Plasmid encoding fibroblast growth factor for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia or diabetes associated angiogenic defects
A technique for hypercholesterolemia and fibroblasts, applied in the field of promoting collateral angiogenesis in ischemic myocardium or skeletal tissue, collateral vessels and arterioles in ischemic tissue, and can solve the problem of collateral vessel reversal, failure Convincingly proven, inability to improve blood flow, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Example 1: Animals and their diets
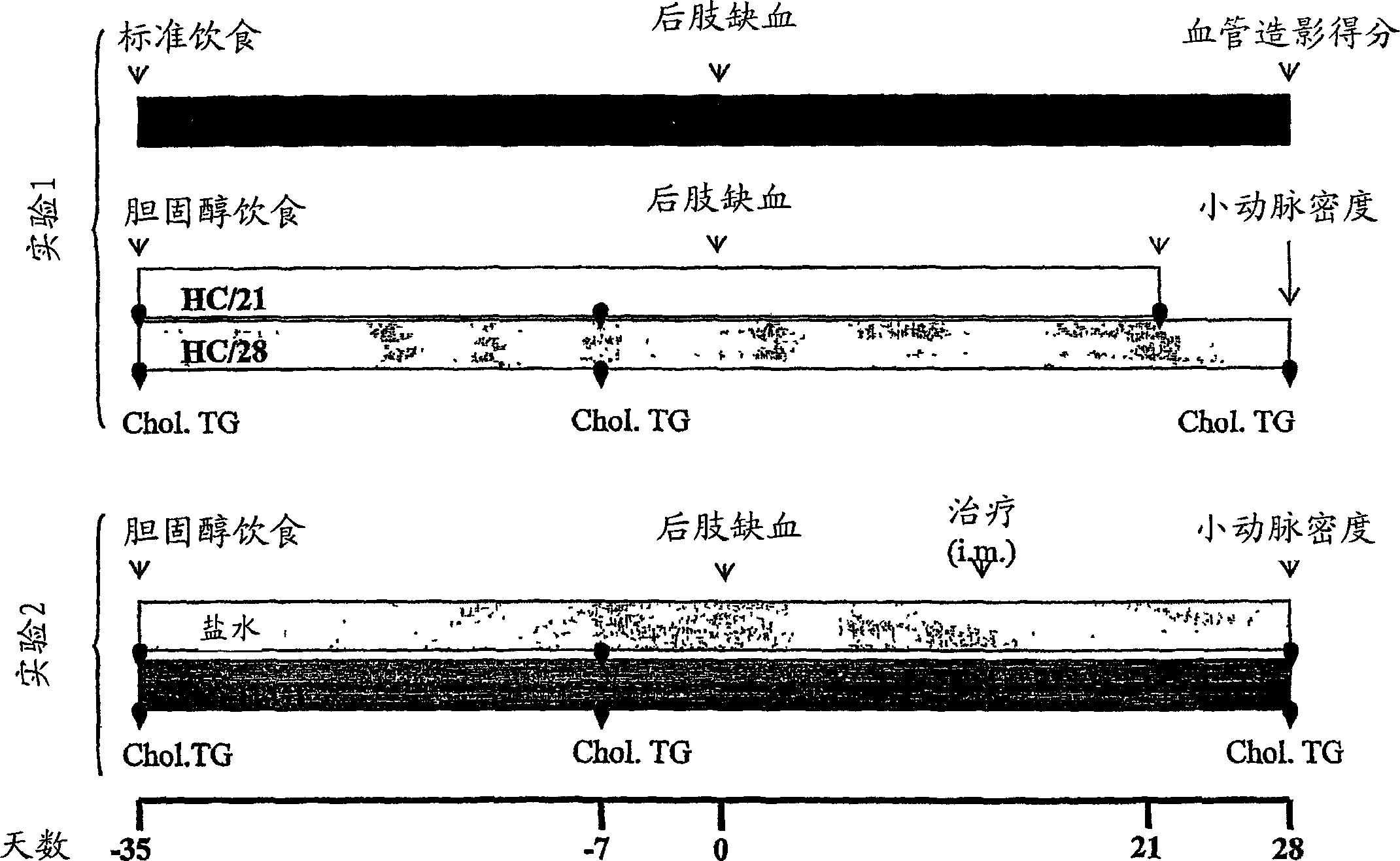
[0123] 11-12 week old Syrian golden hamsters (n=50) (CERJ, Le Genest St Isle, France) were used in this experiment. Animals were allowed to equilibrate in a standard environment at least 7 days prior to the start of the experimental protocol. All animals had free access to water throughout the experiment. All animal procedures were approved by the Animal Use committee of Aventis Pharma and performed in accordance with guidelines published by the National Institutes of Health. (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1985).
