Patents
Literature
415 results about "Common source line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
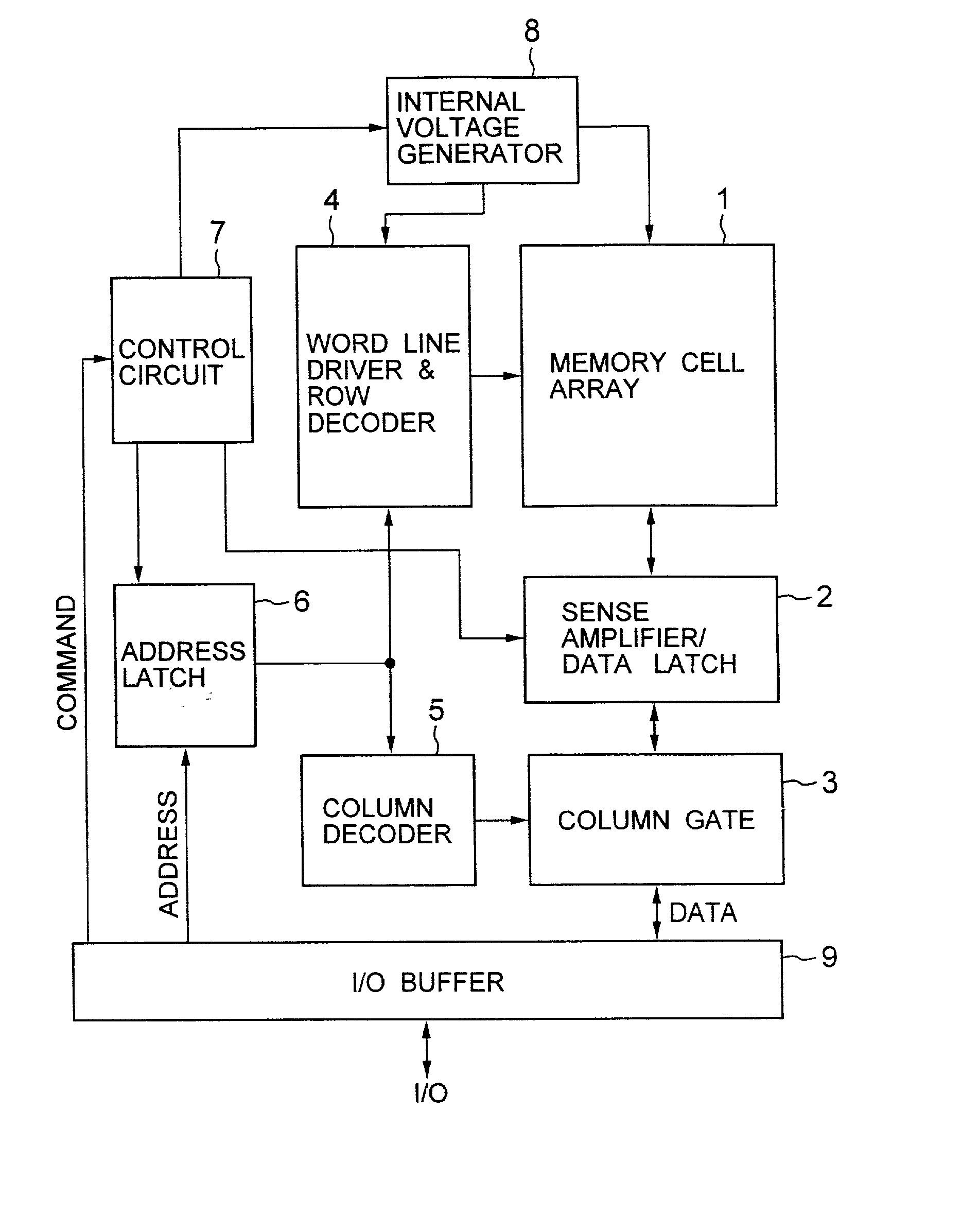
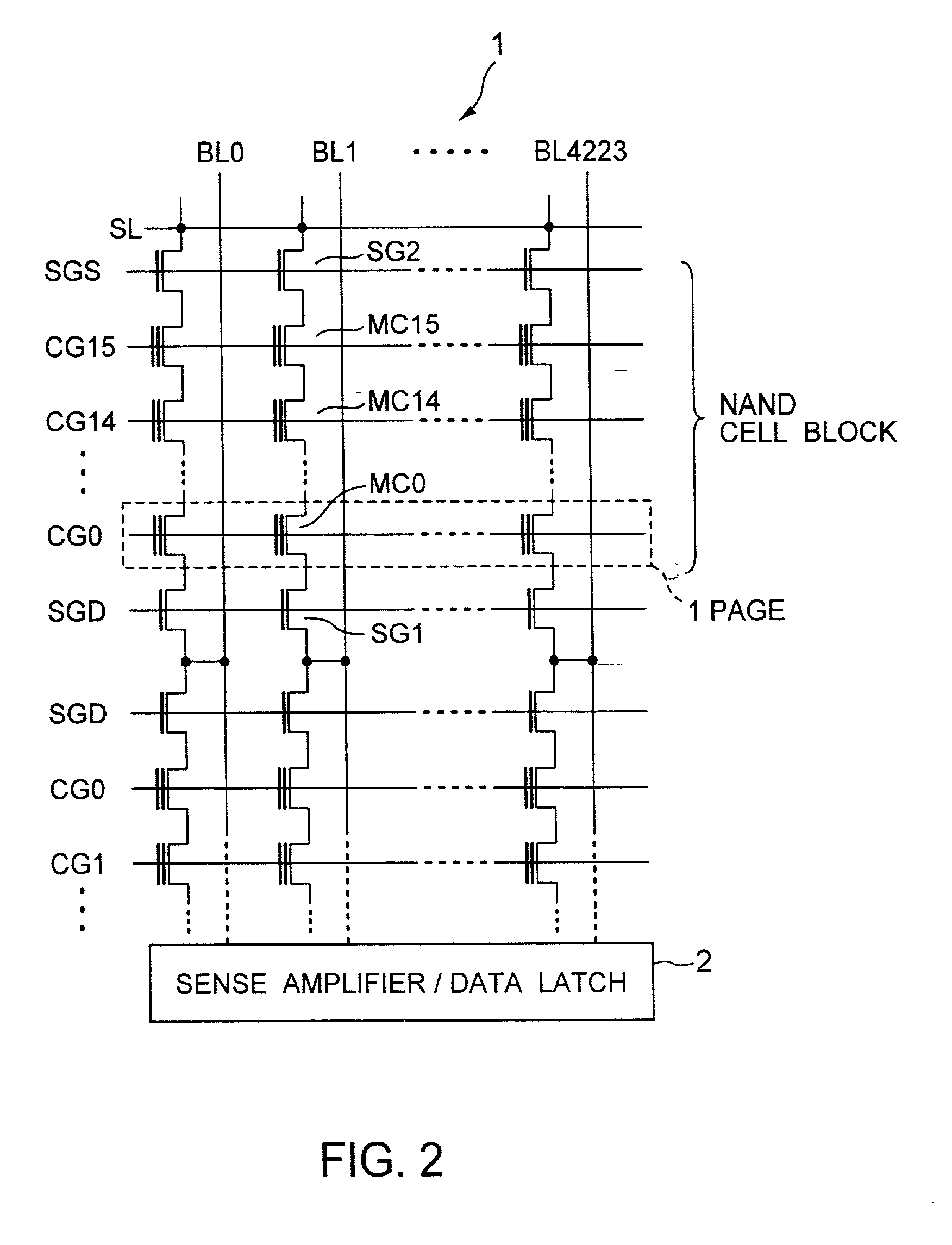
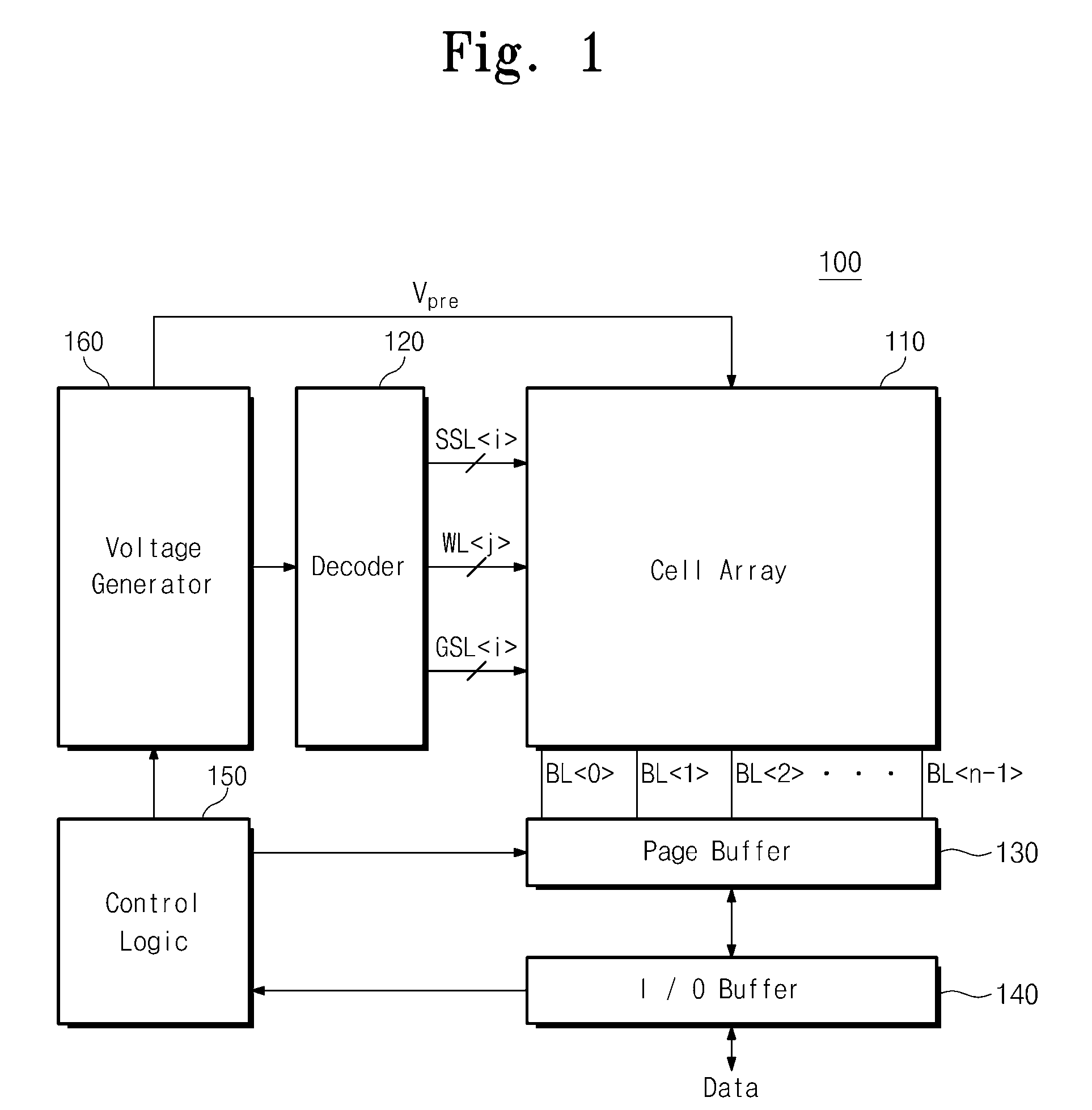
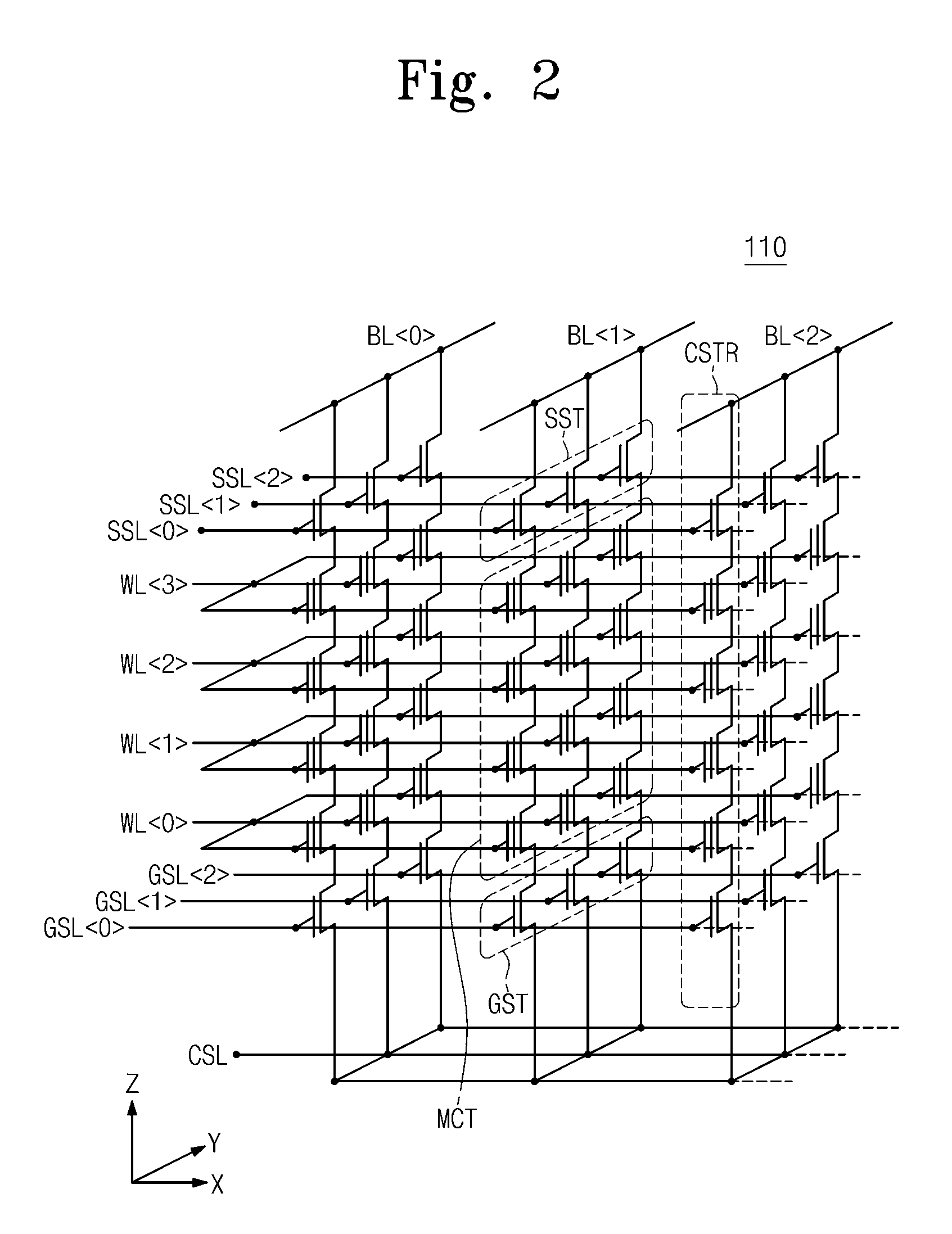
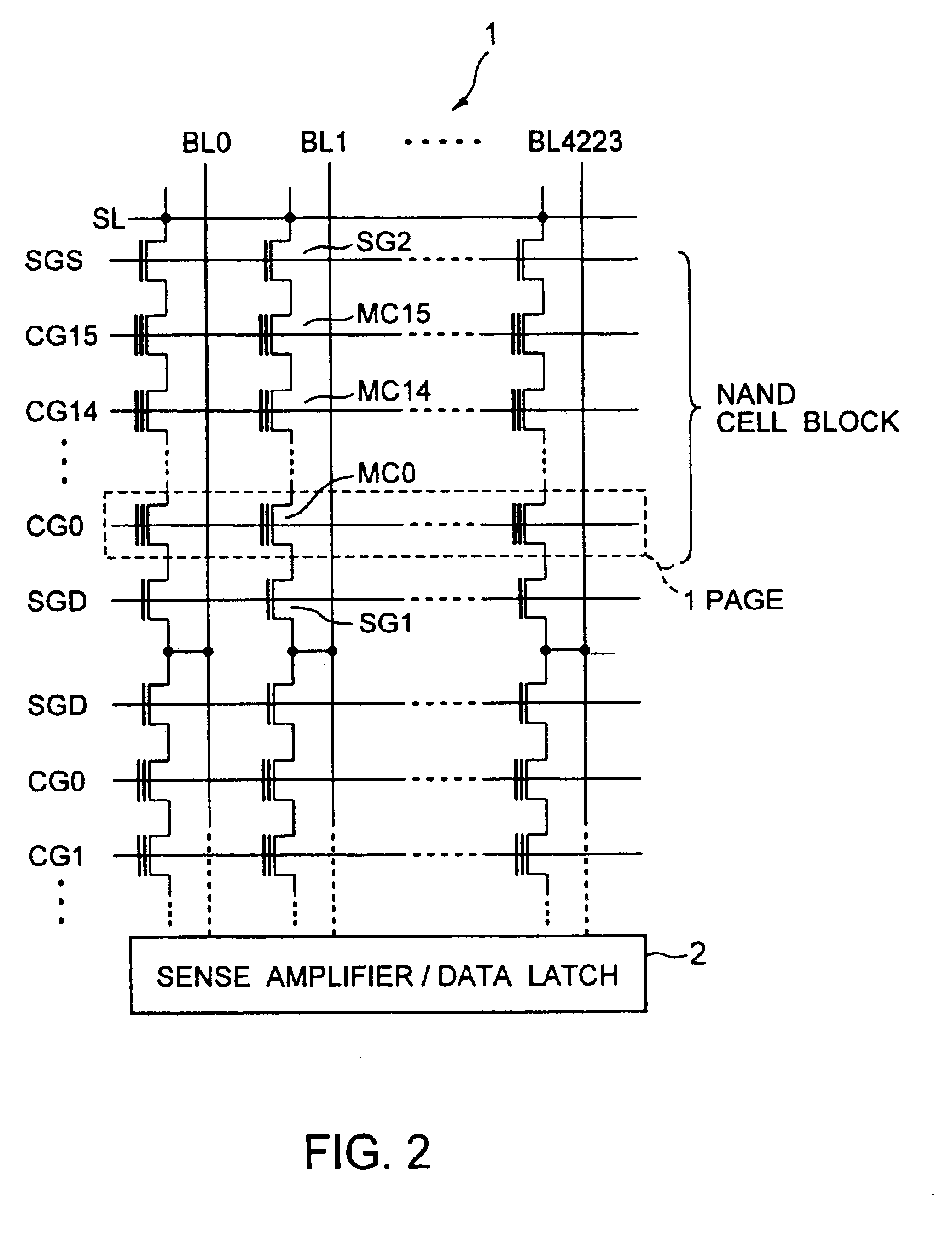
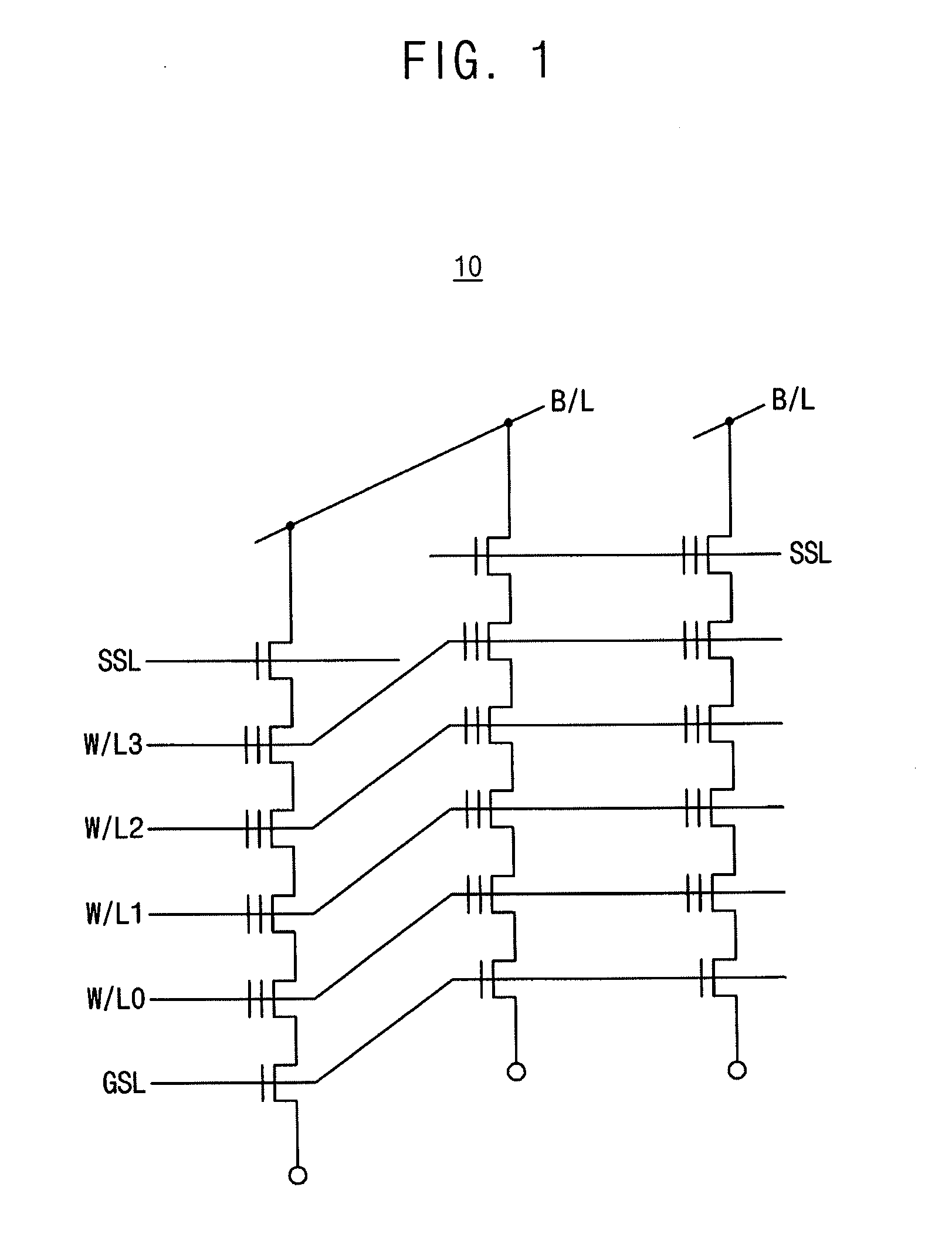
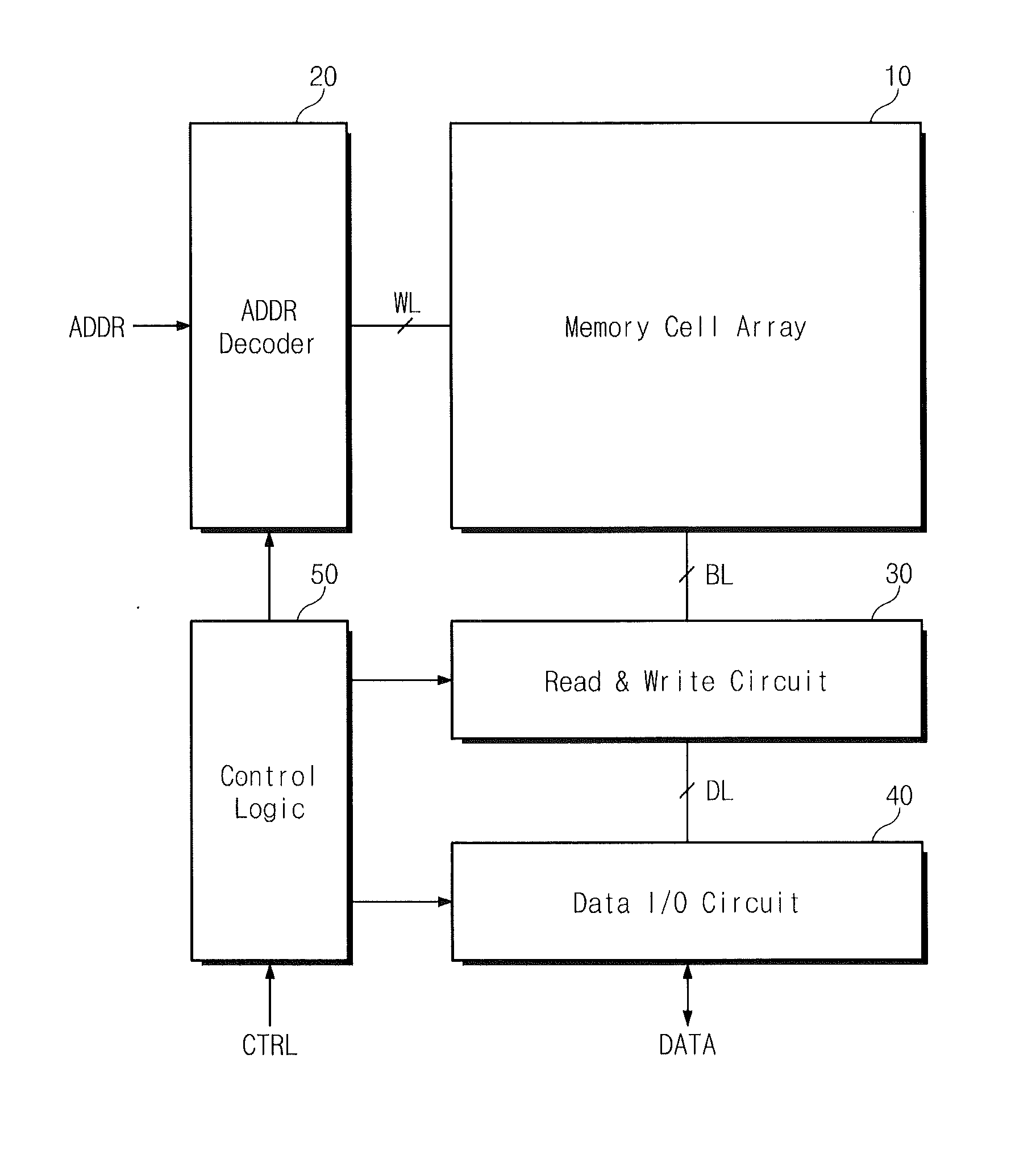
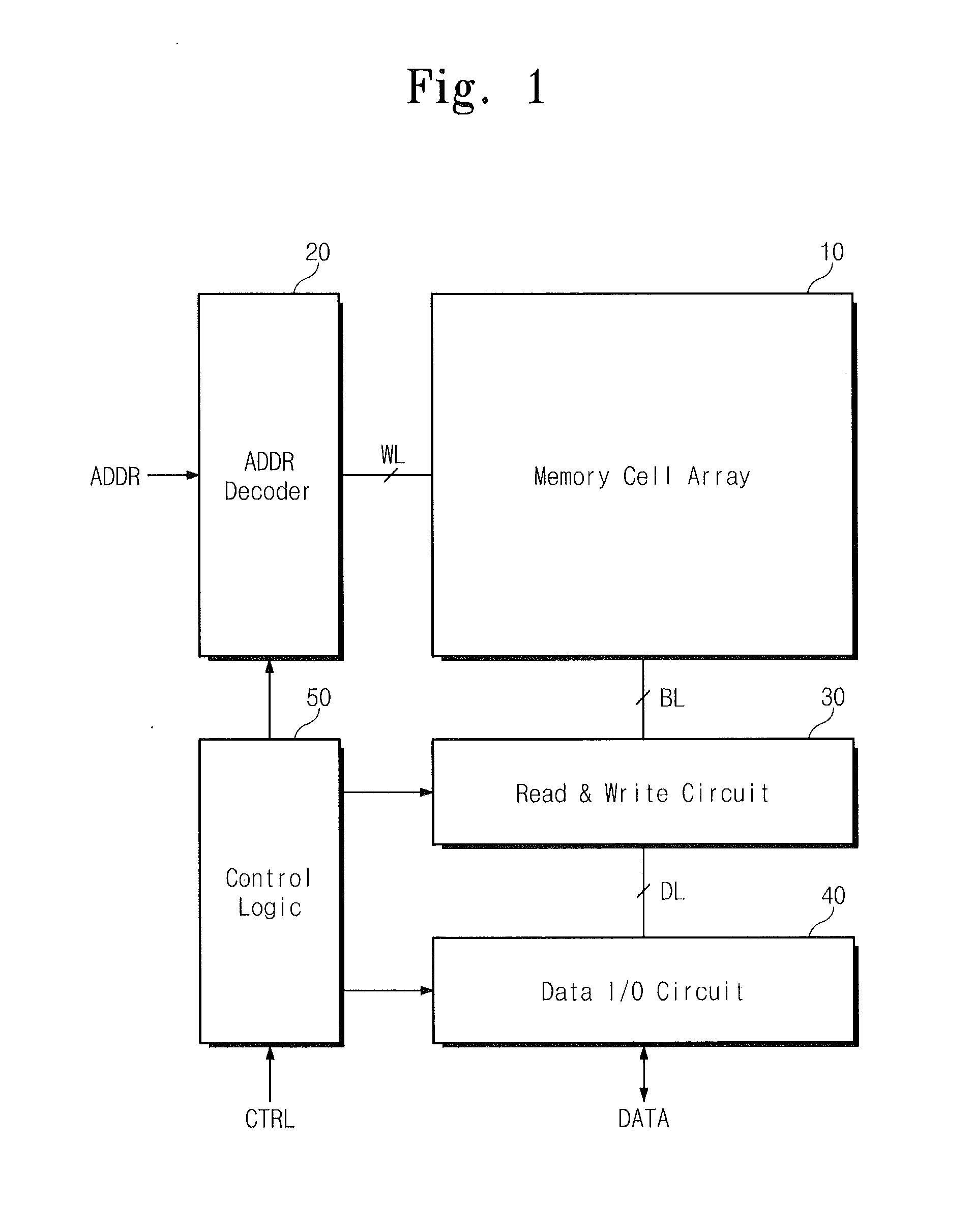
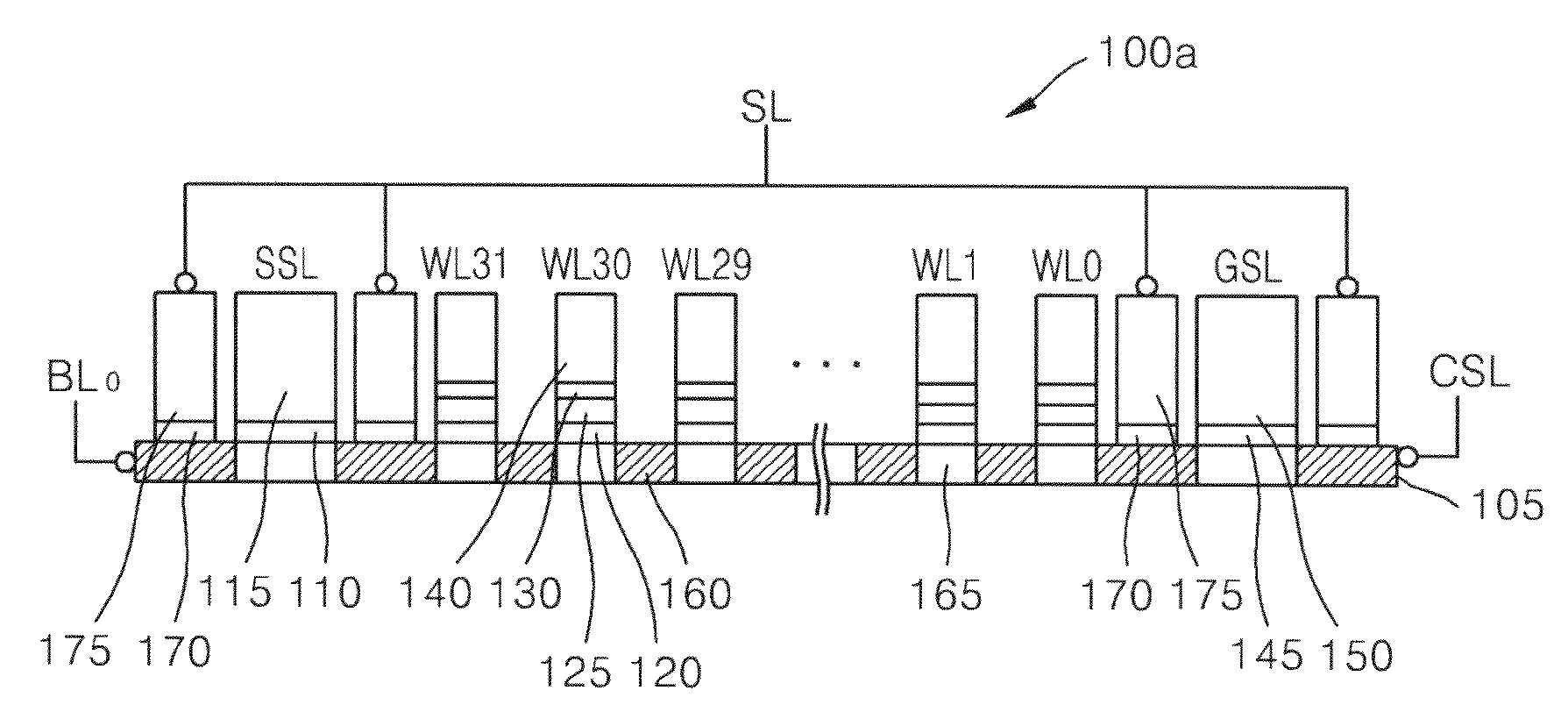
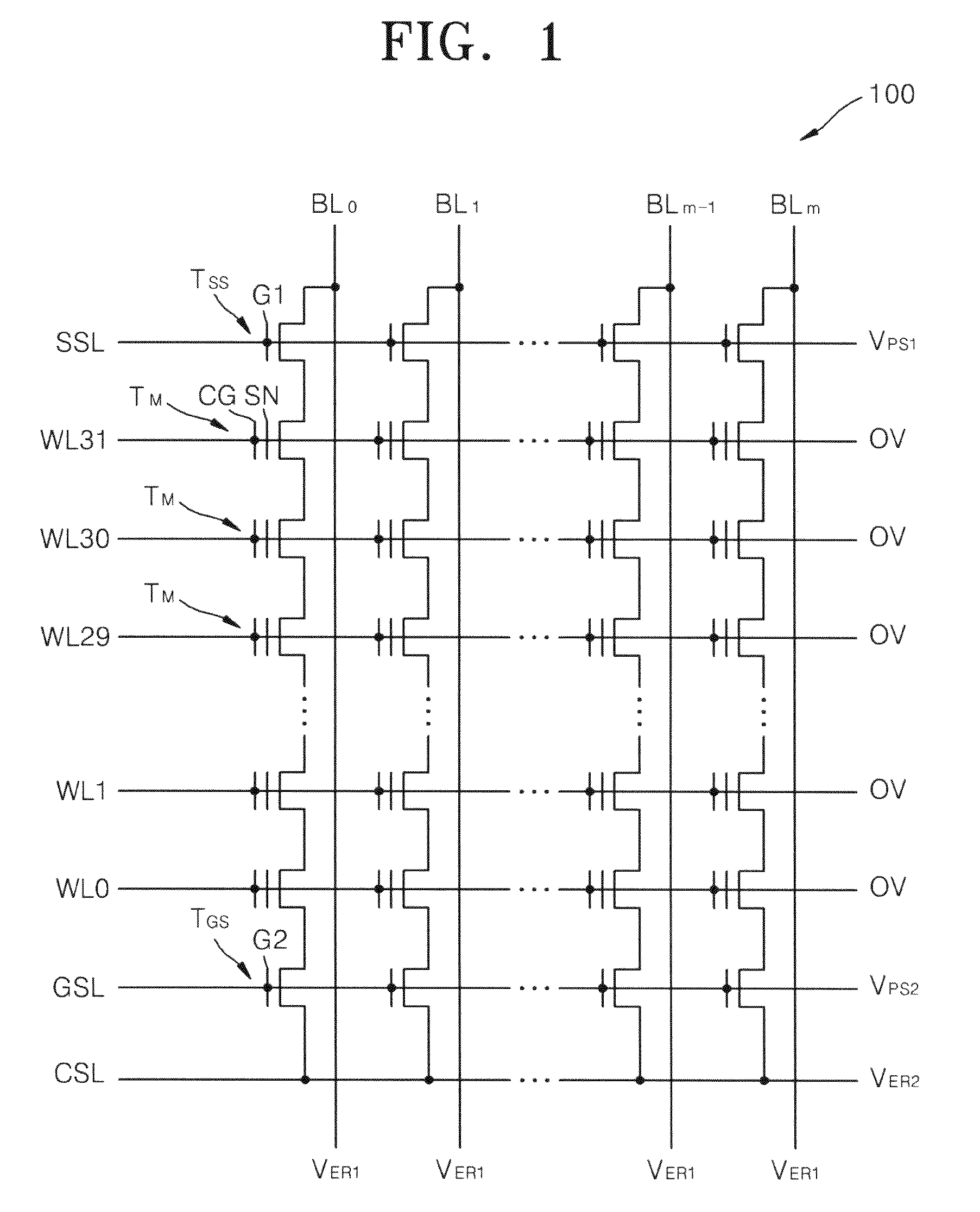
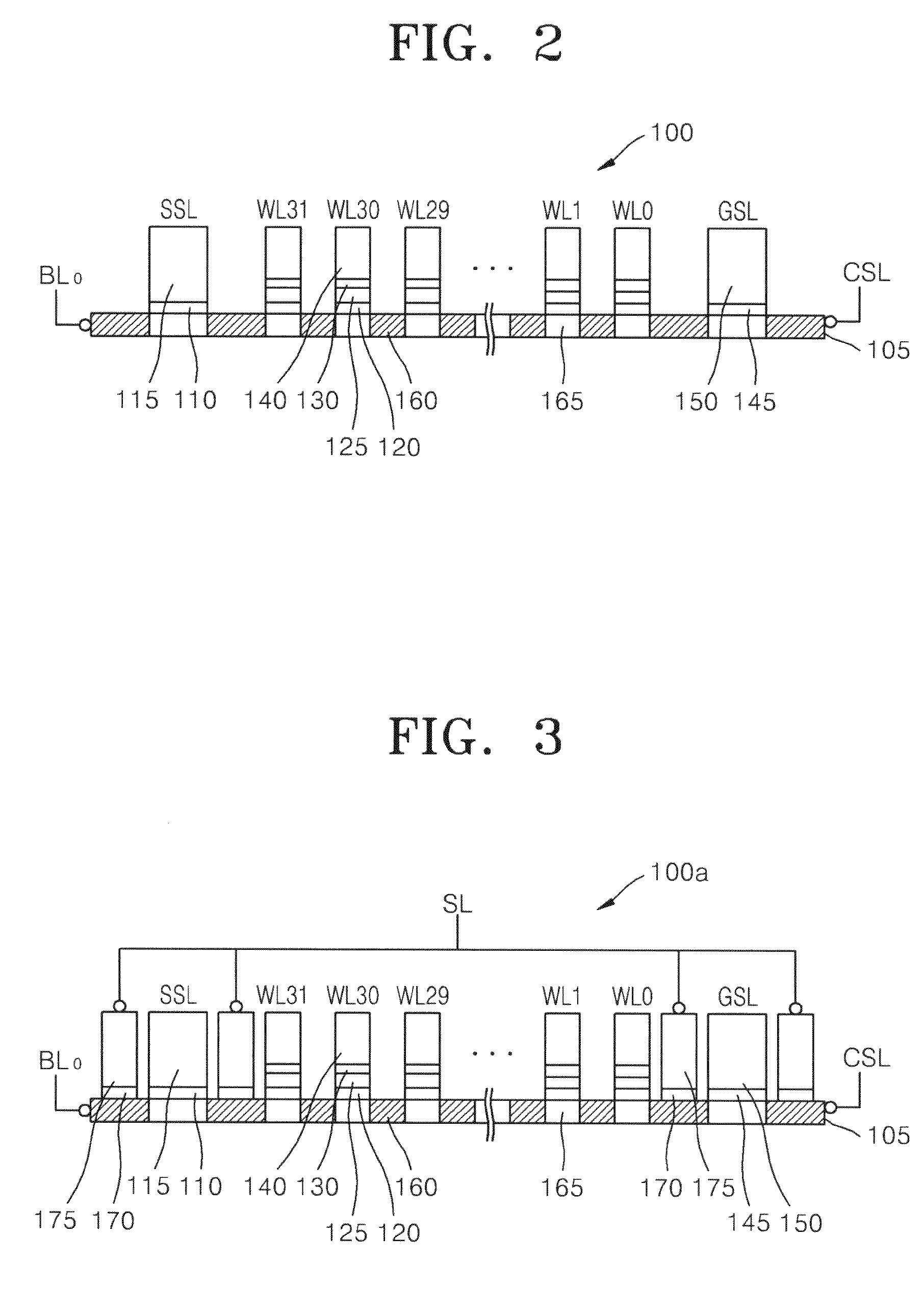
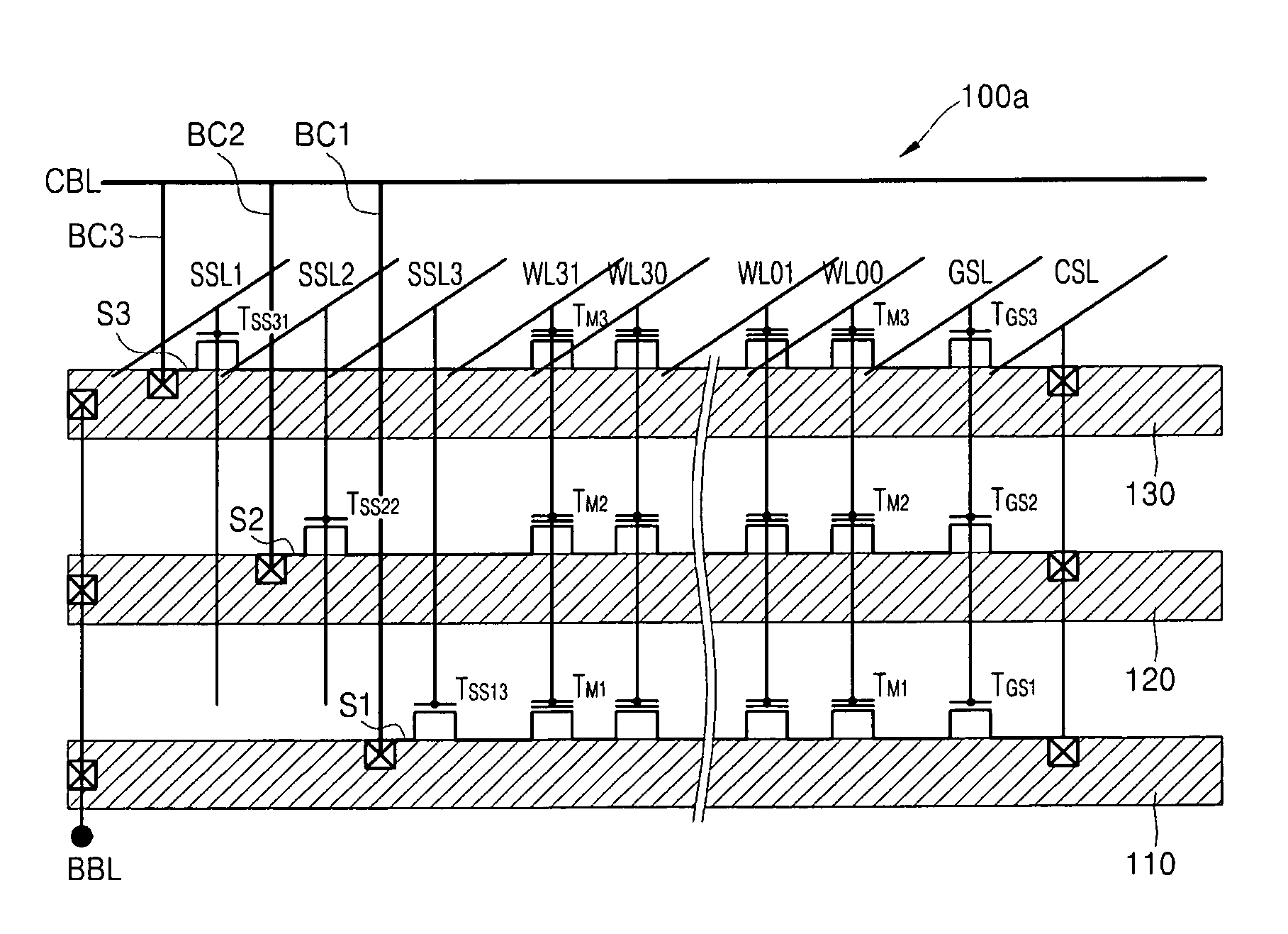
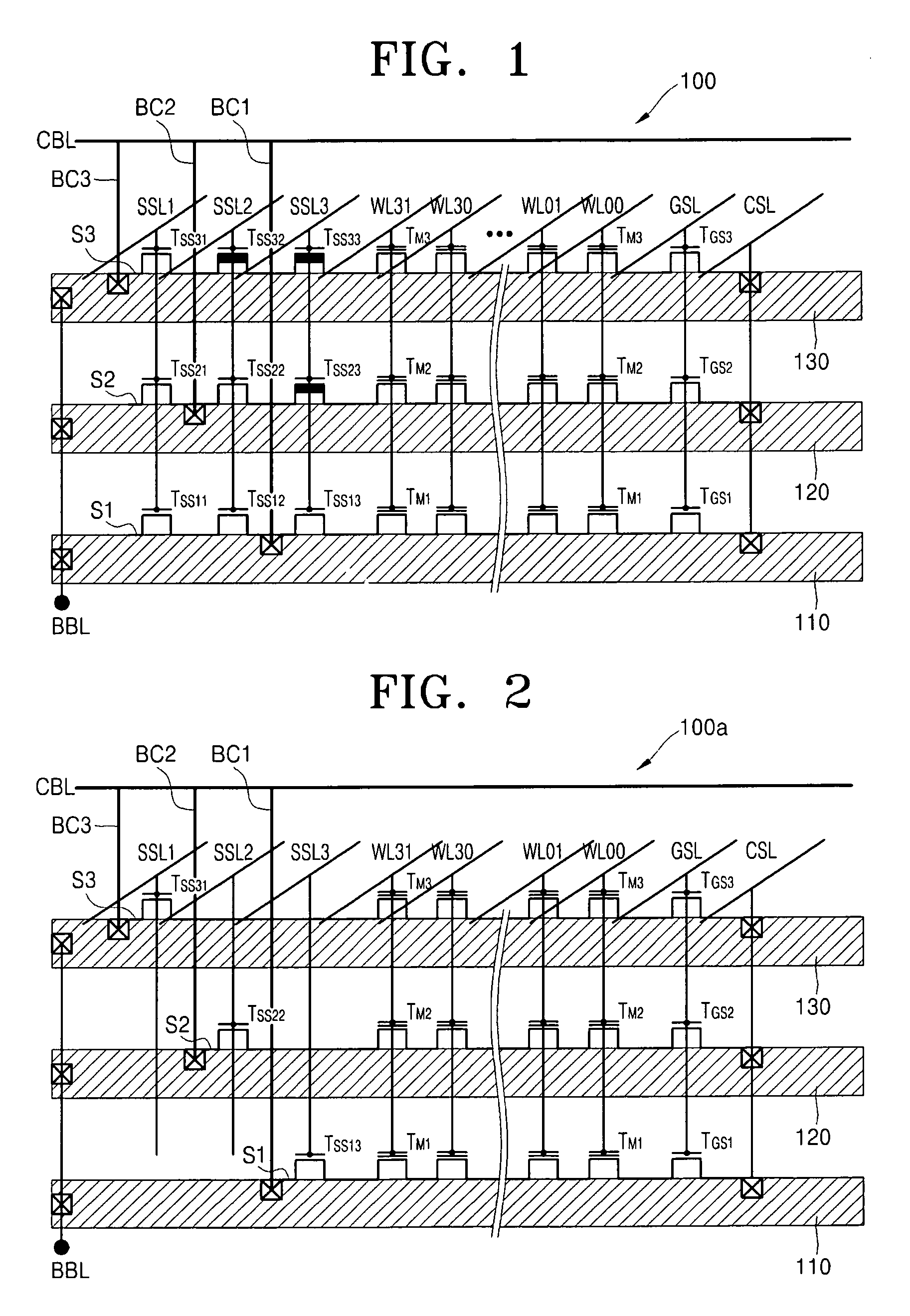
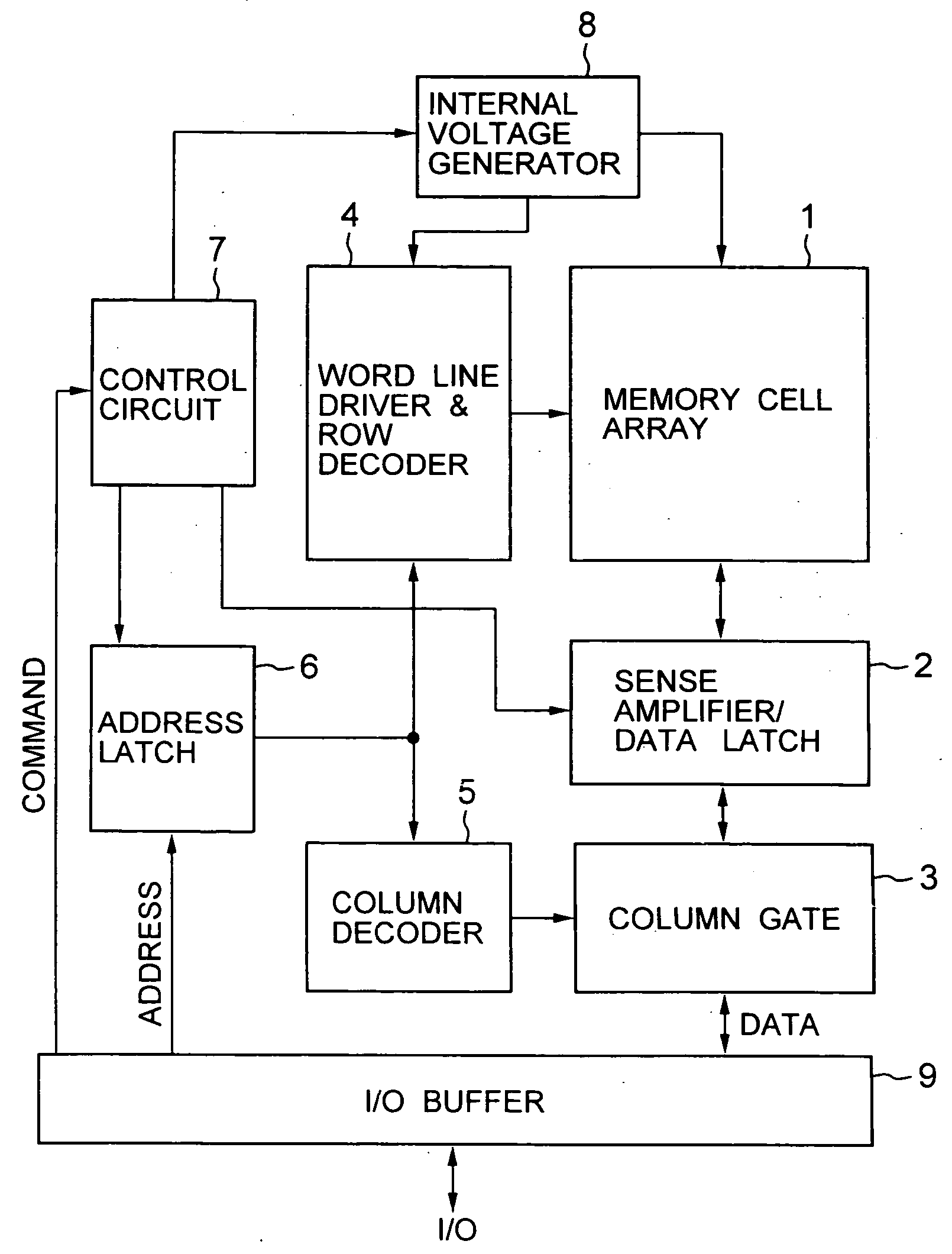
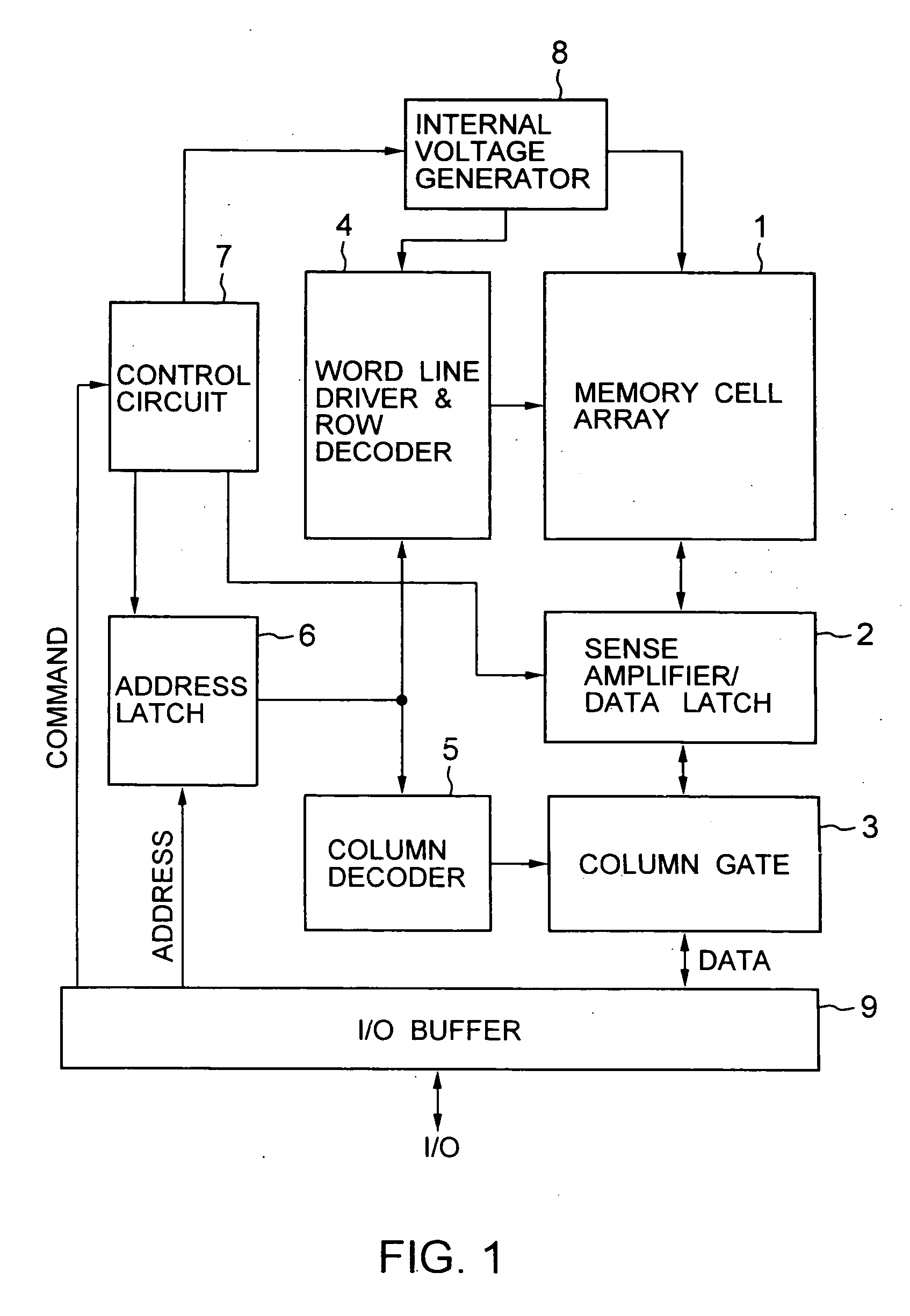
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20020126532A1Wrong writing is prevented surelyTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringComputational physics
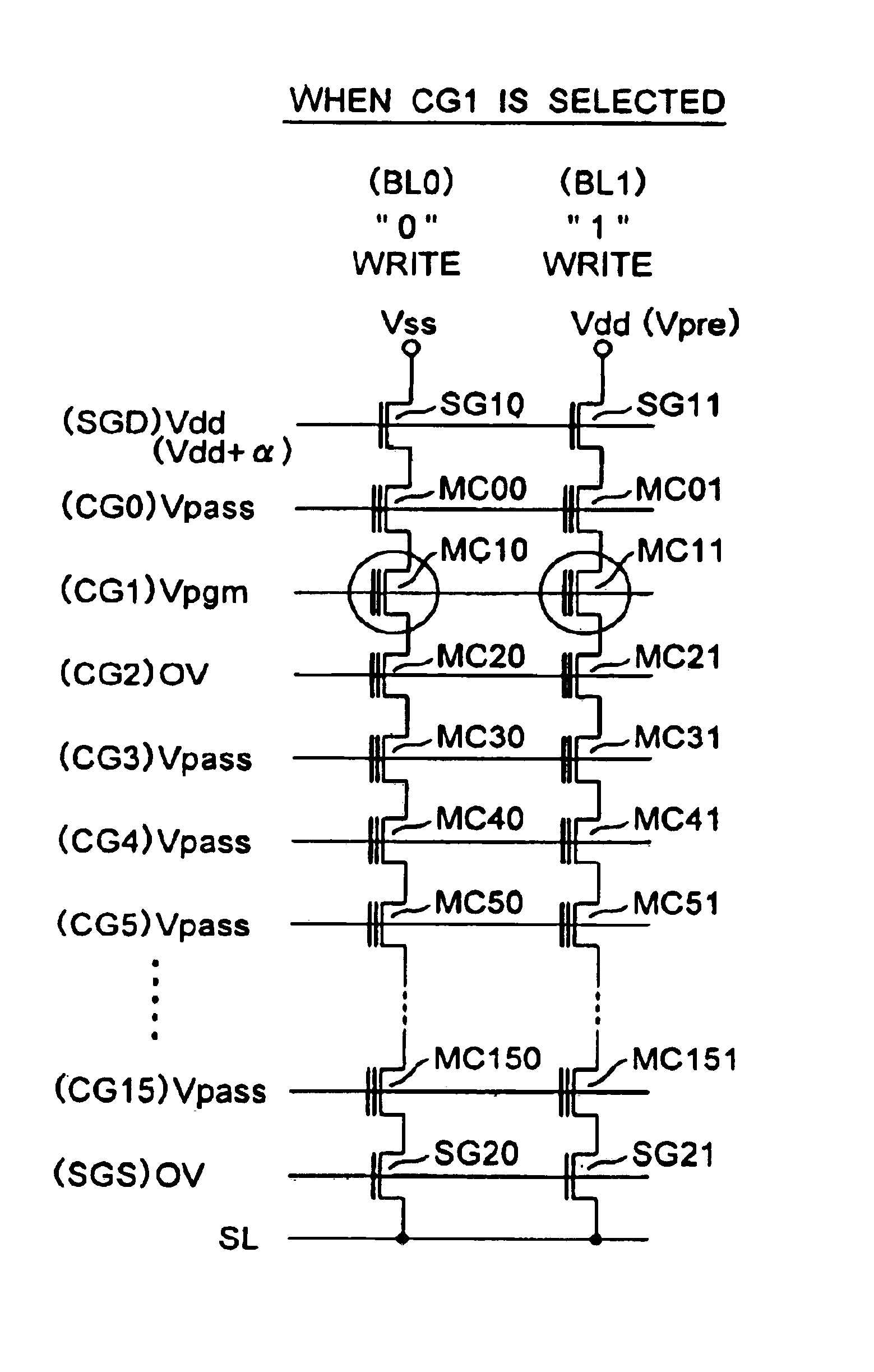
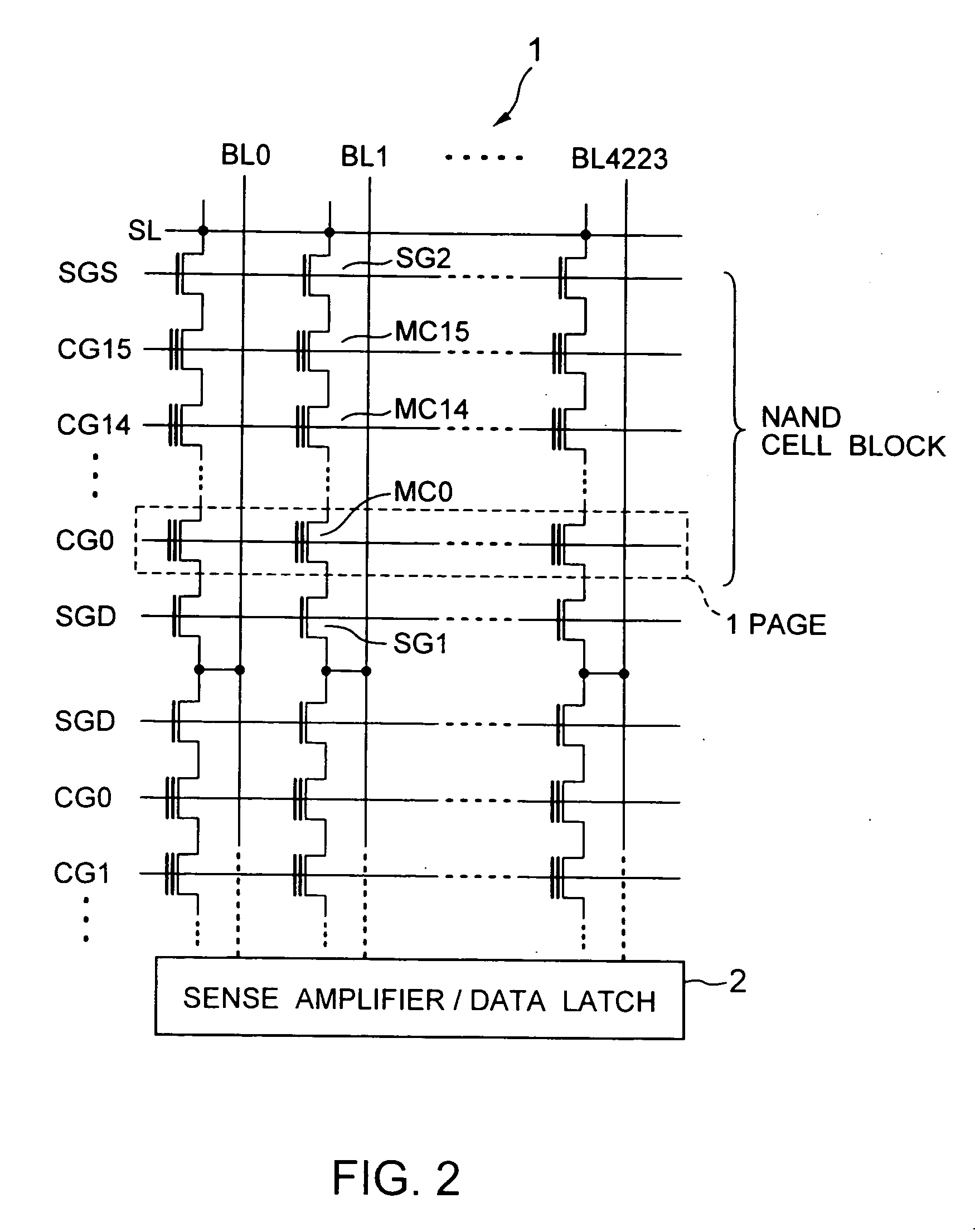
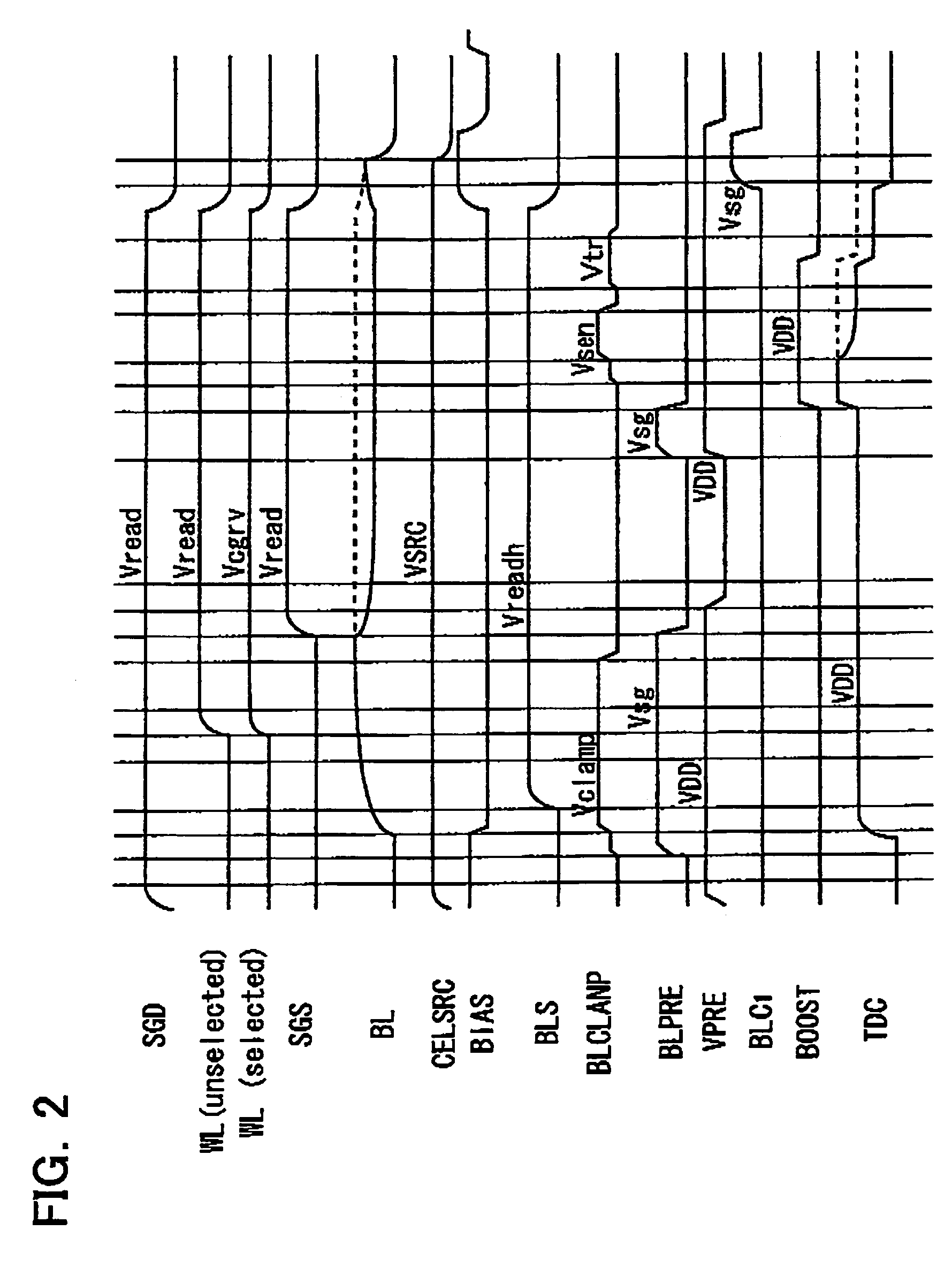
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device having a write mode in which wrong writing is prevented surely. The storage device comprises a NAND cell comprising a plurality of memory transistors connected in series and also connected at one end via a select gate transistor CG1 to a bit line BL and at the other end via a select gate transistor SG2 to a common source line SL. A write voltage Vpgm is applied to a control gate of a selected memory transistor in the NAND cell and Vss is applied to the controls gates of non-select memory transistors each adjacent to the selected memory transistor to thereby write data into the select memory transistor. When a second memory transistor from the bit line BL side is selected in the writing operation, a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gate of a first non-selected memory transistor from the bit line BL side, and a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gates of third and subsequent non-selected memory transistors from the bit line BL side.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
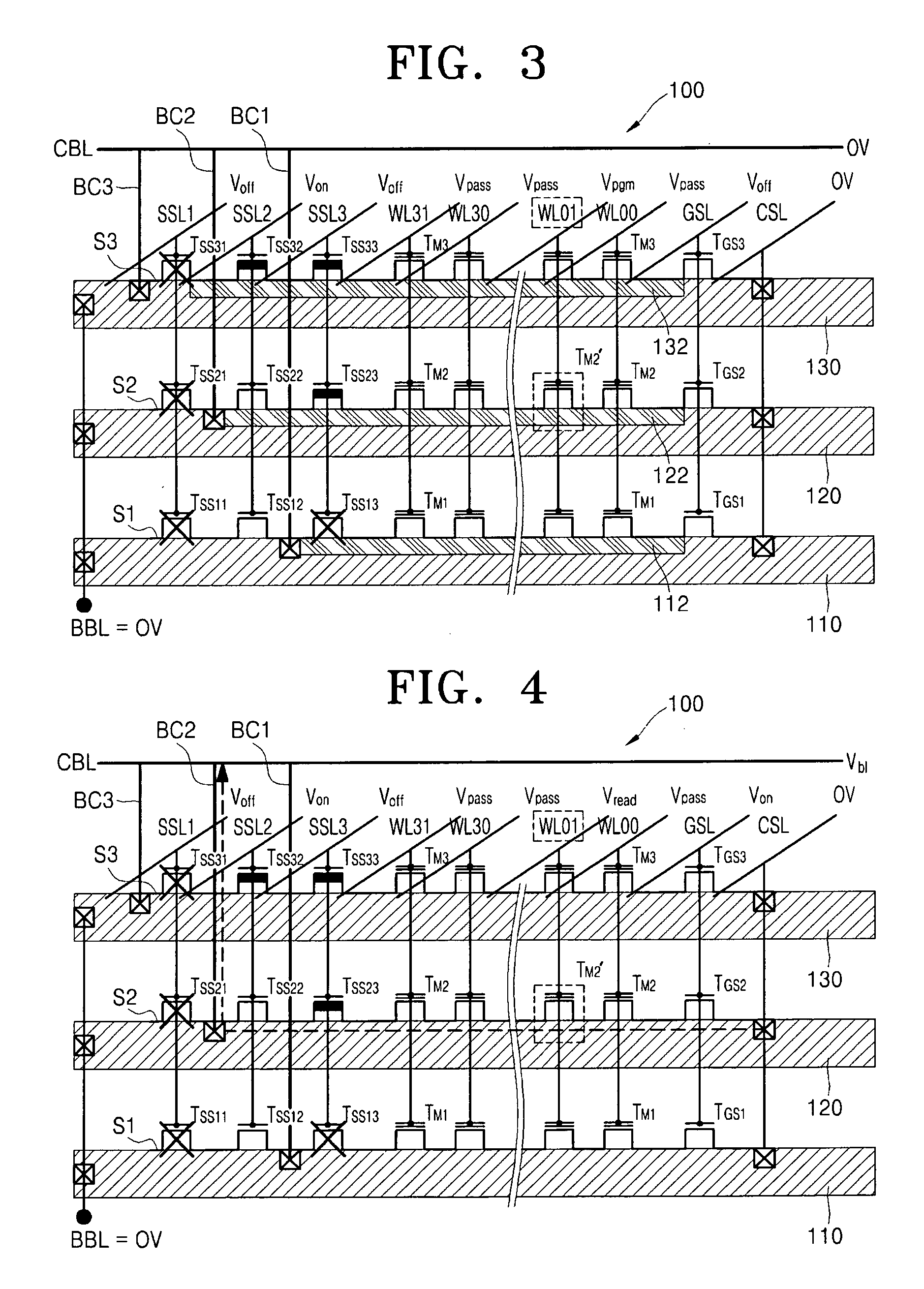
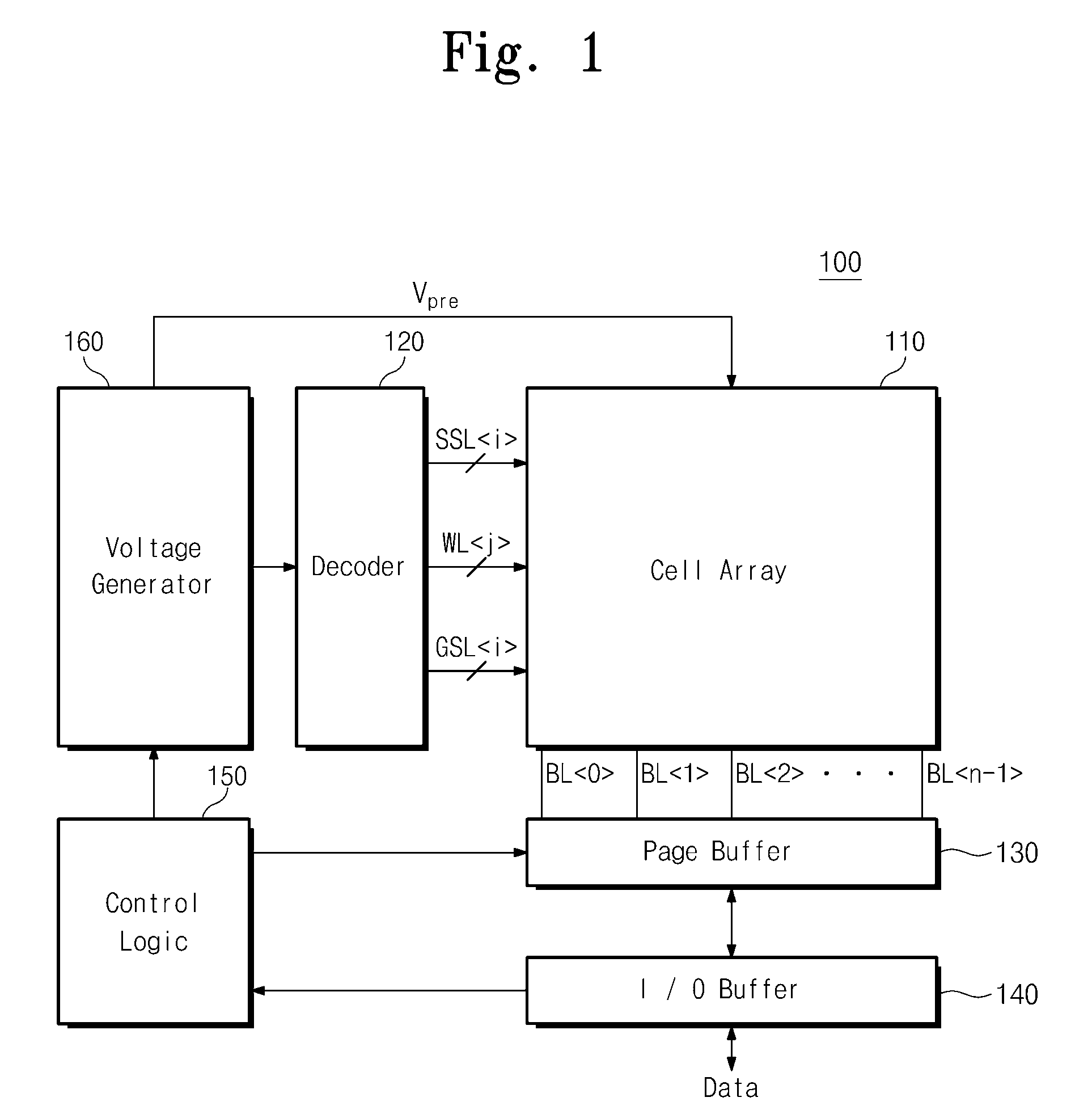
Semiconductor memory device and programming method thereof
ActiveUS20110019486A1Improve reliabilityLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceSemiconductor
A programming method of a semiconductor memory device includes charging a channel of an inhibit string to a precharge voltage provided to the common source line and boosting the charged channel by providing a wordline voltage to the cell strings. The inhibit string is connected to a program bitline among the bitlines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
