Patents
Literature
531results about "Single device manufacturing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
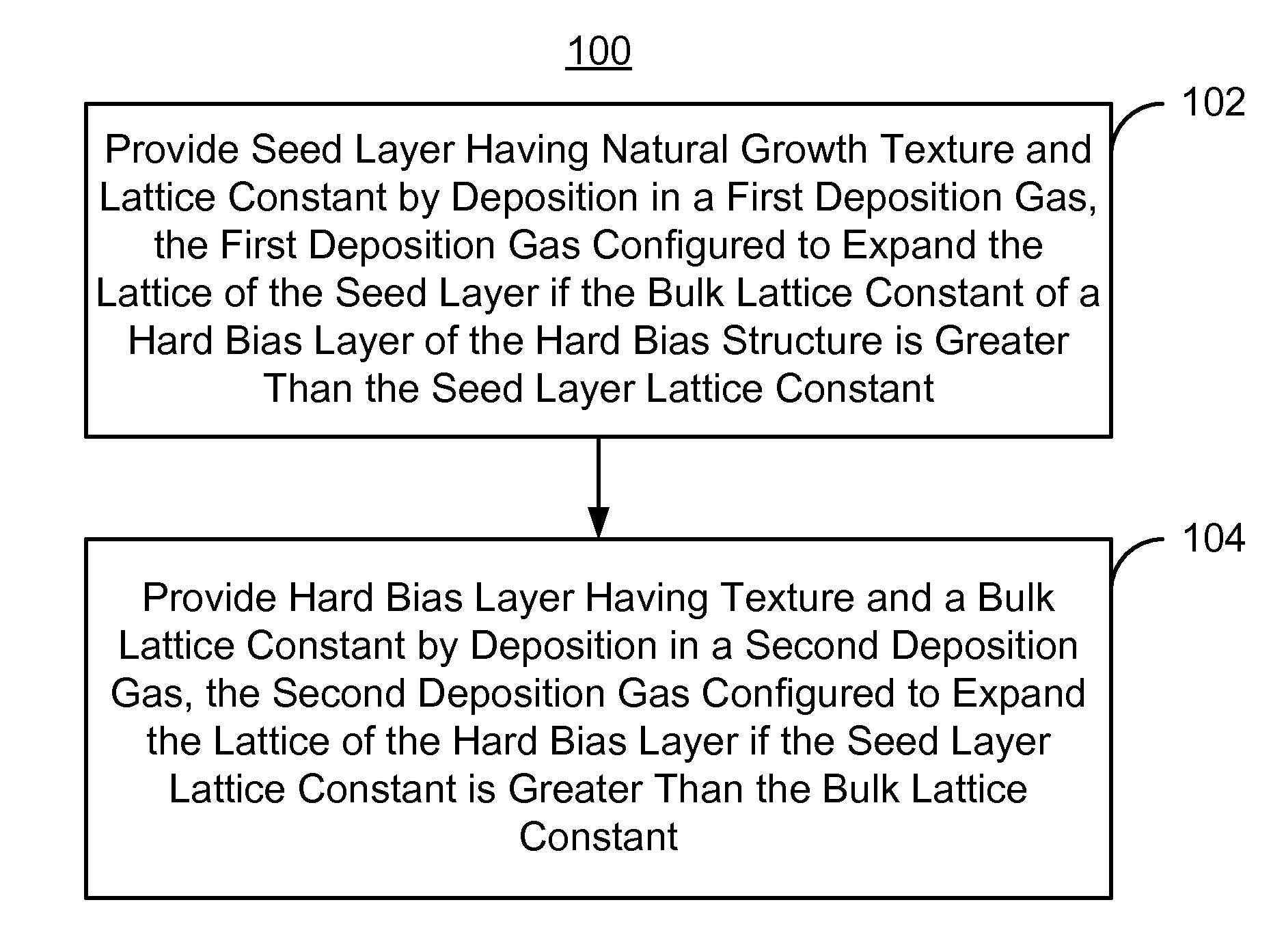
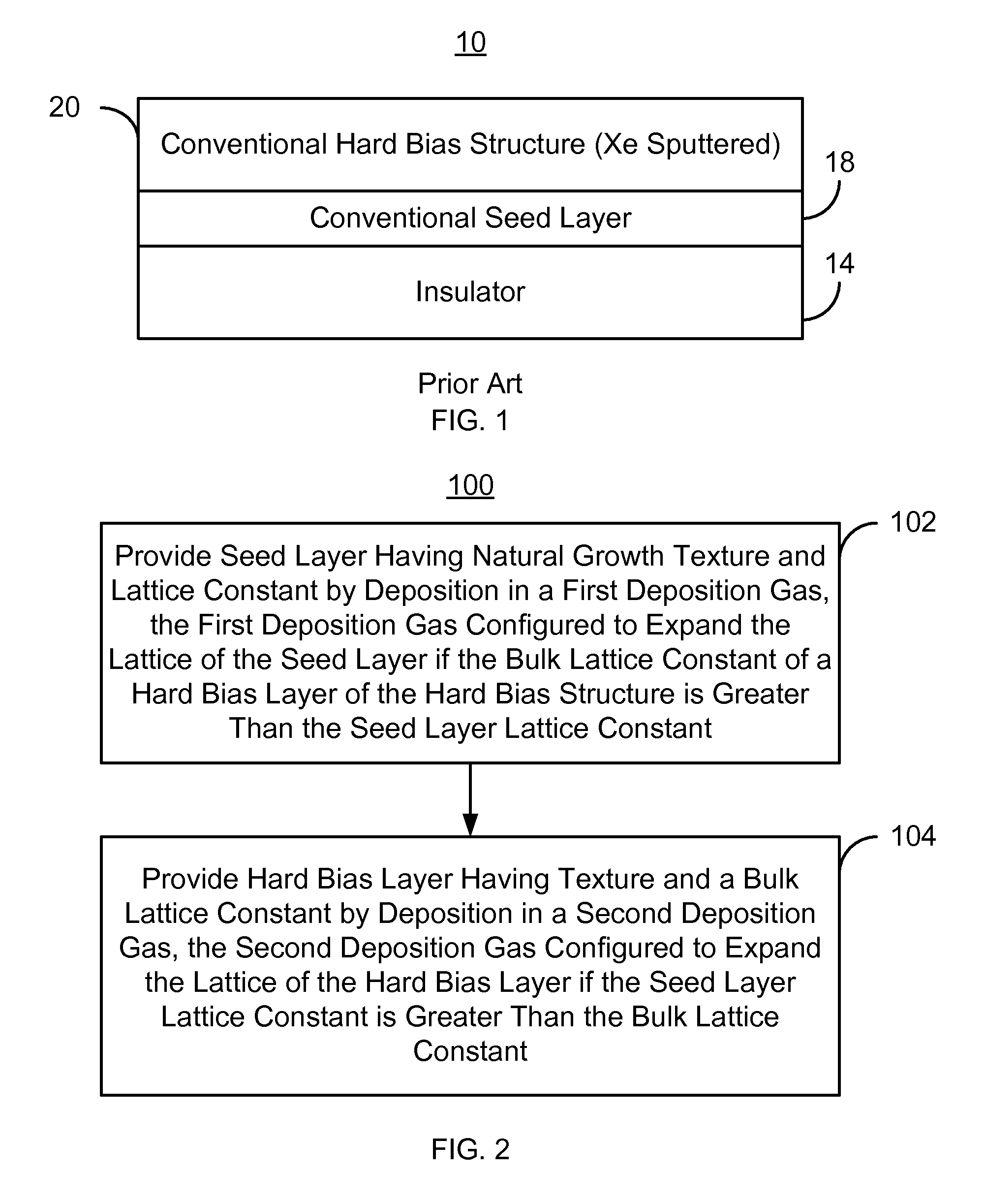
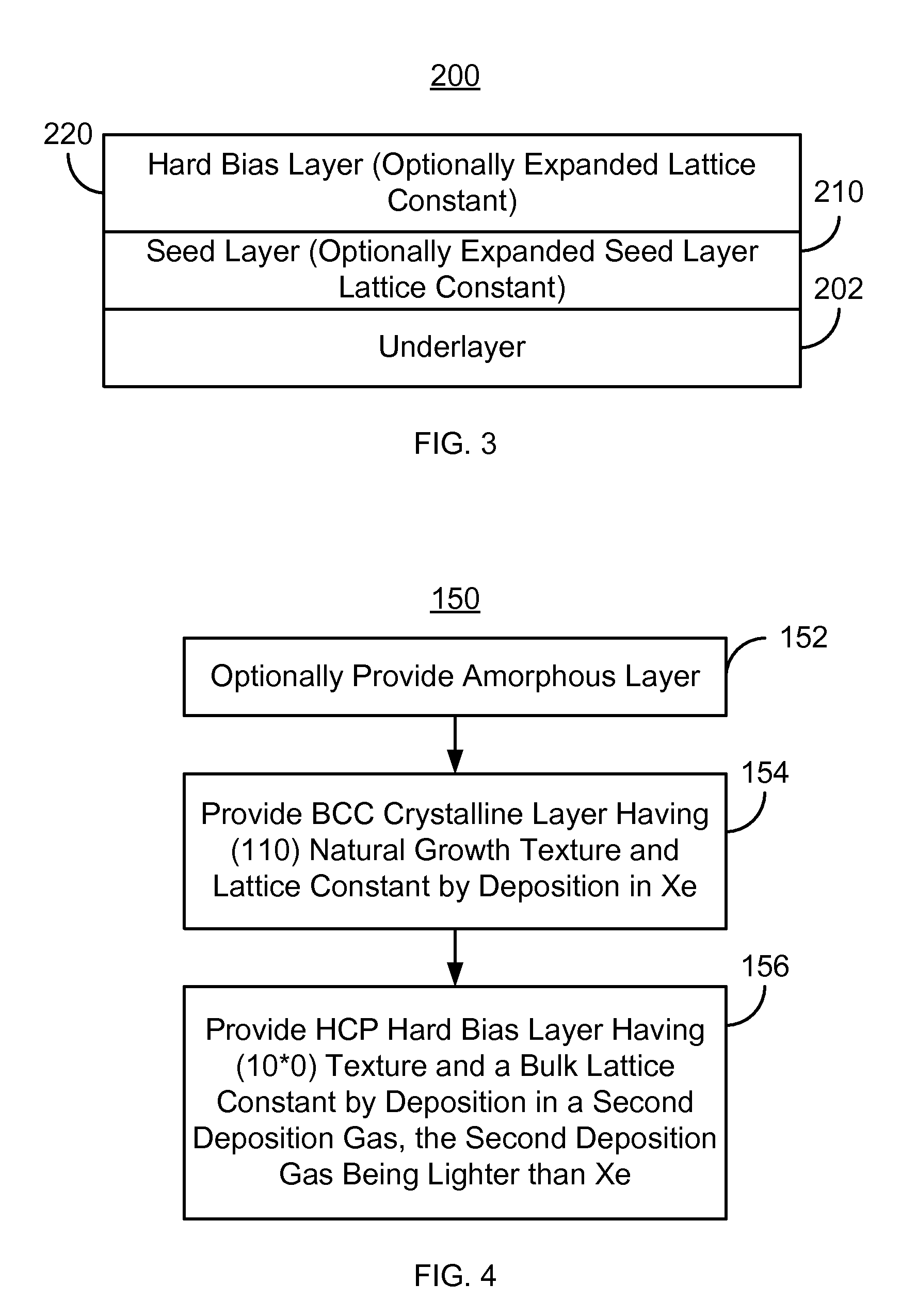
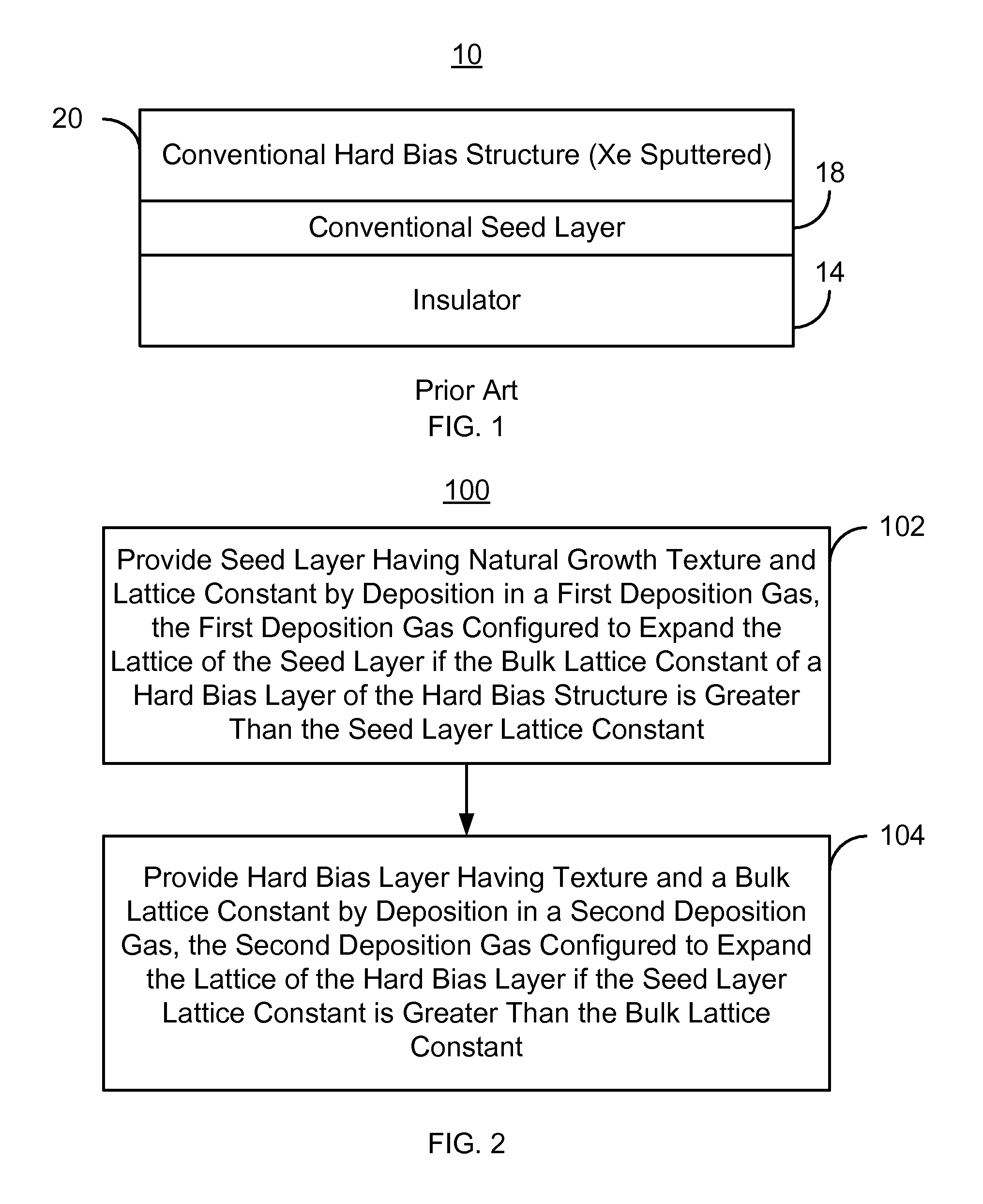
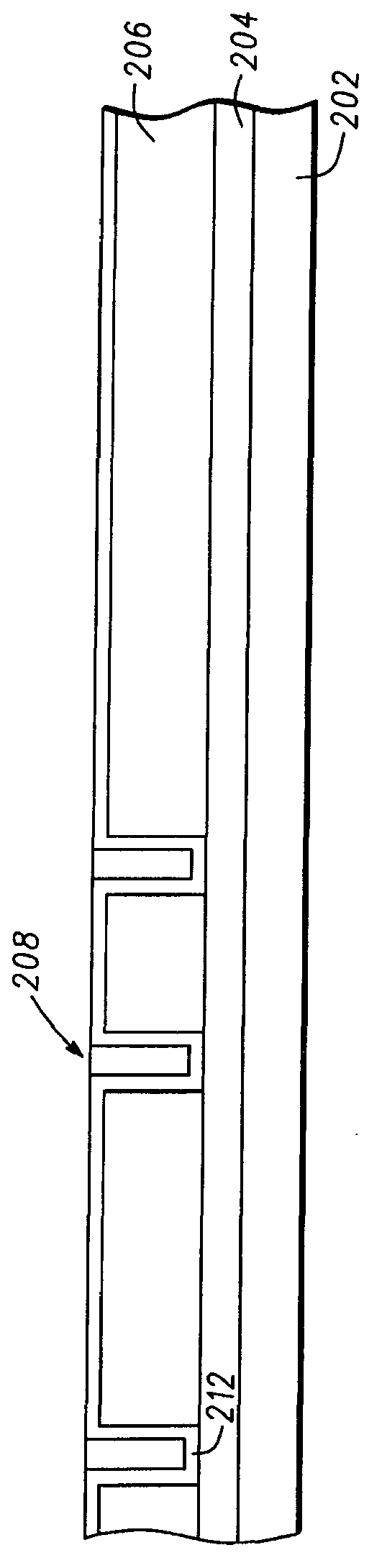
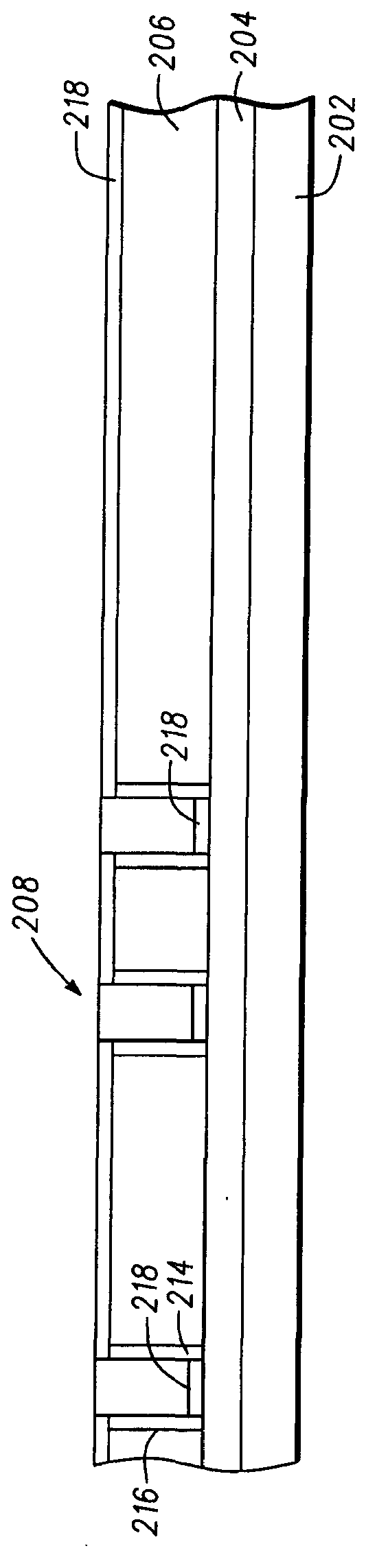
Method for providing an improved hard bias structure
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for providing an improved hard bias structure
ActiveUS8270126B1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsLattice constantEnvironmental geology
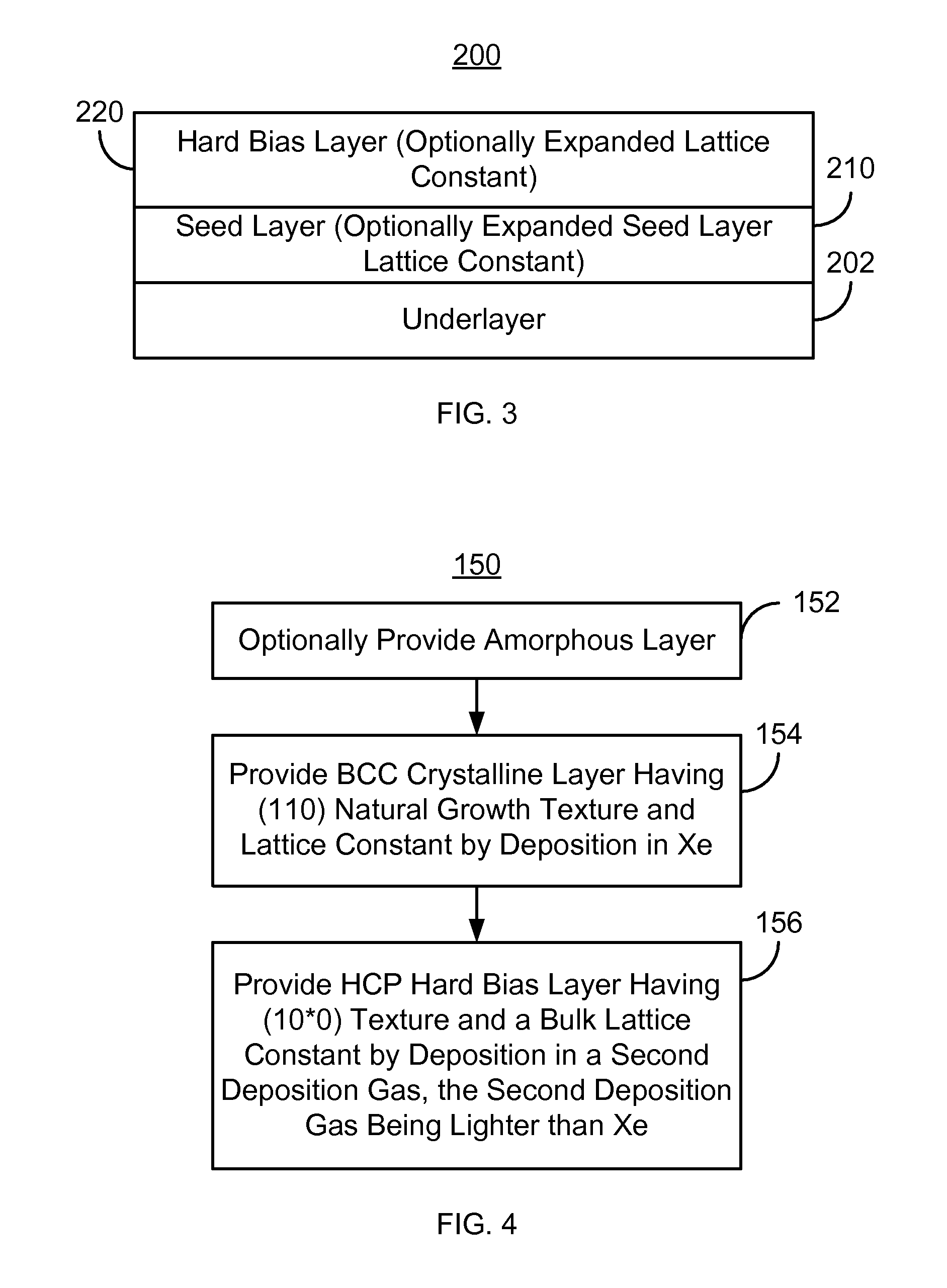
A method and system for providing a hard bias structure include providing a seed layer for a hard bias structure. The seed layer has a lattice constant and a natural growth texture. The method and system further include depositing the hard bias layer for the hard bias structure on the seed layer. The natural growth texture of the seed layer corresponds to a texture for the hard bias layer. The hard bias layer has a bulk lattice constant. Providing the seed layer includes forming a first plasma of a first deposition gas configured to expand the seed layer lattice constant if the bulk lattice constant is greater than the seed layer constant. Depositing the hard bias layer further includes forming a second plasma of a second deposition gas configured to expand the bulk lattice constant if the seed layer lattice constant is greater than the bulk lattice constant.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for providing a read sensor in a magnetic recording transducer using focused ion beam scan polishing
InactiveUS8480911B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineeringIon beam
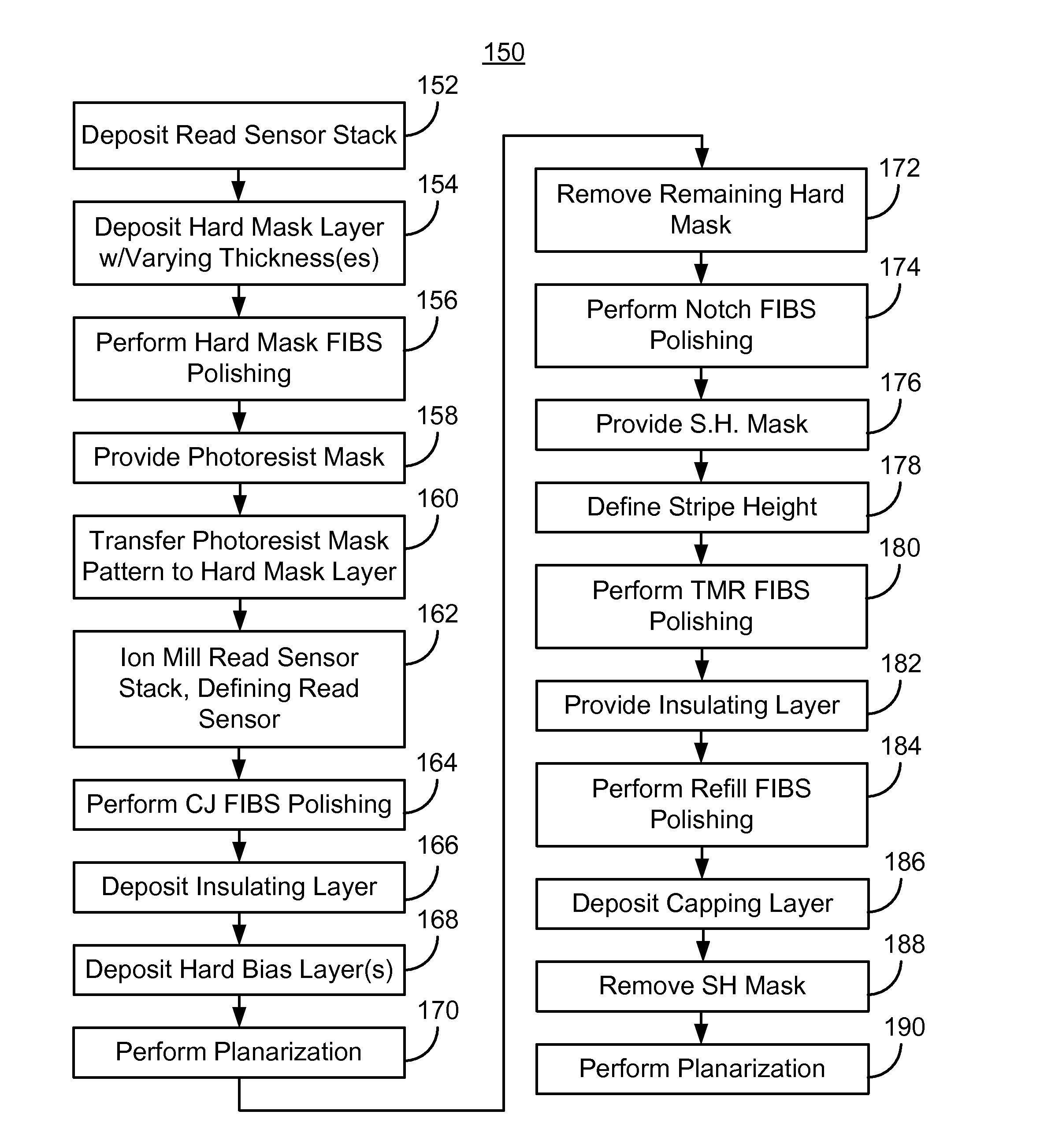
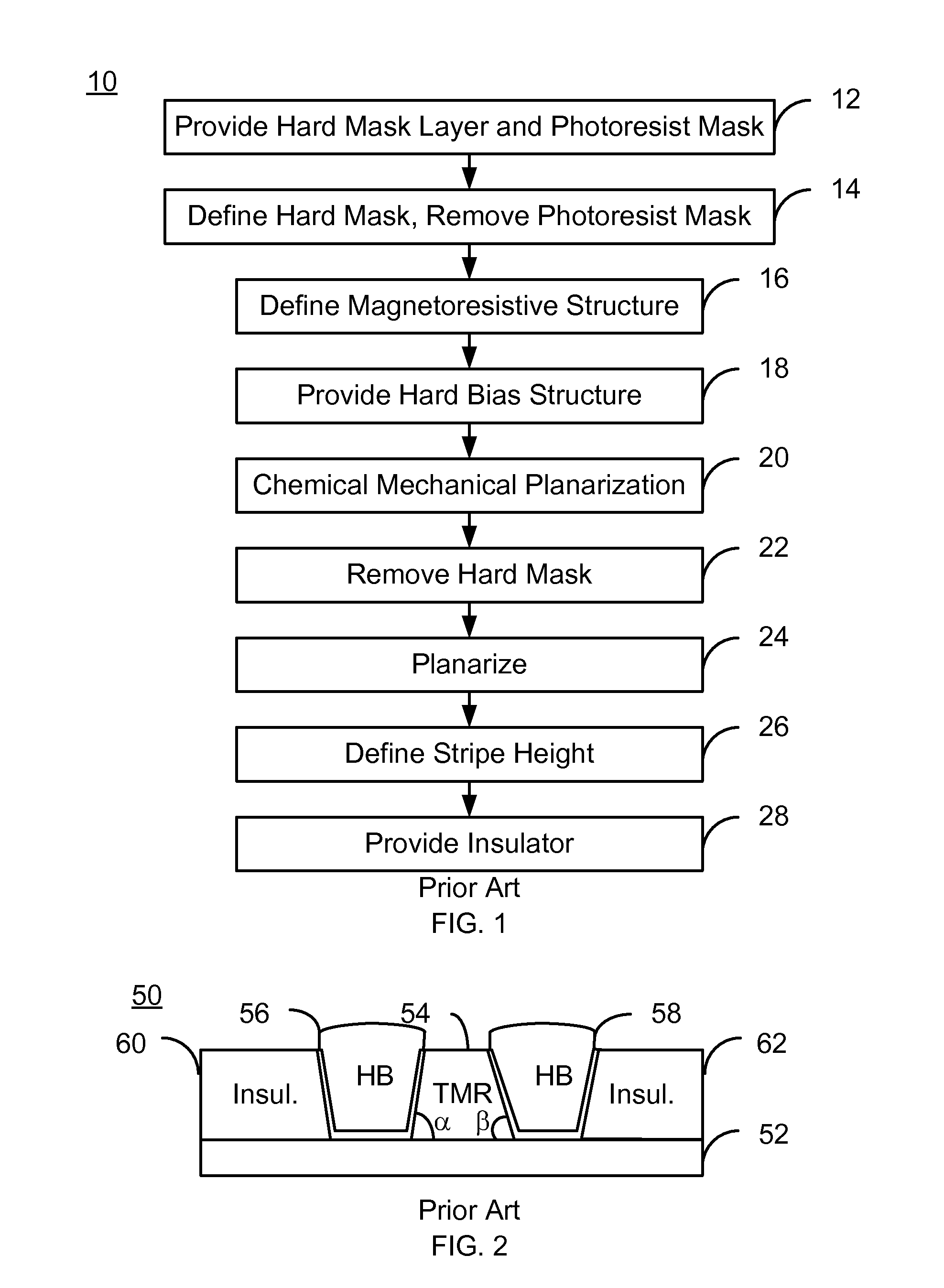
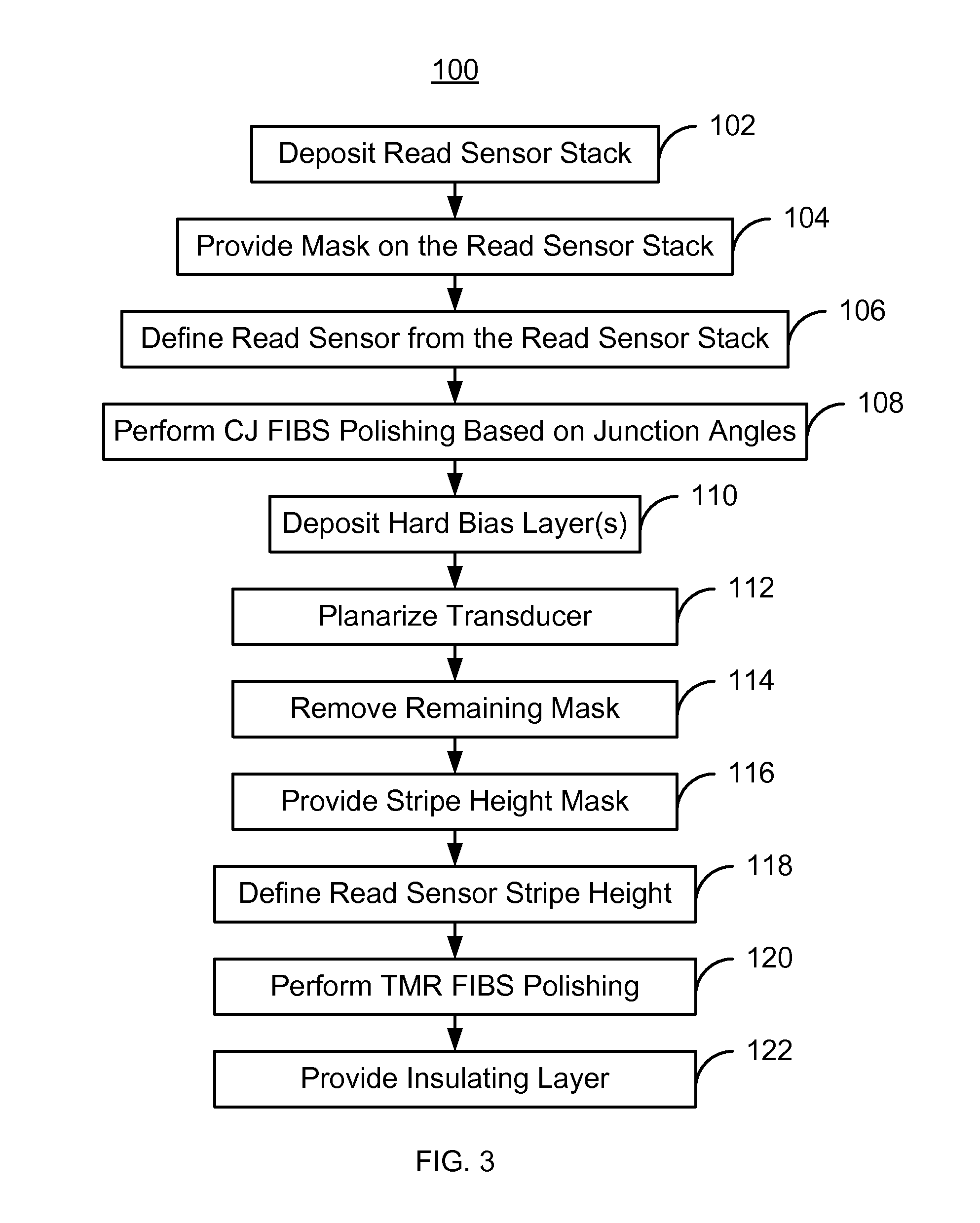
A read sensor for a read transducer is fabricated. The read transducer has field and device regions. A read sensor stack is deposited. A mask covering part of the stack corresponding to the read sensor is provided. The read sensor having inboard and outboard junction angles is defined from the stack in a track width direction. A critical junction (CJ) focused ion beam scan (FIBS) polishing that removes part of the read sensor based on the junction angles is performed. A hard bias structure is deposited and the transducer planarized. A remaining portion of the mask is removed. A stripe height mask covering part of the read sensor and hard bias structure in a stripe height direction is provided. The read sensor stripe height is defined. A tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) FIBS polishing that removes part of the stack in the field region is performed. An insulating layer is provided.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Integrated magnetoresistive sensor, in particular three-axis magnetoresistive sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20130299930A1NanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMagnetic flux
