Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
A non-volatile, storage device technology, applied in semiconductor devices, information storage, static memory, etc., can solve problems such as wrong writing, failure to flow writing current, and failure to consider changes in source potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
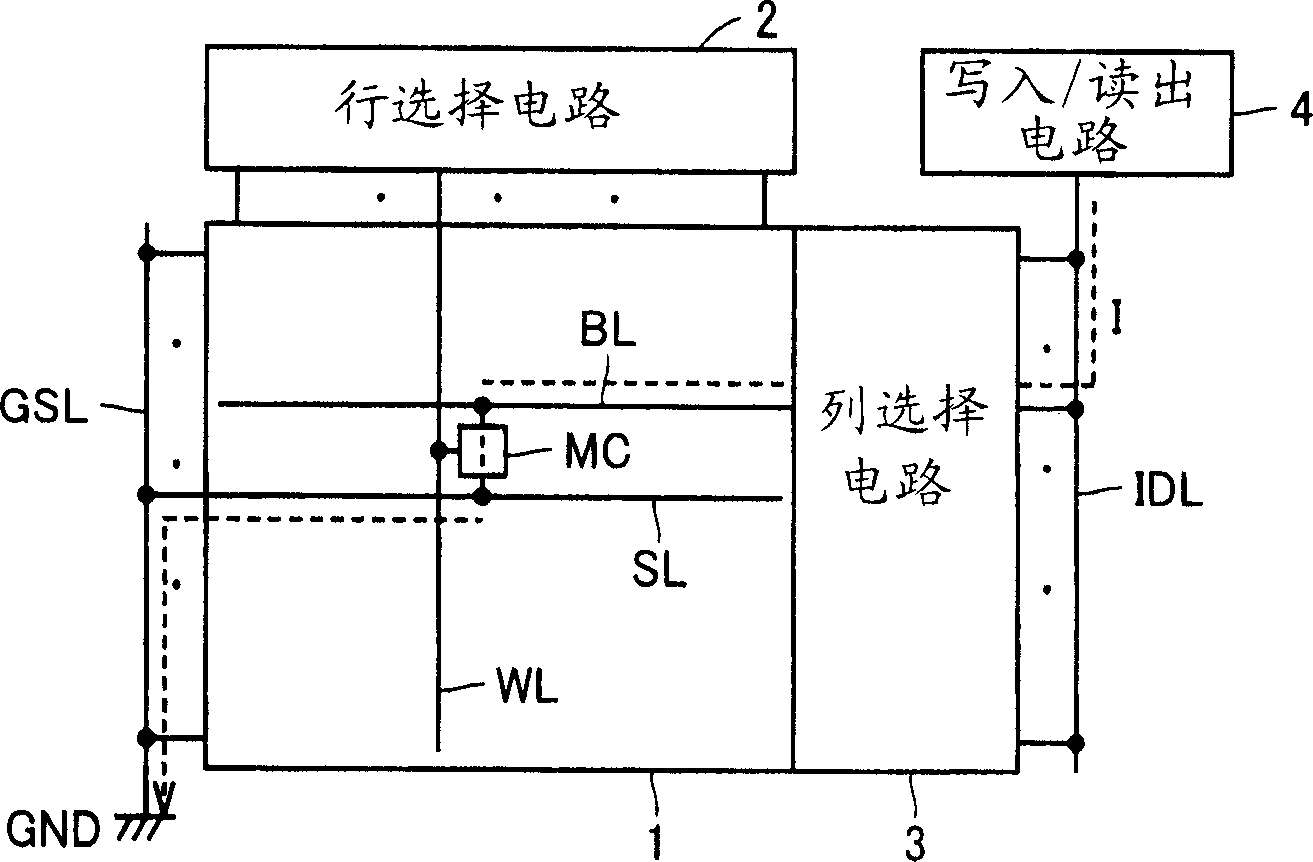
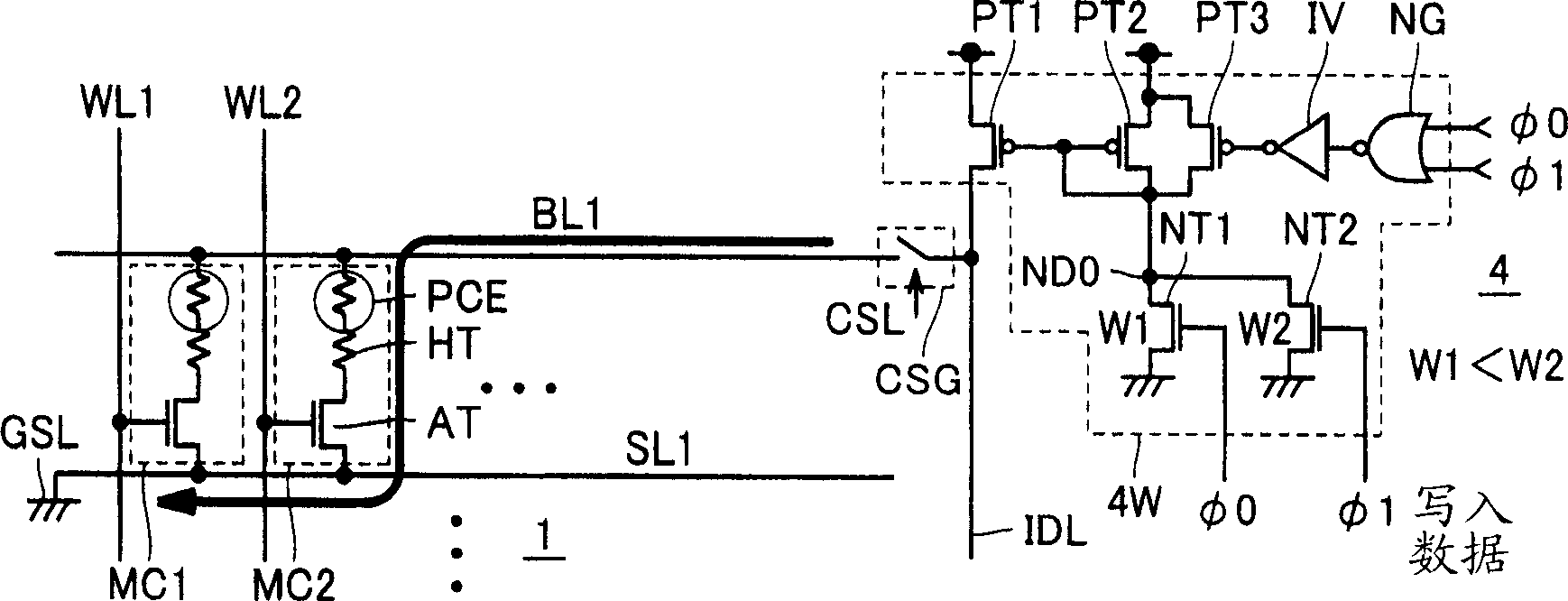
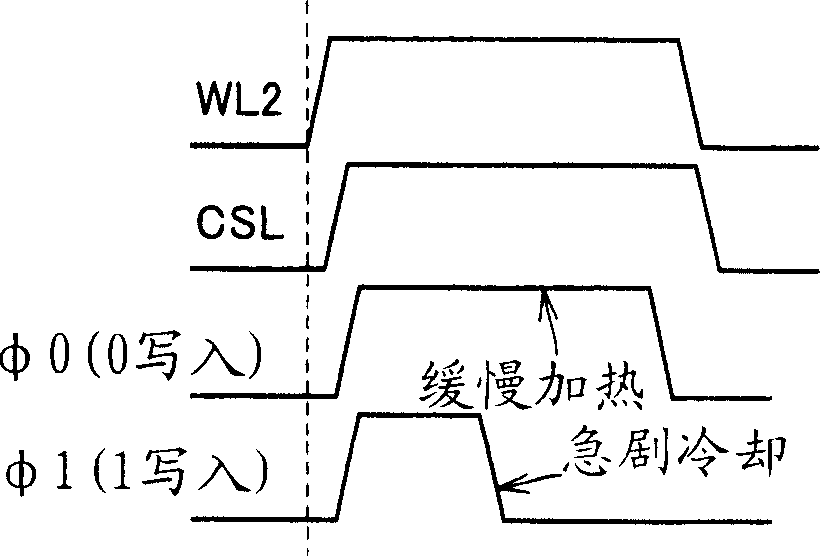
[0098] figure 1 It is a diagram schematically showing the configuration of main parts of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 1 In this example, the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array 1 in which memory cells MC are arranged in rows and columns. In memory cell array 1 , word lines WL are arranged corresponding to rows of memory cells MC, and bit lines BL are arranged corresponding to columns of memory cells. The source lines SL are arranged corresponding to the bit lines in parallel with the bit lines BL. This source line SL is coupled to a global source line GSL extending along the first side of the memory cell array 1 in a direction perpendicular to the bit line BL and the source line SL. The general source line GSL is coupled to the ground node (ground pad: reference potential source). The memory cell MC, whose structure will be described later, includes a phase-change mate...
change example 1
[0133] Figure 8 It is a diagram schematically showing the configuration of main parts of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device according to a modified example of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. in the Figure 8 In the shown nonvolatile semiconductor memory device, a sense amplifier 4S is connected