NAND type non-volatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS6859394B2Wrong writing is prevented surelyTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringCommon source line
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device having a write mode in which wrong writing is prevented surely. The storage device comprises a NAND cell comprising a plurality of memory transistors connected in series and also connected at one end via a select gate transistor CG1 to a bit line BL and at the other end via a select gate transistor SG2 to a common source line SL. A write voltage Vpgm is applied to a control gate of a selected memory transistor in the NAND cell and Vss is applied to the controls gates of non-select memory transistors each adjacent to the selected memory transistor to thereby write data into the select memory transistor. When a second memory transistor from the bit line BL side is selected in the writing operation, a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gate of a first non-selected memory transistor from the bit line BL side, and a medium voltage Vpass is applied to the control gates of third and subsequent non-selected memory transistors from the bit line BL side.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
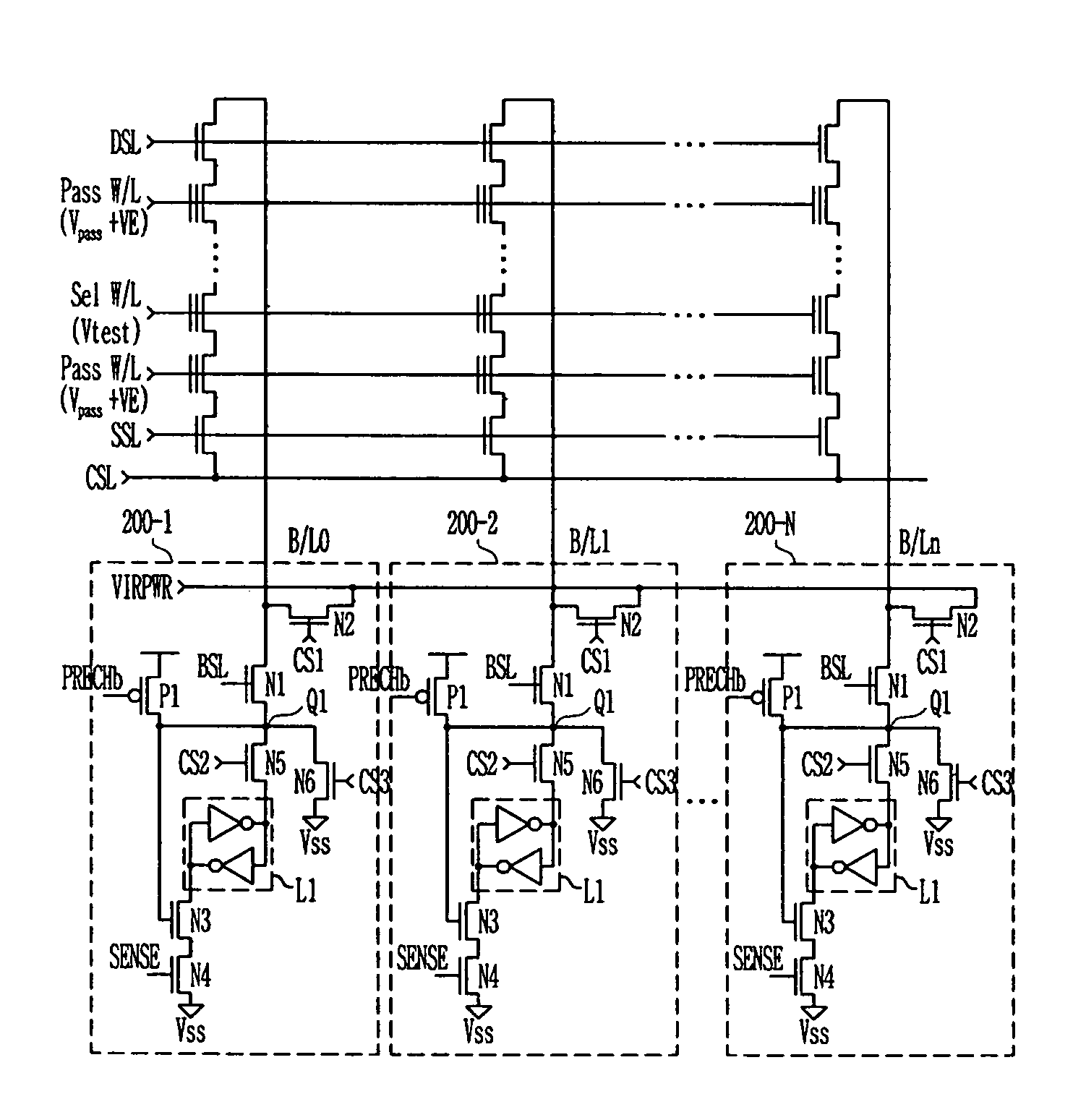
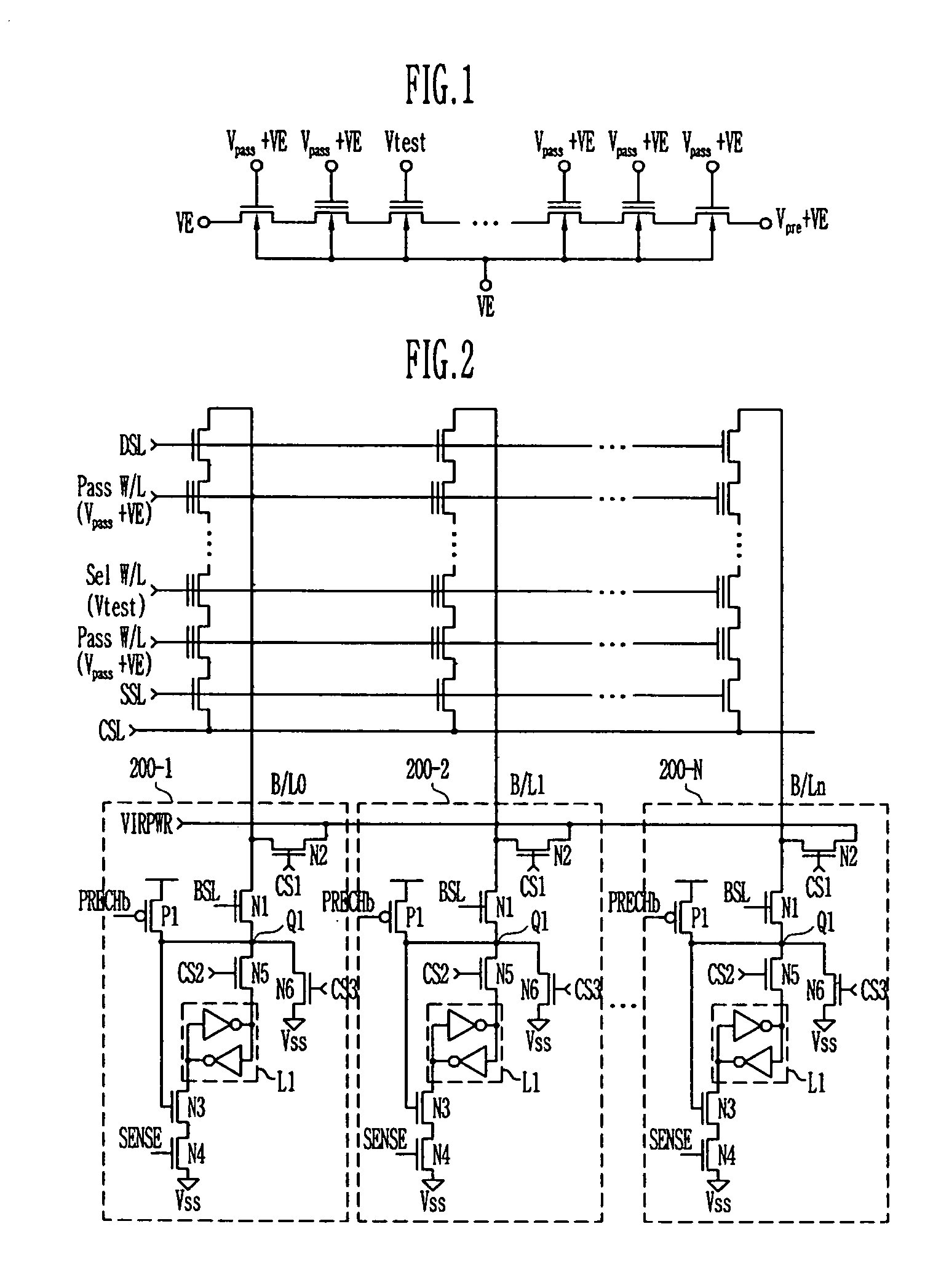
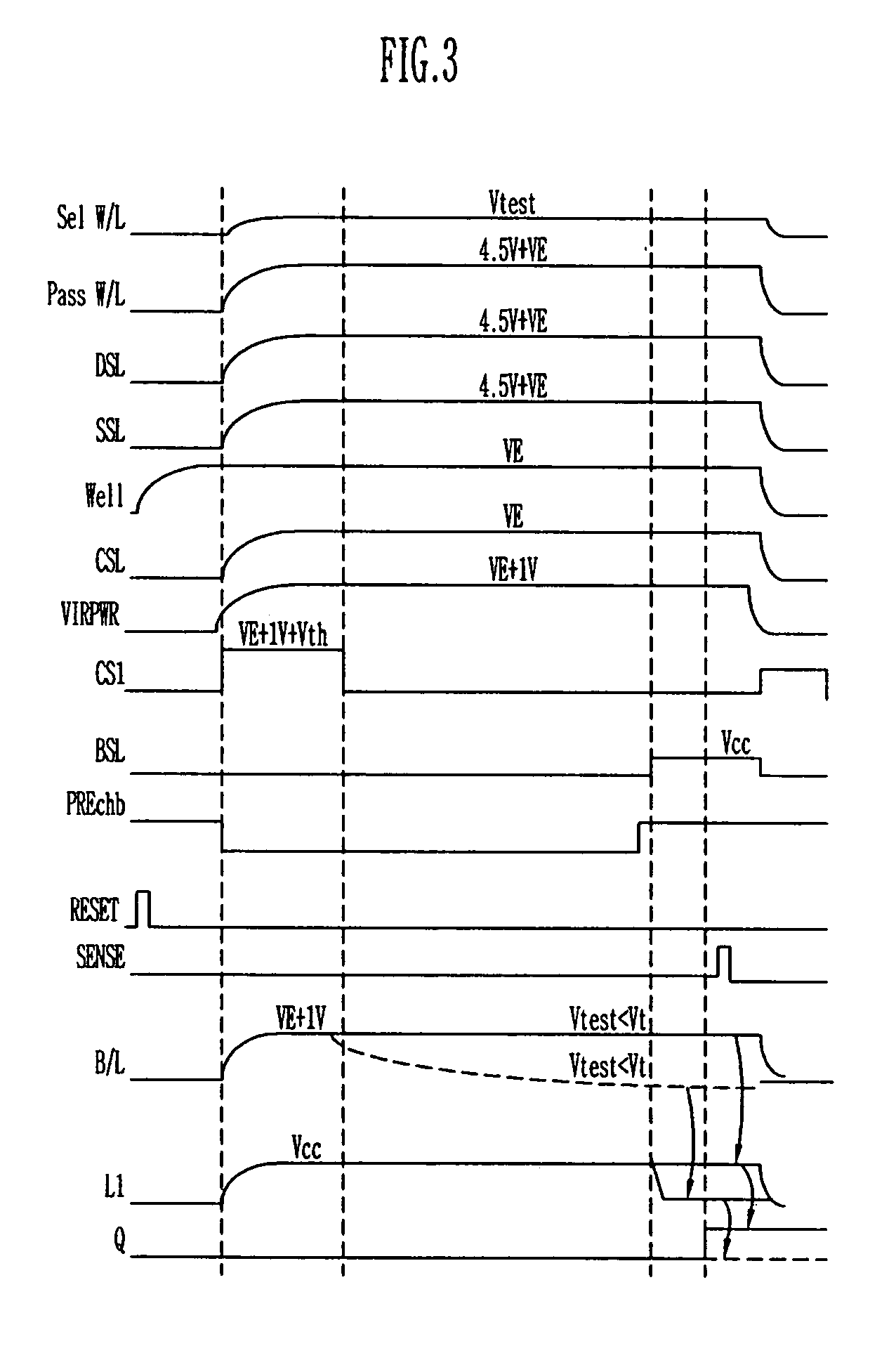
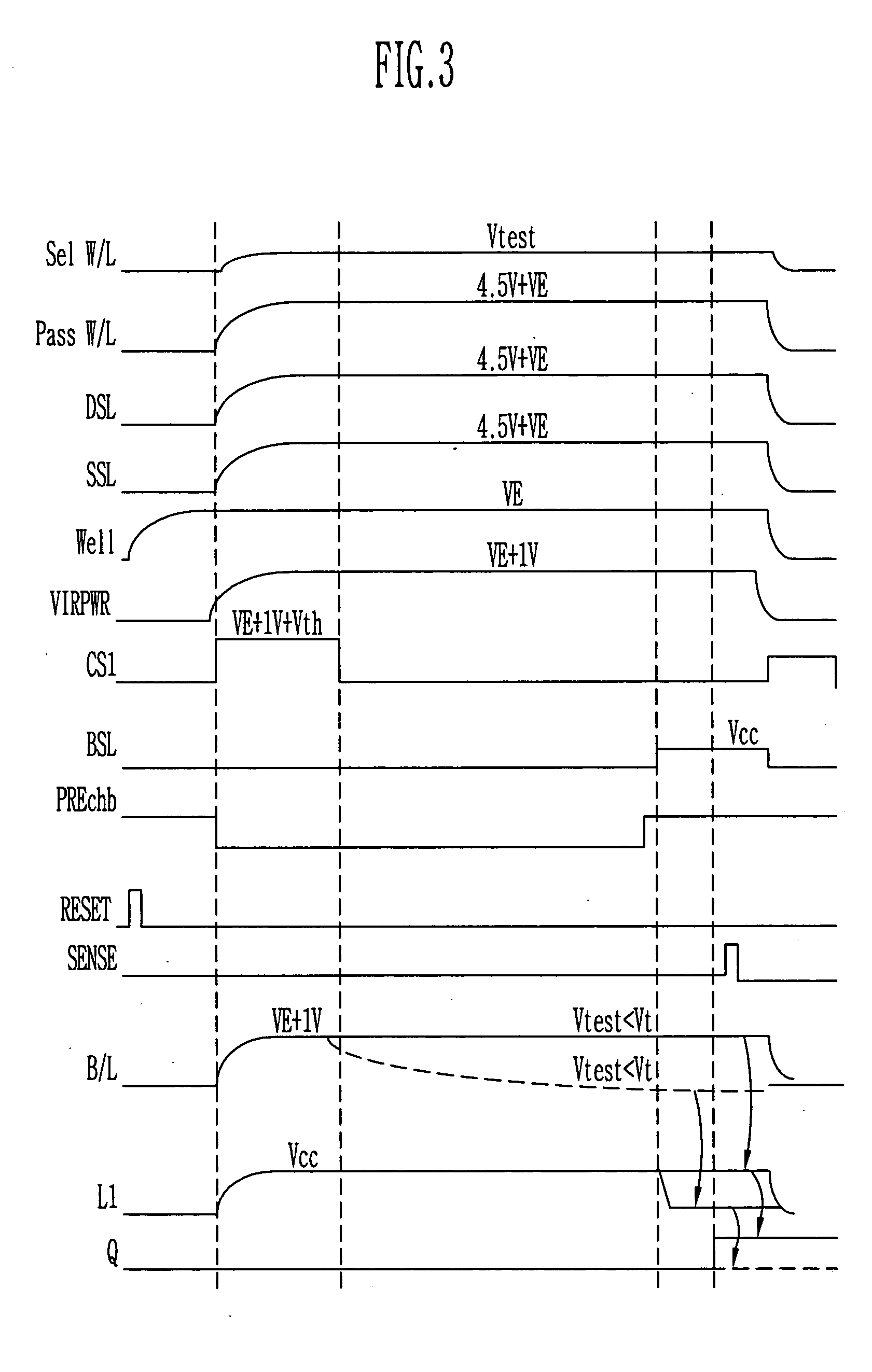
Method of measuring threshold voltage for a NAND flash memory device
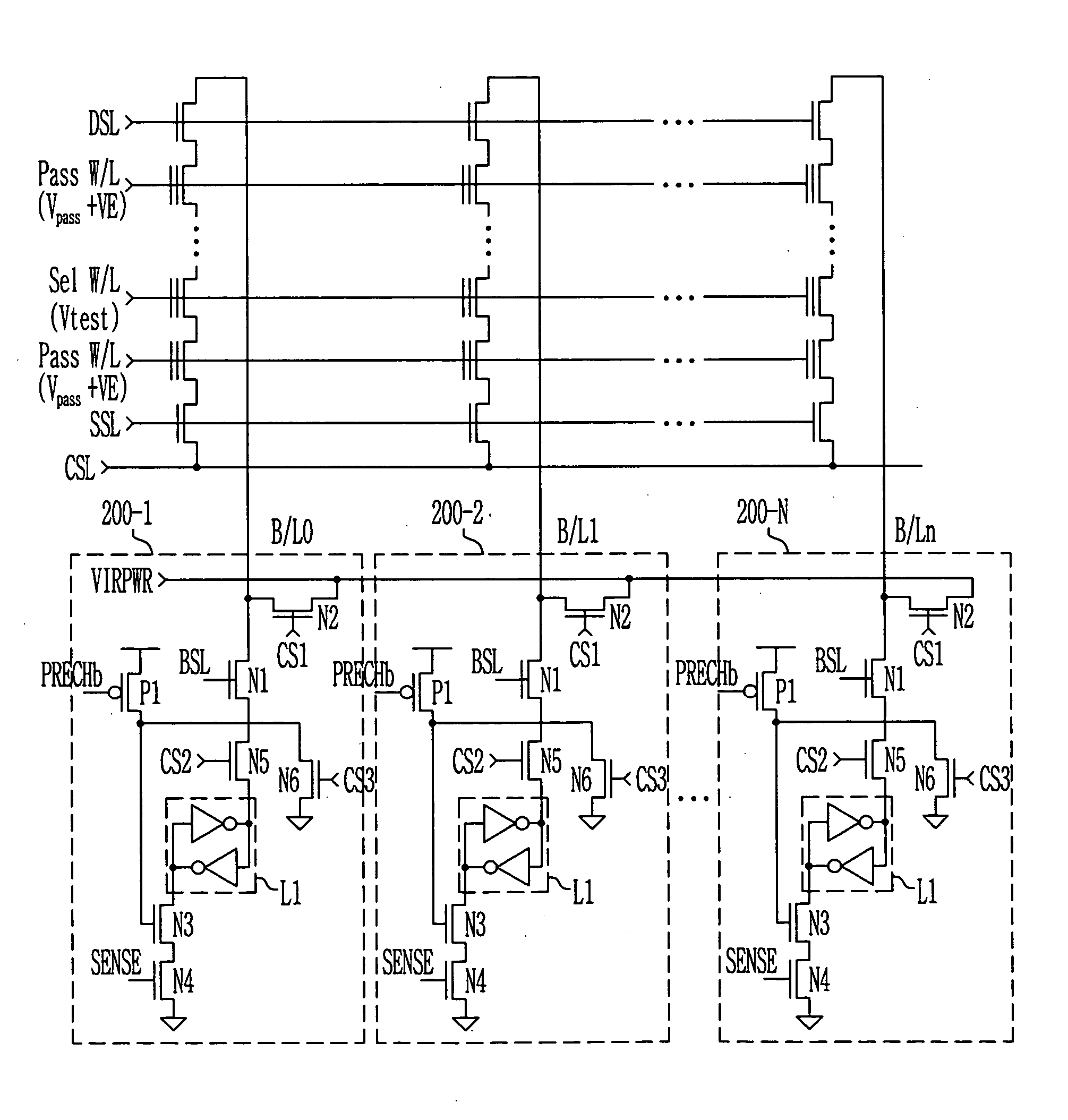
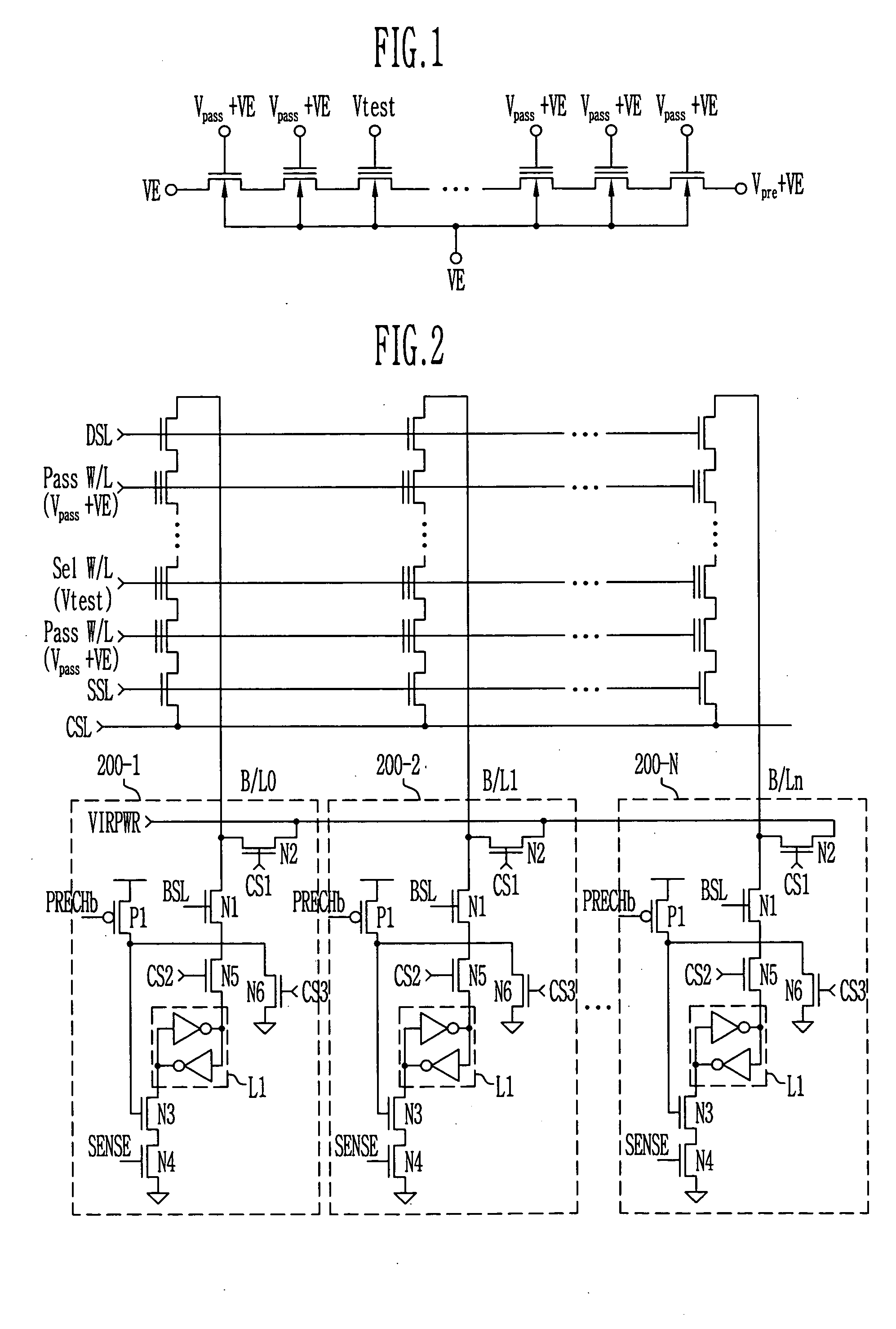
Provided is a method of measuring threshold voltages in a NAND flash memory device. In the method, a test voltage is applied to a wordline of selected memory cells to measure a distribution profile of threshold voltages of memory cells. A voltage summing up a pass voltage and an operation voltage is applied to wordlines of deselected cells. The operation voltage is applied to a well and a common source line. A voltage summing up a precharge voltage and the operation voltage is applied to a bitline. After then, a voltage variation on the bitline can be detected to measure a threshold voltage of a memory cell. A negative threshold voltage can be measured by applying a positive voltage with reference to a voltage, as the threshold voltage of the memory cell, set by subtracting the operation voltage from the test voltage in accordance with the bitline voltage variation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
NAND flash memory device and method of programming the same