An integrated magnetoresistive device, where a substrate of semiconductor material is covered, on a first surface, by an insulating layer. A magnetoresistor of ferromagnetic material extends in the insulating layer and defines a sensitivity plane of the sensor. A concentrator of ferromagnetic material including at least one arm, extending in a transversal direction to the sensitivity plane and vertically offset to the magnetoresistor. In this way, magnetic flux lines directed perpendicularly to the sensitivity plane are concentrated and deflected so as to generate magnetic-field components directed in a parallel direction to the sensitivity plane.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Process integration of a single chip three axis magnetic field sensor
A semiconductor process integrates three bridge circuits, each include magnetoresistive sensors coupled as a Wheatstone bridge on a single chip to sense a magnetic field in three orthogonal directions. The process includes various deposition and etch steps forming the magnetoresistive sensors and a plurality of flux guides on one of the three bridge circuits for transferring a ''Z'' axis magnetic field onto sensors orientated in the XY plane.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Single-chip bridge-type magnetic field sensor and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses a design and manufacturing method for a single-chip magnetic sensor bridge. The sensor bridge comprises four magnetoresistive elements. The magnetization of the pinned layer of each of the four magnetoresistive elements is set in the same direction, but the magnetization directions of the free layers of the magnetoresistive elements on adjacent arms of the bridge are set at different angles with respect to the pinned layer magnetization direction. The absolute values of the angles of the magnetization directions of the free layers of all four magnetoresistive elements are the same with respect with their pinning layers. The disclosed magnetic biasing scheme enables the integration of a push-pull Wheatstone bridge magnetic field sensor on a single chip with better performance, lower cost, and easier manufacturability than conventional magnetoresistive sensor designs.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Integrated magnetic sensor for detecting horizontal magnetic fields and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveUS20110210722A1High sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic sensor packagingSemiconductor materialsConcentrator