in parallel with a variable current source 4W for supplying a write current to an internal data line IDL. Should Figure 8 Other structures of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device shown are the same as figure 1 and figure 2 The illustrated nonvolatile semiconductor memory devices have the same configuration, and the same reference numerals are assigned to corresponding parts, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0134] The sense amplifier 4S may be a voltage sense type sense amplifier, or may be a current sense type sense amplifier. In the case of the voltage read method, the voltage of the internal data line is compared with a reference voltag...
change example 2
[0143] Figure 10 It is a diagram showing a modified example of the memory cell layout according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Figure 10 Here, the bit line BL and the source line SL are respectively composed of a second metal wiring and a first metal wiring, and are arranged in parallel to each other. The first metal wiring and the second metal wiring represent metal wiring on the first layer and metal wiring on the second layer, respectively, in the multilayer wiring structure.
[0144] The word lines WL1-WL4 are arranged at predetermined intervals in a direction crossing the bit line BL. Parallel to the bit line BL, phase change material elements PCE1 and PCE2 are formed close to the word lines WL1 and WL3, respectively. These phase change material elements PCE1 and PCE2 are connected to the bit line BL via contacts CNT11 and CNT12, respectively.
[0145] Contacts CNT21 and CNT22 are formed at positions where contacts CNT11 and CNT12 are point-symmetrical wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com