Provided is directed to a NAND flash memory device and a method of programming the same, which can improve integration of the device by removing a common source line connecting with a source line coupled to a plurality of cell blocks, control a voltage applied to a source line by each cell block, and rise a precharge level in a channel area by applying a pumping voltage to the source line relatively having low capacitance instead of a bitline having a large capacitance, and as a result of those, the NAND flash memory device can reduce disturbance, use a lower voltage than a power supply voltage on the bitline, which leads to reduce a current consumption.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
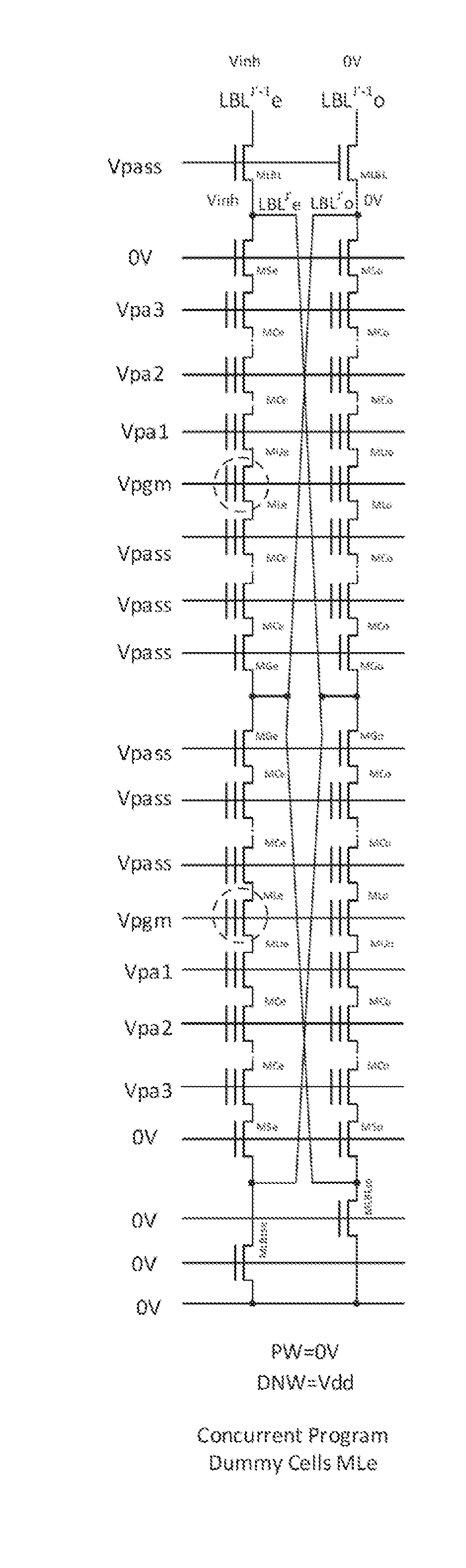
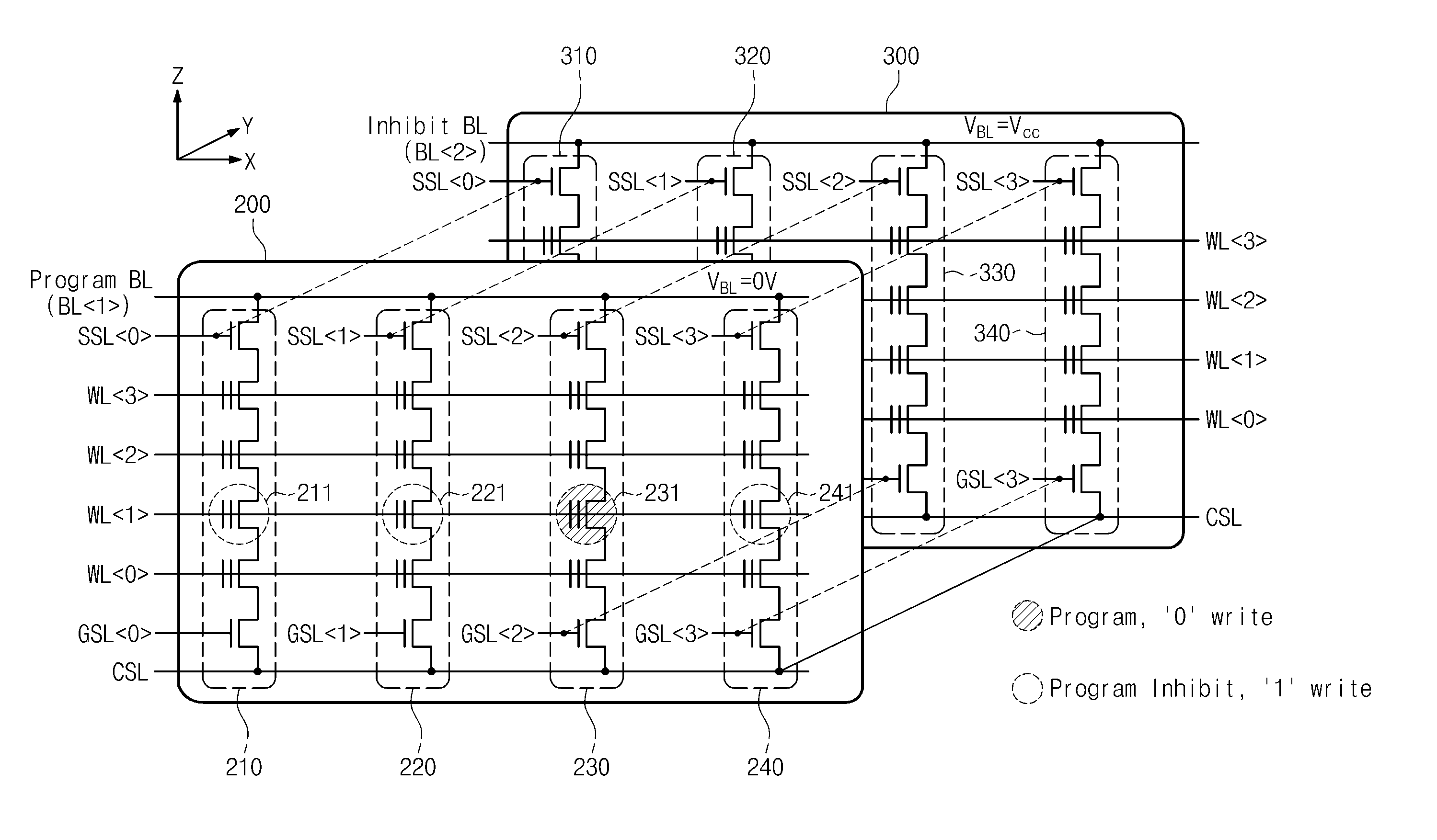
Vsl-based vt-compensation and analog program scheme for NAND array without csl
ActiveUS20160049192A1Lower latencyIncrease in sizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageCommon source lineTheoretical computer science
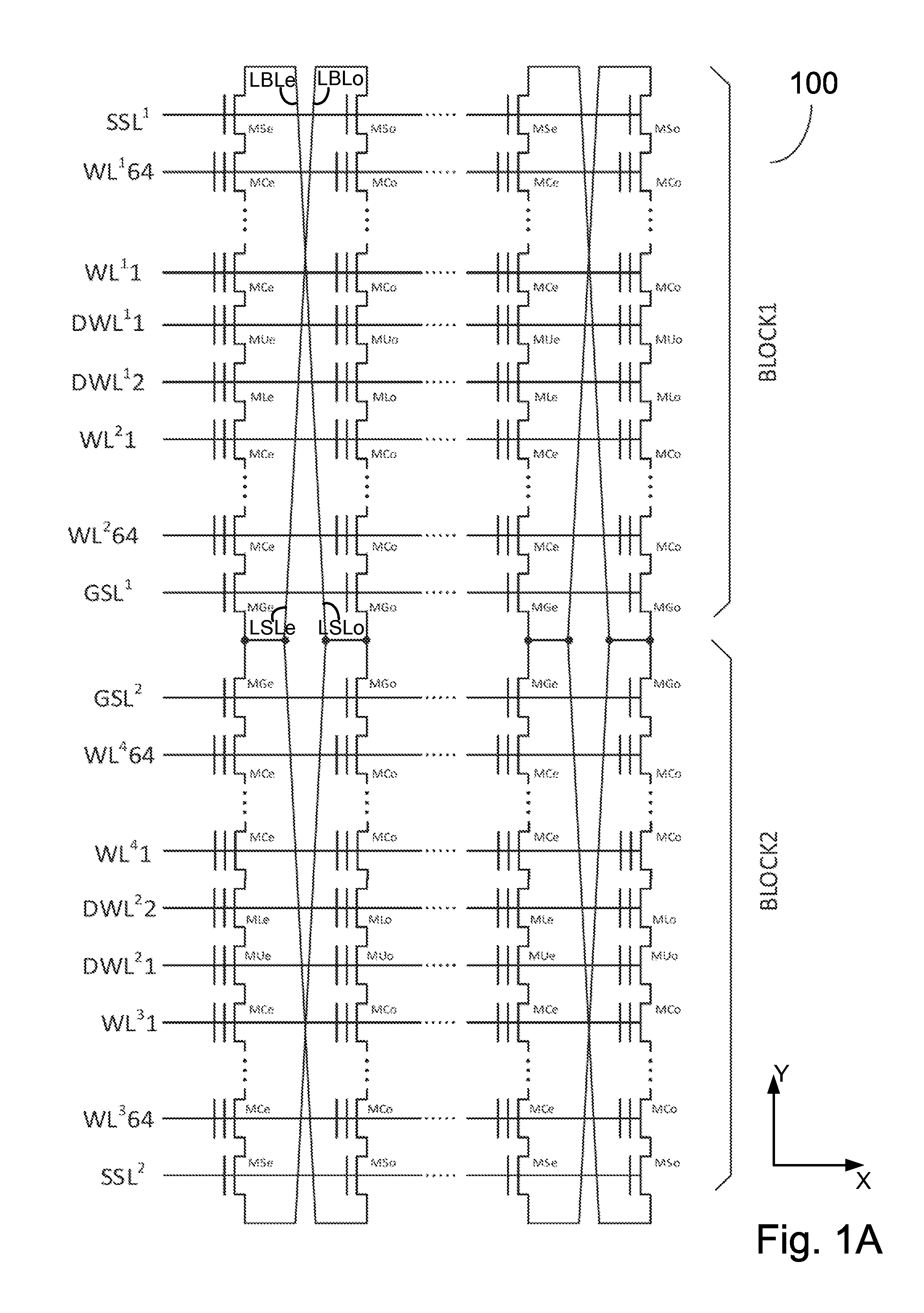
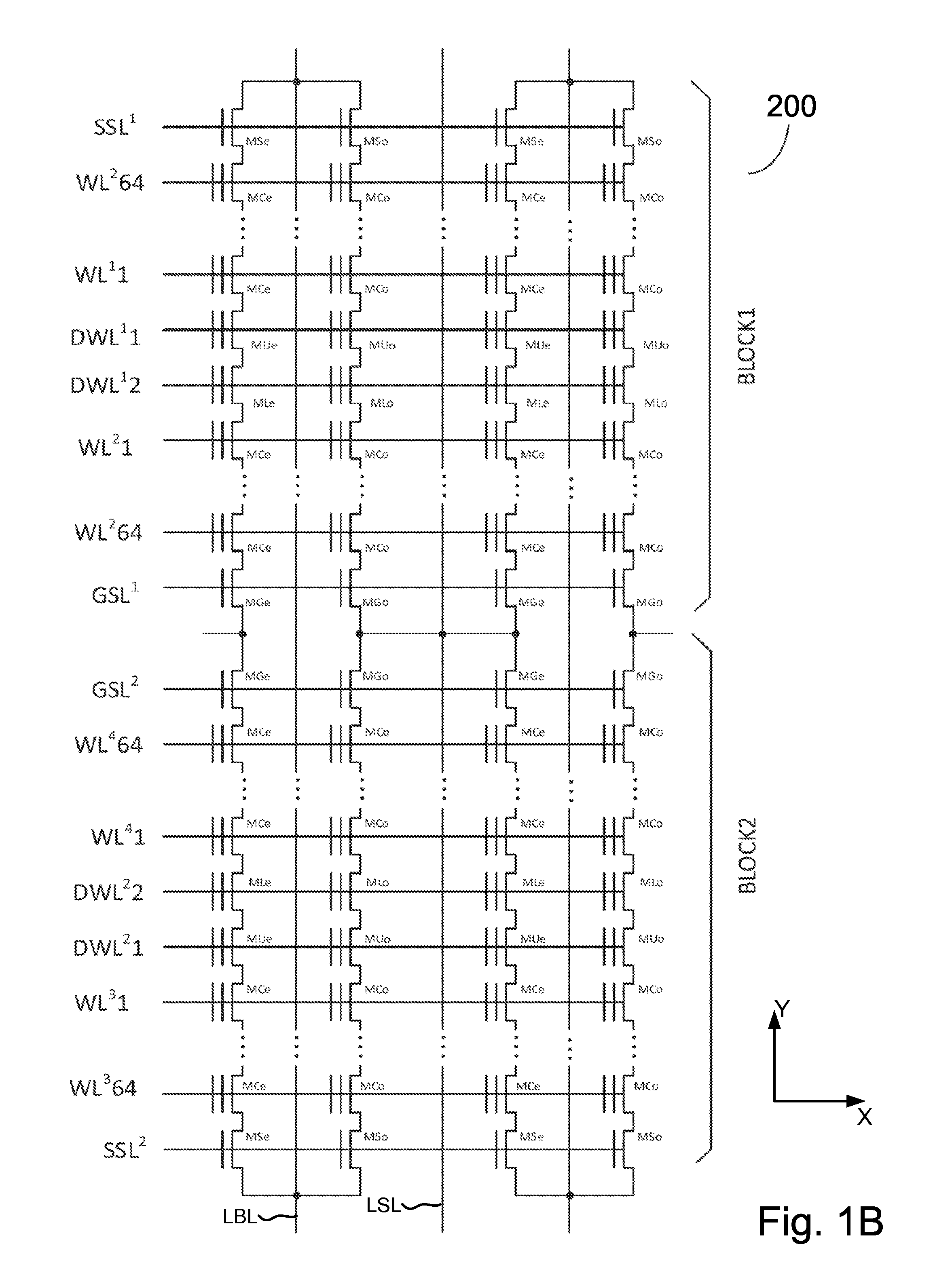
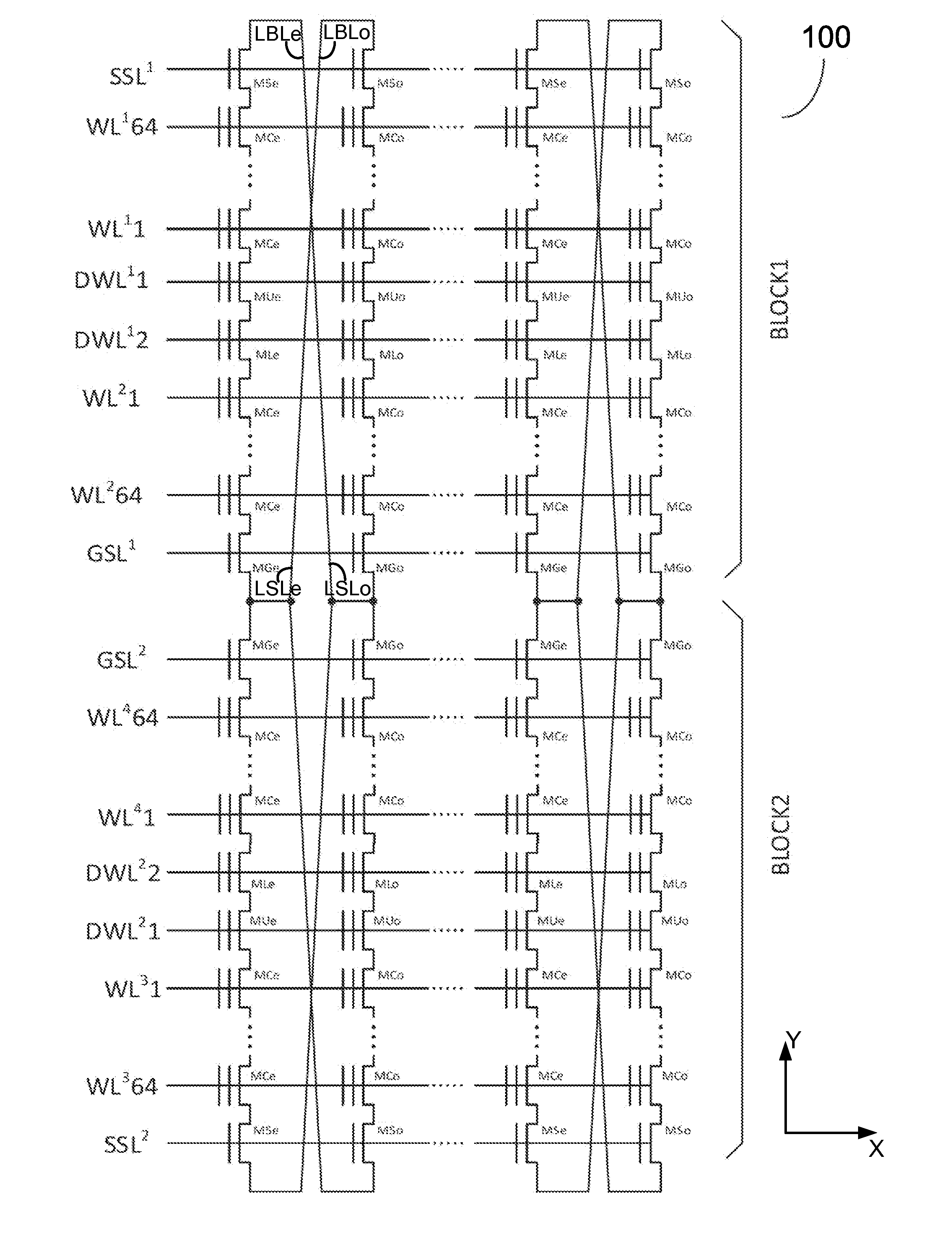
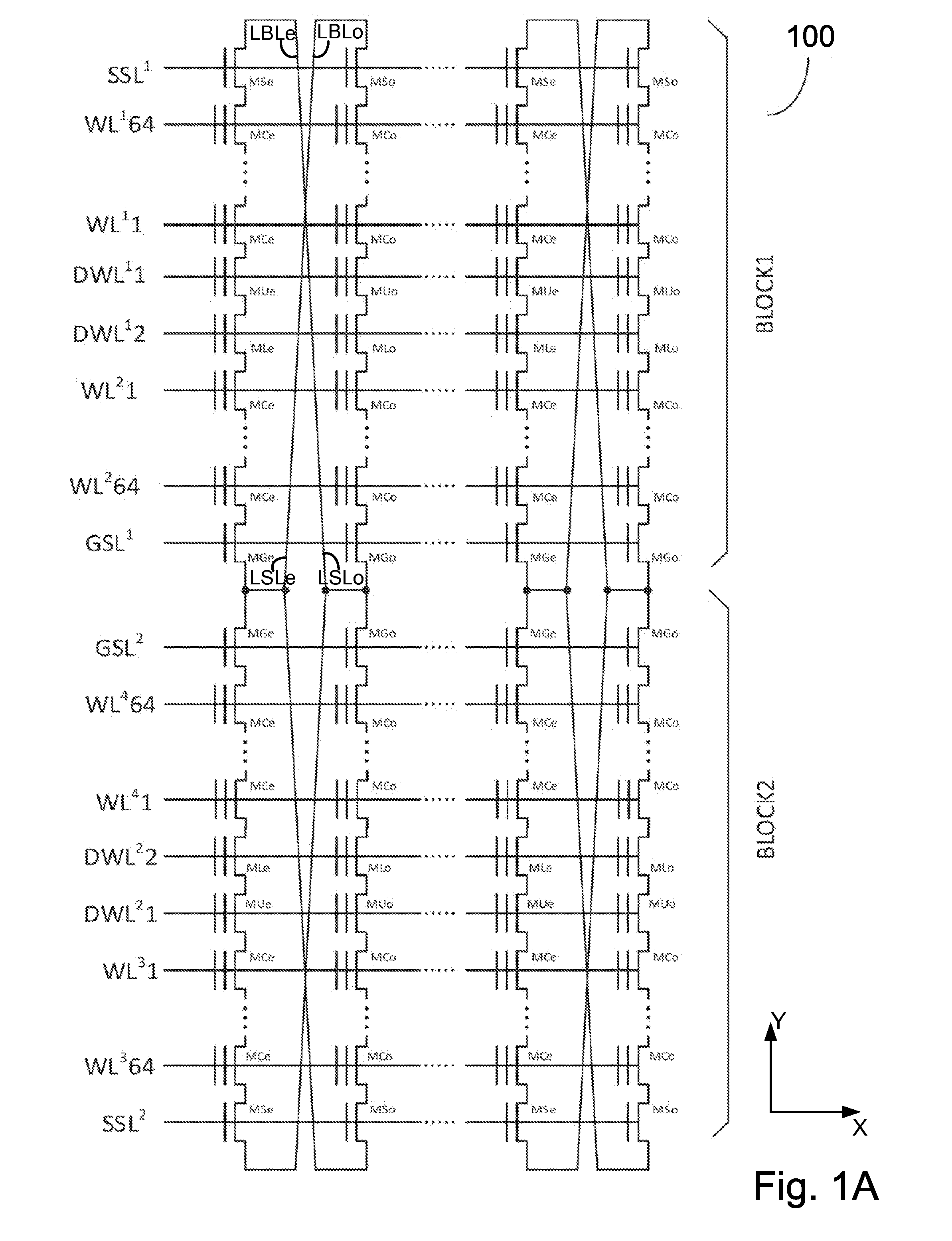
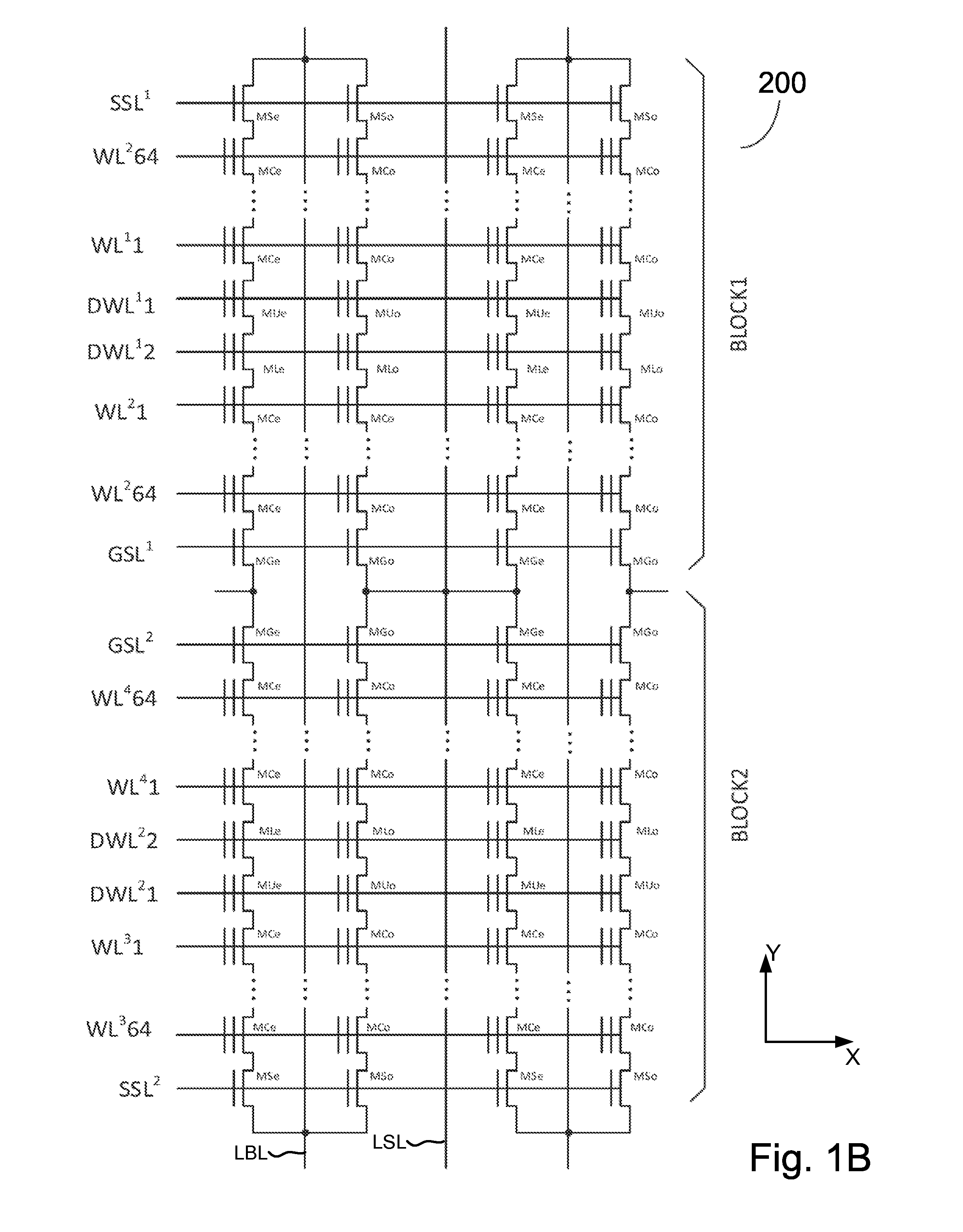
A YUKAI NAND array comprising multiple strings of all TLC and mixed TLC+SLC memory cells associated with hierarchical global / local bit lines (GBL / LBL) and each string being associated with one LBL and having adjacent LBL as a dedicated local source line (LSL) with full BL-shielding without wasting extra silicon area and without a common source line to connect all strings. Each of the LBLs is interleavingly associated with either an Odd or Even string selected via one pair of dummy cells inserted in each string and is used as one on-chip PCACHE register with full BL-shielding to perform concurrent ABL, AnP and Alt-WL program under multi-passes program schemes with LBL program voltage compensations and half-BL Odd / Even program-verify and read operations with individual VSL-based Vt-compensation to mitigate high WL-WL and BL-BL coupling effects.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Method of measuring threshold voltage for a NAND flash memory device
Provided is a method of measuring threshold voltages in a NAND flash memory device. In the method, a test voltage is applied to a wordline of selected memory cells to measure a distribution profile of threshold voltages of memory cells. A voltage summing up a pass voltage and an operation voltage is applied to wordlines of deselected cells. The operation voltage is applied to a well and a common source line. A voltage summing up a precharge voltage and the operation voltage is applied to a bitline. After then, a voltage variation on the bitline can be detected to measure a threshold voltage of a memory cell. A negative threshold voltage can be measured by applying a positive voltage with reference to a voltage, as the threshold voltage of the memory cell, set by subtracting the operation voltage from the test voltage in accordance with the bitline voltage variation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