The integrated magnetic sensor for detecting an external magnetic field, is formed by a body of semiconductor material having a surface; an insulating layer covering the body of semiconductor material; a magnetically sensitive region, for example a Hall cell, extending inside the body; and a concentrator of ferromagnetic material, extending on the Hall cell and having a planar portion extending parallel to the surface of the substrate on the insulating layer. The concentrator terminates with a tip protruding peripherally from, and transversely to, the planar portion toward the Hall cell. When the magnetically sensitive region is a sensing coil of a fluxgate sensor, it is formed on the substrate, embedded in the insulating layer, and the tip of the concentrator can reach as far as the sensing coil.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
RF shielding conduit in an MRI closure assembly
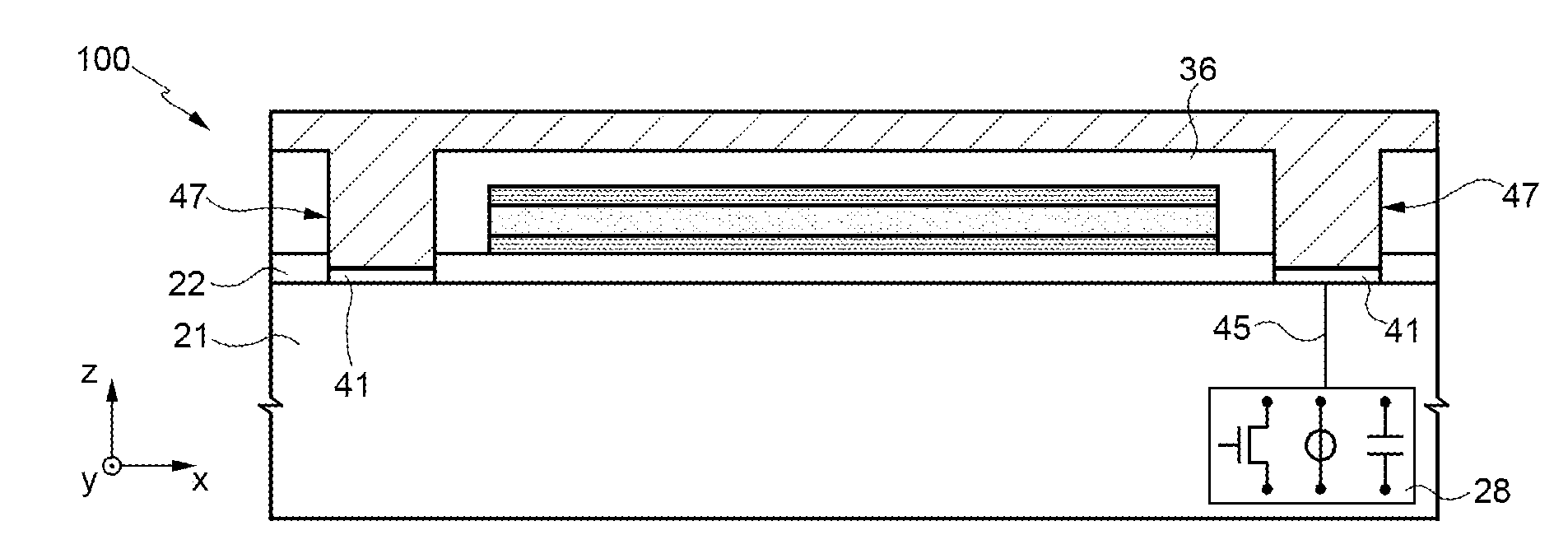
ActiveUS20150168519A1Magnetic/electric field screeningDiagnostic recording/measuringInterior spaceMedical equipment
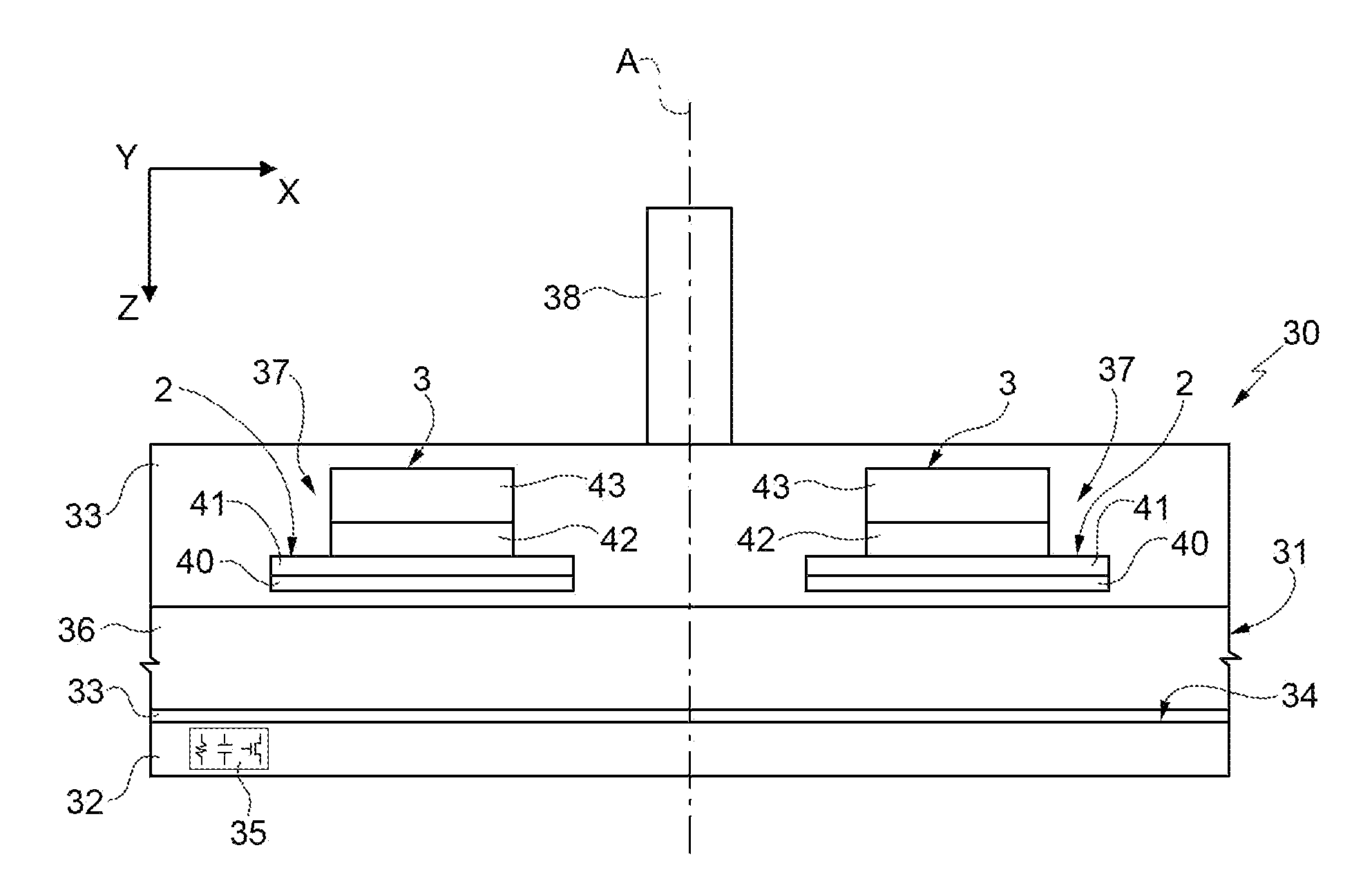
The present invention provides, in a magnetic resonance imaging device (MRD) comprising (a) a main longitudinal axis with a distal and proximal ends; (b) an open bore extended along the axis and terminated by an aperture located in the proximal end; and (c) a closure assembly which is shaped to fit the aperture; an RF shielding conduit (RFSC), having apertures shaped to permit passage of medical equipment tubing from the external environment of the MRD to inner space of the bore, affixed to the closure assembly, wherein the conduit is characterized by a length (l) and width (w), l:w ratio is greater than a predefined value n, thereby providing RF shielding.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Inspection apparatus and inspection method of magnetic sensor
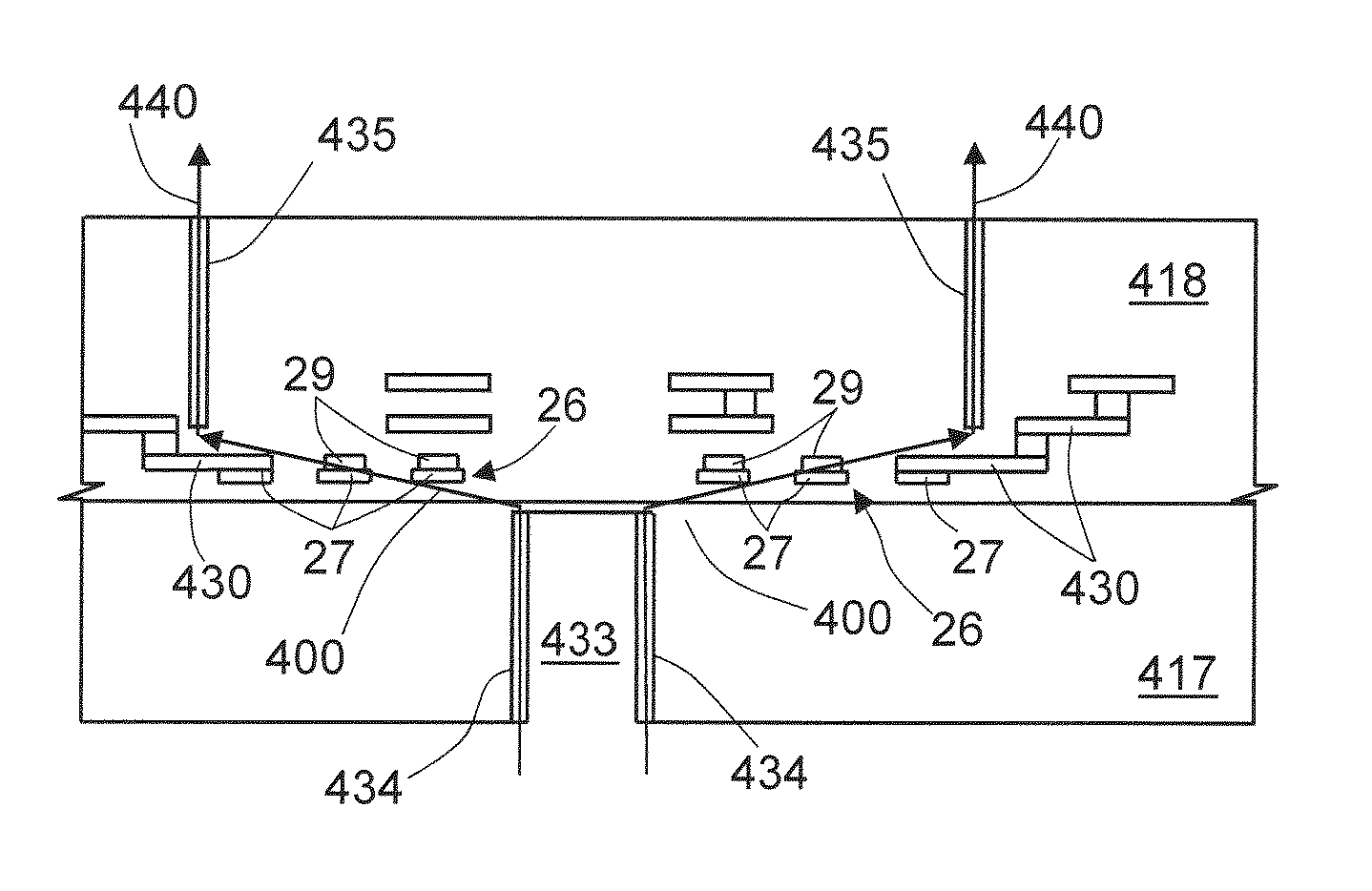
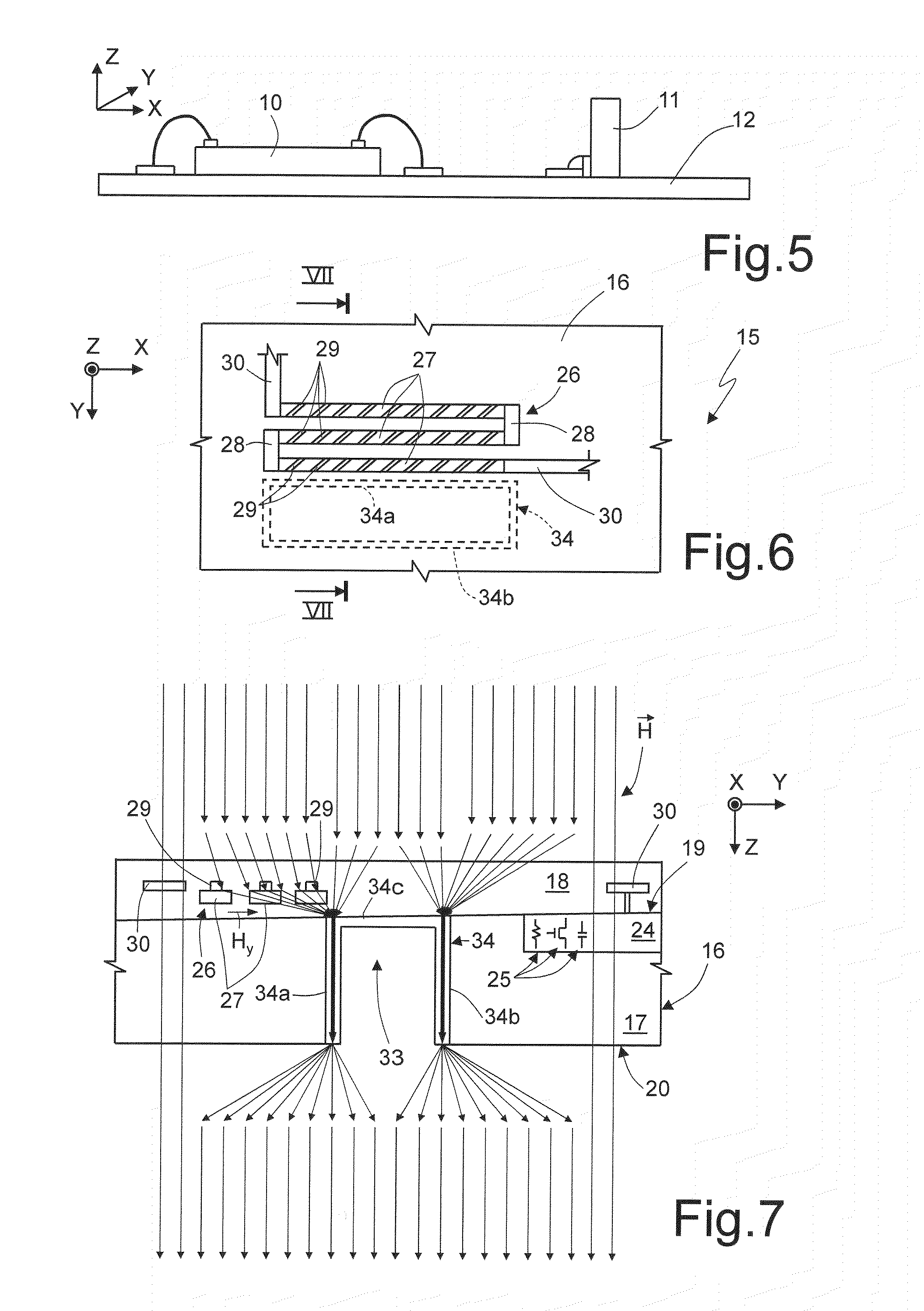
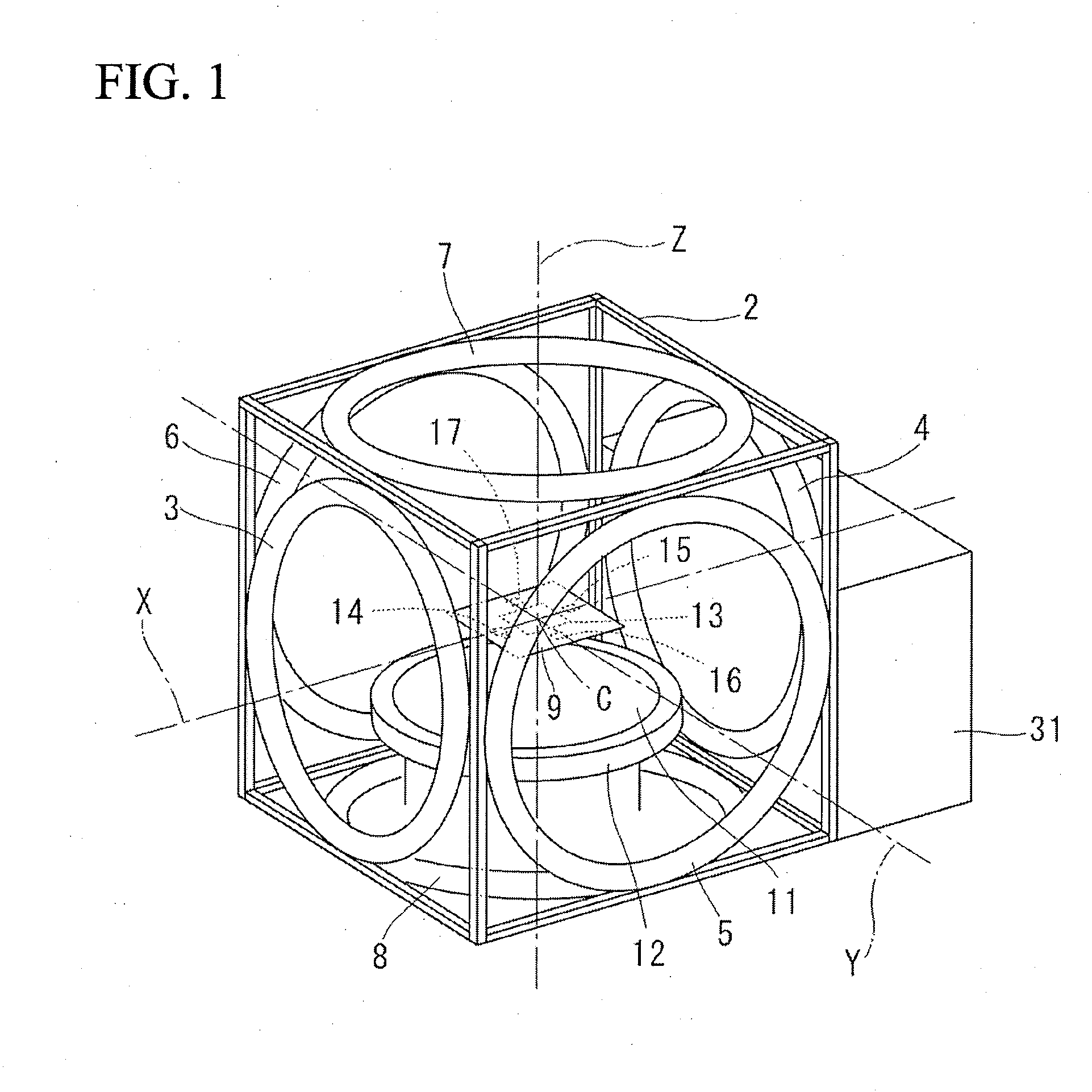
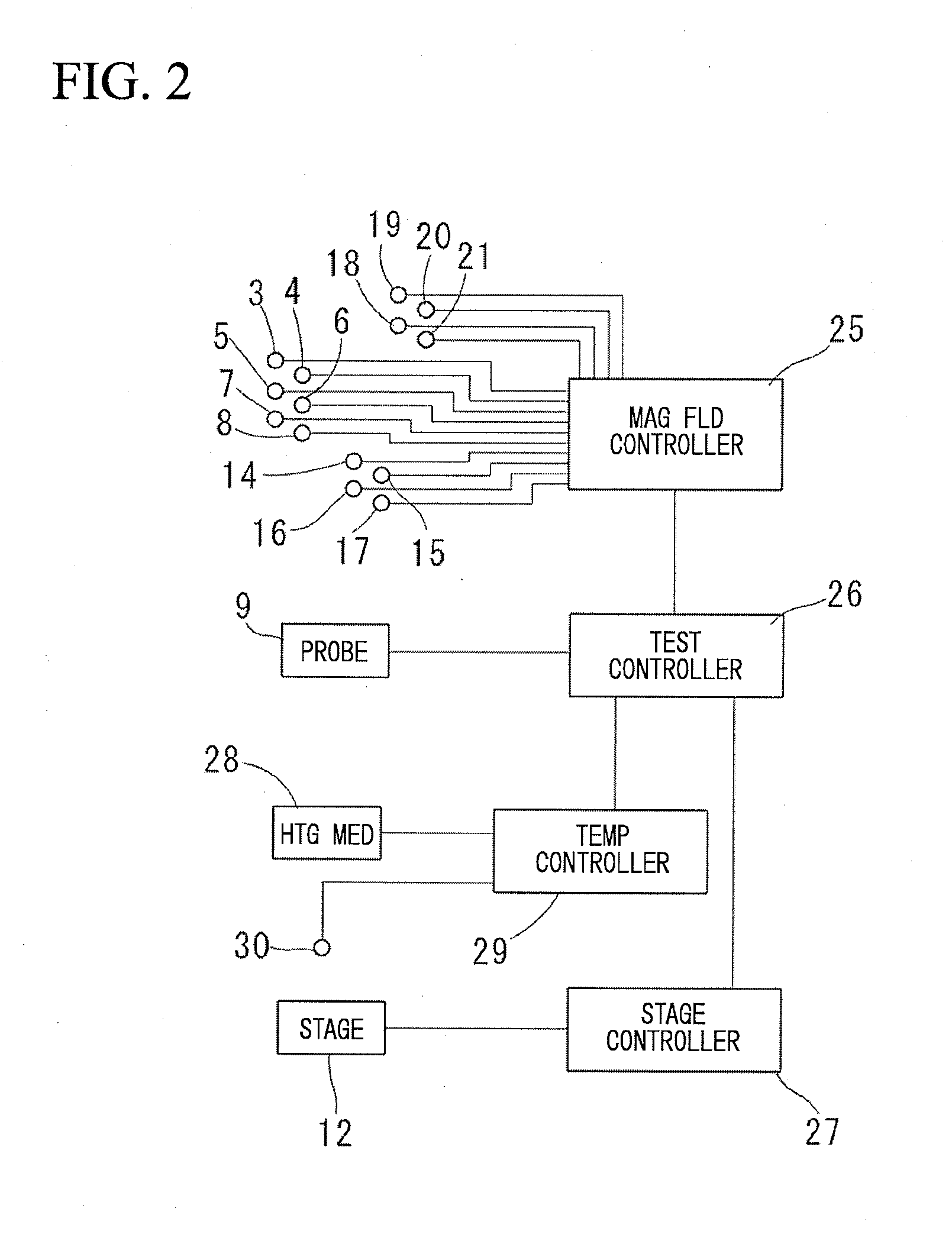
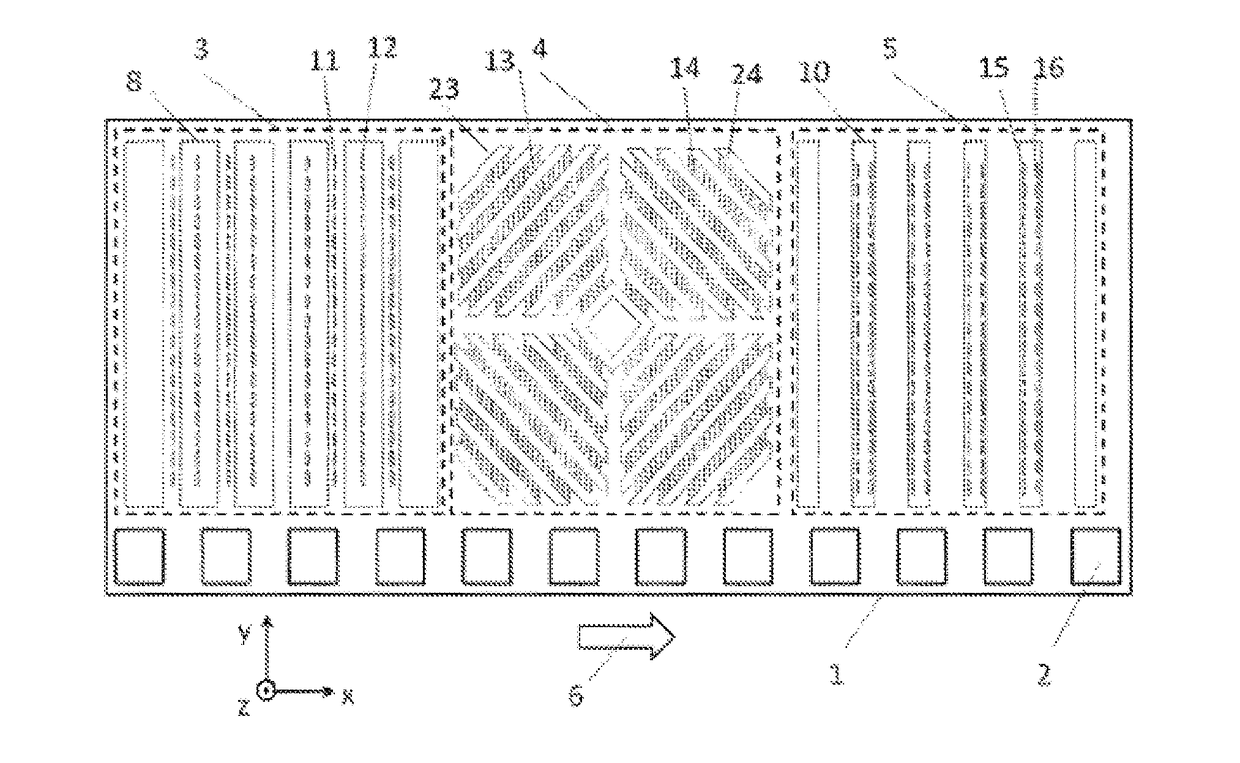
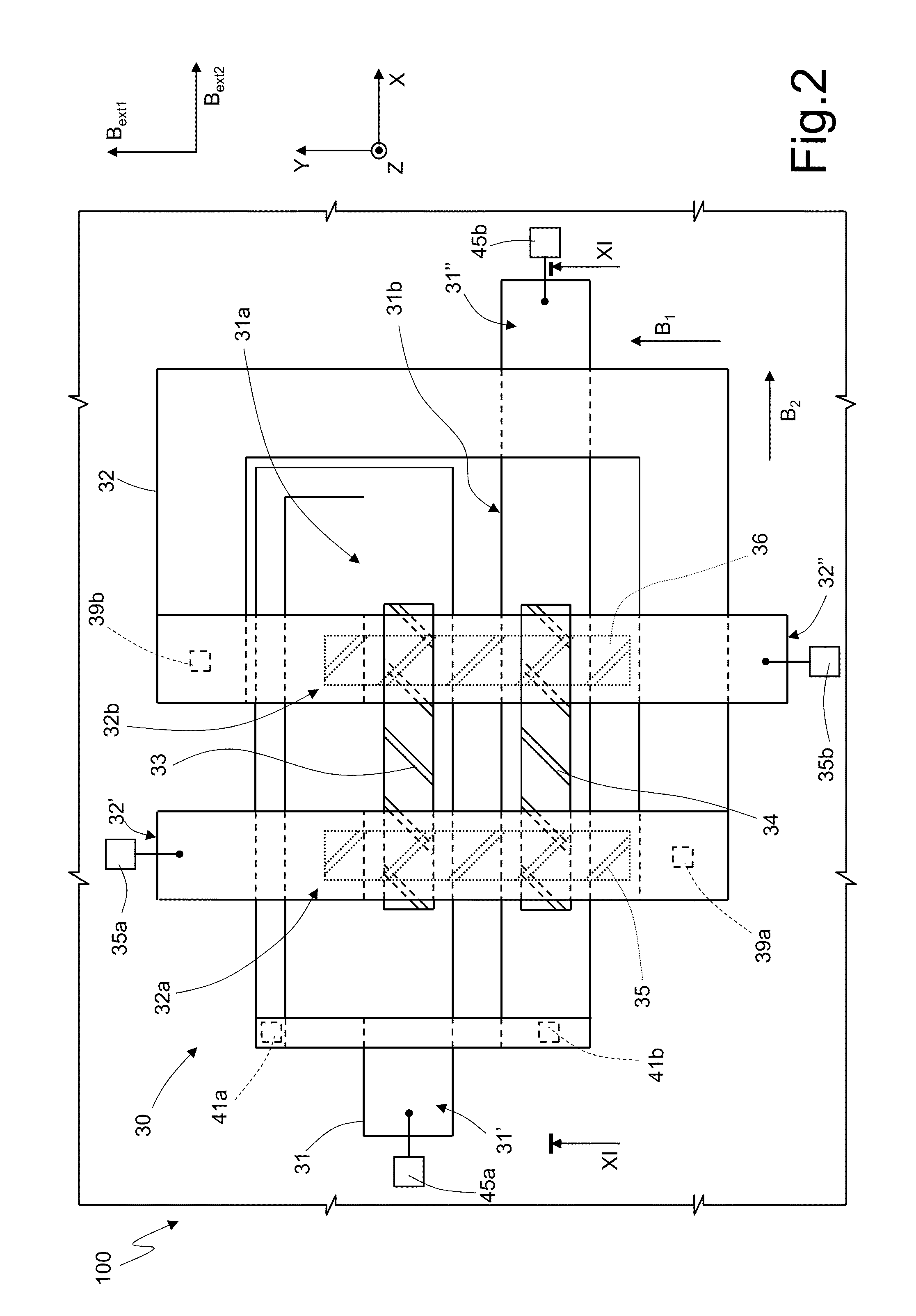
InactiveUS20130038321A1Easy to checkGenerate accuratelyElectrical measurementsSingle device manufacturingProbe cardHorizontal and vertical