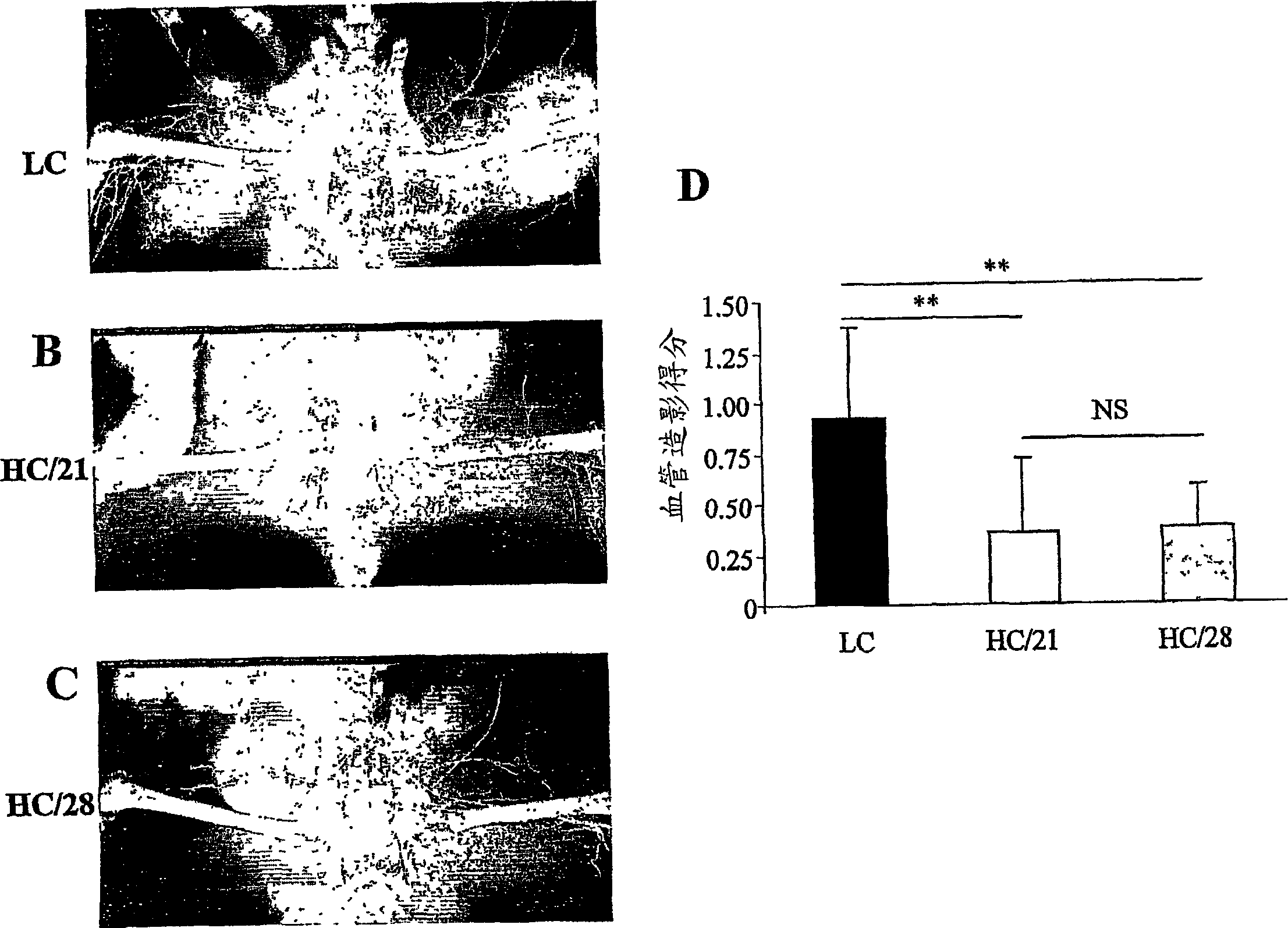
[0124] In Experiment 1, hamsters (n=37) were randomly divided into 3 groups ( figure 1 ). Low cholesterol group (LC) hamsters (n=13) were fed ad libitum with standard chow (cf. A04-C, UAR, Epinay-sur-Orge, France). For hamsters in two high cholesterol (HC) groups, 21 days (HC / 21) and 28 days after treatment (HC / 28) respectively (HC / 21: n=12; HC / 28: n=12) were given daily 20 g per animal of a cholesterol-enriched...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Example 2: Induction of lower extremity ischemia
[0126] After 35 days of LC or HC feeding, animals were susceptible to lower limb ischemia following surgical procedures as described below. Inducing lower extremity ischemia with N 2 O(0.81.min -1 ), O2 (0.41.min -1 ) and isoflurane (2%) gas anesthesia, following procedures used in other animal species. In a sterile surgical setting, make a longitudinal incision on the medial aspect of the right lower extremity, from the inguinal ligament to the point proximal to the patella. Through this incision, using surgical loops, the femoral artery is isolated and its main branches are coagulated. The femoral artery is completely cut off, its proximal end is the origin of the branch from the external iliac artery, and its distal end is where it divides into two branches, the saphenous artery and the popliteal artery (20). The incision was closed in a single layer with 4.0 silk suture.
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3: Gene transfer of lower extremity skeletal muscle
[0128] In Experiment 2, 14 days after the induction of ischemia, the saline group (n=5) or the plasmid group encoding NV1FGF (180 gag DNA, n=8) were blindly given 3 injections, 50 μL each time, and the injection sites were respectively in the ischemic area. Tibialis cranialis, adductors and quadriceps of the lower extremities.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com