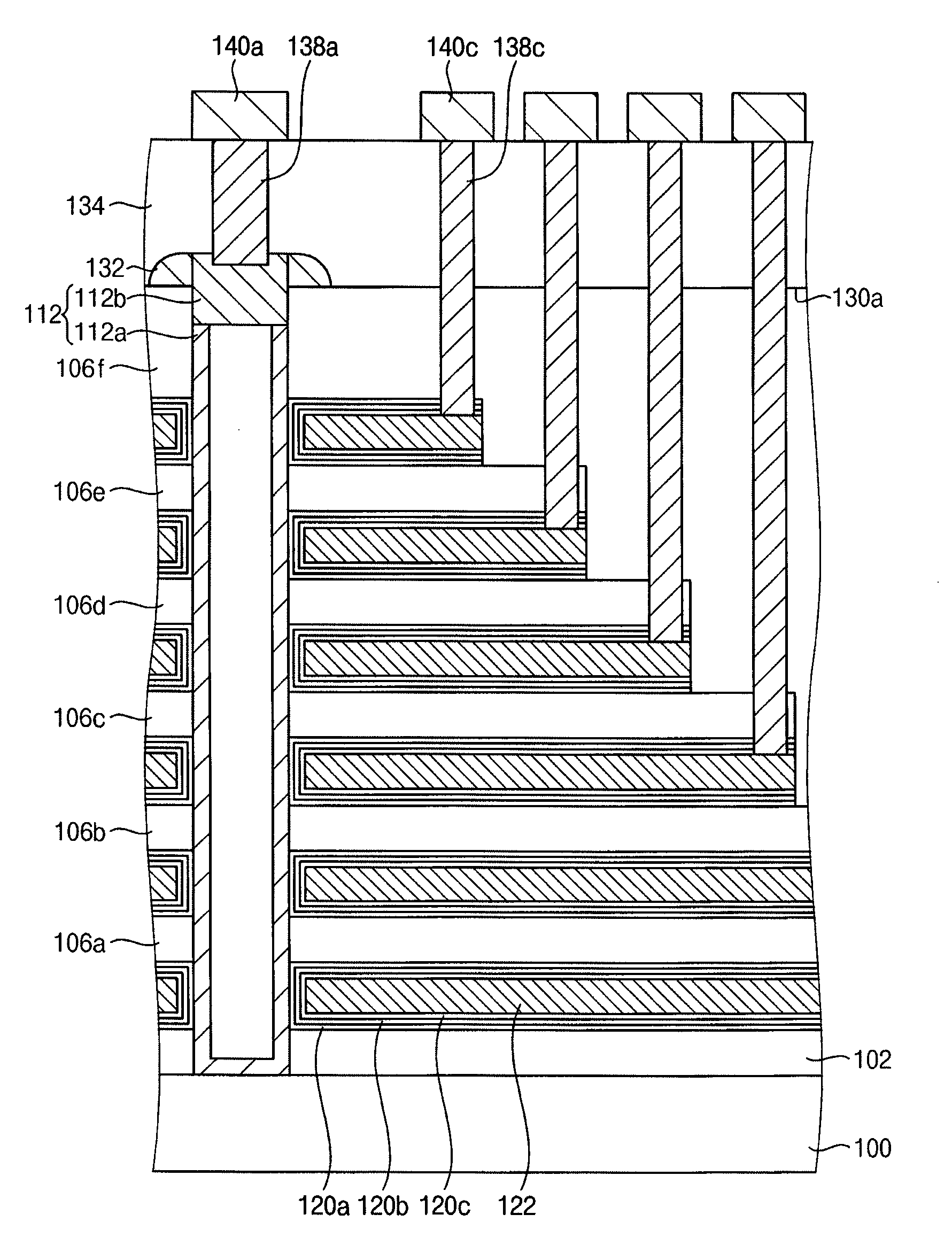
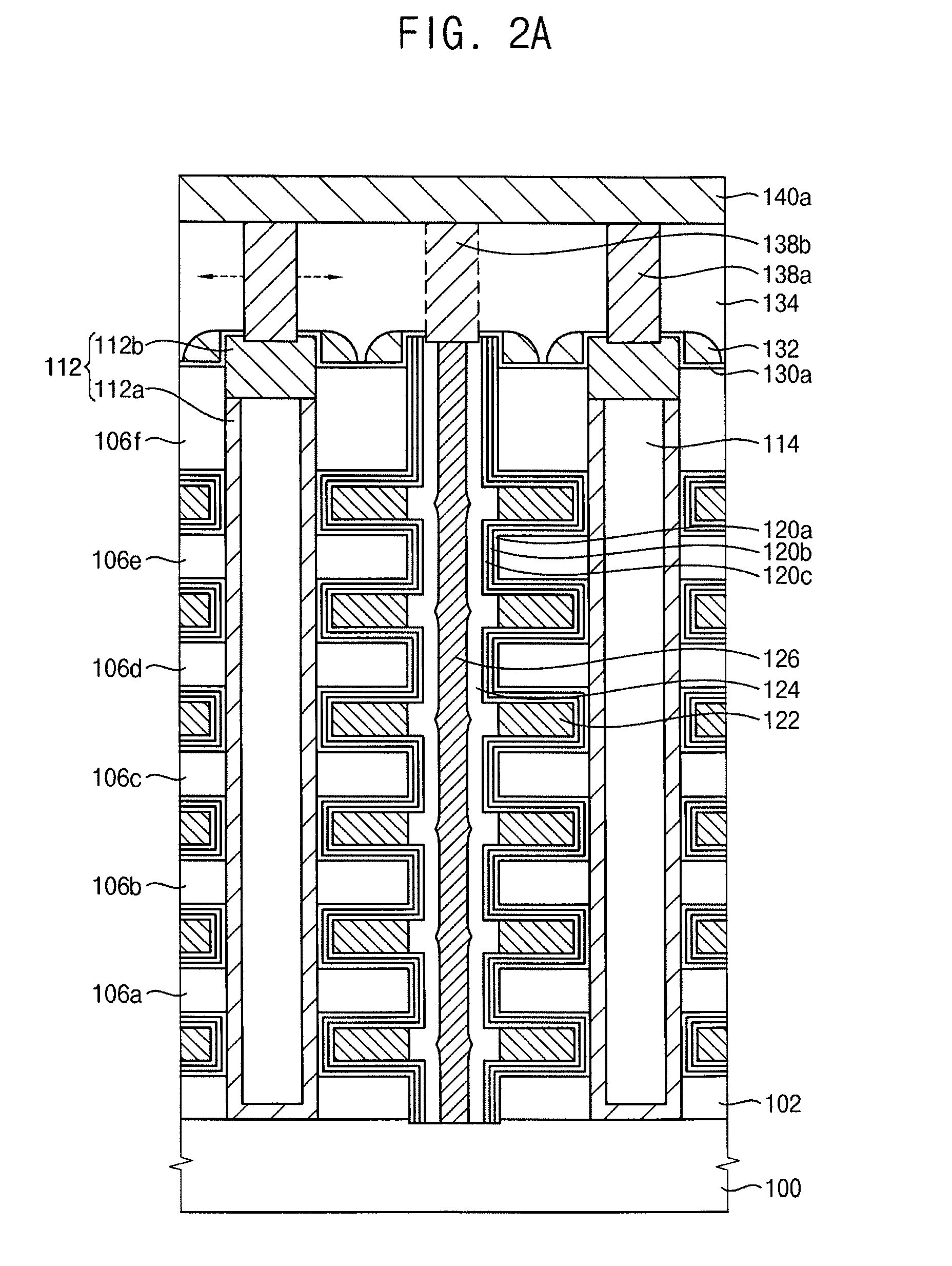
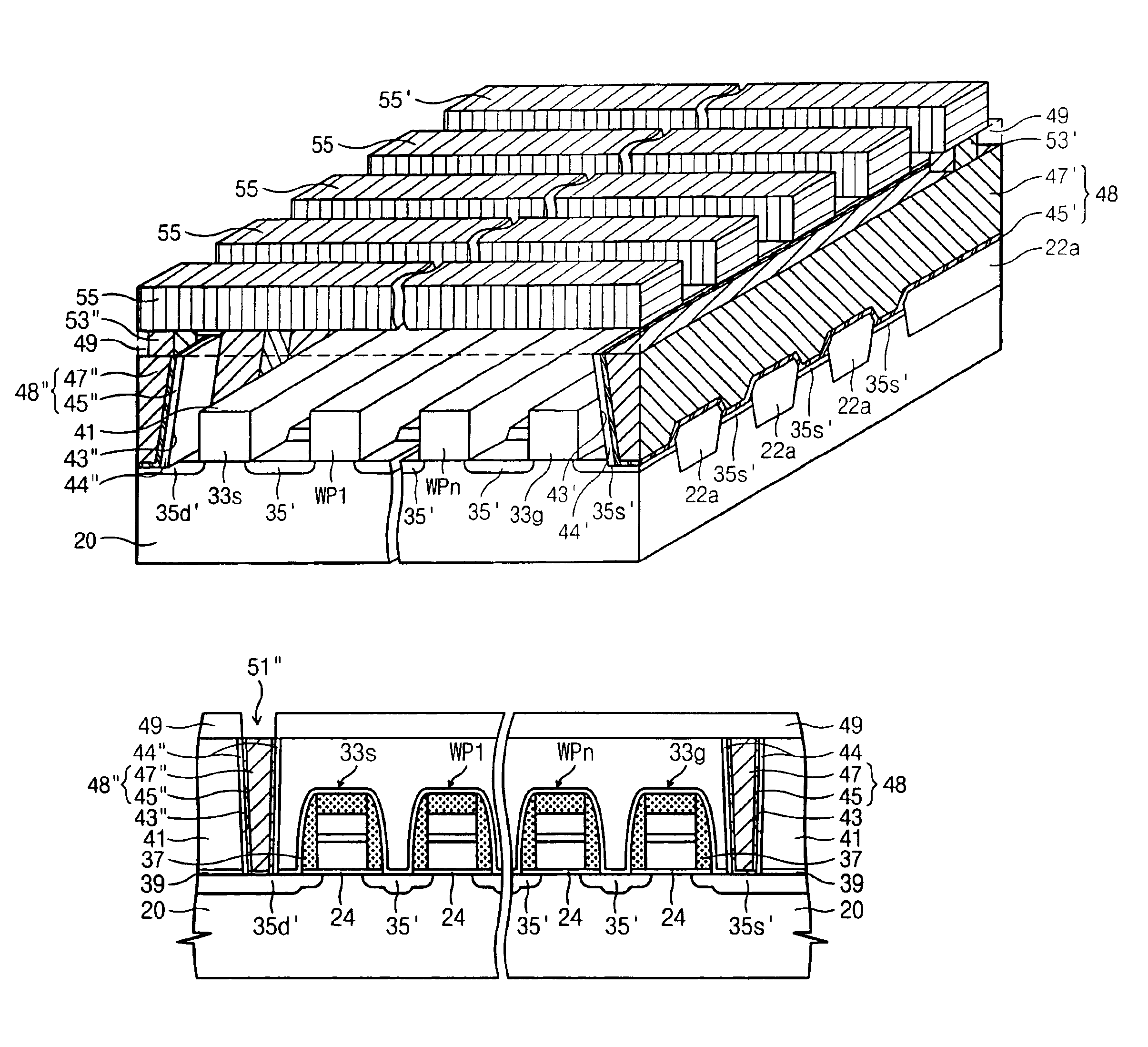
Manufacturing semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20120077320A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor pattern on a substrate, gate structures on sidewalls of the semiconductor pattern, the gate structures being spaced apart from one another, insulating interlayers among the gate structures, wherein an uppermost insulating interlayer is lower than an upper face of the semiconductor pattern, a common source line contacting the substrate and protruding above the uppermost insulating interlayer, an etch stop layer pattern on the semiconductor pattern and on the common source line wherein the common source line protrudes above the uppermost insulating interlayer, an additional insulating interlayer on the uppermost insulating interlayer, and contact plugs extending through the additional insulating interlayer so as to make contact with the semiconductor pattern and the common source line, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
YUKAI VSL-BASED Vt-COMPENSATION FOR NAND MEMORY
ActiveUS20160027504A1Less Yupin coupling effectLess capacitanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageVirtual cellBatch processing
A YUKAI NAND array comprising multiple strings associated with hierarchical global / local bit lines (GBL / LBL) and each string being associated with one LBL and having adjacent LBL as a dedicated local source line (LSL) without a common source line to connect all strings. Each of the LBLs is interleavingly associated with either an Odd or Even string selected via one pair of dummy cells inserted in each string and is used as one on-chip PCACHE register with full BL-shielding without wasting extra silicon area to allow batch-based multiple concurrent MLC All-BL, All-Vtn-Program and Alternative-WL program, Odd / Even read and verify operations with options of providing individual and common VSL-based Vt-compensation and VLBL compensations to mitigate high WL-WL and BL-BL coupling effects. Bias conditions in each string are provided to correctly sense highly-negative erase-verify voltage, multiple negative program-verify voltages and without VDS punch-through, breakdown and body-effect in both boundary and non-boundary WLs cells.