A magnetic sensor inspection apparatus has a rectangular frame including a stage, a probe card, and a plurality of magnetic field generating coils. A wafer-like array of magnetic sensors is mounted on the stage, which is movable in horizontal and vertical directions. The probe card includes a plurality of probes which are brought into contact with a plurality of magnetic sensors encompassed in a measurement area. The magnetic field generating coils are driven to generate a magnetic field toward the stage. A plurality of magnetic field environment measuring sensors is arranged in the peripheral portion of the probe card surrounding the probes. A magnetic field controller controls magnetic fields generated by the magnetic field generating coils based on the measurement result of the magnetic field environment measuring sensors. Thus, it is possible to concurrently inspect a wafer-like array of magnetic sensors with the probe card.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Integrated dual axis fluxgate sensor using double deposition of magnetic material
ActiveUS20150338474A1Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleSolid-state devicesDual axisCondensed matter physics
A method of fabricating fluxgate devices to measure the magnetic field in two orthogonal, in plane directions, by using a composite-anisotropic magnetic core structure.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Triaxial magnetic field sensor
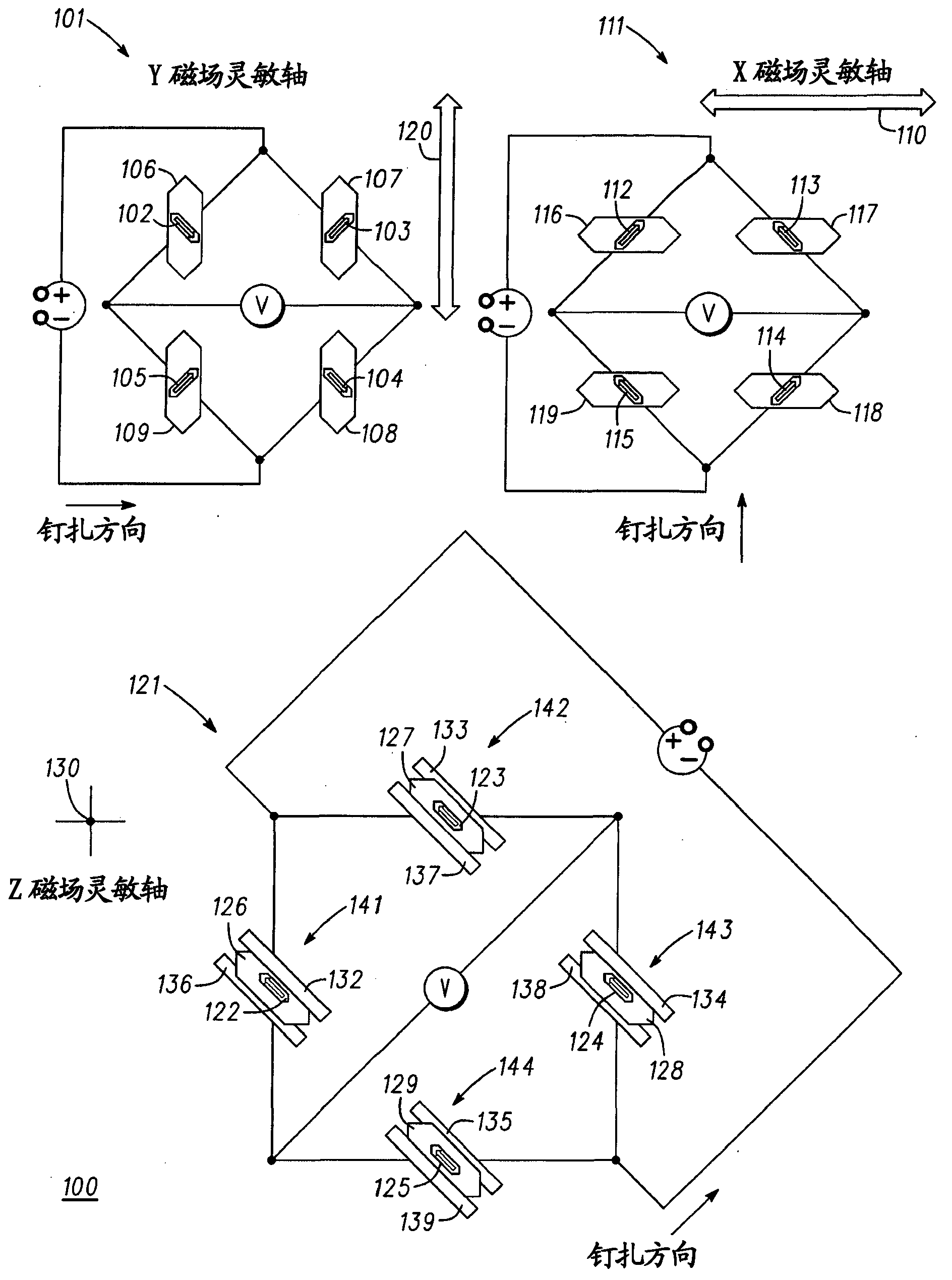
ActiveUS20140247042A1Easy to integrateReduce magnetic noiseMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectrodynamic magnetometersThermal stabilitySingle chip
The present invention discloses a triaxial magnetoresistive sensor. It comprises a substrate integrated with a biaxial magnetic field sensor, a Z-axis sensor that has a sensing direction along Z-axis perpendicular to the two axes of the biaxial magnetic field sensor, and an ASIC. The biaxial magnetic field sensor comprises an X-axis bridge sensor and a Y-axis bridge sensor. The Z-axis sensor and the two-axis sensor are electrically interconnected with the ASIC. A single-chip implementation of the triaxial magnetic field sensor comprises a substrate, onto which a triaxial magnetic field sensor and an ASIC are stacked. The triaxial magnetic field sensor comprises an X-axis bridge sensor, a Y-axis bridge sensor, and a Z-axis bridge sensor. The above design provides a highly integrated sensor with high sensitivity, low power consumption, good linearity, wide dynamic range, excellent thermal stability, and low magnetic noise.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Extended signal paths in microfabricated sensors
ActiveUS20180128885A1Apparatus using atomic clocksMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesSignal detectorPhysics
