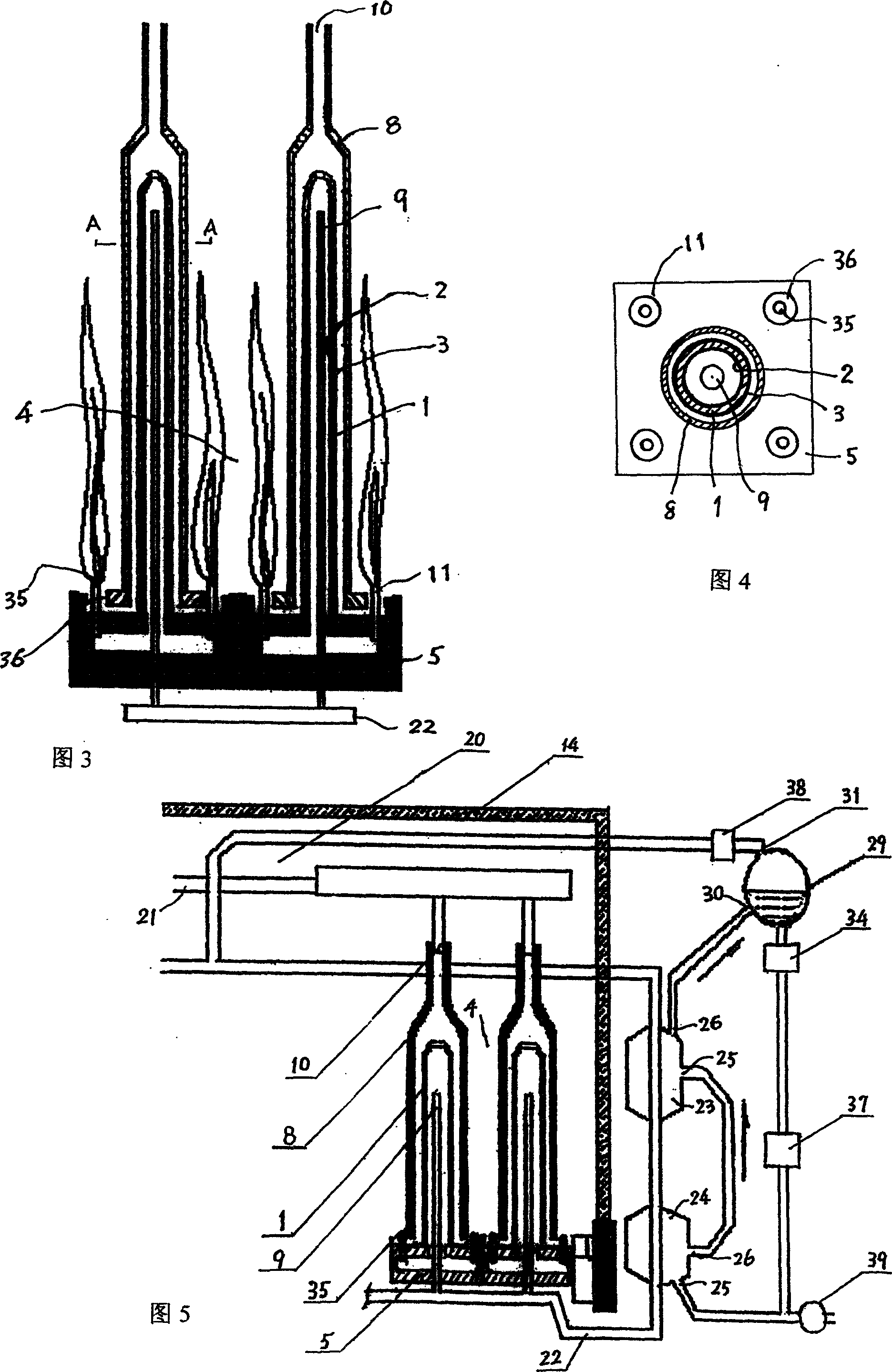
[0024] Fig. 3 shows a schematic cross-sectional view of the structure of a single battery module and adjacent modules. Wherein 1 is an electrolyte tube, and 2 is an anode, which is made on the inner side of the electrolyte tube 1 . 3 is the cathode, which is made on the outside of the electrolyte tube 1. 4 is a combustion chamber, which is the space between the upper top cover 14 and the base 5 of the fuel cell. 5 is a hollow base. 8 is an outer sleeve, and the opening at the upper end of the outer sleeve 8 is an oxidant (air) inflow port 10, and the oxidant (air) inflow port 10 communicates with the oxidant (air) input pipe 21. 9 is a fuel inlet pipe, which passes through the base 5 and communicates with the fuel input pipe 22, and the outside of the outer sleeve 8 is the fuel chamber 4. 11 is the nozzle of the burner, which is composed of a central pipe 35 and an outer ring hole 36. The central pipe 35 ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2 The indirect internal reforming system of the present invention
[0028]When the fuel is city gas or natural gas, a reforming process is required. Fig. 5 shows a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the fuel cell power generation system including the reforming system. In Fig. 4, the upper half of the fuel chamber 4 is a high-temperature reforming chamber 20, which has an oxidant (air) inlet pipe 21 and a fuel inlet pipe 22, where they are preheated. 23 is a high-temperature converter, and 24 is a low-temperature converter, and they have a water inlet 25 and a water outlet 26 respectively. The fuel inlet pipe 22 passes through them to reform the fuel gas, that is, to convert methane into hydrogen and carbon dioxide, and then enters the electrolyte pipe 1 through the fuel inlet pipe 9 . The water vapor required for fuel reforming is provided by the high temperature converter 23 and recycled. The process is that the water outlet 26 and the gas-water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com