Owner:LEE PETER WUNG
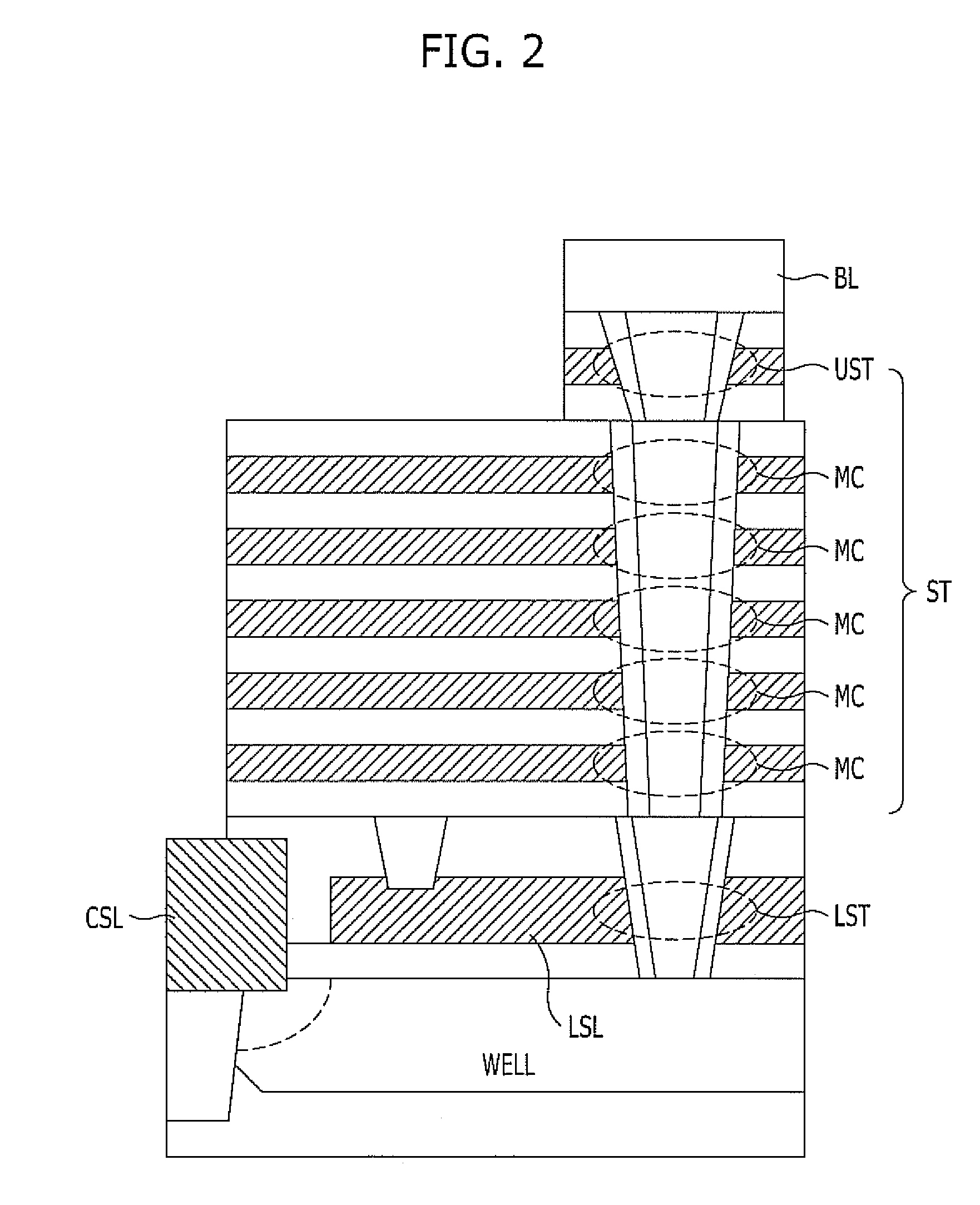
Vertically-integrated nonvolatile memory devices having laterally-integrated ground select transistors
ActiveUS20110310670A1Reduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCouplingThreshold voltage
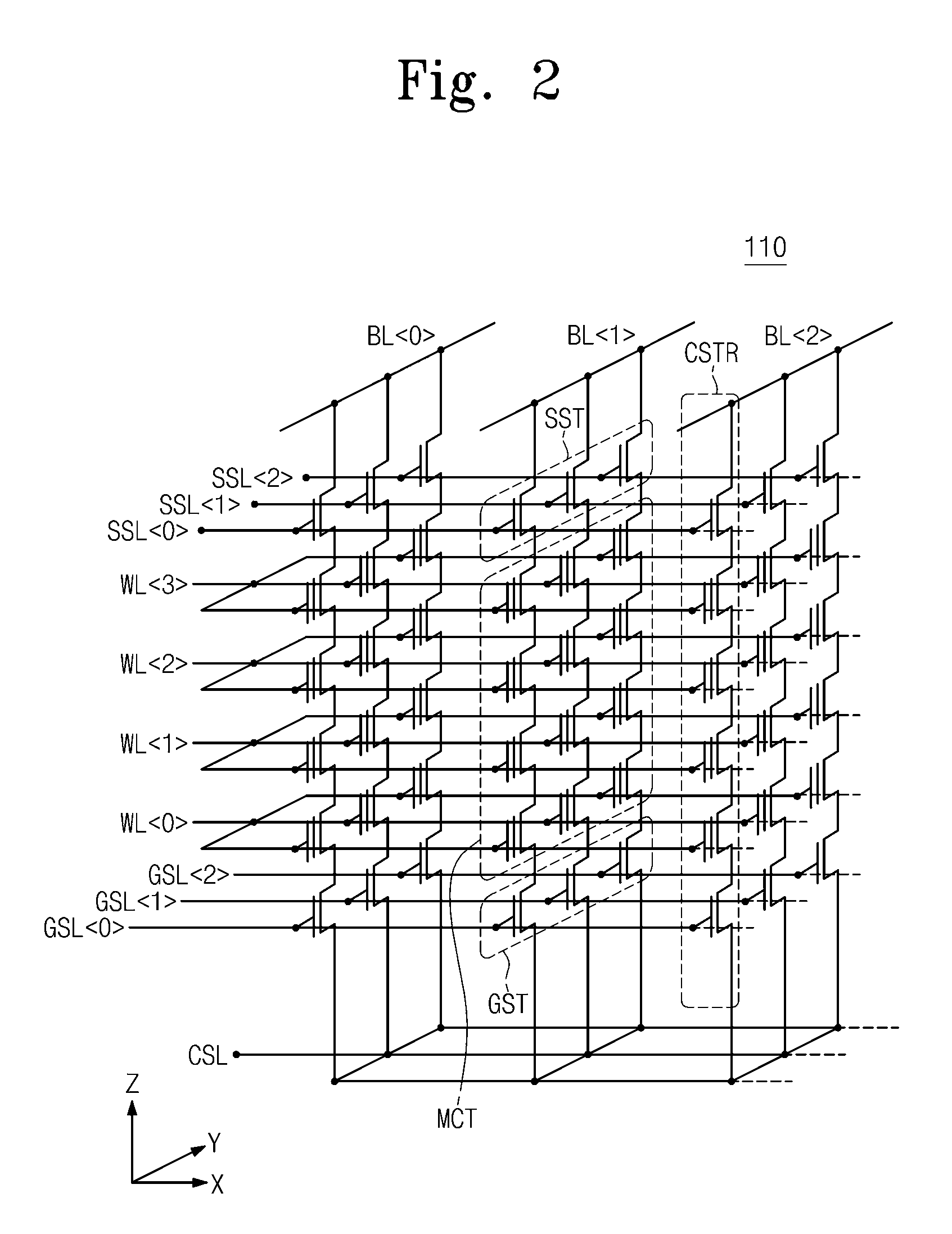
Nonvolatile memory devices utilize vertically-stacked strings of nonvolatile memory cells (e.g., NAND-type strings) that can be selectively coupled to common source lines within a substrate. This selective coupling may be provided by lateral ground select transistors having different threshold voltages that account for different lateral spacings between the vertically-stacked strings of nonvolatile memory cells and the common source lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
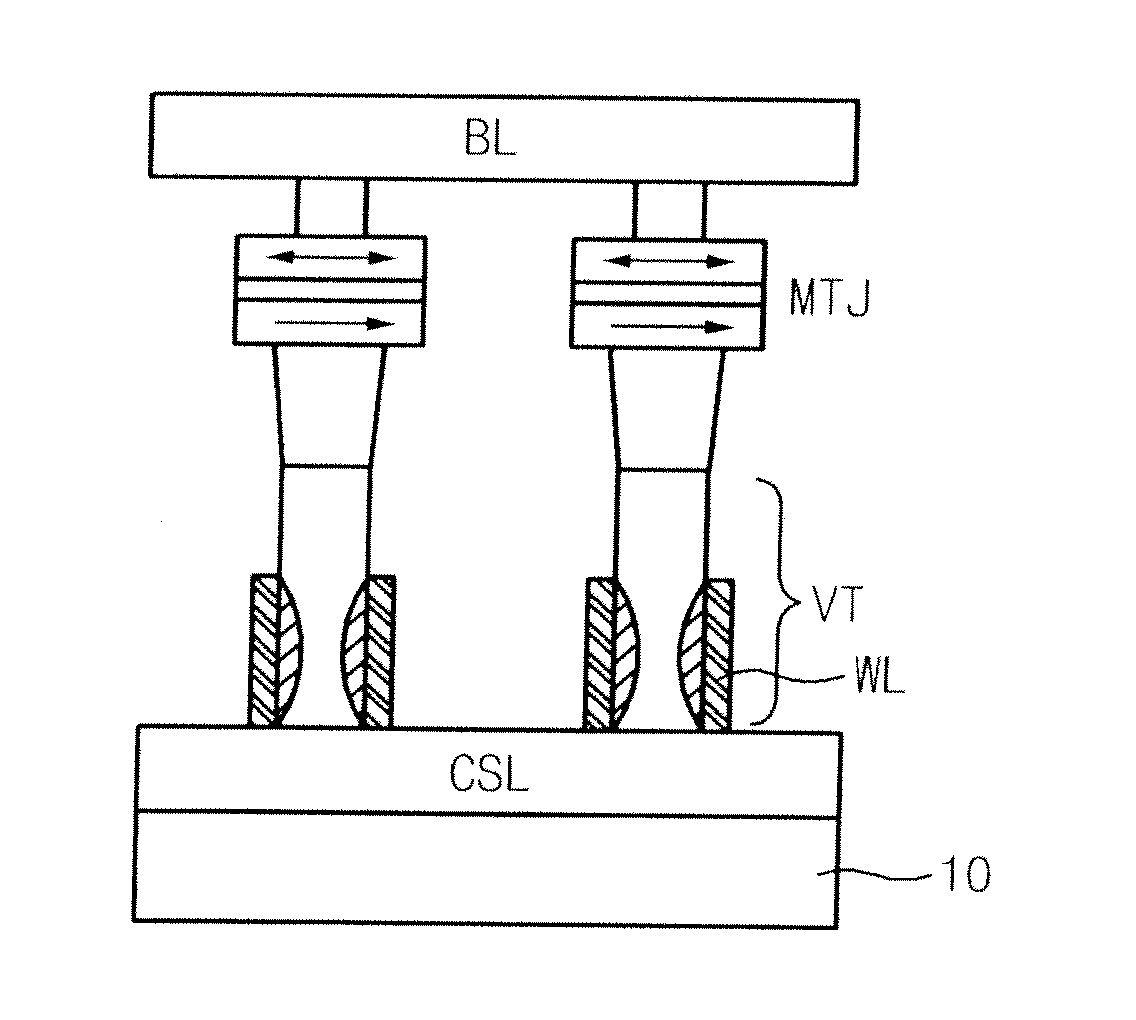
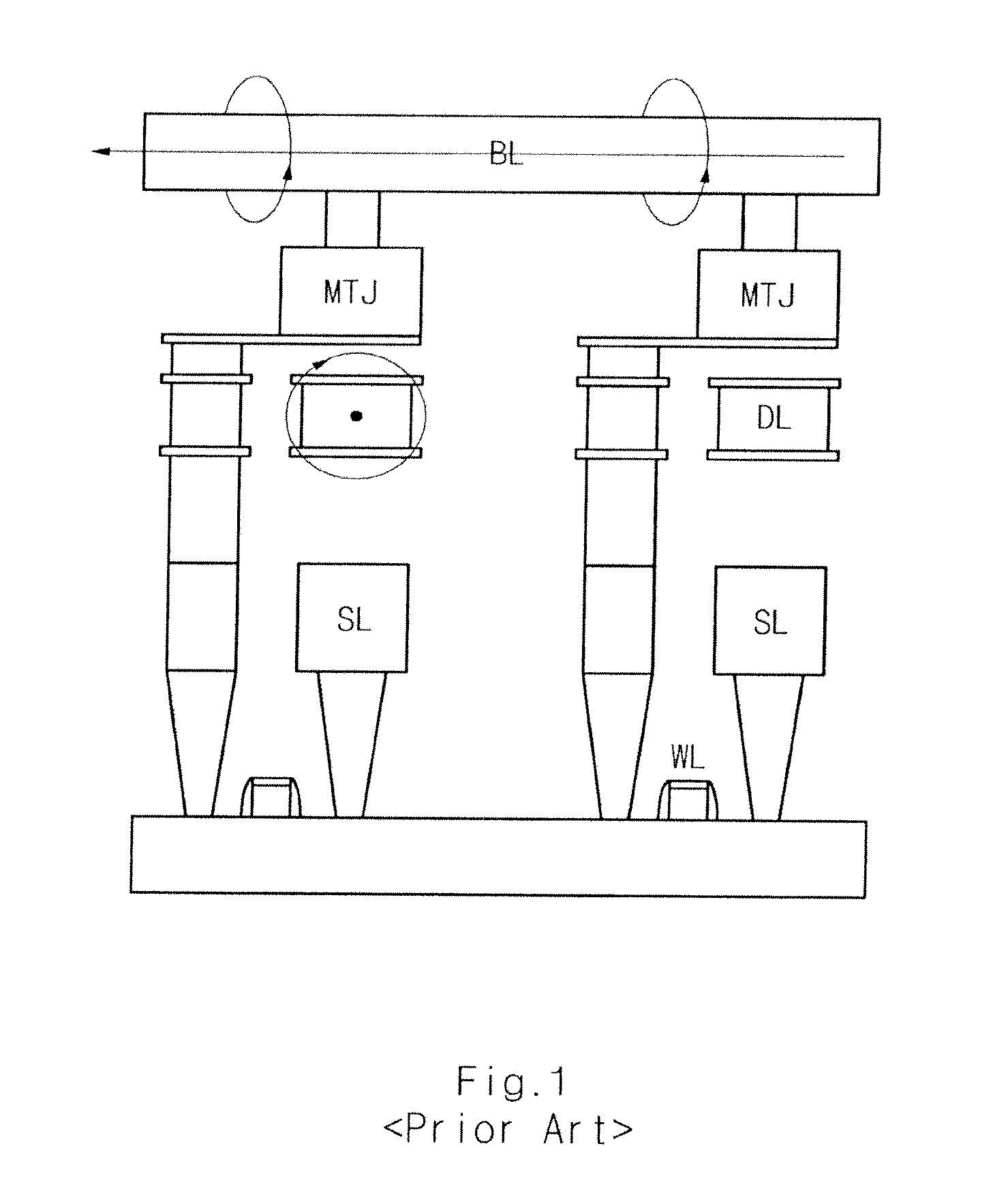
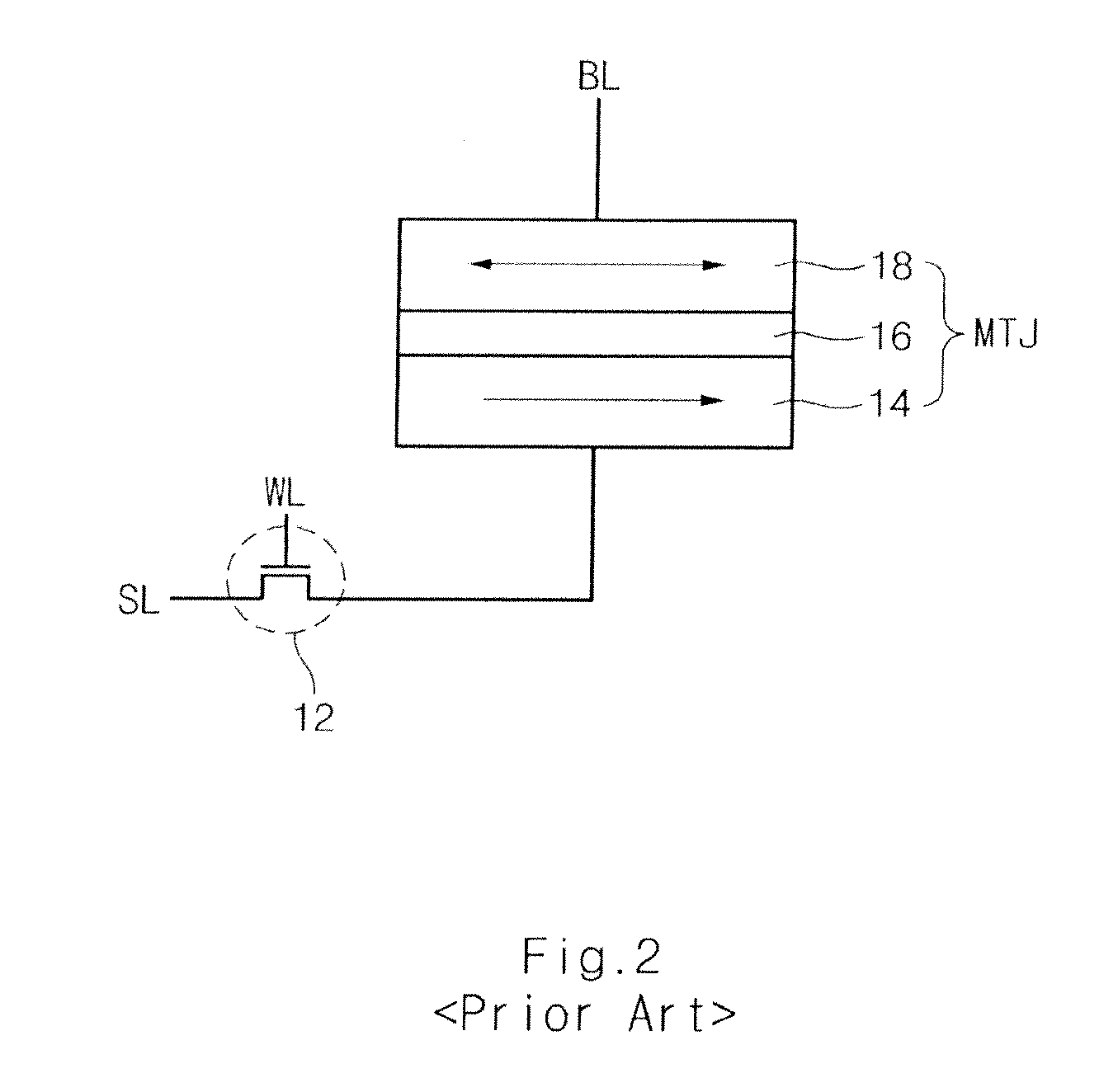
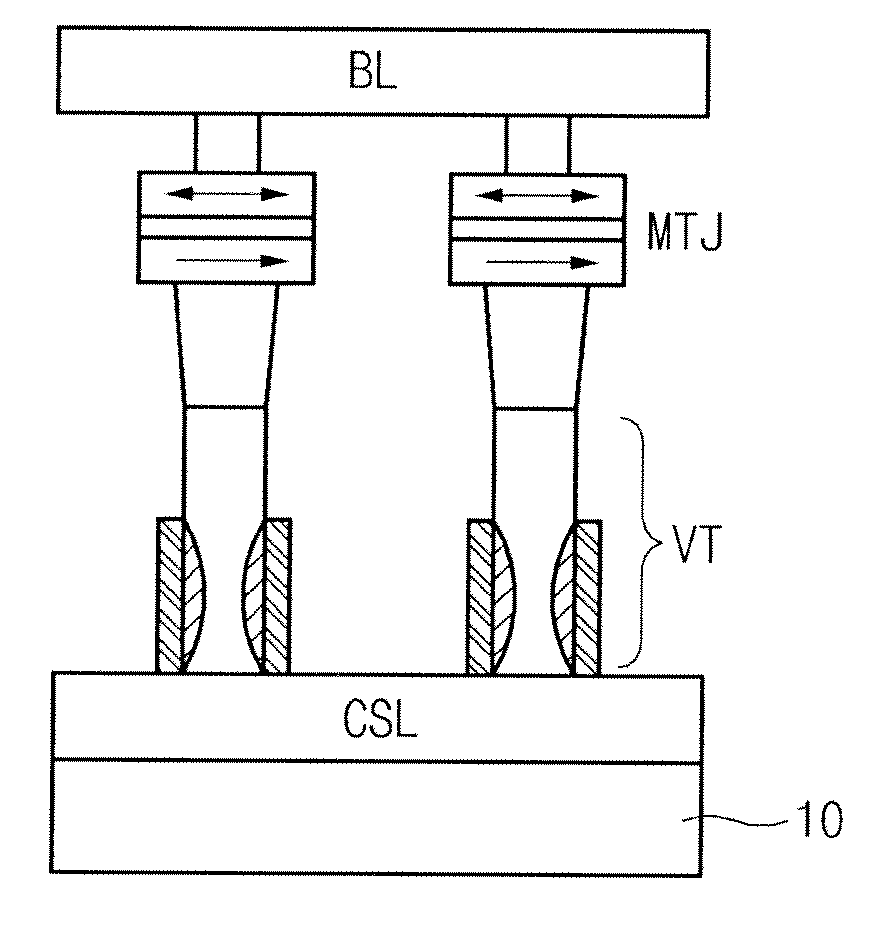
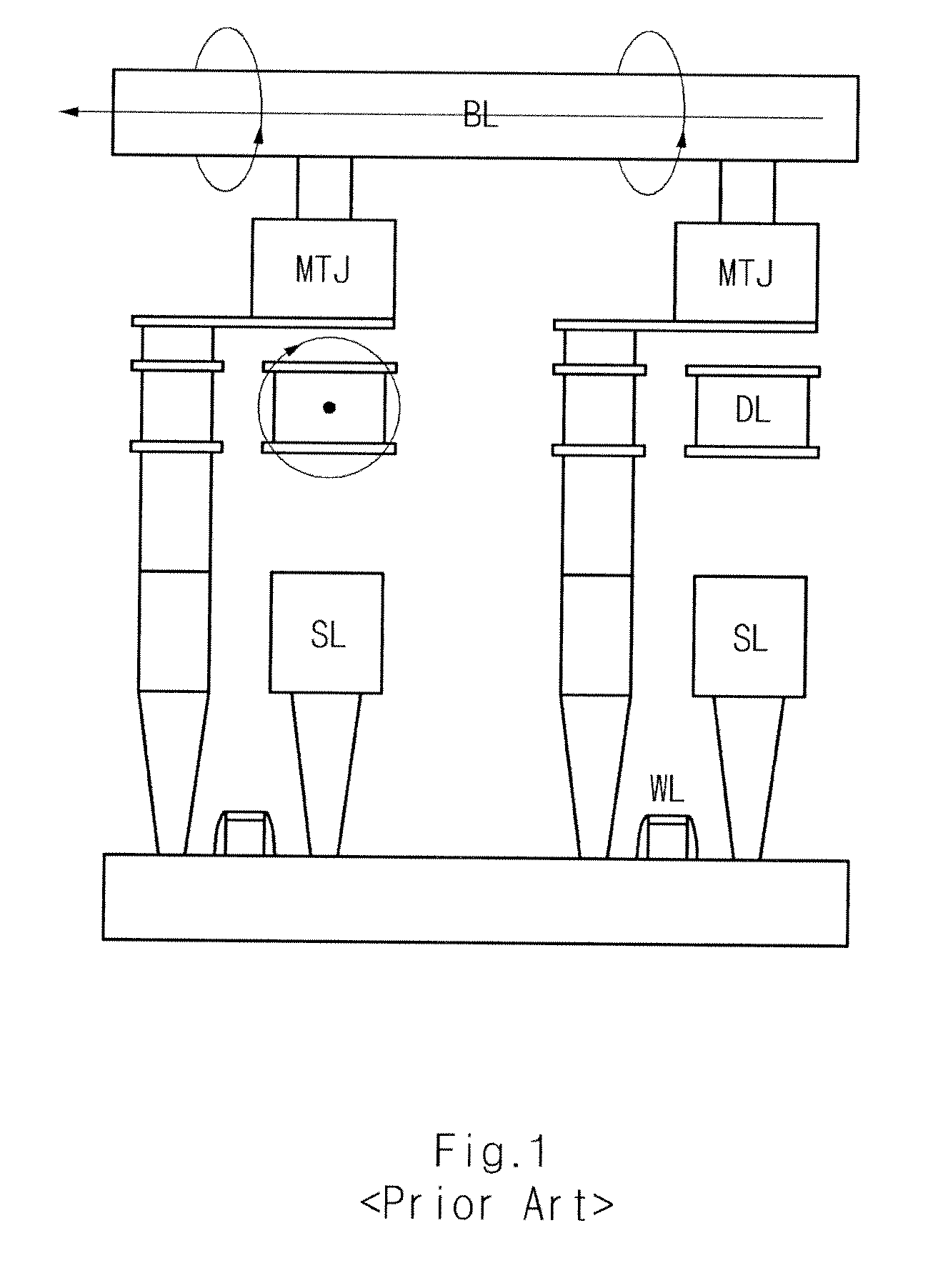
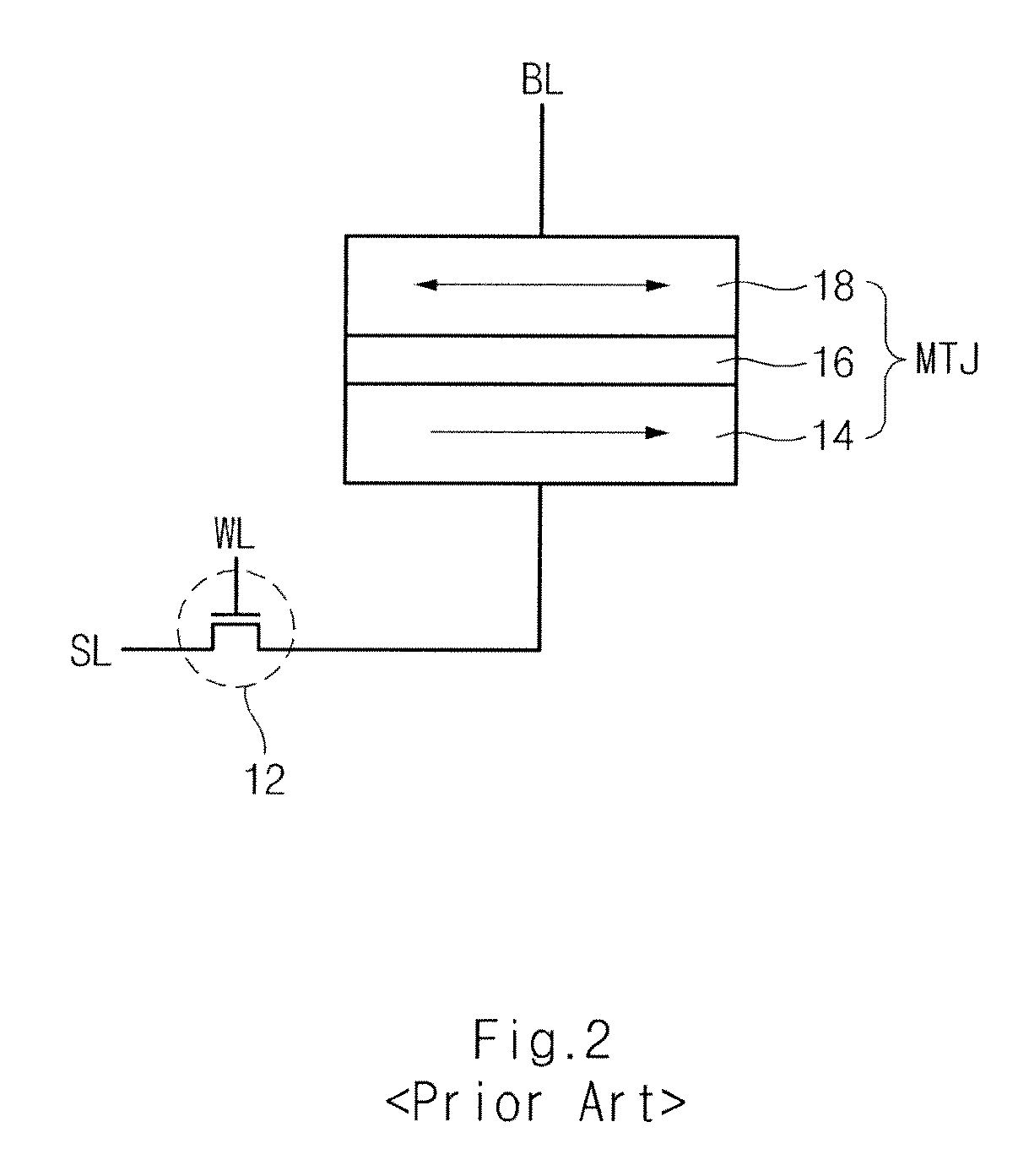
Spin Transfer Torque Memory Device Having Common Source Line and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20110269251A1Reduce resistanceEasy to integrateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpin-transfer torqueEngineering
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
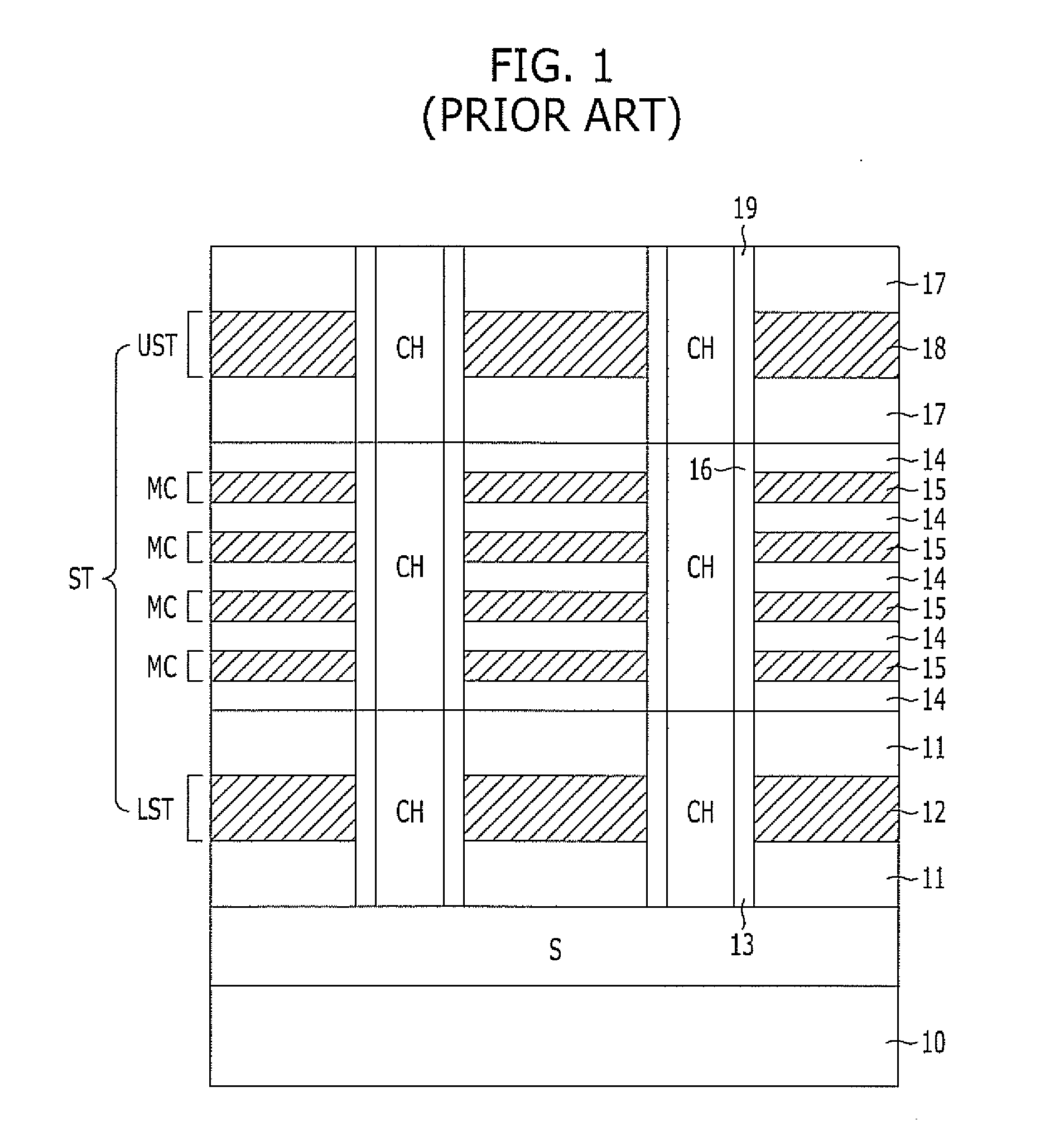
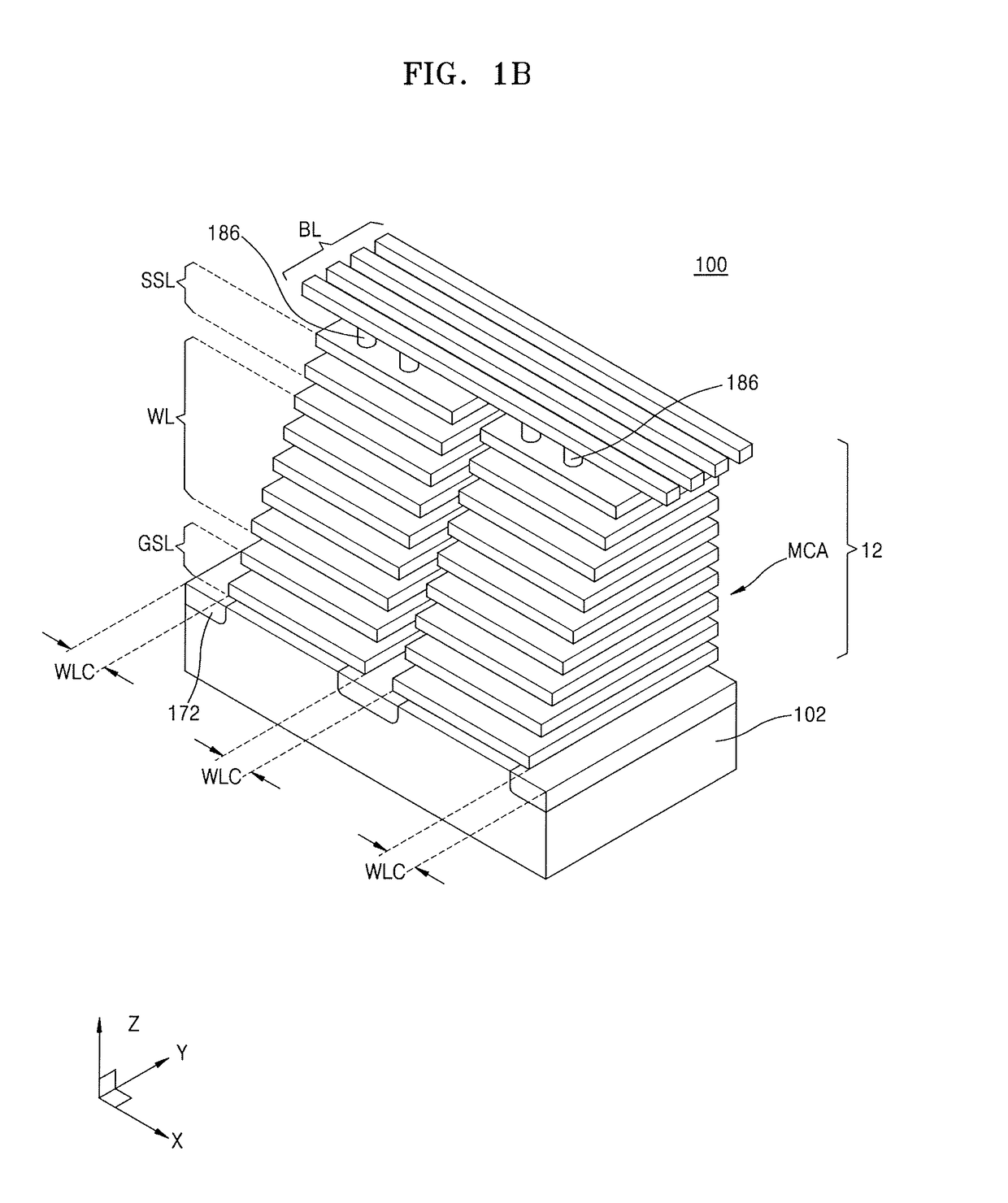
3D non-volatile memory device and method for operating and fabricating the same
ActiveUS20110090737A1Simplify the manufacturing processImprove performanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringTransistor
A 3D non-volatile memory device includes a plate-type lower select line formed over a substrate, a lower select transistor formed in the lower select line, a plurality of memory cells stacked over the lower select transistor, an upper select transistor formed over the memory cells, and a line-type common source line formed over the substrate and spaced from the lower select line.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Nonvolatile memory device and method of operating fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090021988A1Guaranteed uptimeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
Provided is a method of reliably operating a highly integratable nonvolatile memory device. The nonvolatile memory device may include a string selection transistor, a plurality of memory transistors, and a ground selection transistor between a bit line and a common source line. In the nonvolatile memory device, data may be erased from the memory transistors by applying an erasing voltage to the bit line or the common source line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20090122613A1Easy to integrateMore reliableRead-only memoriesDigital storageEngineeringSemiconductor
A non-volatile memory device may include a plurality of stacked semiconductor layers, a plurality of NAND strings, a common bit line, a common source line, and / or a plurality of string selection lines. The plurality of NAND strings may be on the plurality of semiconductor layers. Each of the plurality of NAND strings may include a plurality of memory cells and / or at least one string selection transistor arranged in a NAND-cell array. The common bit line may be commonly connected to each of the NAND strings at a first end of the memory cells. The common source line may be commonly connected to each of the NAND strings at a second end of the memory cells. The plurality of string selection lines may be coupled to the at least one string selection transistor included in each of the NAND strings such that a signal applied to the common bit line is selectively applied to the NAND strings.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and programming method thereof
ActiveUS8427881B2Highly reliable productsLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceSemiconductor
A programming method of a semiconductor memory device includes charging a channel of an inhibit string to a precharge voltage provided to the common source line and boosting the charged channel by providing a wordline voltage to the cell strings. The inhibit string is connected to a program bitline among the bitlines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