A microfabricated sensor includes a first reflector and a second reflector in a sensor cell, separated by a cavity path segment through a sensor cavity in the sensor cell. A signal window is part of the sensor cell. A signal emitter and a signal detector are disposed outside of the sensor cavity. The signal emitter is separated from the first reflector by an emitter path segment which extends through the signal window. The second reflector is separated from the second reflector by a detector path segment which extends through the signal window.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for fabrication of high aspect ratio trenches and formation of nanoscale features therefrom
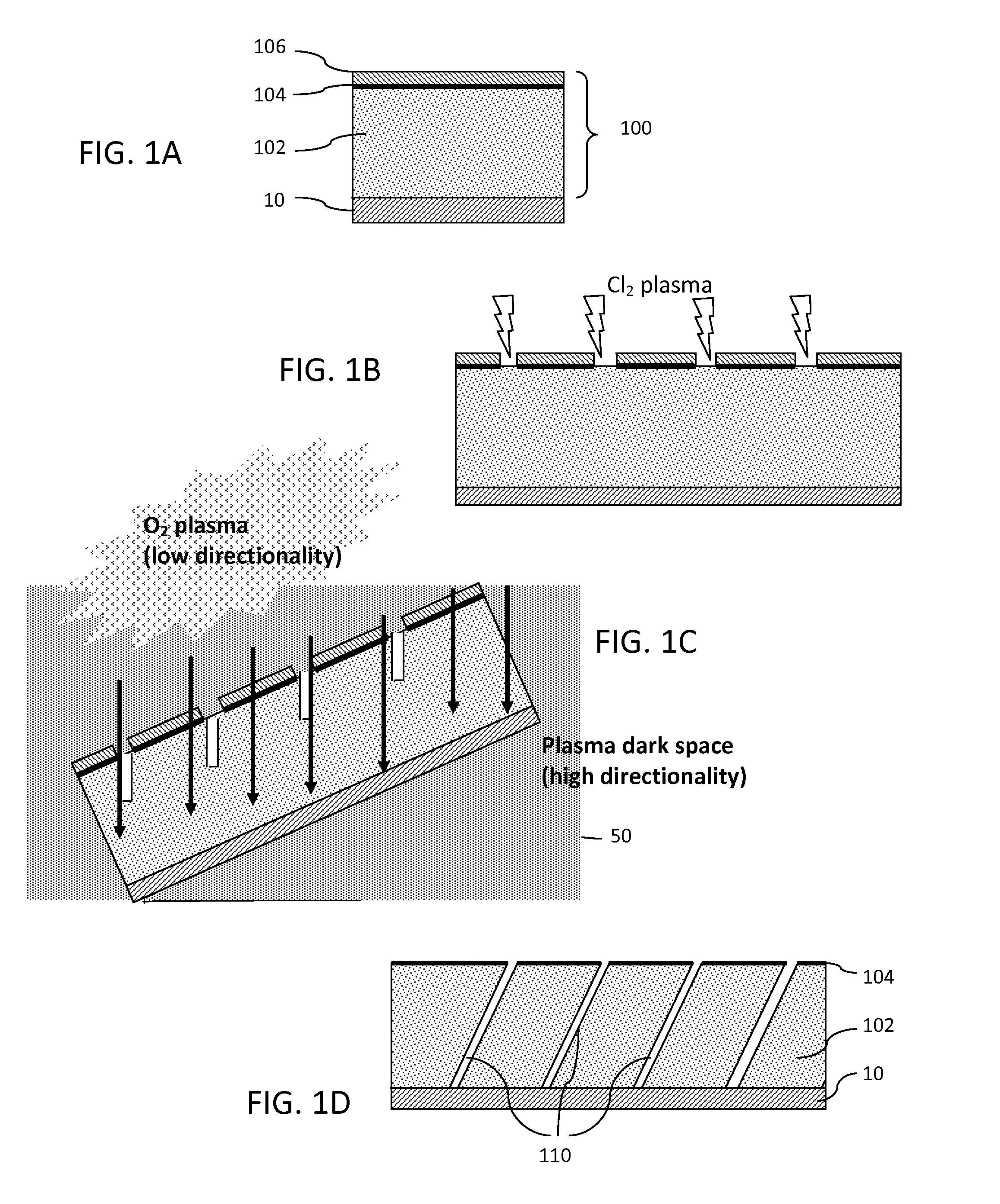
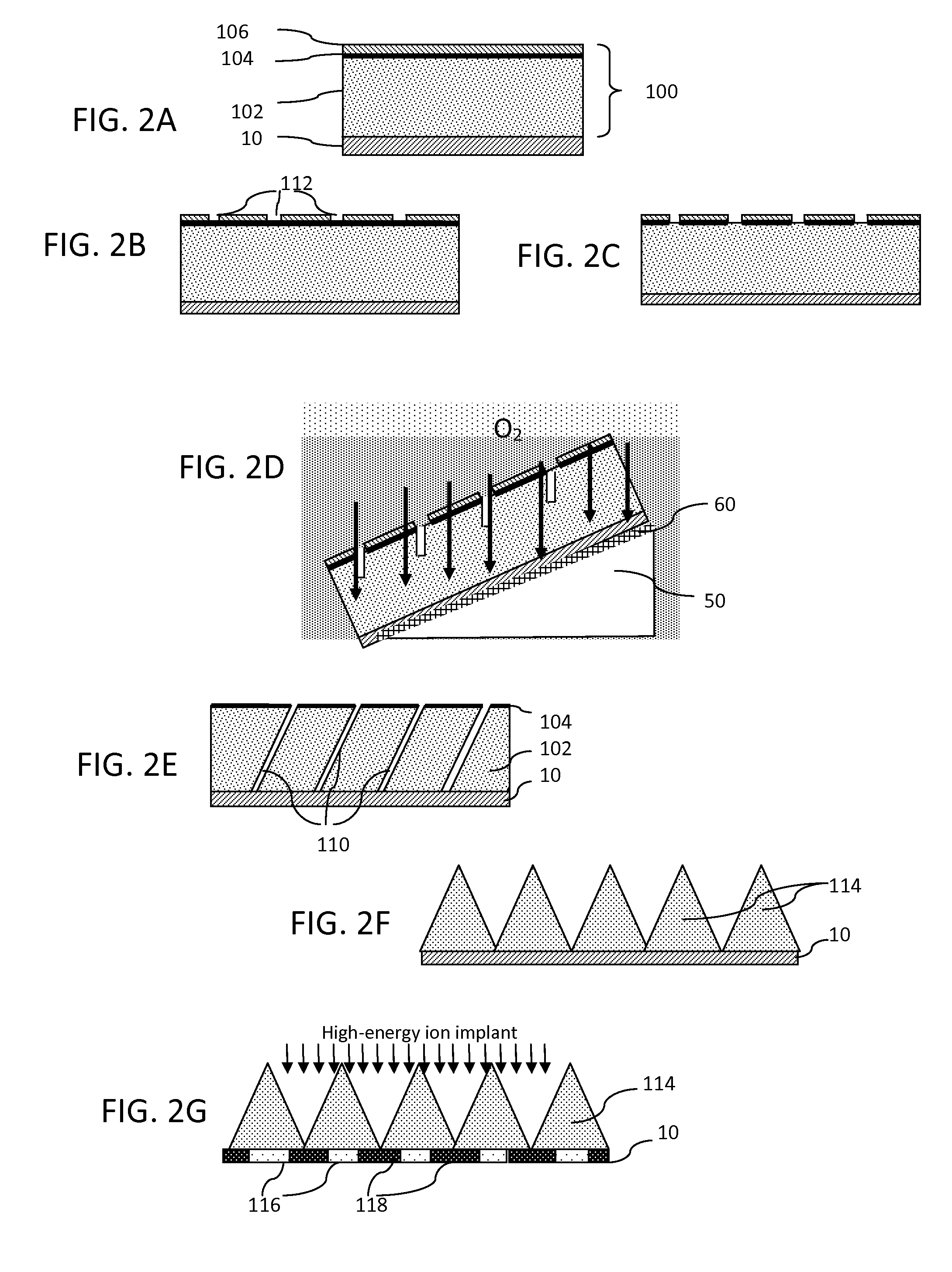
ActiveUS20150118604A1Simple structureHighly directional mean free pathsElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusHigh selectivityAtomic physics
A process for forming trenches in a target material includes forming a masking layer onto the target material, where the masking layer comprises a material having high selectivity to a plasma etch gas adapted for etching the target material. A pattern is formed in the masking layer to expose portions of the target material and the sample is placed on an angle mount at a pre-determined angle relative to a cathode of a reactive ion etcher so that the target material is within a plasma dark space of the plasma etch gas. Ballistic ions within the plasma dark space form a trench structure within the target material. The process may further include repeating the steps of positioning the sample and etching the exposed portions of the target material with the substrate at a dif ferent angle to define a triangular structure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
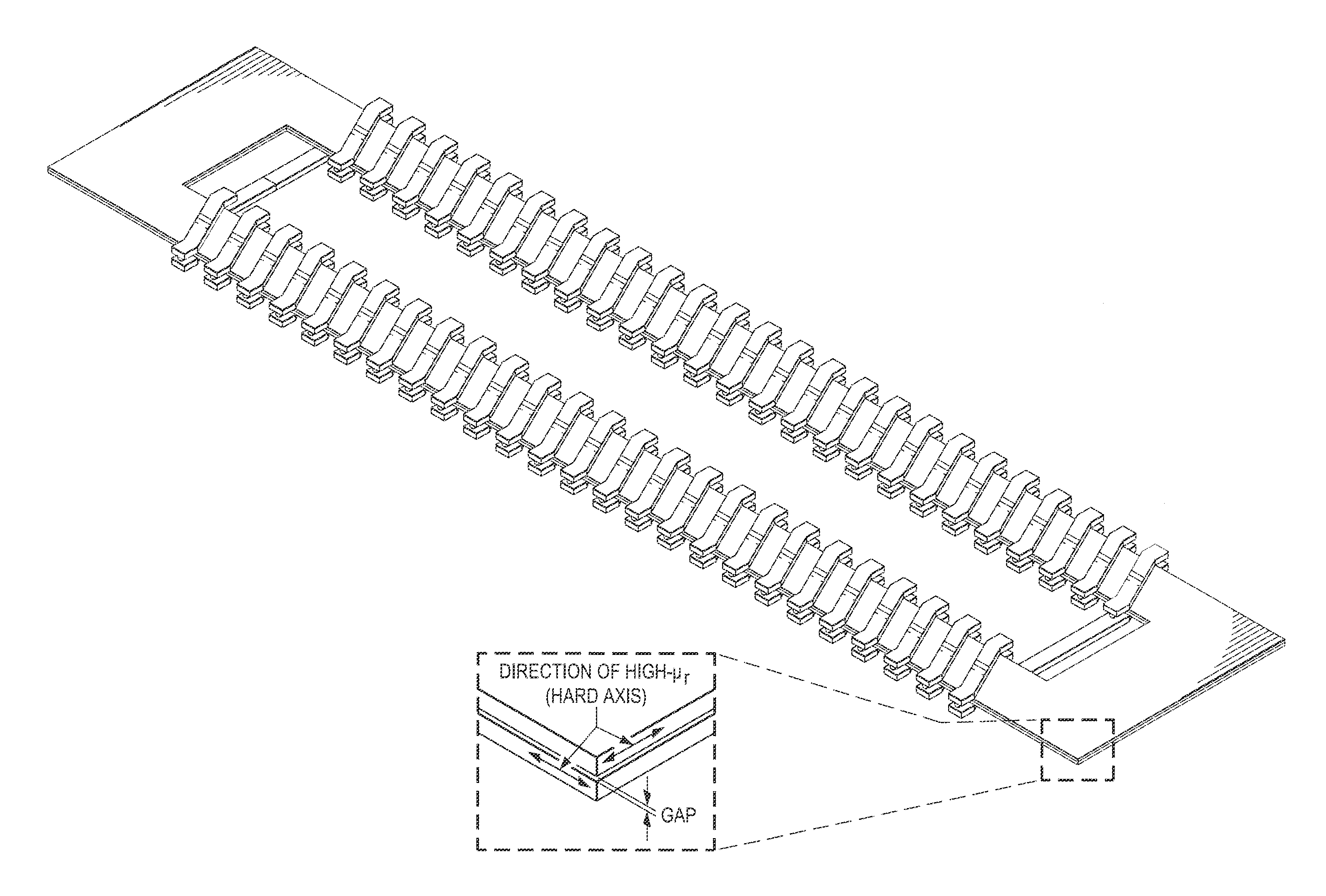
GMR biosensor with enhanced sensitivity
ActiveUS20080032423A1Adverse hysteresis effectPointing stableNanomagnetismBiological particle analysisHysteresisSensor array
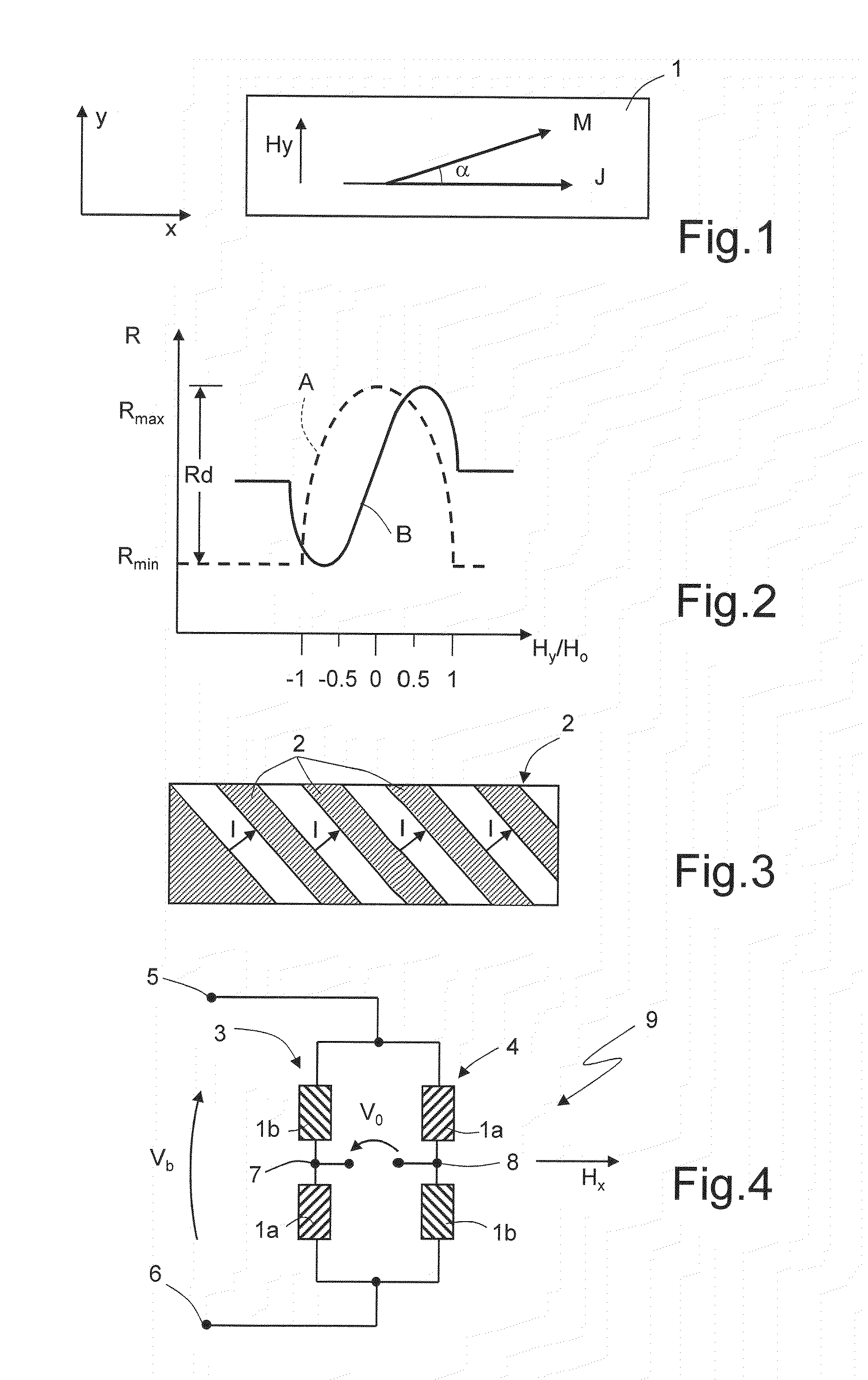
A sensor array comprising a series connection of parallel GMR sensor stripes provides a sensitive mechanism for detecting the presence of magnetized particles bonded to biological molecules that are affixed to a substrate. The adverse effect of hysteresis on the maintenance of a stable bias point for the magnetic moment of the sensor free layer is eliminated by a combination of biasing the sensor along its longitudinal direction rather than the usual transverse direction and by using the overcoat stress and magnetostriction of magnetic layers to create a compensatory transverse magnetic anisotropy. By making the spaces between the stripes narrower than the dimension of the magnetized particle and by making the width of the stripes equal to the dimension of the particle, the sensitivity of the sensor array is enhanced.