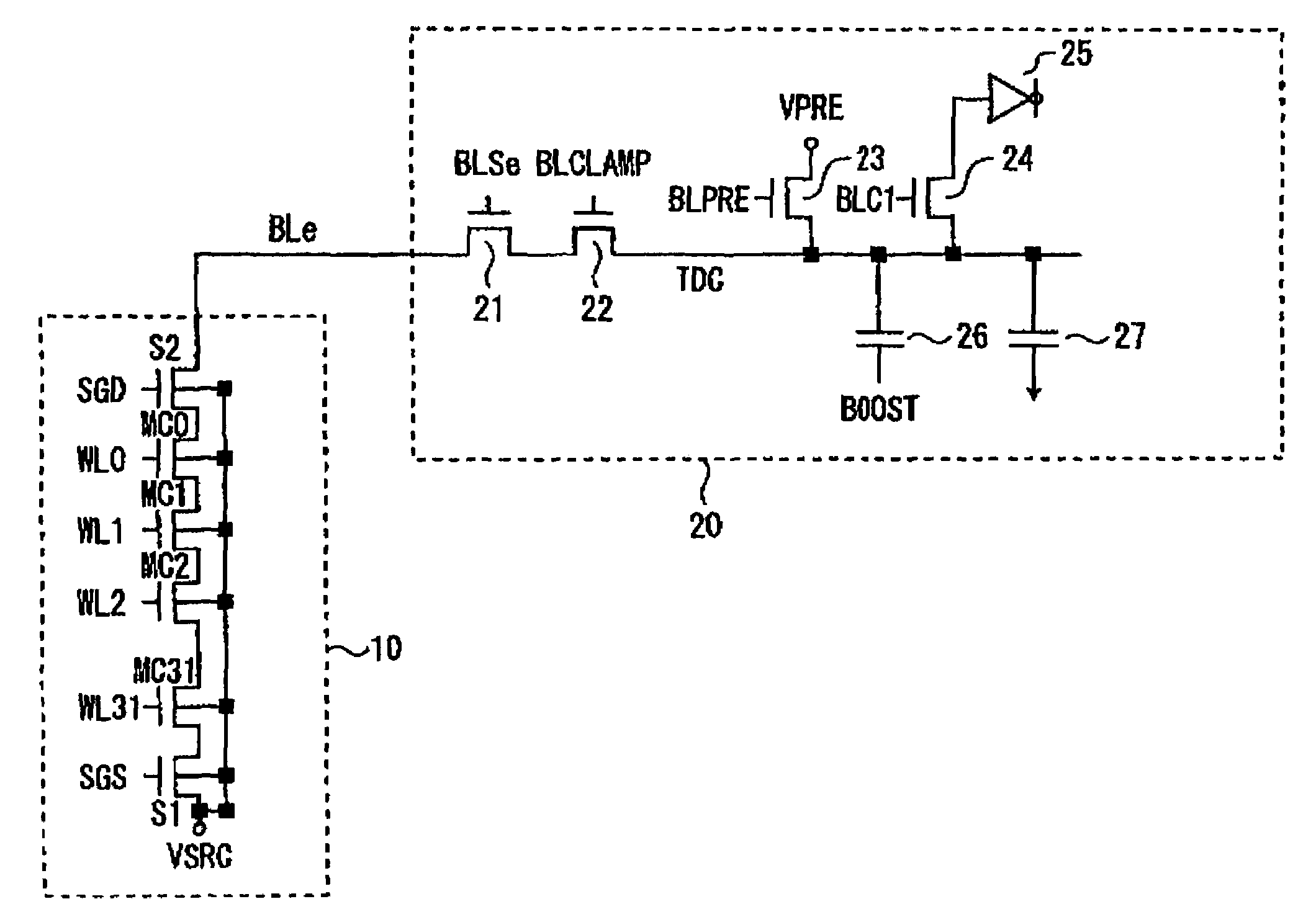
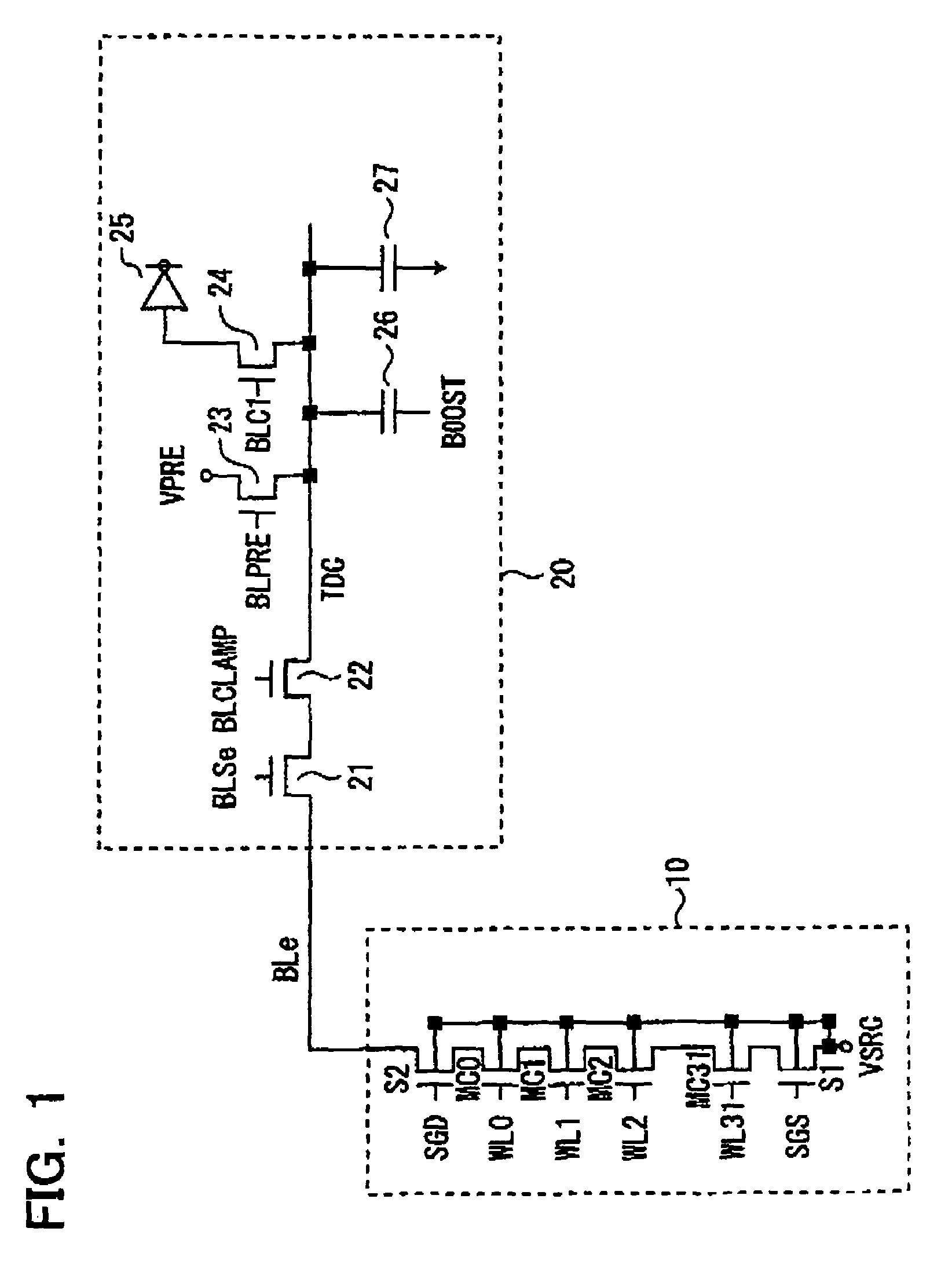
Sense amplifier for semiconductor memory device
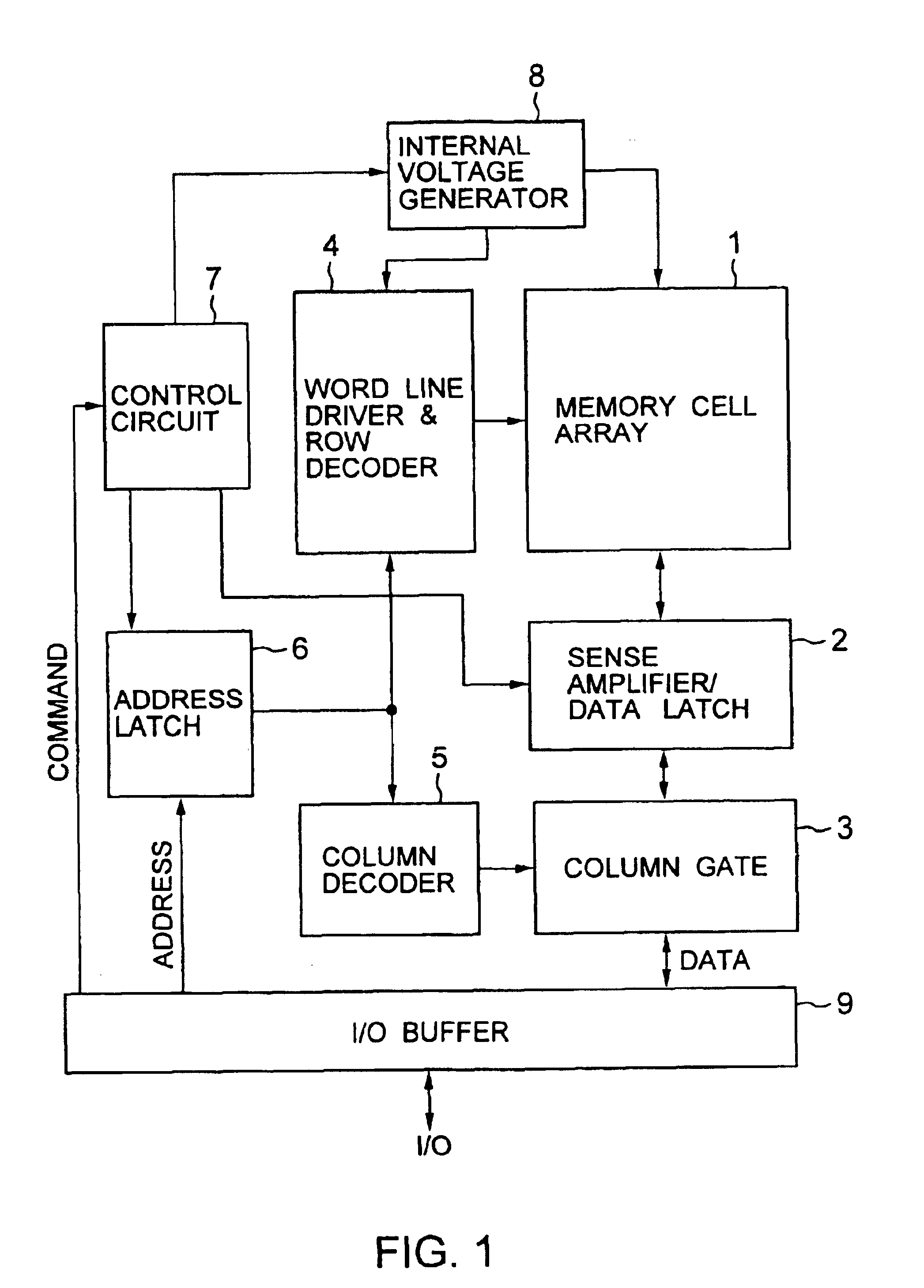
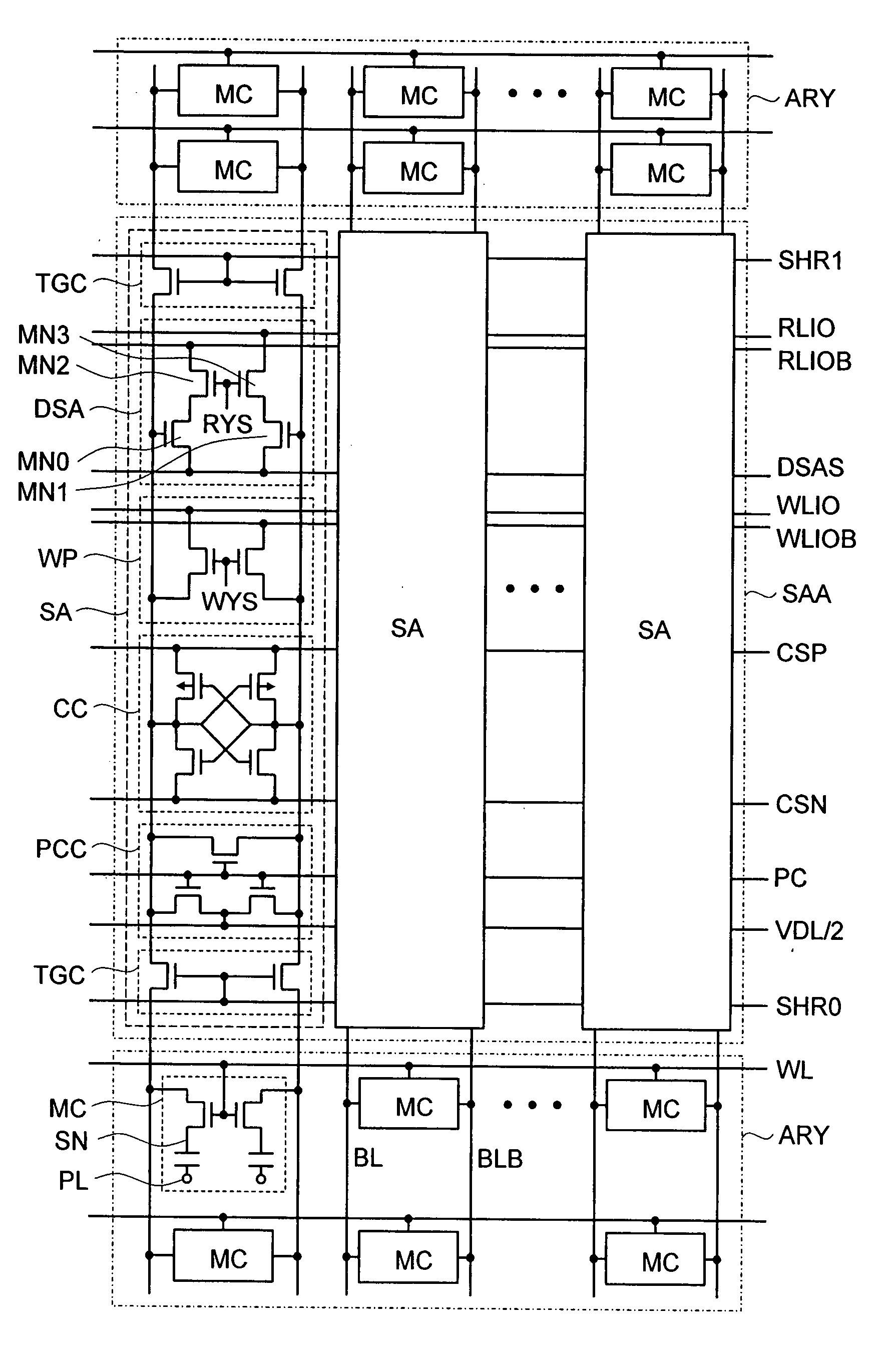
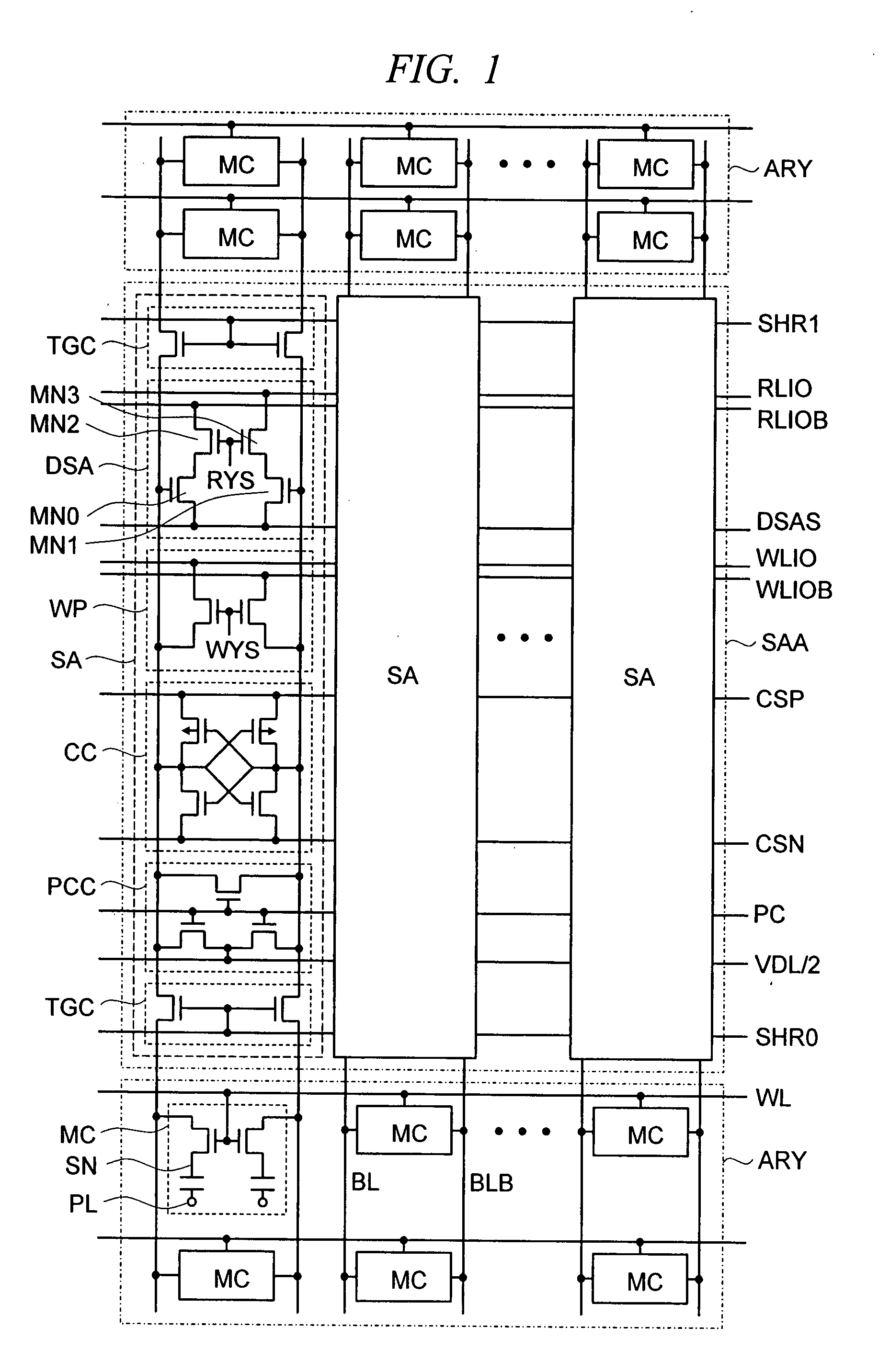
A direct sense amplifier of the present invention incorporates and isolates: an MOS transistor serving as a differential pair and having a gate connected to a bit line; and an MOS transistor controlled by a column select line wired between RLIO lines in a bit-line direction, and further connects a source of the MOS transistor serving as the differential pair to a common source line wired in the word-line direction. Since the direct sense amplifier only in a select map is activated by the column select line and the common source line during an read operation, power consumption is significantly reduced during the read operation. Also, since a parasitic capacitance of the MOS transistor serving as the differential pair is separated from the local IO line, a load capacity of the local IO line is reduced and the read operation is speeded up. In addition, during the read operation, a data pattern dependency of the load capacity of the local IO line is reduced and a post-manufacture test is easily made.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Semiconductor memory device and method of operating the same
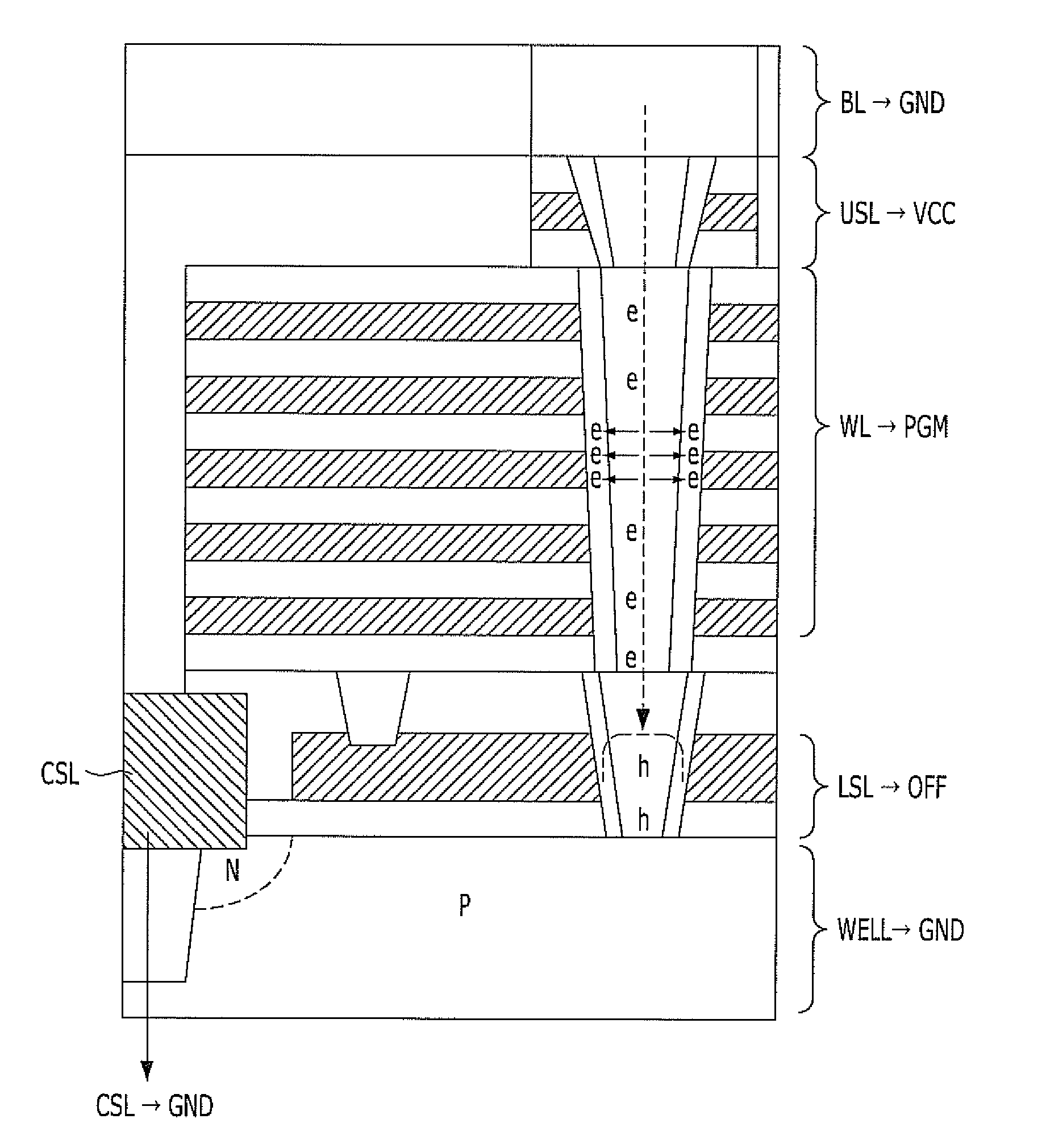
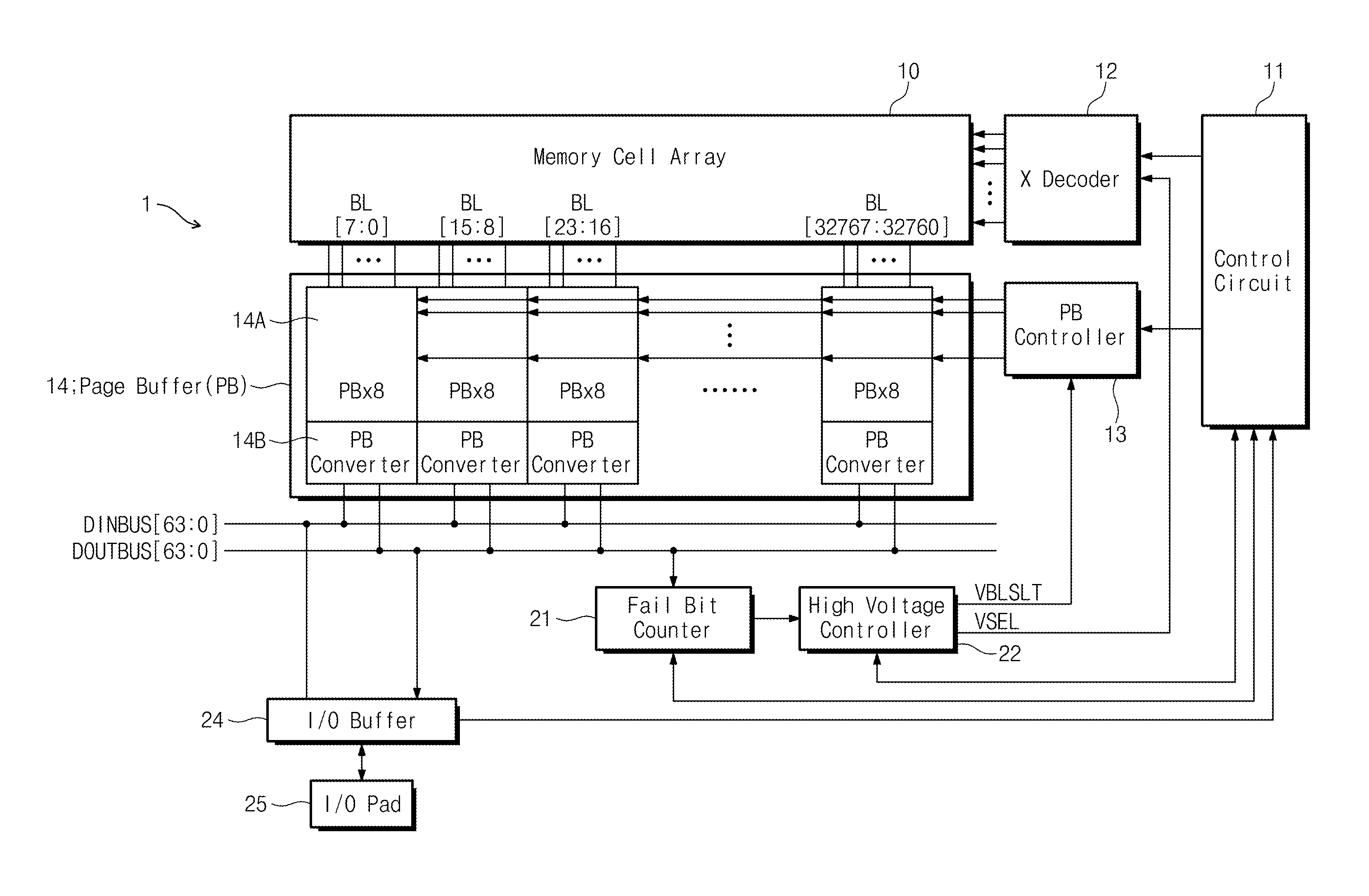
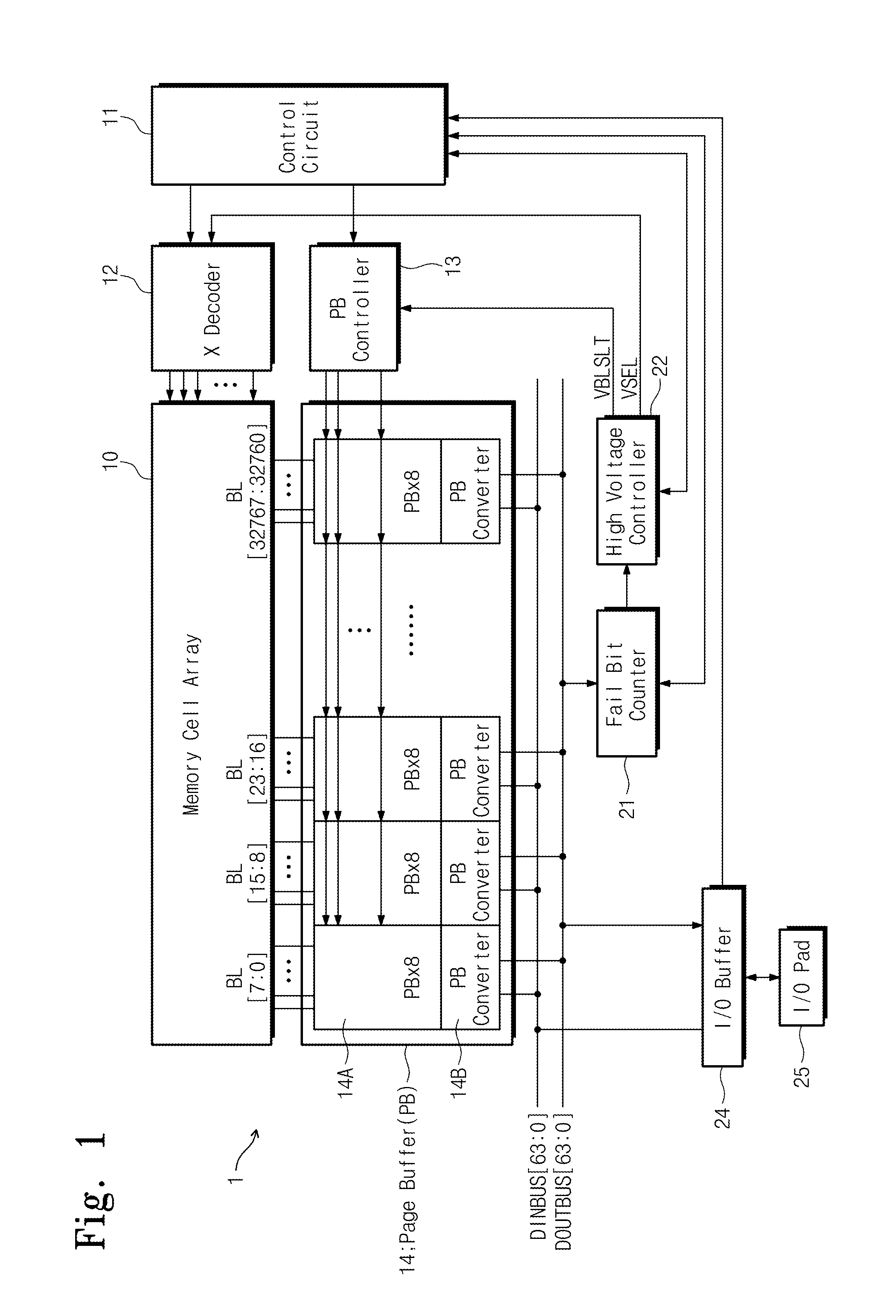
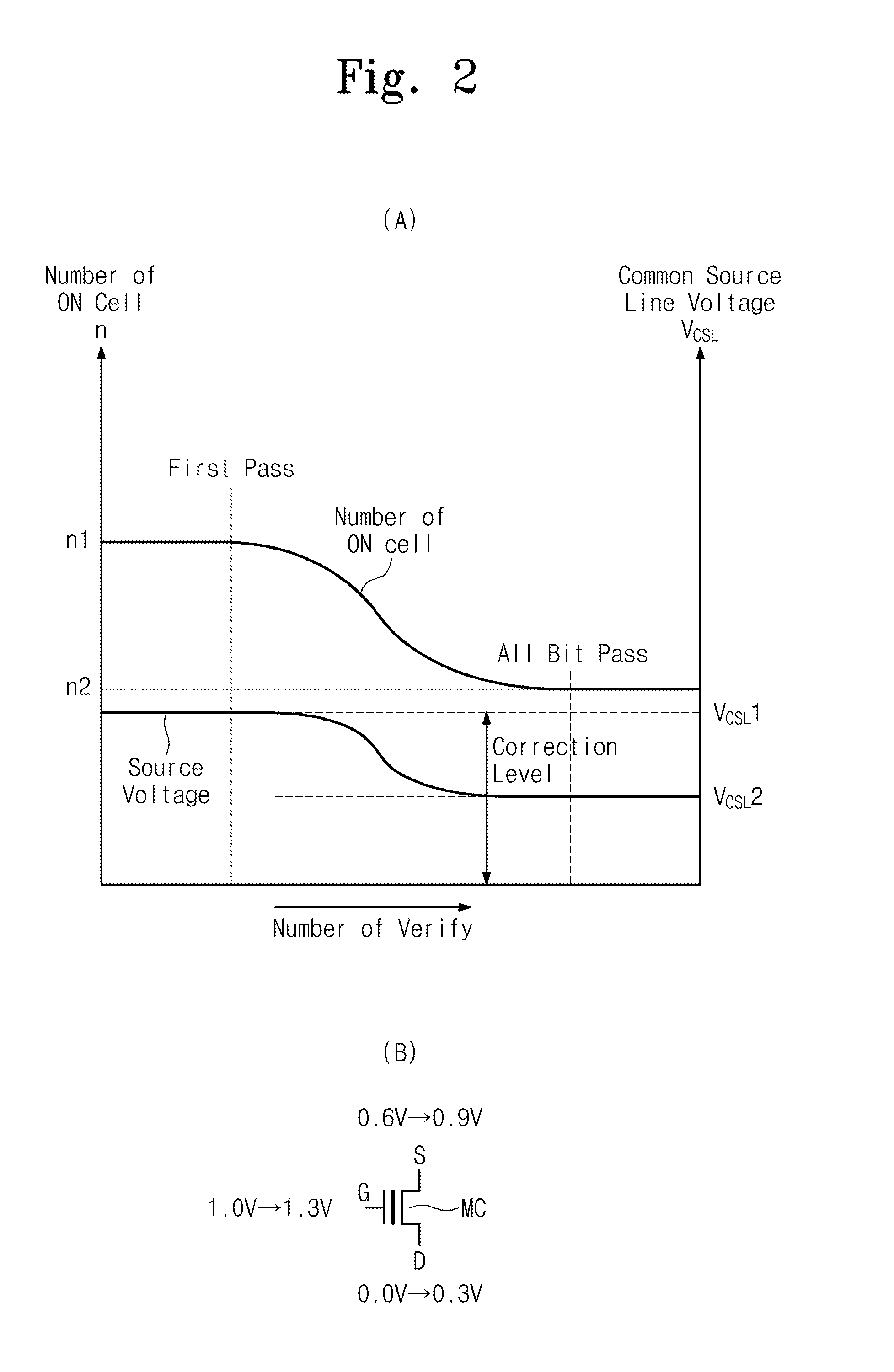
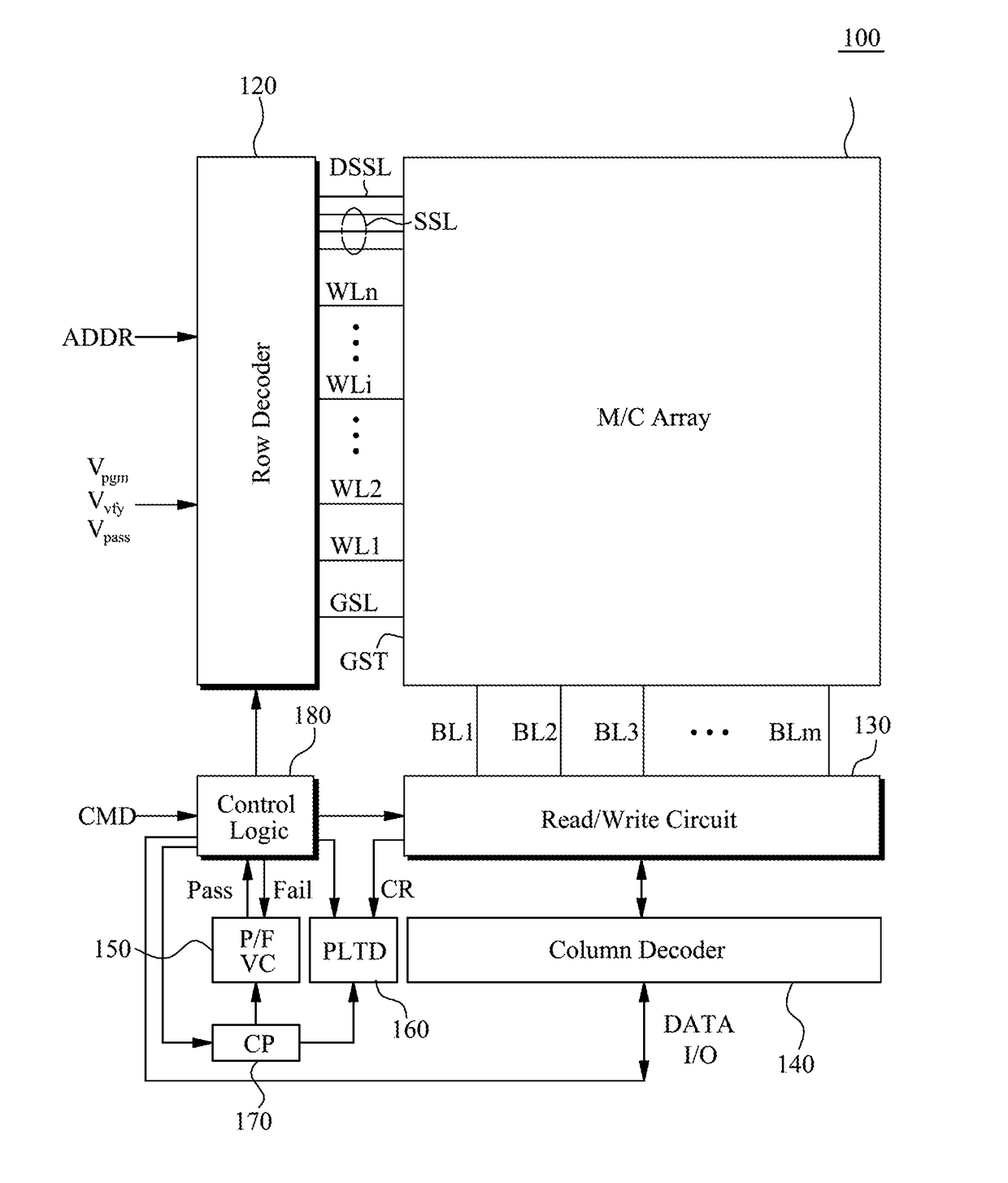
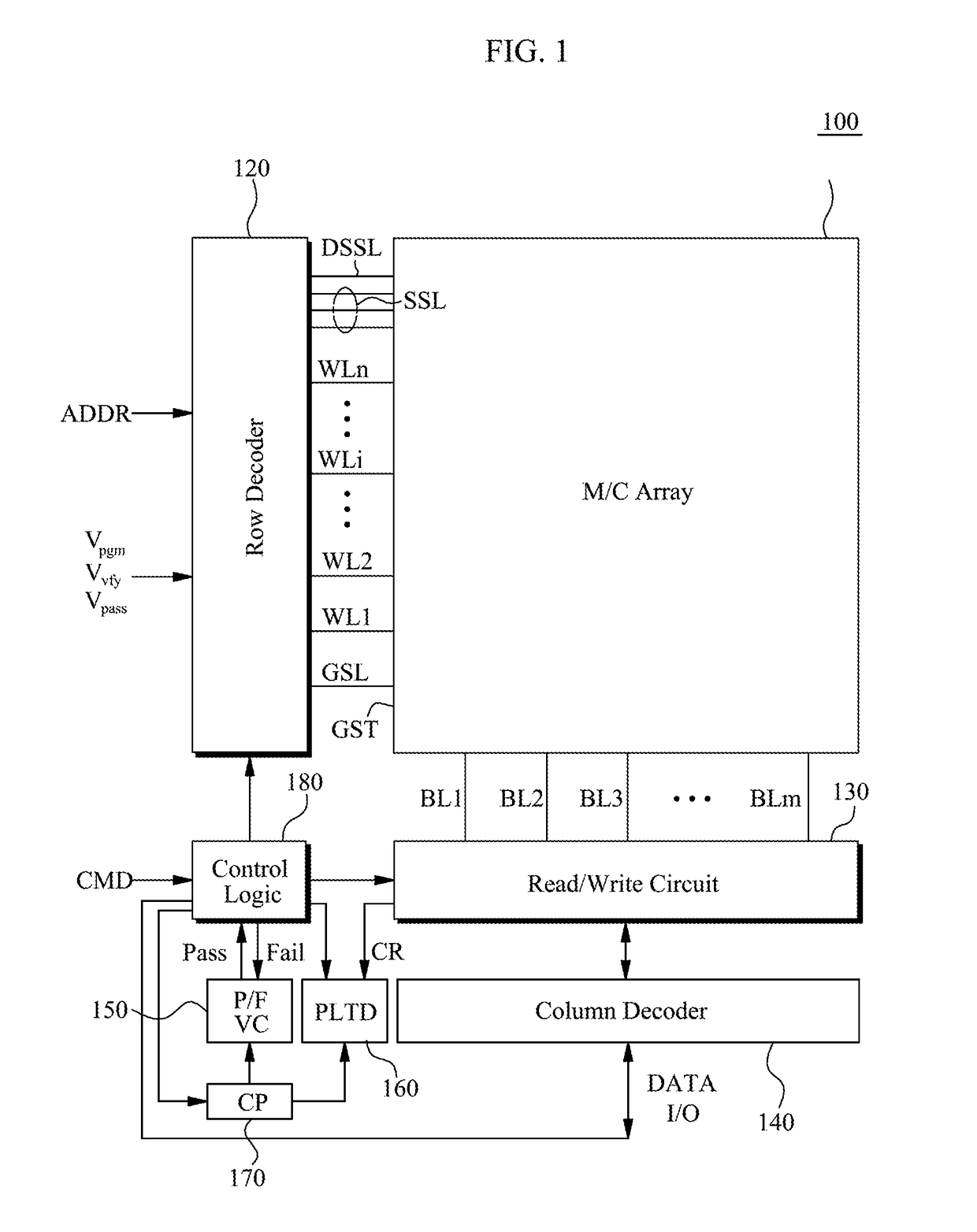
A semiconductor memory device operate during a program verification operation to apply a read voltage to a word line and a pre-charge voltage to a bit line in order to provide output data. A number of fail cells is determined in view of the output data, wherein the number of fail cells is directly related to an increase in voltage on a common source line (CSL) connected to memory cells providing the output data. During a subsequent program verification operation, the level of at least one of the read voltage and the pre-charge voltage is adjusted in response to the number of fail cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spin Transfer Torque Memory Device Having Common Source Line and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20100059837A1Easy to optimizeReduce resistance of source lineSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpin-transfer torqueTransistor
A spin transfer torque memory device and a method for manufacturing the same. The spin transfer torque memory device comprises a MRAM cell using a MTJ and a vertical transistor. A common source line is formed in the bottom of the vertical transistor, thereby obtaining the high-integrated and simplified memory device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20050047210A1Wrong writing is preventedTransistorSolid-state devicesCommon source lineSemiconductor memory
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of initializing 3D non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20170140829A1Highly integratedRead-only memoriesDigital storageTheoretical computer scienceTransistor
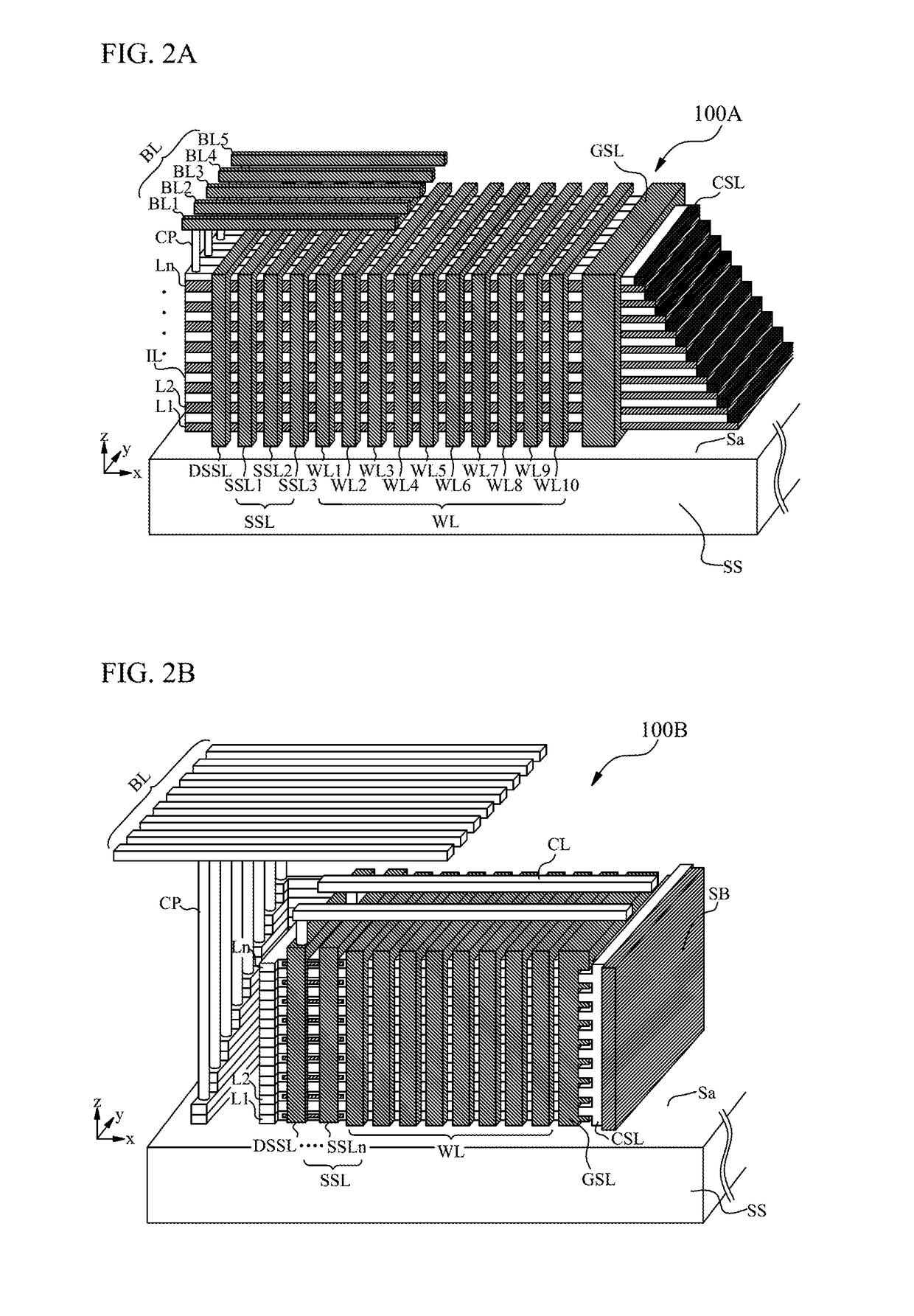
A 3D non-volatile memory device may include a dummy string selection line, string selection lines, wordlines, bitlines, a ground selection line, and memory layers. Each of the memory layers comprising channel lines respectively coupled to the bitlines via first ends and coupled to a common source line of the memory layer via second ends. The dummy string selection line, the string selection lines, the wordlines, and the ground selection line intersect with the channel lines, and each of the channel lines defines a memory string. Initializing the 3D non-volatile memory device may include programming string selection transistors coupled with the string selection lines to have one or more threshold values, and programming a dummy string selection transistor coupled with the dummy string selection line to have a predetermined threshold value, such that the dummy string selection transistor together with the string selection transistors function as string selection transistors.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
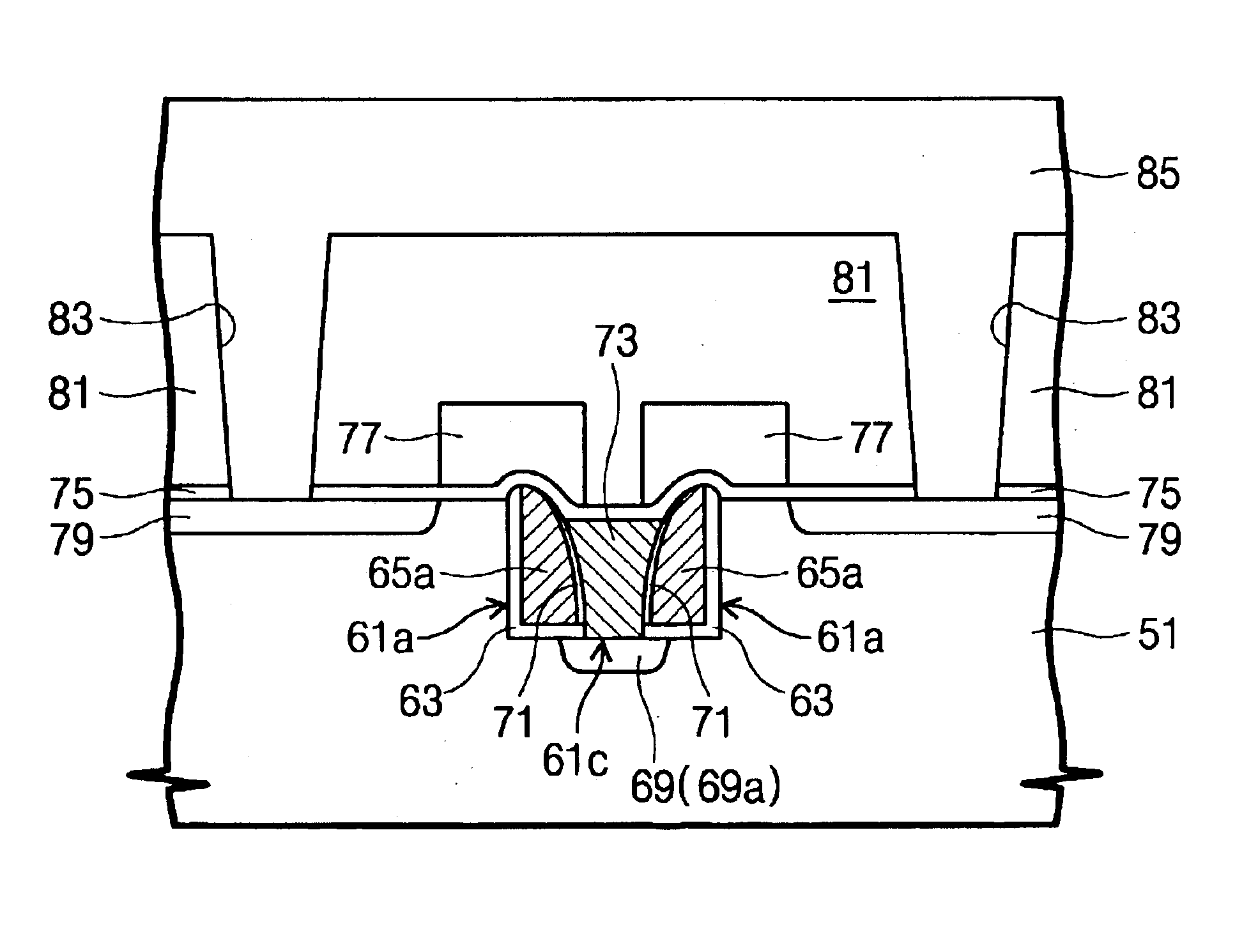
A semiconductor device includes gate stacked structures surrounding channel layers, a common source line filling a separation area between the gate stacked structures adjacent to each other and having an upper surface including first concave portions, and a support insulating layer filling the first concave portions and having sidewalls facing portions of the channel layers.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
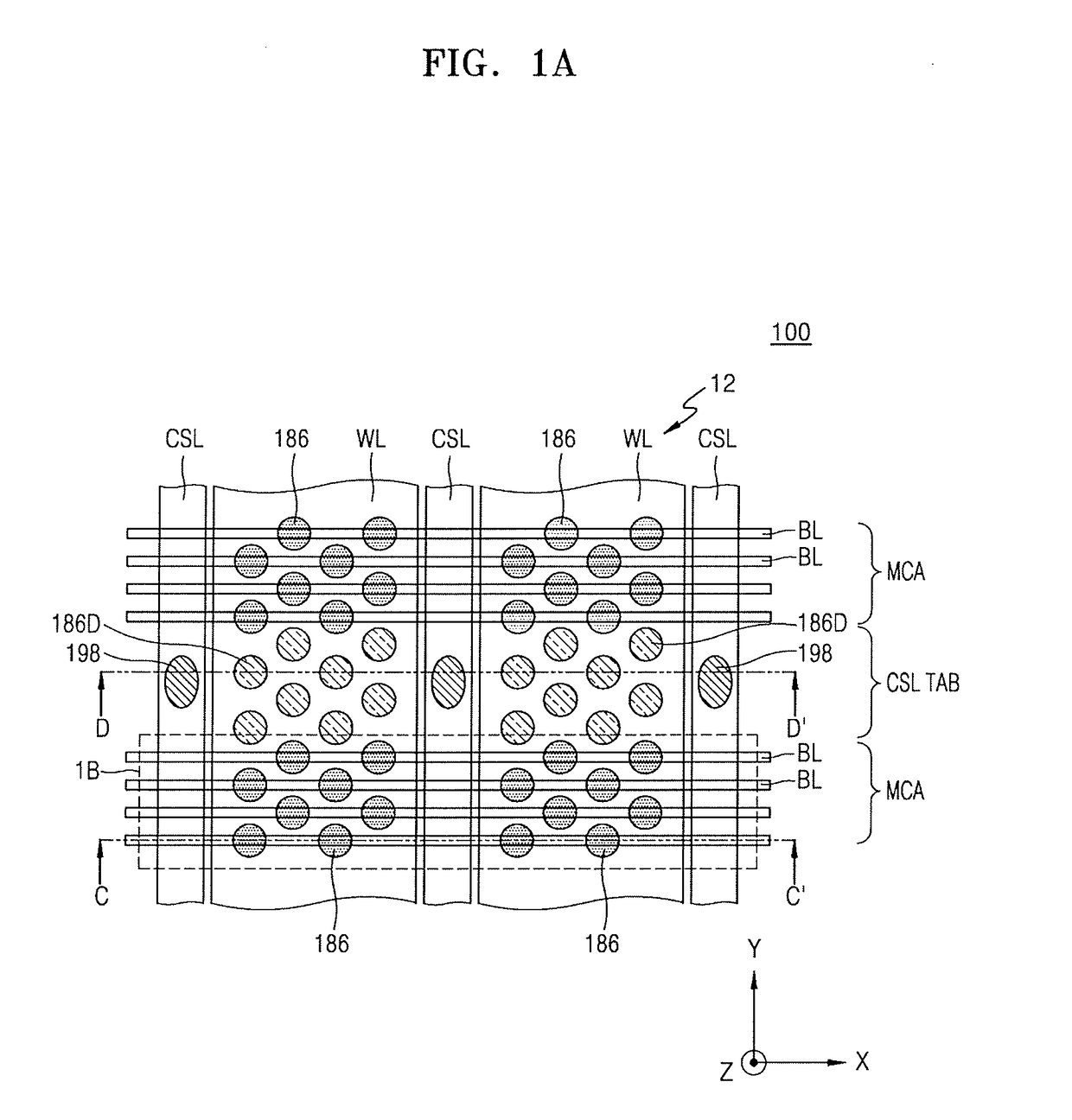
Integrated circuit device including vertical memory device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170221813A1Reduce the overall heightSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
An integrated circuit (IC) device includes: a channel region that extends on the substrate to penetrate a plurality of word lines; a bit line contact pad that contacts an upper surface of the channel region; a bit line that contacts the bit line contact pad and extends on the bit line contact pad in a direction parallel to the main surface of the substrate; a common source line that partially fills a word line cut region and has a height lower than that of the channel region; and a common source via contact that contacts an upper surface of the common source line in the word line cut region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
A semiconductor memory device, comprising: a memory cell array of a plurality of memory cell units, each memory cell unit including a plurality of serially connected memory cells formed on the same well region, each memory cell having a floating gate and a control gate stacked, said serially connected memory cells having one end serially connected to a first selection gate transistor, said serially connected memory cells having the other end connected to a common source line via a second selection gate transistor; a sense amp connected to one end of said first selection gate transistor via a bit line and operative to read data out of said memory cell array; and wherein a voltage applied to said well region and said source line varies to cancel a change of threshold of said memory cells depending on the temperature.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Nonvolatile memory cells having split gate structure and methods of fabricating the same
Nonvolatile memory cells having a split gate structure and methods of fabricating the same are provided. The nonvolatile memory cells include active regions defined at a predetermined region of a semiconductor substrate. A portion of each of the active regions is etched to form a cell trench region. Insulated floating gates are disposed on a pair of sidewalls parallel with the direction that crosses the active region. A source region is disposed at a bottom surface of the cell trench region. A gap region between the floating gates is filled with a common source line electrically connected to the source region. The common source line is extended along the direction that crosses the active regions. The active regions, which are adjacent to the floating gates, are covered with word lines parallel with the common source line. Drain regions are disposed in the active regions adjacent to the word lines. The drain regions are electrically connected to bit lines that cross over the word lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
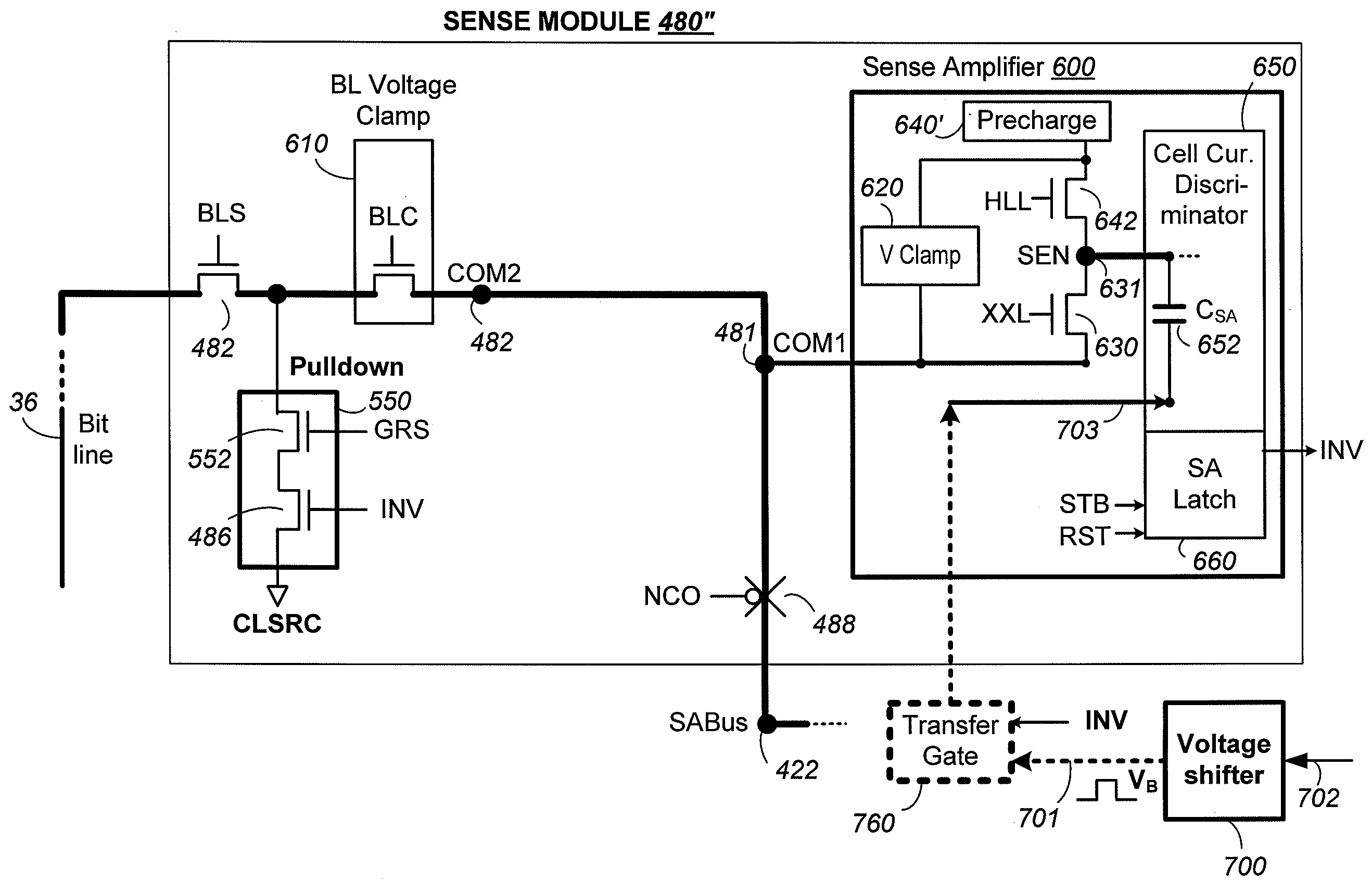
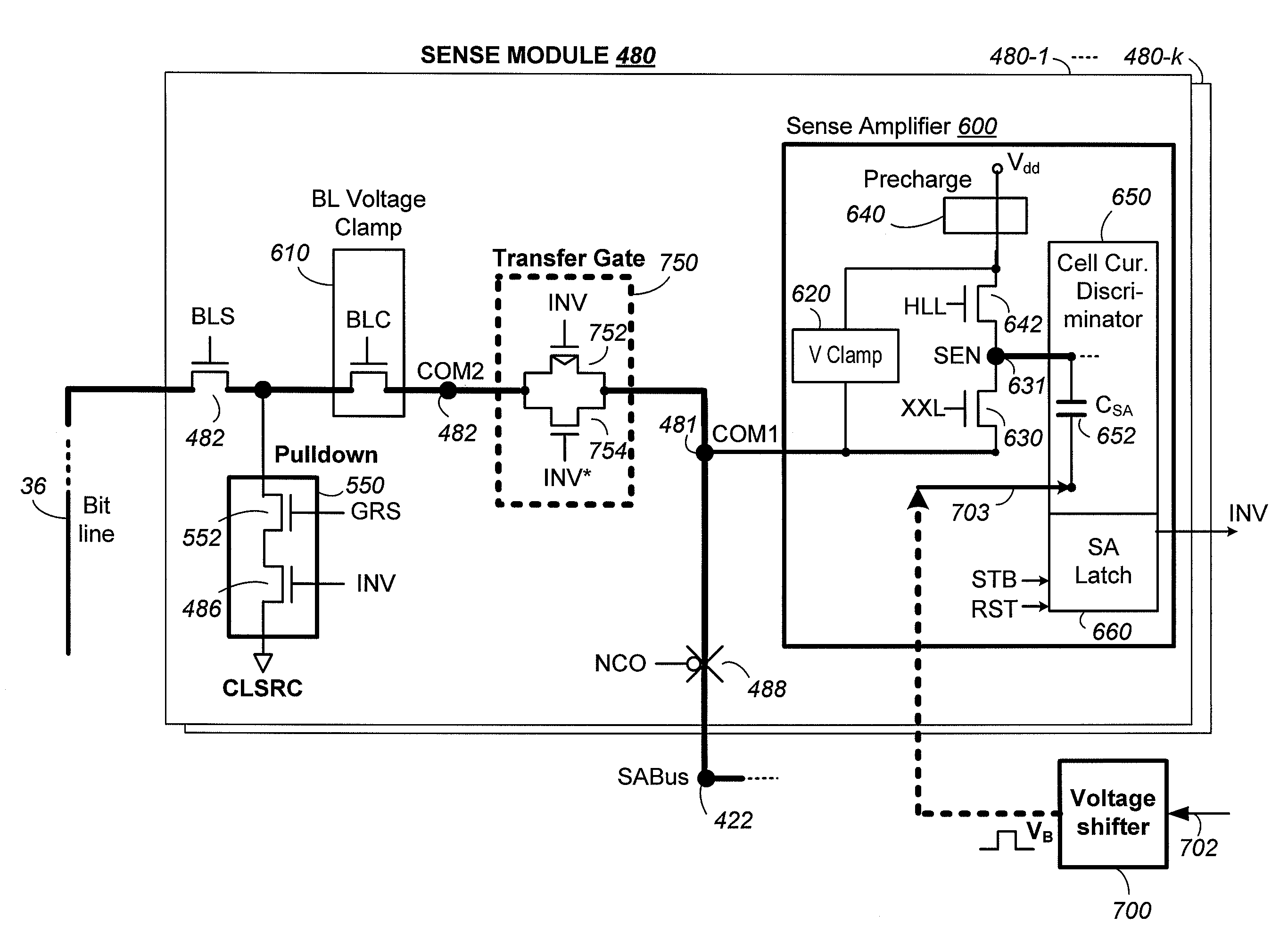
Low Noise Sense Amplifier Array and Method for Nonvolatile Memory
ActiveUS20090168540A1Improve performanceImprove sensing accuracyRead-only memoriesDigital storageLow noiseAudio power amplifier