Owner:APPLIED SPINTRONICS +1
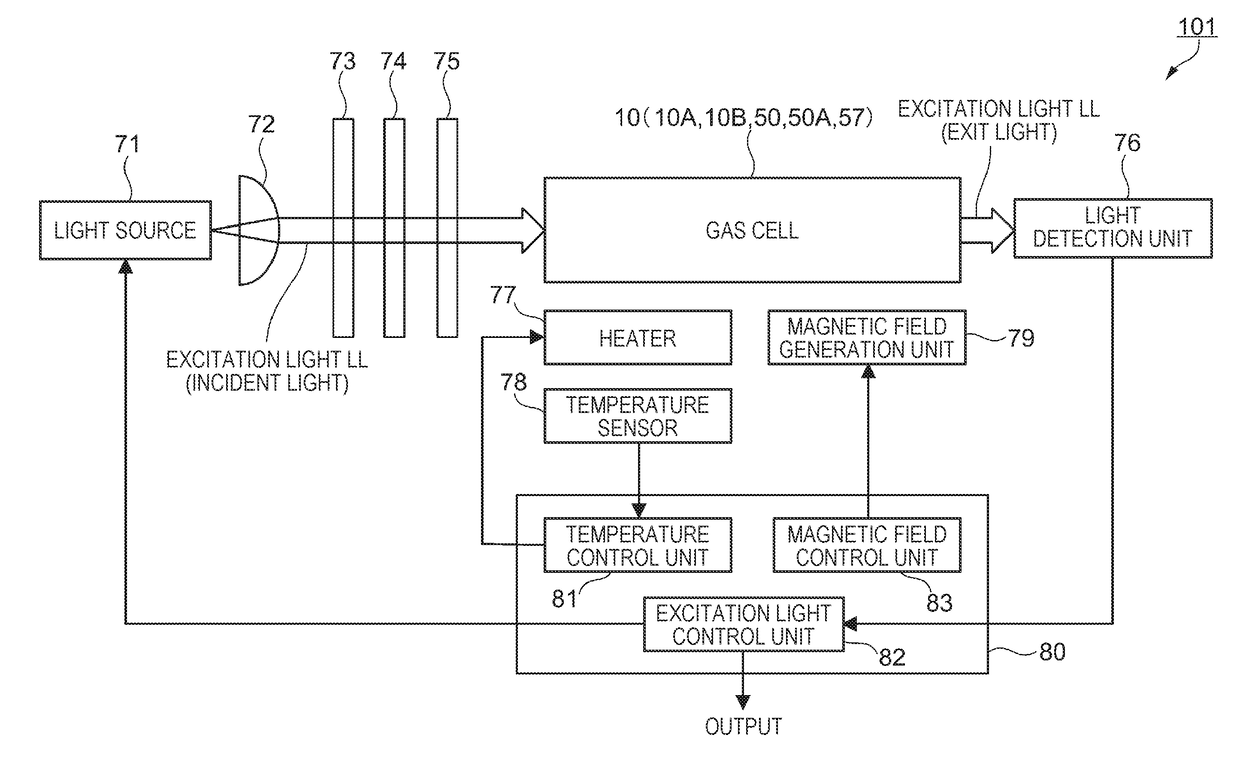
Magnetism measuring device, gas cell, manufacturing method of magnetism measuring device, and manufacturing method of gas cell
InactiveUS20170199251A1Lower manufacturing yieldReduce the numberMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesSingle device manufacturingEngineeringAlkali metal
A magnetism measuring device which measures a magnetic field, includes: a gas cell including a cell portion which includes a main chamber, a reservoir that communicates with the main chamber and has a longitudinal direction, and an opening that is provided in the longitudinal direction of the reservoir on a side opposite to the main chamber, a sealing portion which seals the opening, and an alkali metal gas filling the main chamber and the reservoir; and a holding portion provided in the reservoir along the longitudinal direction.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
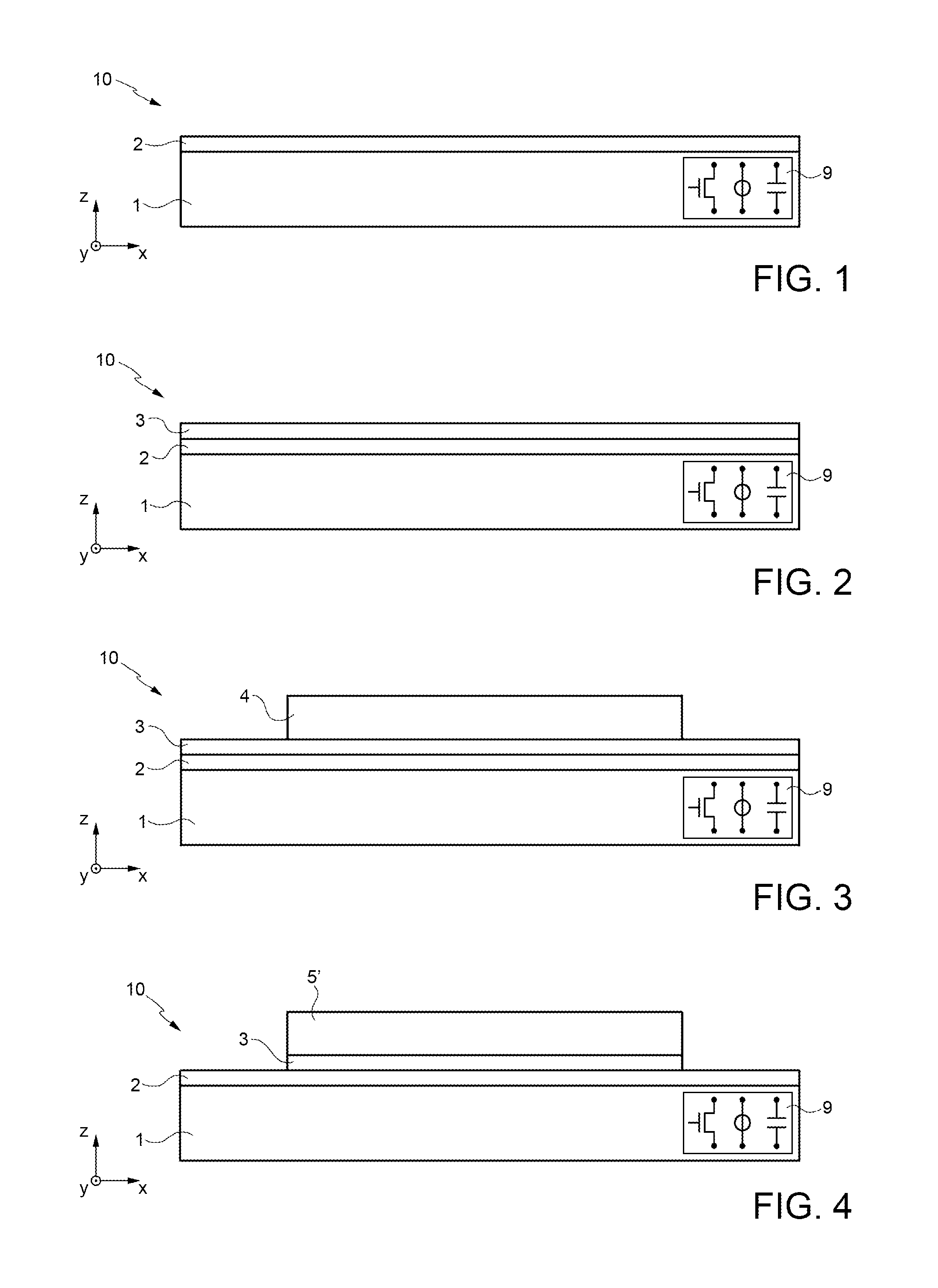
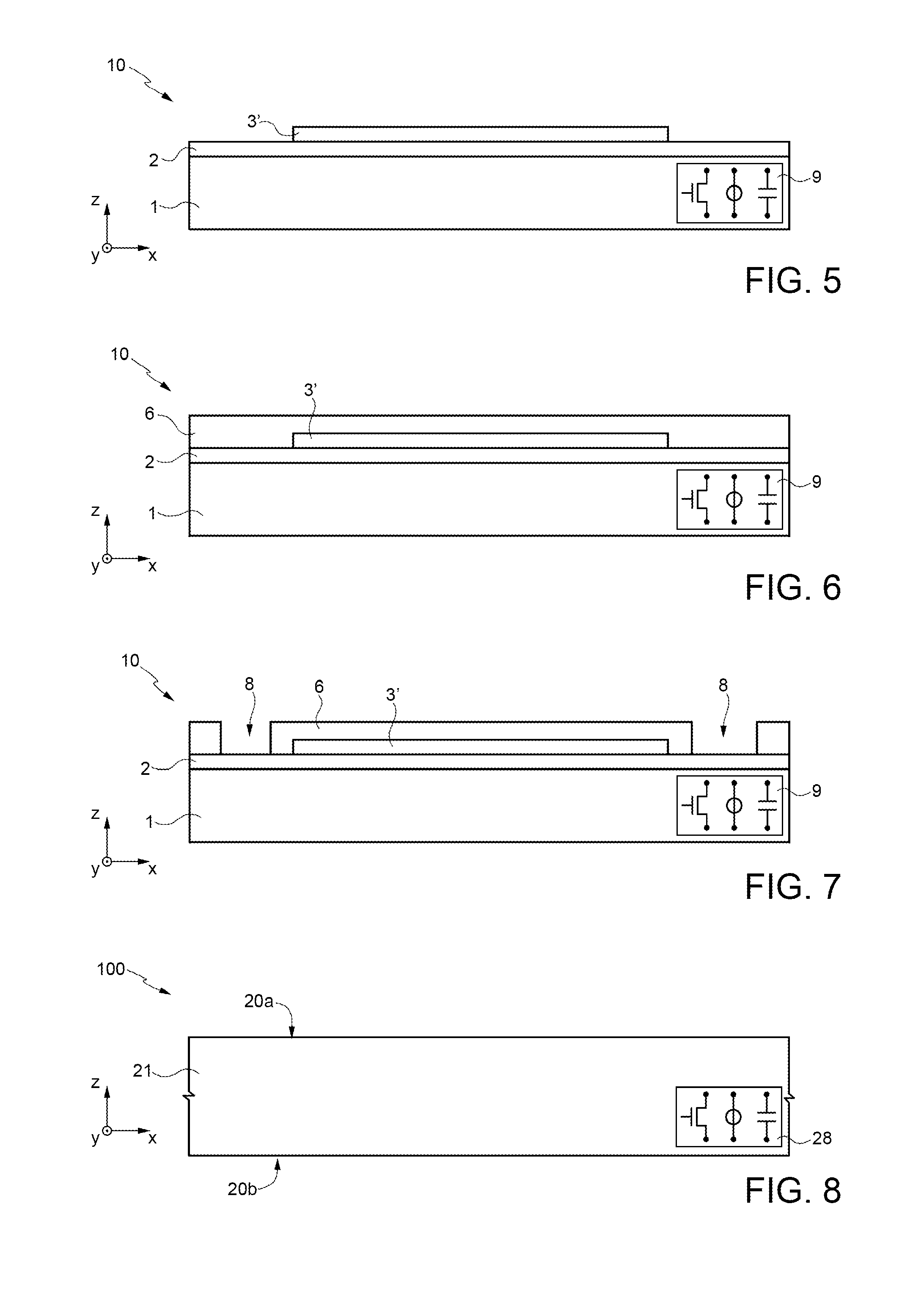
Production of a device comprising magnetic structures formed on one and the same substrate and having respective different magnetization orientations
ActiveUS20110151589A1Avoid problemsSaturation magnetizationNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNéel temperatureMultiple layer
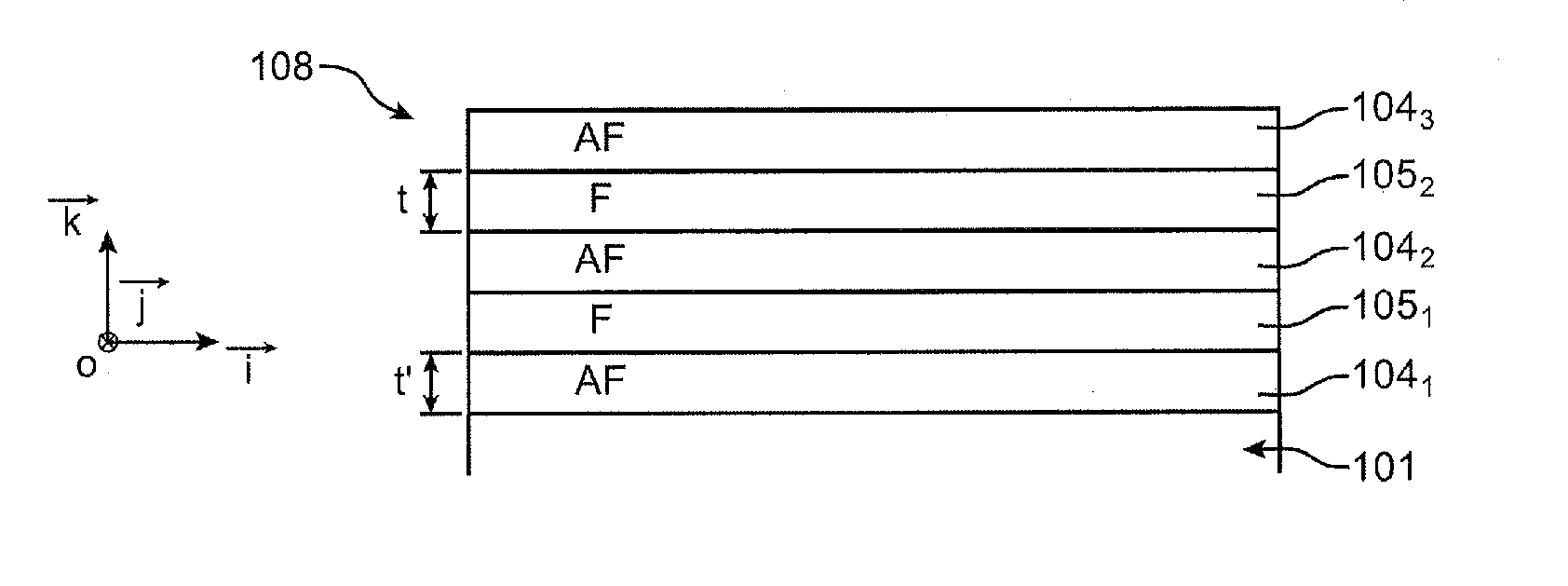
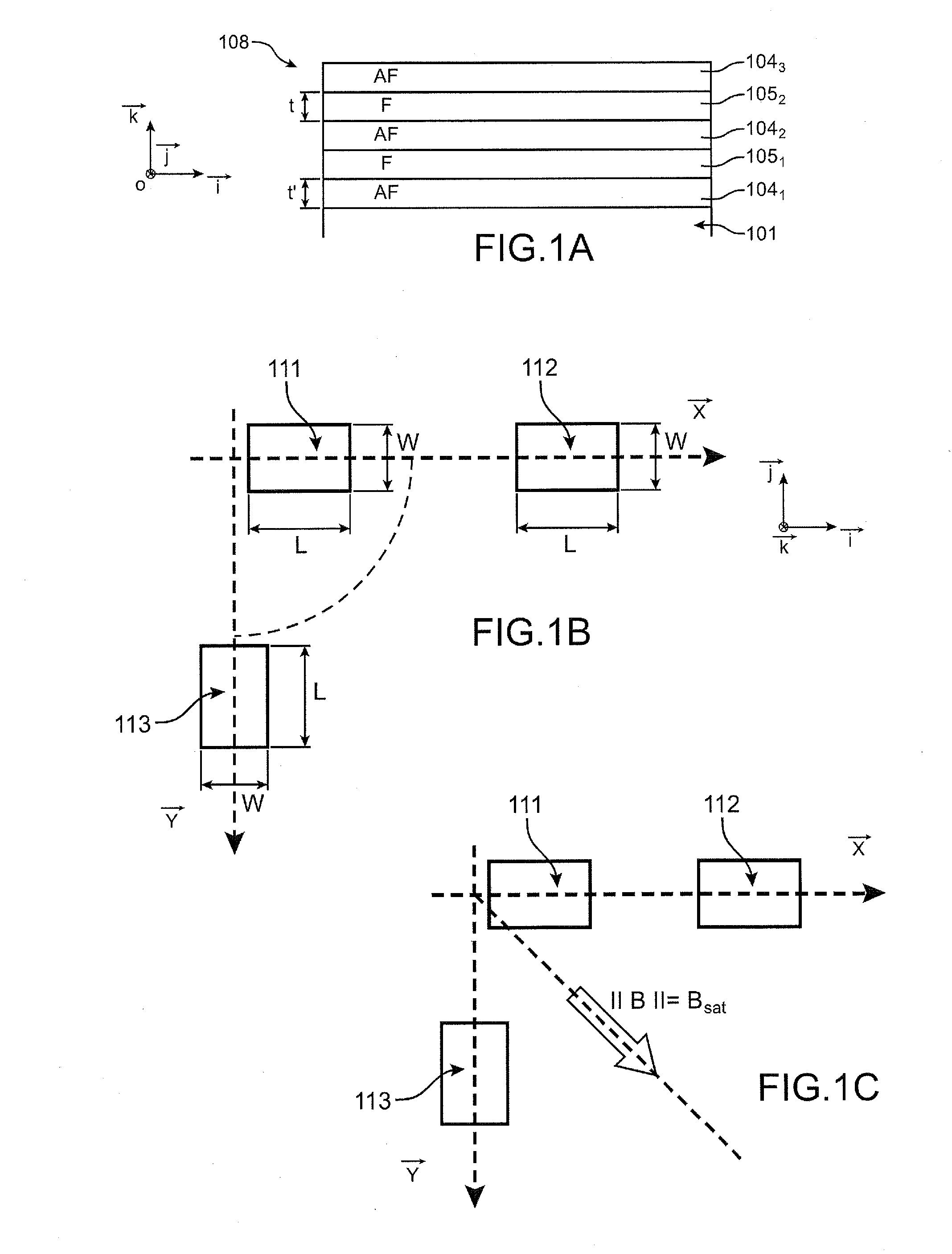
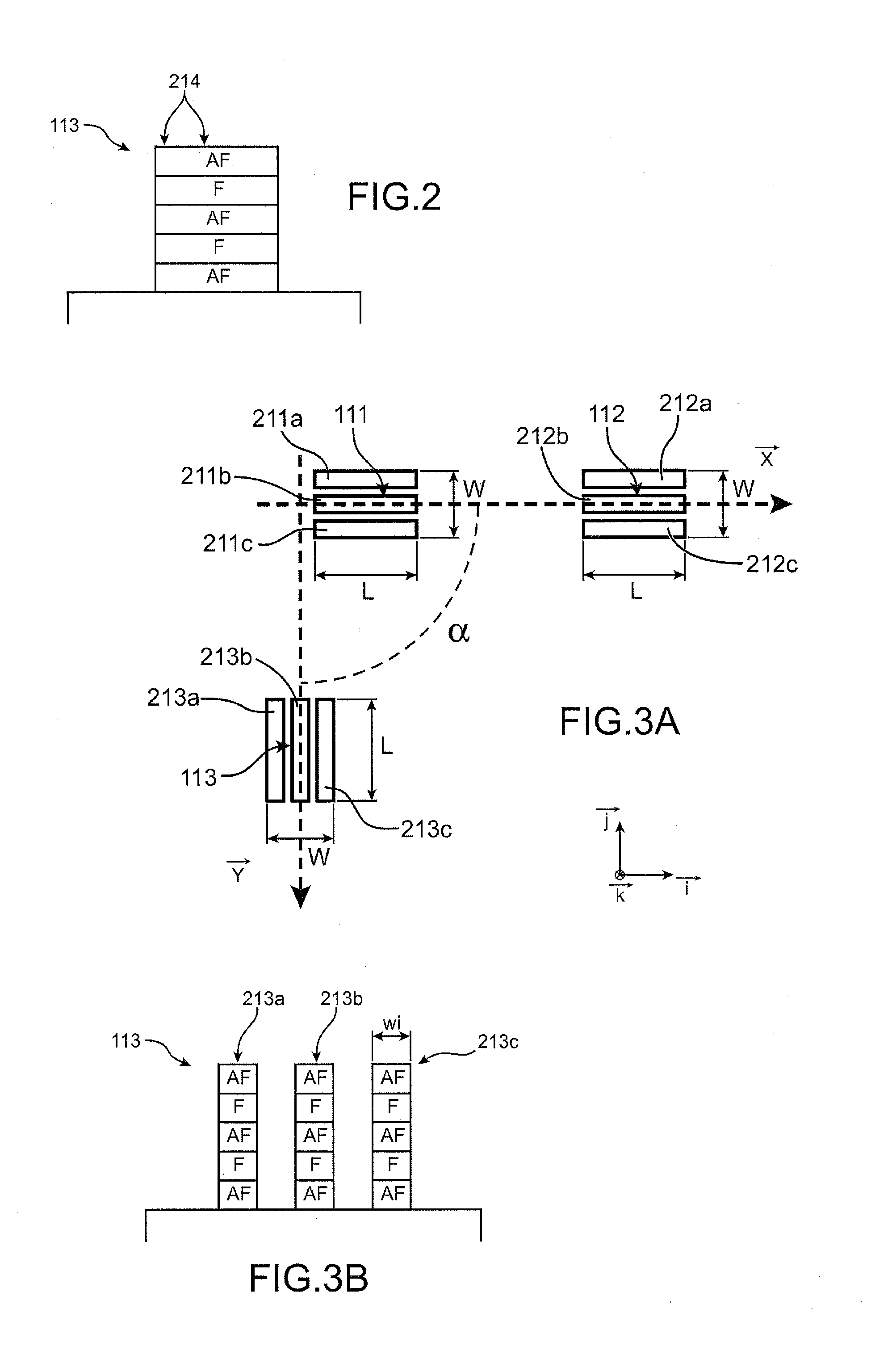
The invention relates to a method for producing a device comprising magnetic blocks magnetized in different directions, comprising steps of:a) forming, in a stack of one or more layers of at least one antiferromagnetic material and one or more layers of at least one ferromagnetic material resting on a substrate, at least one first block and at least one second block, said blocks being longilineal and separate and extending respectively in a first main direction and in a second main direction, the first and the second main direction forming between them a first non-zero angle α,b) annealing said blocks at a temperature greater than the ordering temperature of said antiferromagnetic material or than the blocking temperature or than the Néel temperature of said antiferromagnetic material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGLE ATOMIQUE & AUX ENERGIES AKTERNATIV
Die-Sized Atomic Magnetometer and Method of Forming the Magnetometer
ActiveUS20130015850A1Improved signal-to-noise ratio performanceHigh output signal accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl electronicsEngineering
The cost and size of an atomic magnetometer are reduced by attaching together a first die which integrates together a vapor cell, top and side photo detectors, and processing electronics, a second die which integrates together an optics package and a heater for the vapor cell, and a third die which integrates together a VCSEL, a heater for the VCSEL, and control electronics.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Magnetic sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110068786A1Compact configurationEasy to detectNanomagnetismPretreated surfacesAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetization
A magnetic sensor includes: a first and a second magnetoresistive elements each including: a magnetization free layer; a nonmagnetic spacing layer; a magnetization pinned layer having one or more first layers of a first group of ferromagnetic layers and one or more second layers of a second group of ferromagnetic layers, in which the first layer and the second layer are stacked alternately with a nonmagnetic coupling layer in between, and so antiferromagnetically coupled to each other as to have opposite magnetizations to each other; and an antiferromagnetic layer pinning magnetization orientation in the one or more first and the second layers. The first layers in the first magnetoresistive element are one more in number than that of the one or more second layers. The number of the one or more first layers and that of the one or more second layers in the second magnetoresistive element are equal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Integrated circuit package having a split lead frame
A magnetic field sensor includes a lead frame having a plurality of leads, at least two of which have a connection portion and a die attach portion. A semiconductor die is attached to the die attach portion of the at least two leads. The sensor further includes at least one wire bond coupled between the die and a first surface of the lead frame. The die is attached to a second, opposing surface of the lead frame in a lead on chip configuration. In some embodiments, at least one passive component is attached to the die attach portion of at least two leads.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Amr-type integrated magnetoresistive sensor for detecting magnetic fields perpendicular to the chip
ActiveUS20160202329A1Low efficiencyHigh concentration effectLine/current collector detailsSingle device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMagnetization
An AMR-type integrated magnetoresistive sensor sensitive to perpendicular magnetic fields is formed on a body of semiconductor material covered by an insulating region. The insulating region houses a set / reset coil and a magnetoresistor arranged on the set / reset coil. The magnetoresistor is formed by a magnetoresistive strip of an elongated shape parallel to the preferential magnetization direction. A concentrator of ferromagnetic material is arranged on top of the insulating region as the last element of the sensor and is formed by a plurality of distinct ferromagnetic regions aligned parallel to the preferential magnetization direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Magnetoresistive sensor integrated in a chip for detecting magnetic fields perpendicular to the chip and manufacturing process thereof
An integrated magnetoresistive sensor, formed in a chip including a substrate having a surface and an insulating region covering the surface of the substrate. A magnetoresistor, of a first ferromagnetic material, is formed in the insulating region and has a sensitivity plane parallel to the surface. A concentrator of a second ferromagnetic material is formed in the substrate and has at least one arm extending in a transverse direction to the sensitivity plane. The arm has one end in contact with the magnetoresistor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
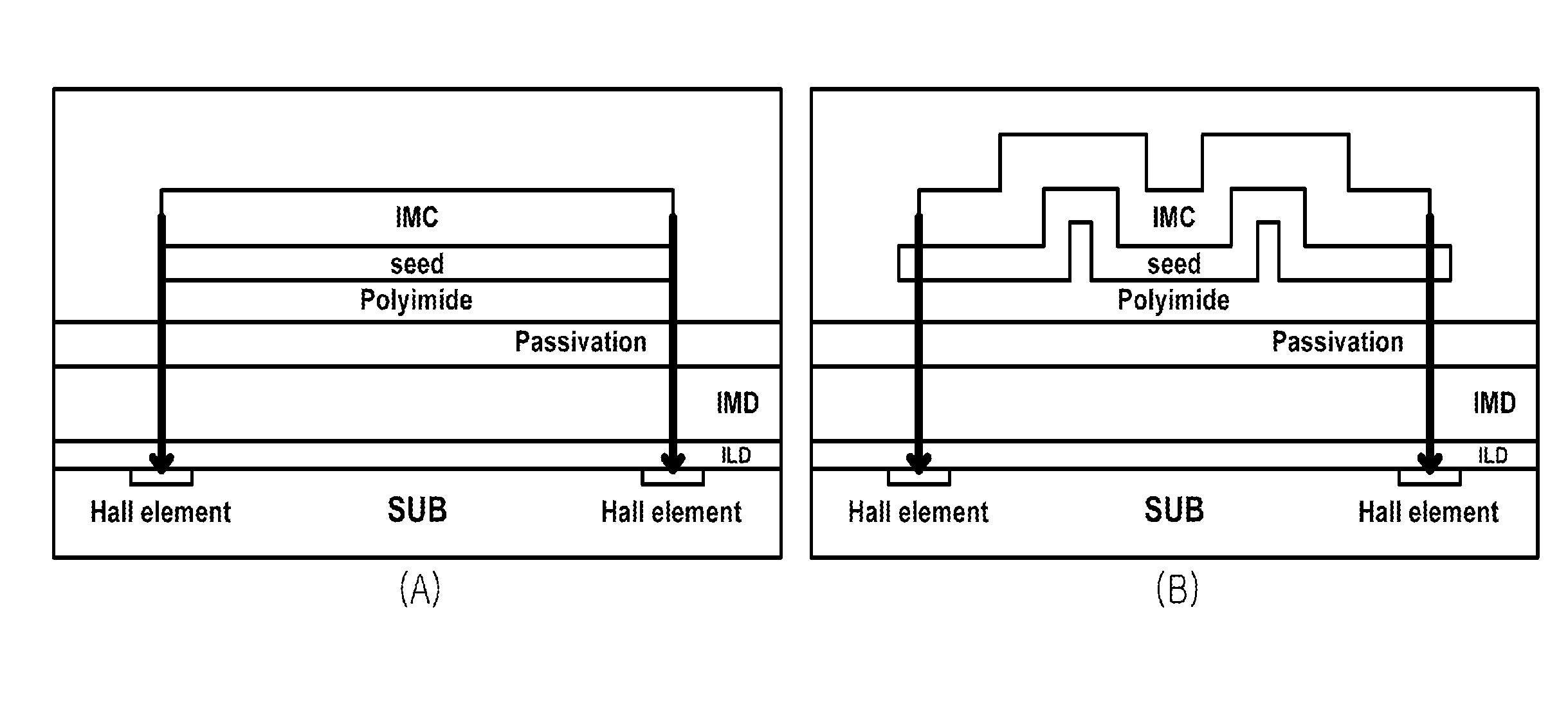
Magnetic sensor and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20140367813A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsHall elementOptoelectronics
A magnetic sensor and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The magnetic sensor includes: a substrate comprising a plurality of Hall elements, a protective layer formed on the substrate, a base layer formed on the protective layer, and an integrated magnetic concentrator (IMC) formed on the base layer and comprising a surface with an elevated portion. The base layer has a larger cross-sectional area than the IMC.
Owner:MAGNACHIP SEMICONDUCTOR LTD
Charge dissipative dielectric for cryogenic devices
InactiveUS20050107261A1Reduce riskAvoid charge accumulationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsConductive materialDielectricElectrical conductor
A Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) is disclosed comprising a pair of resistively shunted Josephson junctions connected in parallel within a superconducting loop and biased by an external direct current (dc) source. The SQUID comprises a semiconductor substrate and at least one superconducting layer. The metal layer(s) are separated by or covered with a semiconductor material layer having the properties of a conductor at room temperature and the properties of an insulator at operating temperatures (generally less than 100 Kelvins). The properties of the semiconductor material layer greatly reduces the risk of electrostatic discharge that can damage the device during normal handling of the device at room temperature, while still providing the insulating properties desired to allow normal functioning of the device at its operating temperature. A method of manufacturing the SQUID device is also disclosed.
Owner:STAR CRYOELECTRONICS
Semiconductor device with integrated magnetic element provided with a barrier structure against metal contamination, and manufacturing
ActiveUS20140167193A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceTitanium
A semiconductor device including: a semiconductor body having a first side and a second side opposite to one another; a first barrier element, which extends over the first side of the semiconductor body and is made of a first material configured to act as barrier against metal ions, for example chosen from among titanium, tantalum, titanium alloys or compounds, tantalum alloy; a magnetic element, which extends over the first barrier layer and is made of a second material having magnetic properties, for example a ferromagnetic material; a second barrier element, which extends over the magnetic layer and is made of a third material configured to act as barrier against metal ions, for example chosen from among titanium, tantalum, titanium alloys or compounds, tantalum alloys or compounds. The first and second barrier elements form a top encapsulating structure and a bottom encapsulating structure for the magnetic element.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Monolithic three-axis linear magnetic sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20170123016A1Increasing thickness LzHigh sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleResistorsMagnetizationMagnetic reluctance
A monolithic three-axis linear magnetic sensor and manufacturing method wherein the sensor comprises an X-axis sensor, a Y-axis sensor and a Z-axis sensor. The X-axis sensor comprises a referenced bridge and at least two X ferromagnetic flux guides. The Y-axis sensor comprises a push-pull bridge and at least two Y ferromagnetic flux guides. The Z-axis sensor comprises a push-pull bridge and at least one Z ferromagnetic flux guide. The bridge arms of the referenced bridge and push-pull bridge are each formed by one or more magnetoresistive elements that are electrically interconnected. The directions of the sensing axes and the directions of magnetization of the pinned layers of the magnetoresistive elements are all oriented along the X-axis. This manufacturing method comprises first depositing a magnetoresistive thin film on a wafer, and then performing several processes such as magnetic annealing, photolithography, etching, coating, and the like in order to realize a sensor. This monolithic three-axis linear magnetic sensor has the advantages of low cost, easy manufacturability, good linearity, and high sensitivity.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Integrated multilayer magnetoresistive sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140015525A1Magnetic field offset compensationSingle device manufacturingField lineMagnetization
A magnetic-field sensor includes: a chip including a substrate having a first surface and an insulating layer covering the first surface; first and second magnetoresistors each extending into the insulating layer and having a main axis of magnetization and a secondary axis of magnetization; a first magnetic-field generator configured to generate a first magnetic field having field lines along the main axis of magnetization of the first magnetoresistor; a second magnetic-field generator configured to generate a second magnetic field having field lines along the main axis of magnetization of the second magnetoresistor. The main axes of magnetization extending transversely to each other and the secondary axes of magnetization extending transversely to each other. The first and second magnetoresistors extend into the insulating layer at a first distance and a second distance, respectively, that differ from one another, from the first surface.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Diamond crystal, diamond element, magnetic sensor, magnetic measurement device, and method for manufacturing sensor array
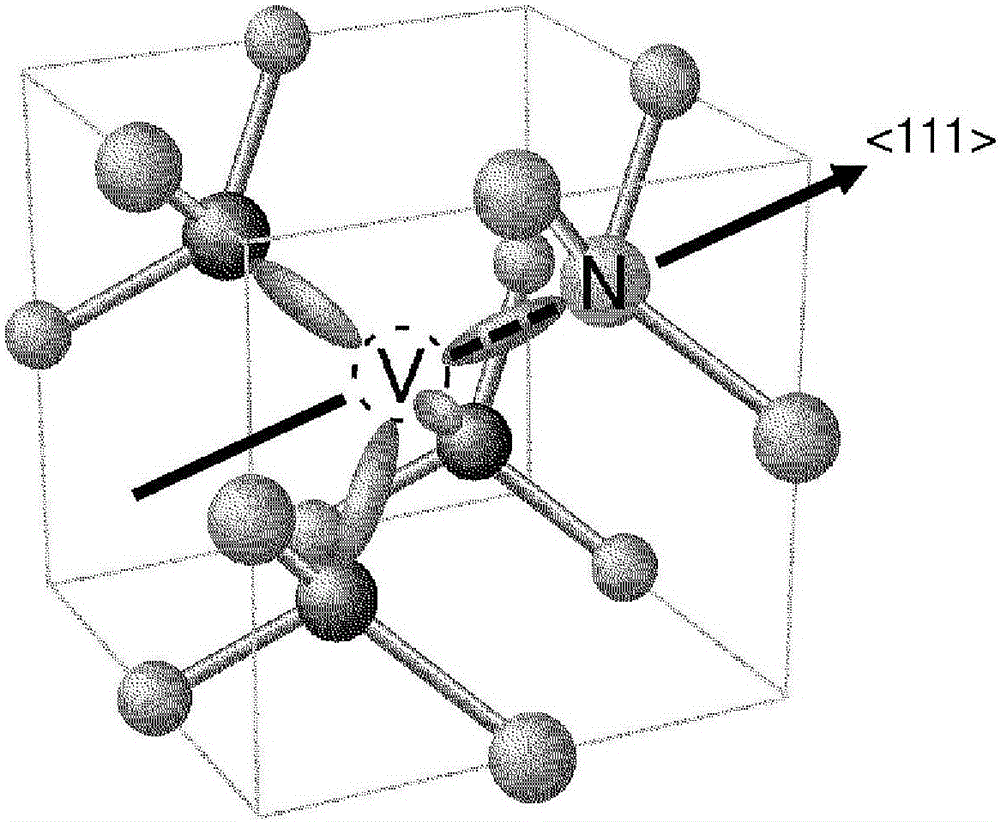
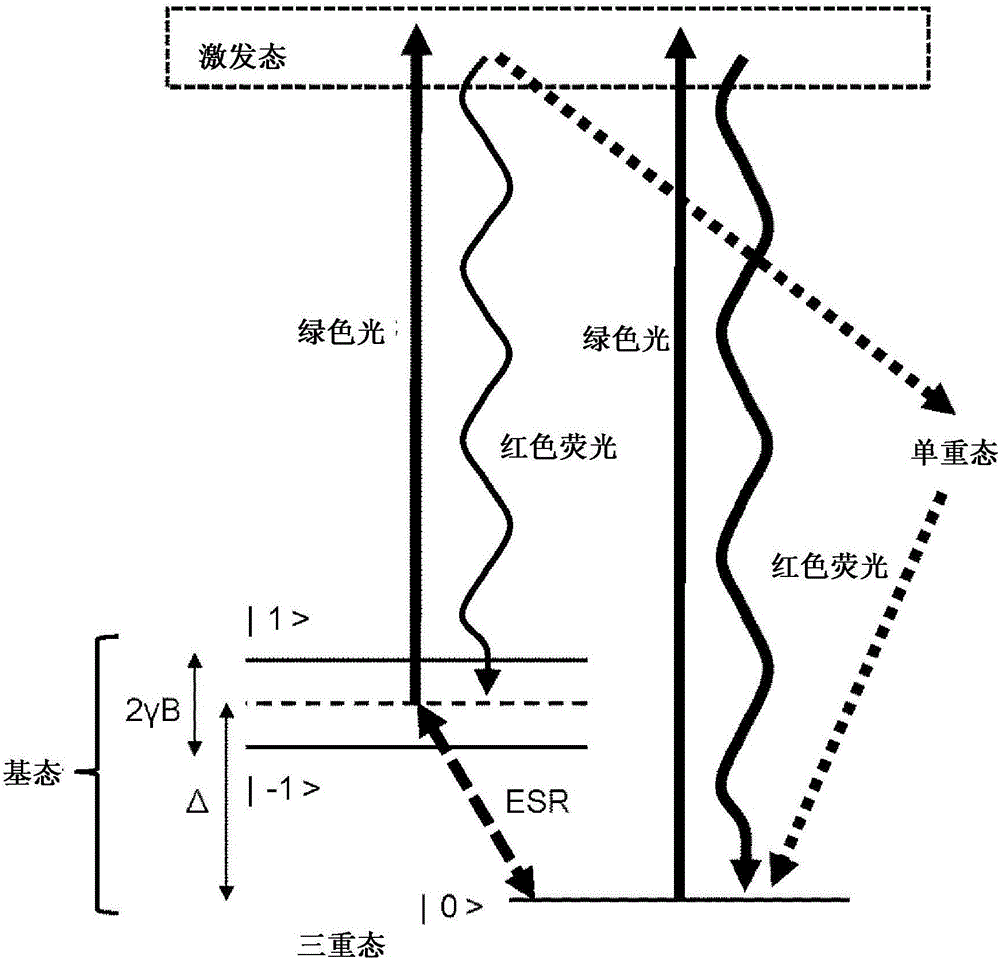
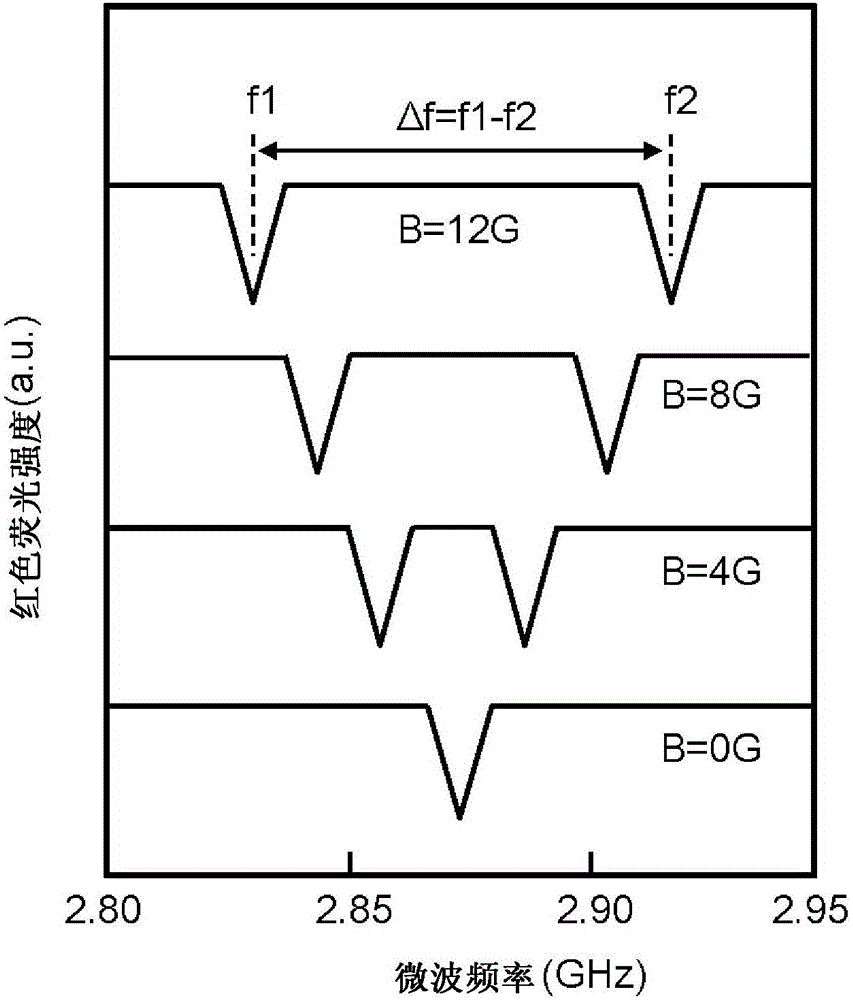
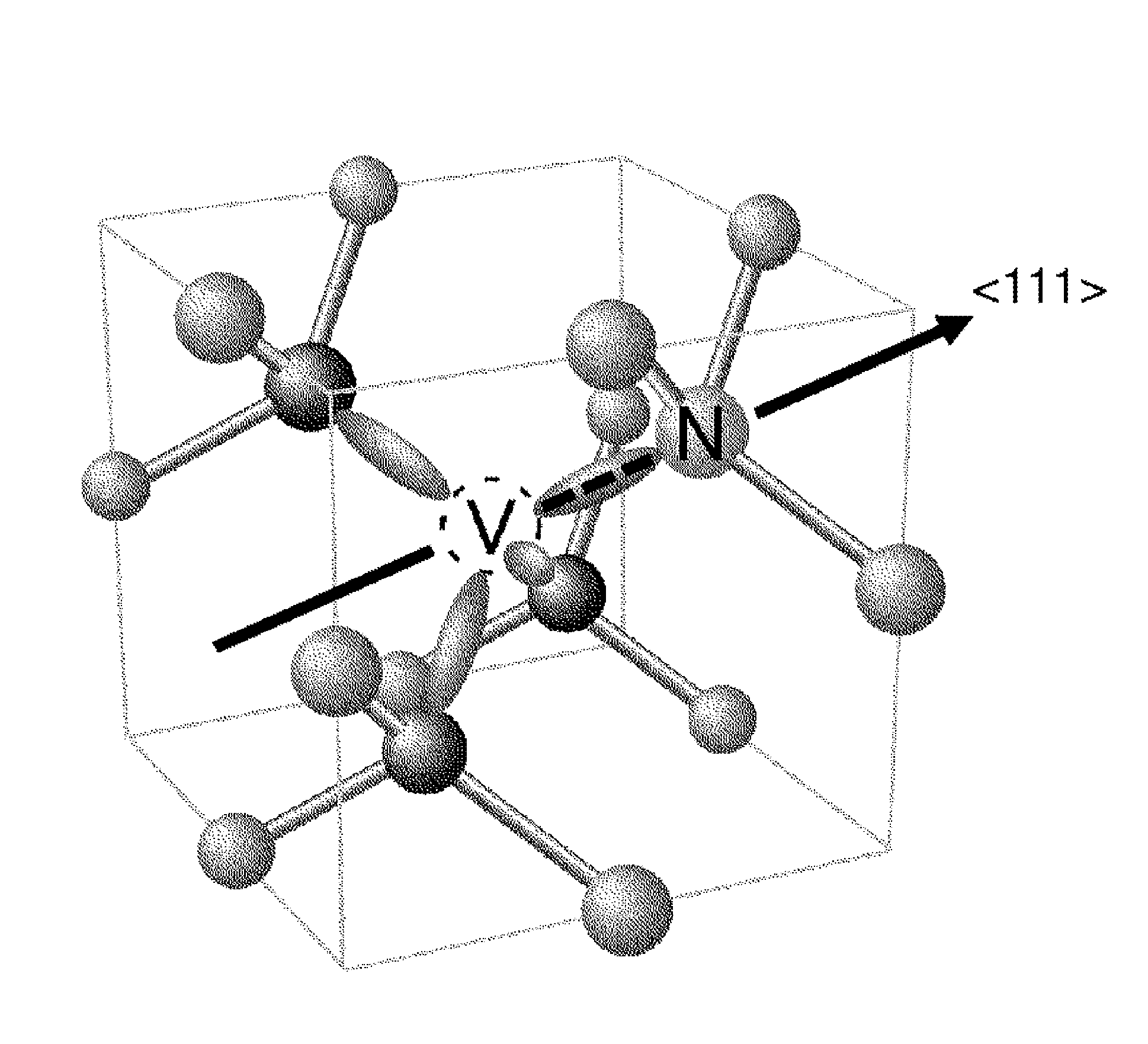
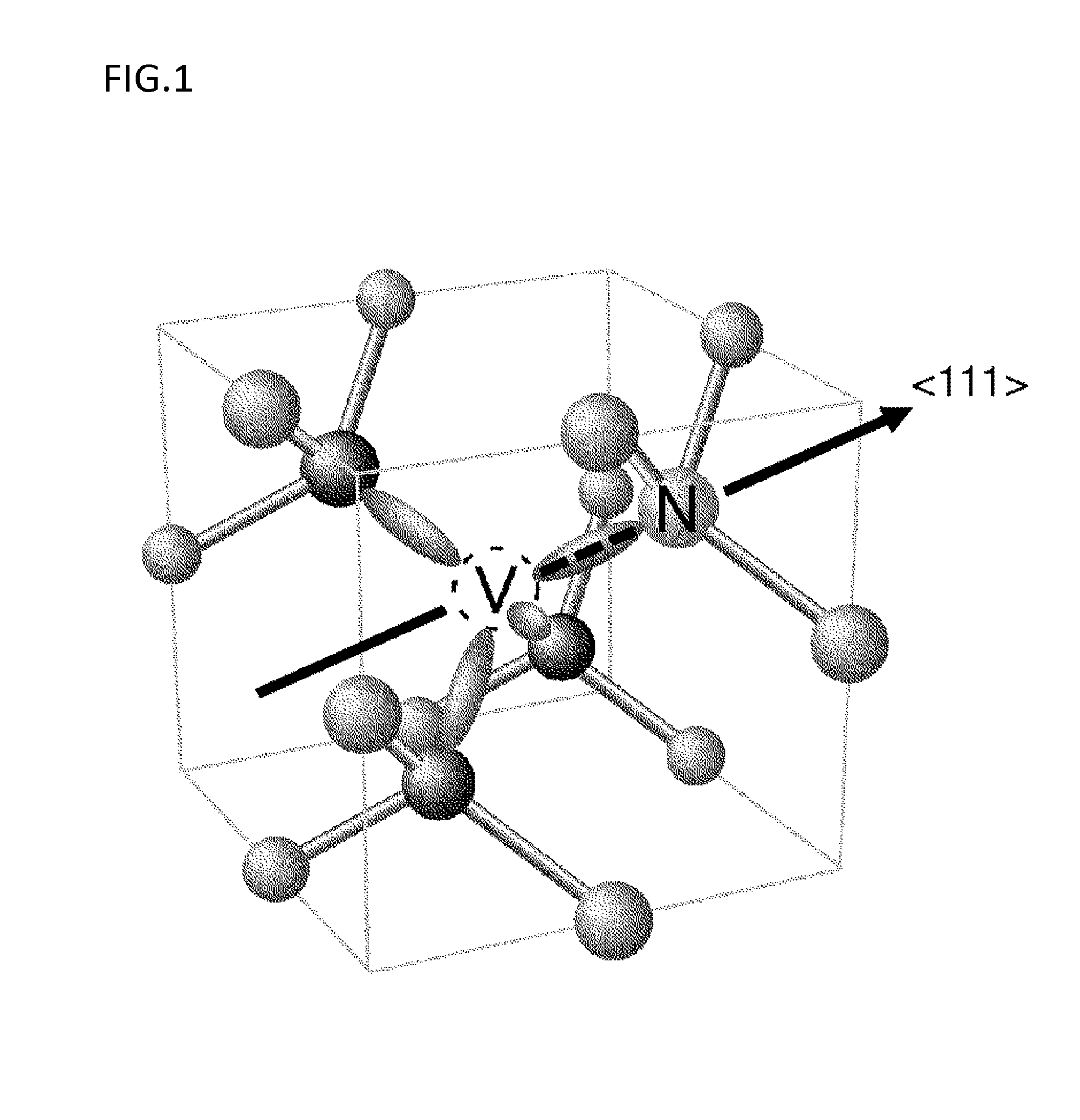
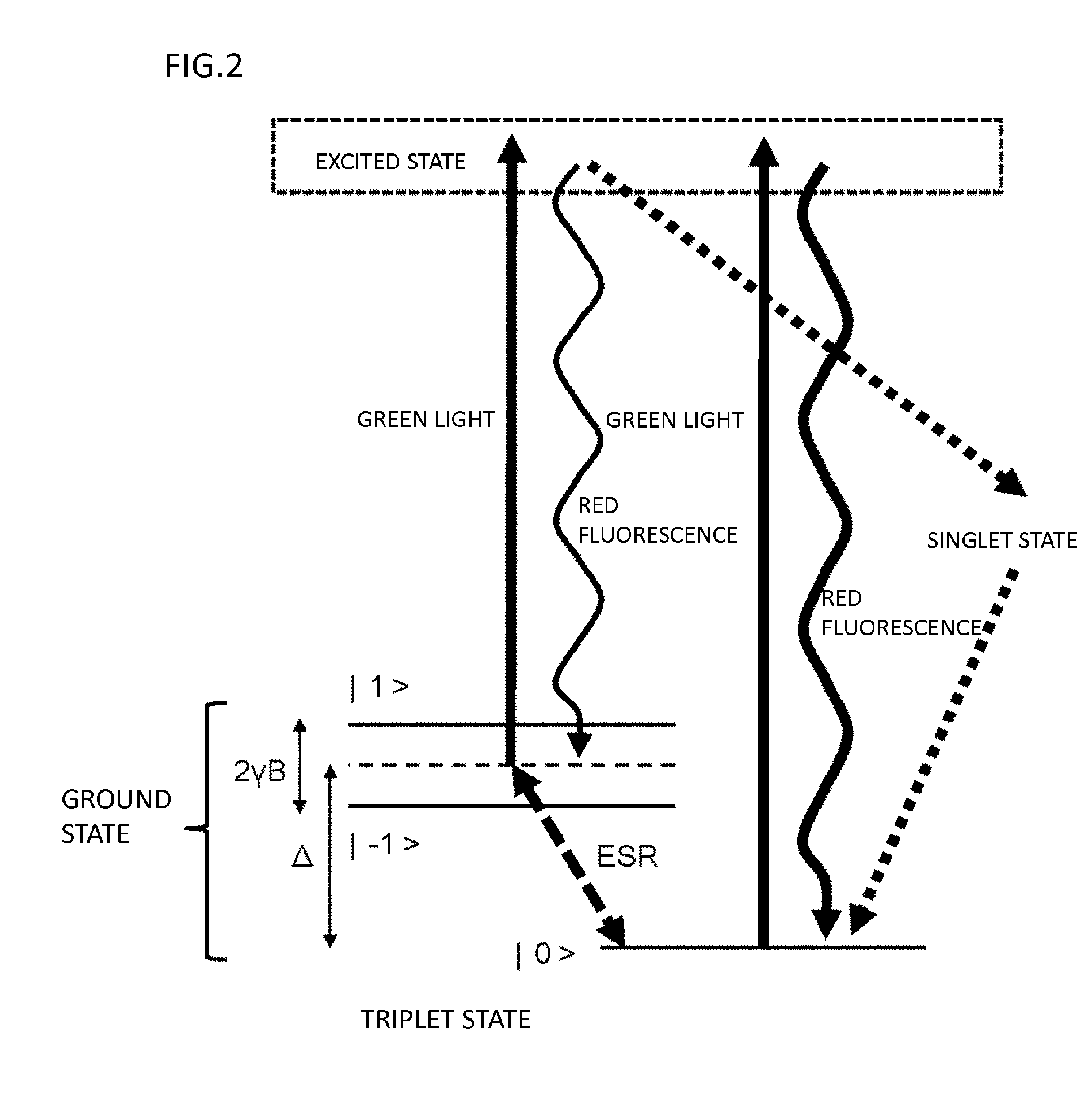
ActiveCN106414818AIncrease contrastPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSensor arrayMagnetic measurements
Provided is a technique for making two-dimensional magnetic measurement with high sensitivity possible at normal temperature in the atmosphere. The diamond crystal pertaining to the present invention is characterized by having an NV region including a complex (NV center) of nitrogen substituted for a carbon atom and a vacancy adjacent to the nitrogen on or near the surface thereof, the NV region having a donor concentration equal to or greater than the concentration of the NV center, or the crystal in the NV region being the (111) face or a face having an off angle no more than + / -10 degrees of the (111) face, and the principal axis of the NV center being a < 111 > axis orthogonal to the (111) face. Through such a diamond crystal, substantially 100% of the NV center can be placed in a negatively charged state (NV-), the spin state of the NV- center can be aligned in one direction, and ODMR signal peaks also become sharp. Through the sensor array pertaining to the present invention, the NV center generated in the diamond crystal can be maintained in the negatively charged state (NV-).
Owner:THE JAPAN SCI & TECH AGENCY +1
Diamond crystal, diamond devices, magnetic sensor, magnetic sensor system, and method for manufacturing sensor array
ActiveUS20160334474A1Increase contrastSharp peakPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSensor arrayDiamond crystal
A diamond crystal according to the present invention has an NV region containing a complex (NV center) of nitrogen substituted with a carbon atom and a vacancy located adjacent to the nitrogen, on a surface or in the vicinity of the surface, wherein the NV region has a donor concentration equal to or higher than the concentration of the NV centers, or a crystal of the NV region is a {111} face or a face having an off-angle that is ±10 degrees or less against the {111} face, and a principal axis of the NV center is a <111> axis that is perpendicular to the {111} face. Such a diamond crystal enables almost 100% of the NV center to be a state (NV−) of having a negative electric charge, and spin states of the NV− centers to be aligned in one direction.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
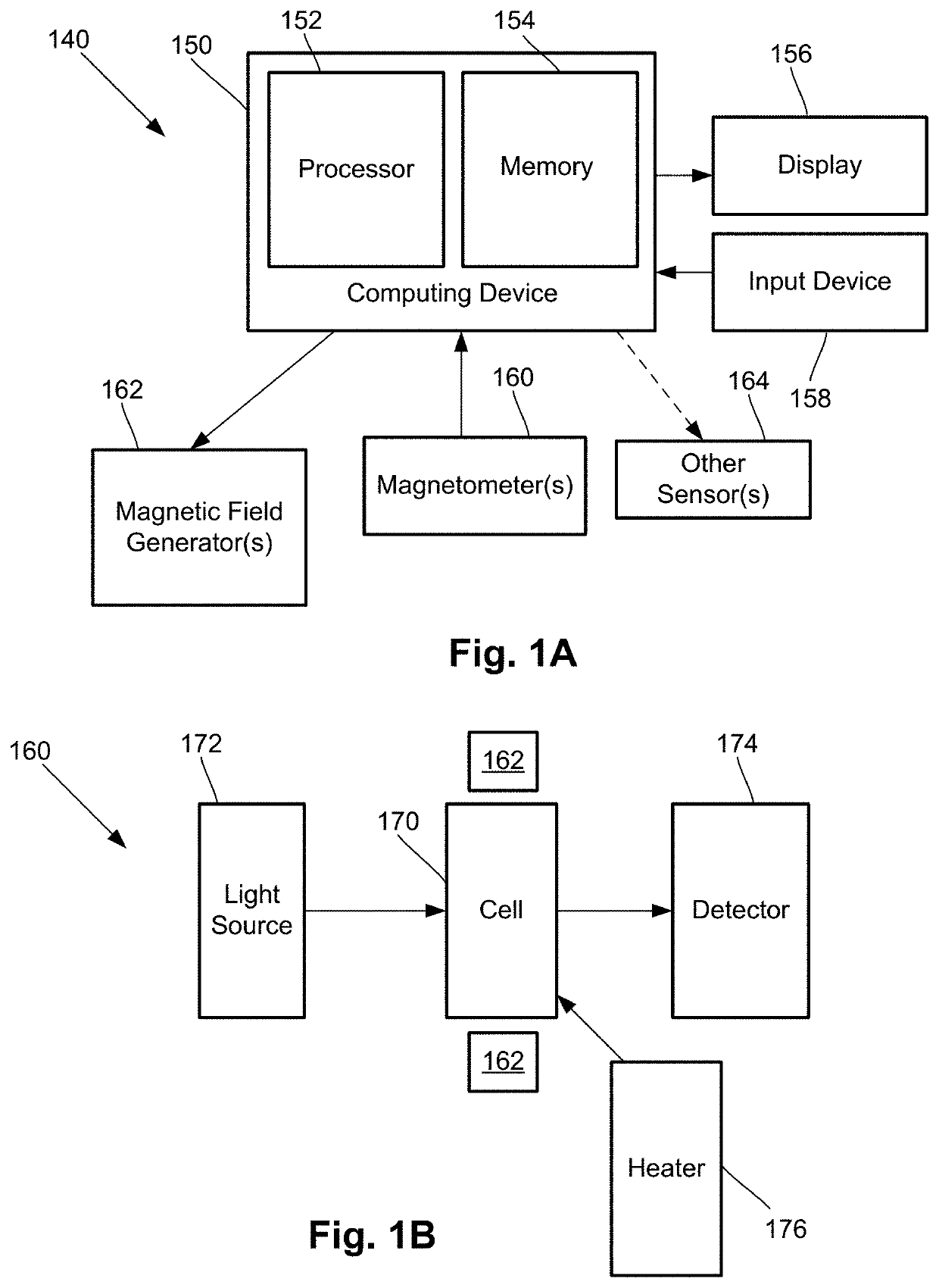
Methods and systems for homogenous optically-pumped vapor cell array assembly from discrete vapor cells
ActiveUS20210139742A1Easy to insertReduce widthApparatus using atomic clocksManufacture of electrical instrumentsEngineeringBiology
A method of making an array of vapor cells for an array of magnetometers includes providing a plurality of separate vapor cell elements, each vapor cell element including at least one vapor cell; arranging the vapor cell elements in an alignment jig to produce a selected arrangement of the vapor cells; attaching at least one alignment-maintaining film onto the vapor cell elements in the alignment jig; transferring the vapor cells elements and the at least one alignment-maintaining film from the alignment jig to a mold; injecting a bonding material into the mold and between the vapor cell elements to bond the vapor cell elements in the selected arrangement; removing the at least one alignment maintaining film from the vapor cell elements; and removing the bonded vapor cells elements in the selected arrangement from the mold to provide the array of vapor.
Owner:HI LLC
Magnetic sensor and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20050054120A1Uniform layersImprove output stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsTectorial membraneMagnetic reluctance
A magnetic sensor comprises a substrate, magnetoresistive element of a spin-valve type, a bias magnetic layer (or a permanent magnet film), and a protective film, wherein the bias magnetic layer is connected with both ends of the magnetoresistive element and the upper surface thereof is entirely covered with the lower surface of the magnetoresistive element at both ends. Herein, distances between the side surfaces of the both ends of the magnetoresistive element and the side surfaces of the bias magnetic layer viewed from the protective film do not exceed 3 μm. In addition, a part of the bias magnetic layer can be covered with both ends of the magnetoresistive element, and an intermediate layer is arranged in relation to the magnetoresistive element, bias magnetic layer, and protective film so as to entirely cover the upper surface of the bias magnetic layer.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Popular searches
Magnetic recording Plasma technique Galvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatment Three-component magnetometers Semiconductor devices Magnitude/direction of magnetic fields Using electrical means Magnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devices Measurements using NMR imaging systems Sensors
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com