In sensing a page of nonvolatile memory cells with a corresponding group of sense modules in parallel, as each high current cell is identified, it is locked out from further sensing while others in the page continued to be sensed. The sense module involved in the locked out is then in a lockout mode and becomes inactive. A noise source from the sense module becomes significant when in the lockout mode. The noise is liable to interfere with the sensing of neighboring cells by coupling through its bit line to neighboring ones. The noise can also couple through the common source line of the page to affect the accuracy of ongoing sensing of the cells in the page. Improved sense modules and method isolate the noise from the lockout sense module from affecting the other sense modules still active in sensing memory cell in the page.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS7315472B2Increase currentLower channel resistanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageOperating systemStorage cell
A non-volatile memory device may include a plurality of memory blocks including memory cells connected in series to bit lines, respectively. Each of the plurality of memory blocks may include a first sub memory block having a first group of memory cells, which are respectively connected in series between first select transistors connected to the bit lines, respectively, and second select transistors connected to a common source line, and a second sub memory block having a second group of memory cells, which are respectively connected in series between third select transistors connected to the bit lines, respectively, and fourth select transistors connected to the common source line.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
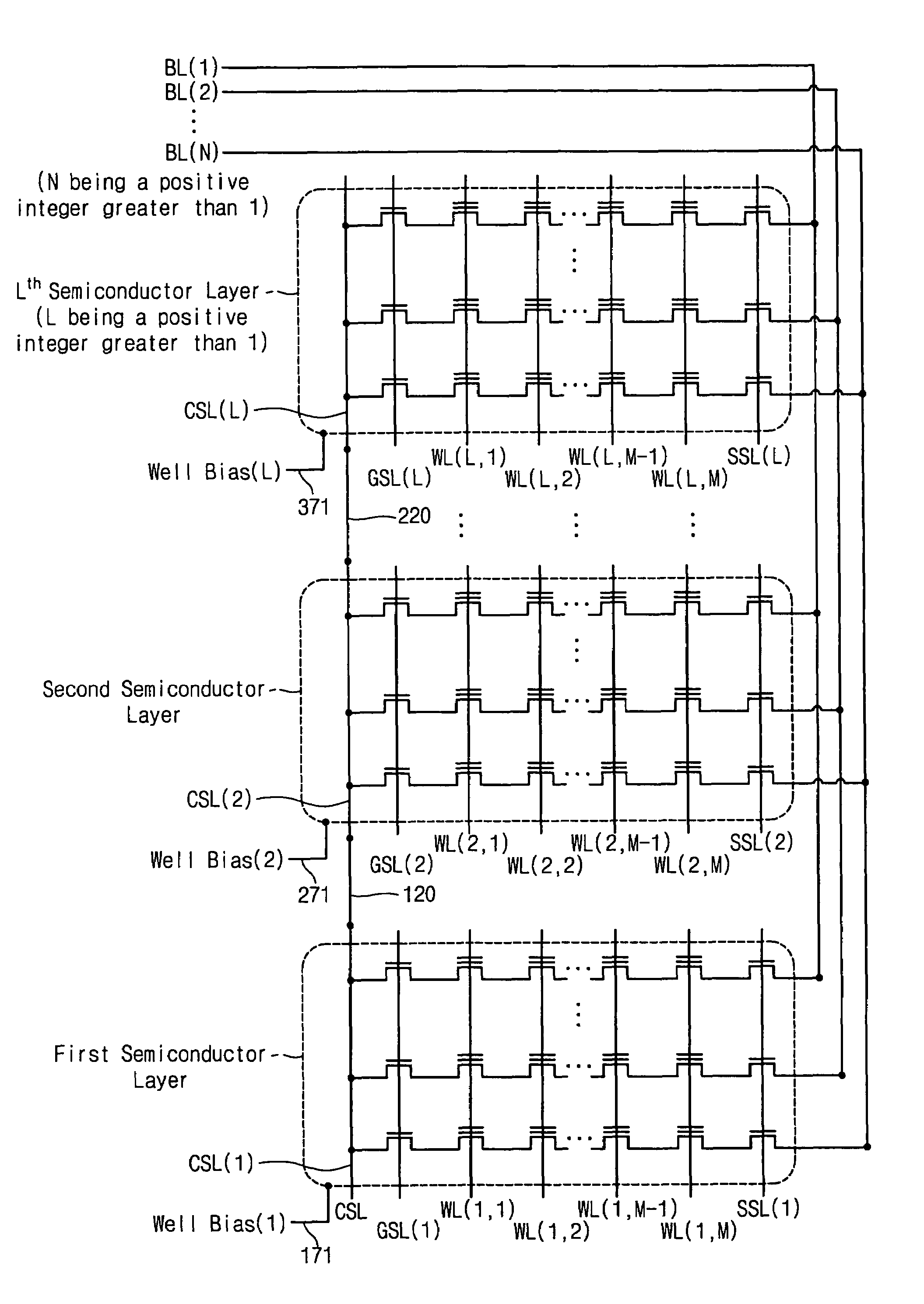
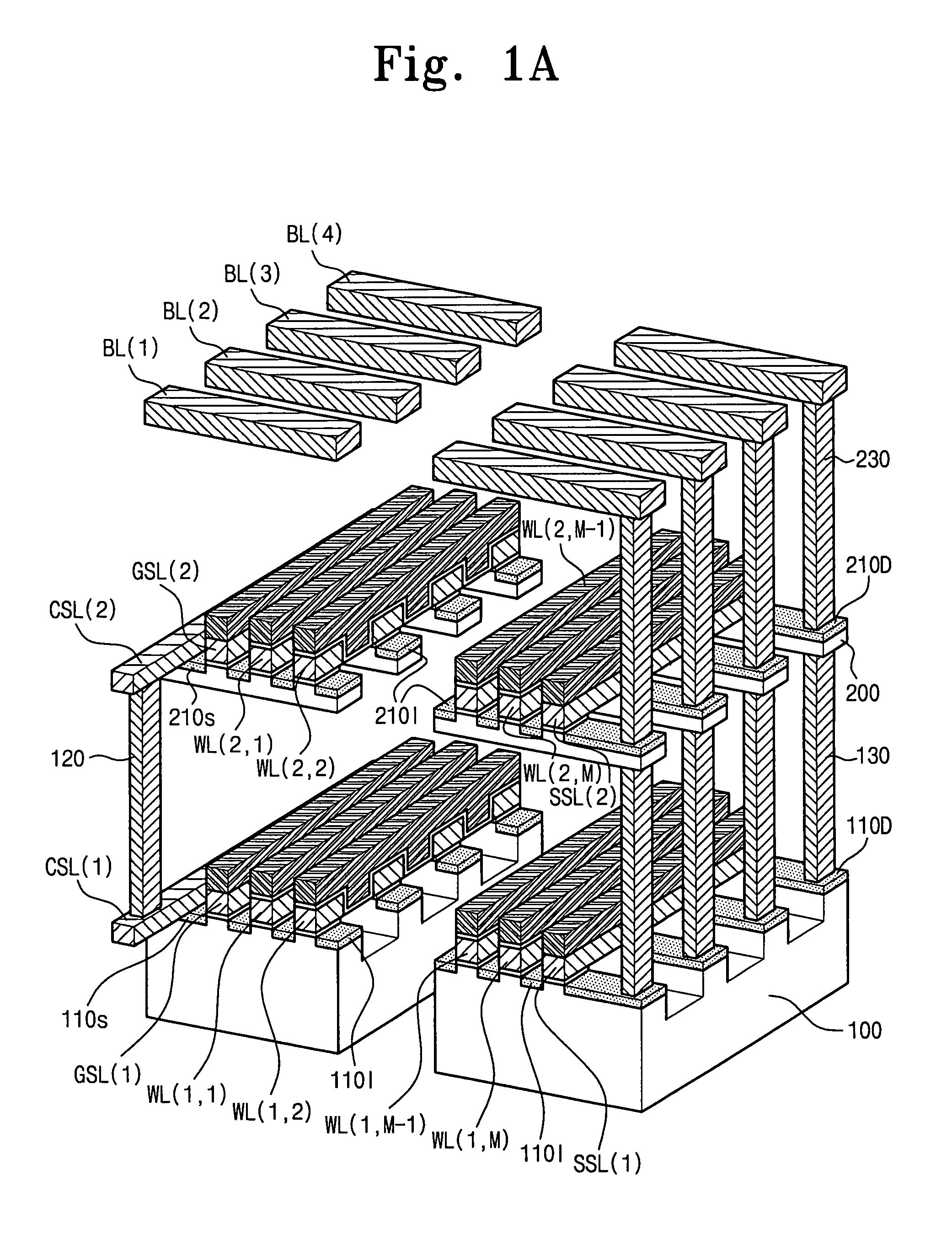
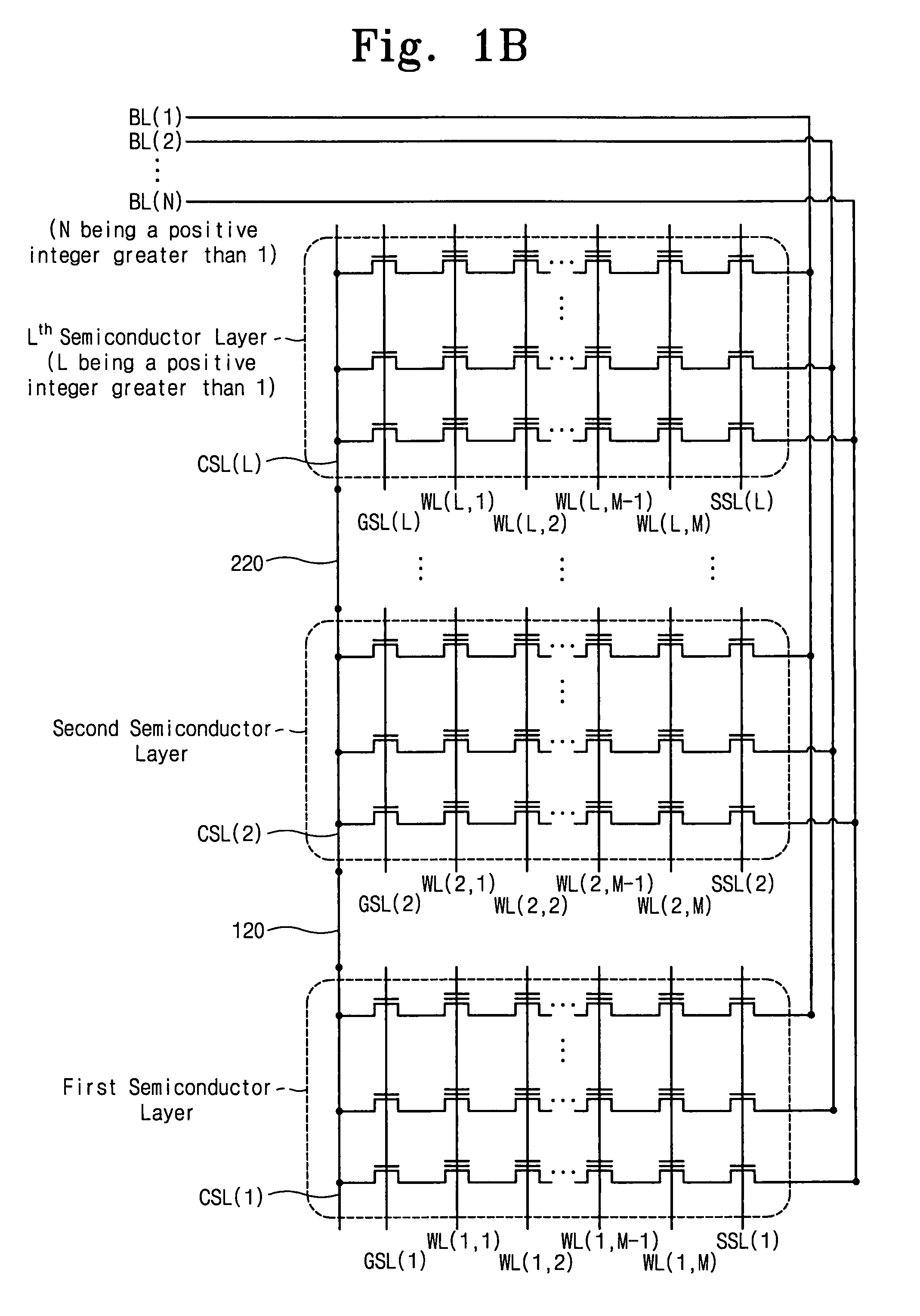
Memory device including 3-dimensionally arranged memory cell transistors and methods of operating the same
A memory device may include L semiconductor layers, a gate structure on each of the semiconductor layers, N bitlines, and / or a common source line on each of the semiconductor layers. The L semiconductor layers may be stacked, and / or L may be an integer greater than 1. The N bitlines may be on the gate structures and crossing over the gate structures, and / or N may be an integer greater than 1. Each of the common source lines may be connected to each other such that the common source lines have equipotentiality with each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low noise sense amplifier array and method for nonvolatile memory
ActiveUS7593265B2Improve sensing accuracyImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageLow noiseAudio power amplifier
In sensing a page of nonvolatile memory cells with a corresponding group of sense modules in parallel, as each high current cell is identified, it is locked out from further sensing while others in the page continued to be sensed. The sense module involved in the locked out is then in a lockout mode and becomes inactive. A noise source from the sense module becomes significant when in the lockout mode. The noise is liable to interfere with the sensing of neighboring cells by coupling through its bit line to neighboring ones. The noise can also couple through the common source line of the page to affect the accuracy of ongoing sensing of the cells in the page. Improved sense modules and method isolate the noise from the lockout sense module from affecting the other sense modules still active in sensing memory cell in the page.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
NAND-type flash memory devices and methods of fabricating the same
InactiveUS6936885B2Lower resistanceMinimize aspect ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerSemiconductor
NAND-type flash memory devices and methods of fabricating the same are provided. The NAND-type flash memory device includes a plurality of isolation layers running parallel with each other, which are formed at predetermined regions of a semiconductor substrate. This device also includes a string selection line pattern, a plurality of word line patterns and a ground selection line pattern which cross over the isolation layers and active regions between the isolation layers. Source regions are formed in the active regions adjacent to the ground selection line patterns and opposite the string selection line pattern. The source regions and the isolation layers between the source regions are covered with a common source line running parallel with the ground selection line pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
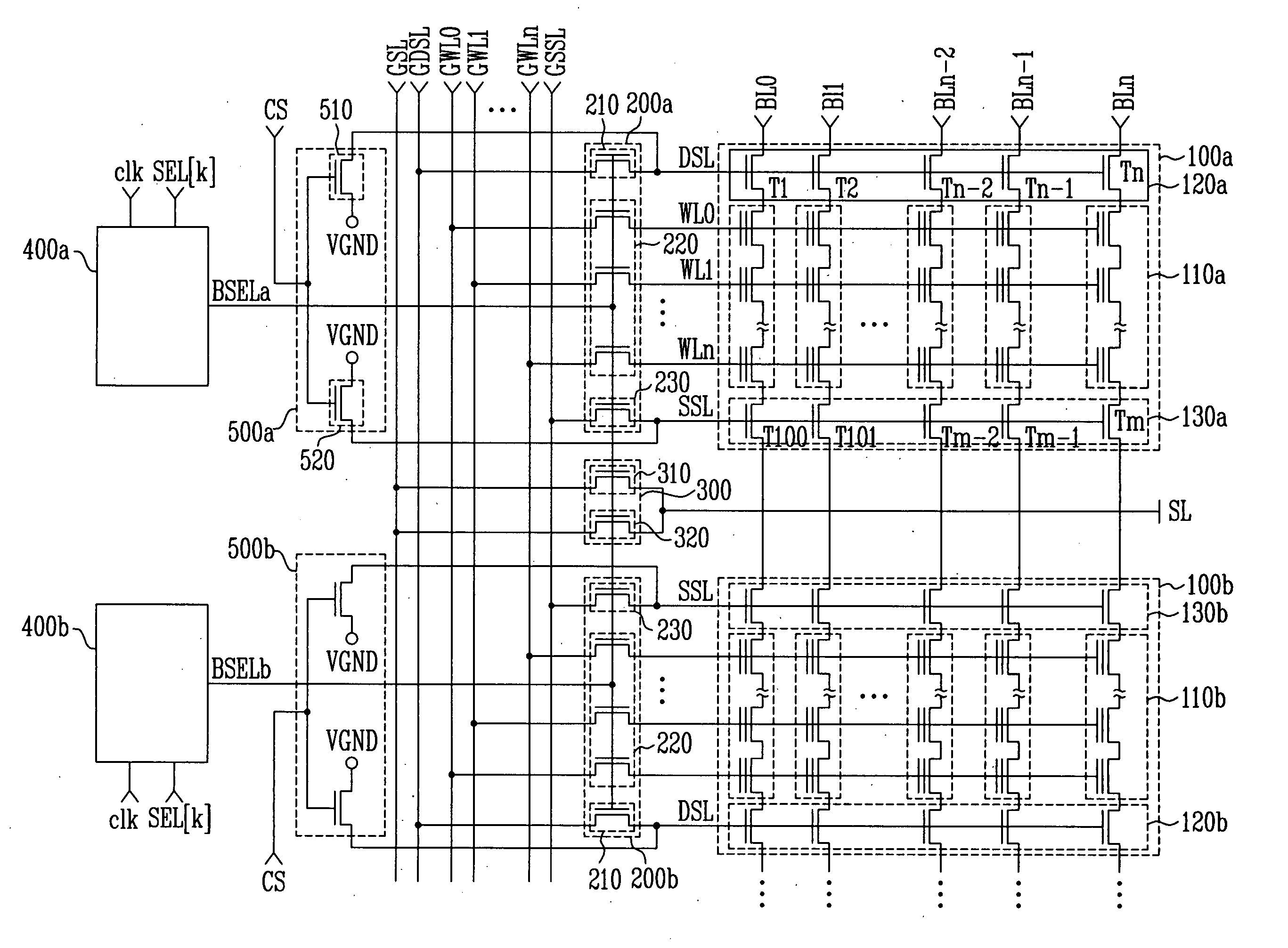
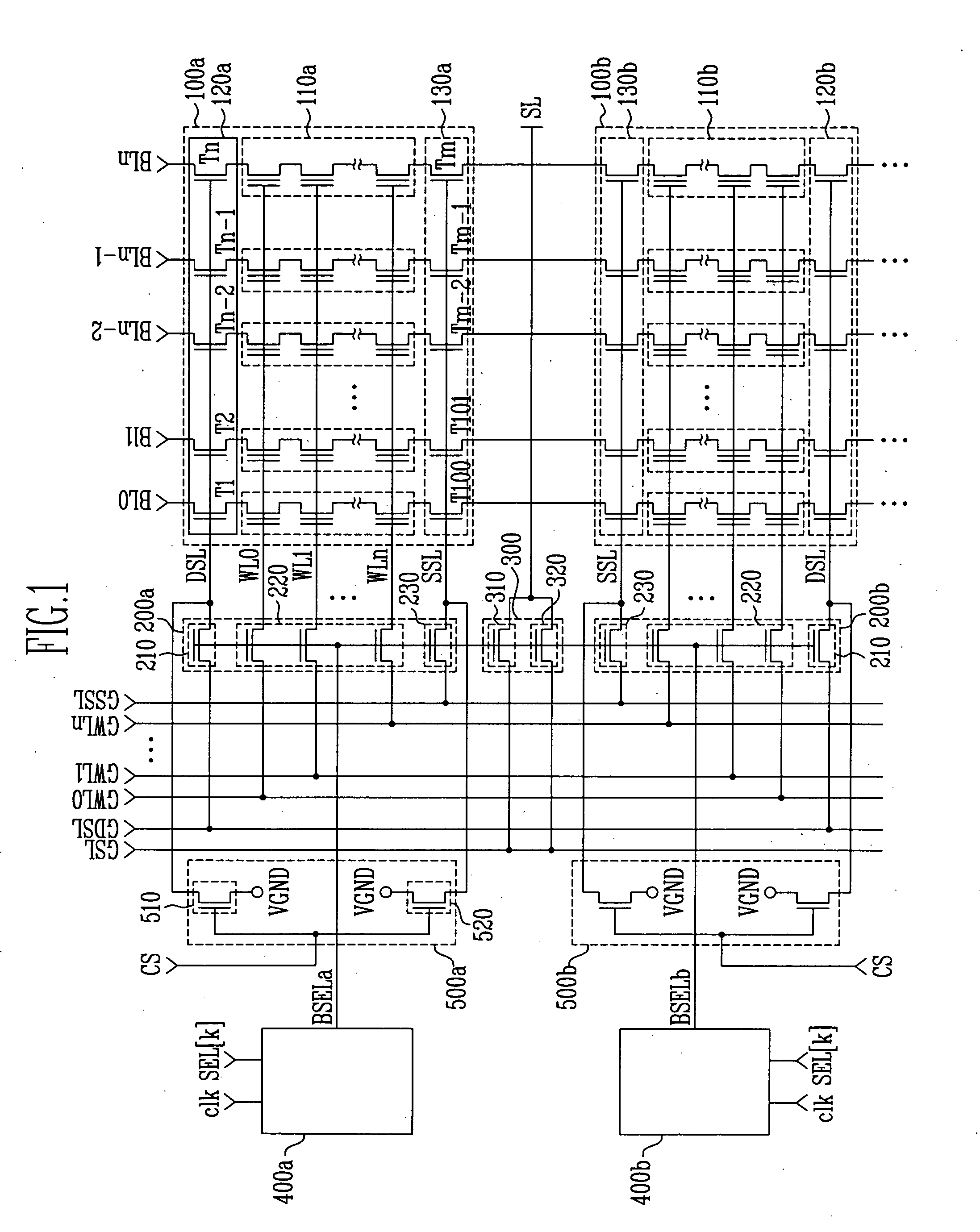
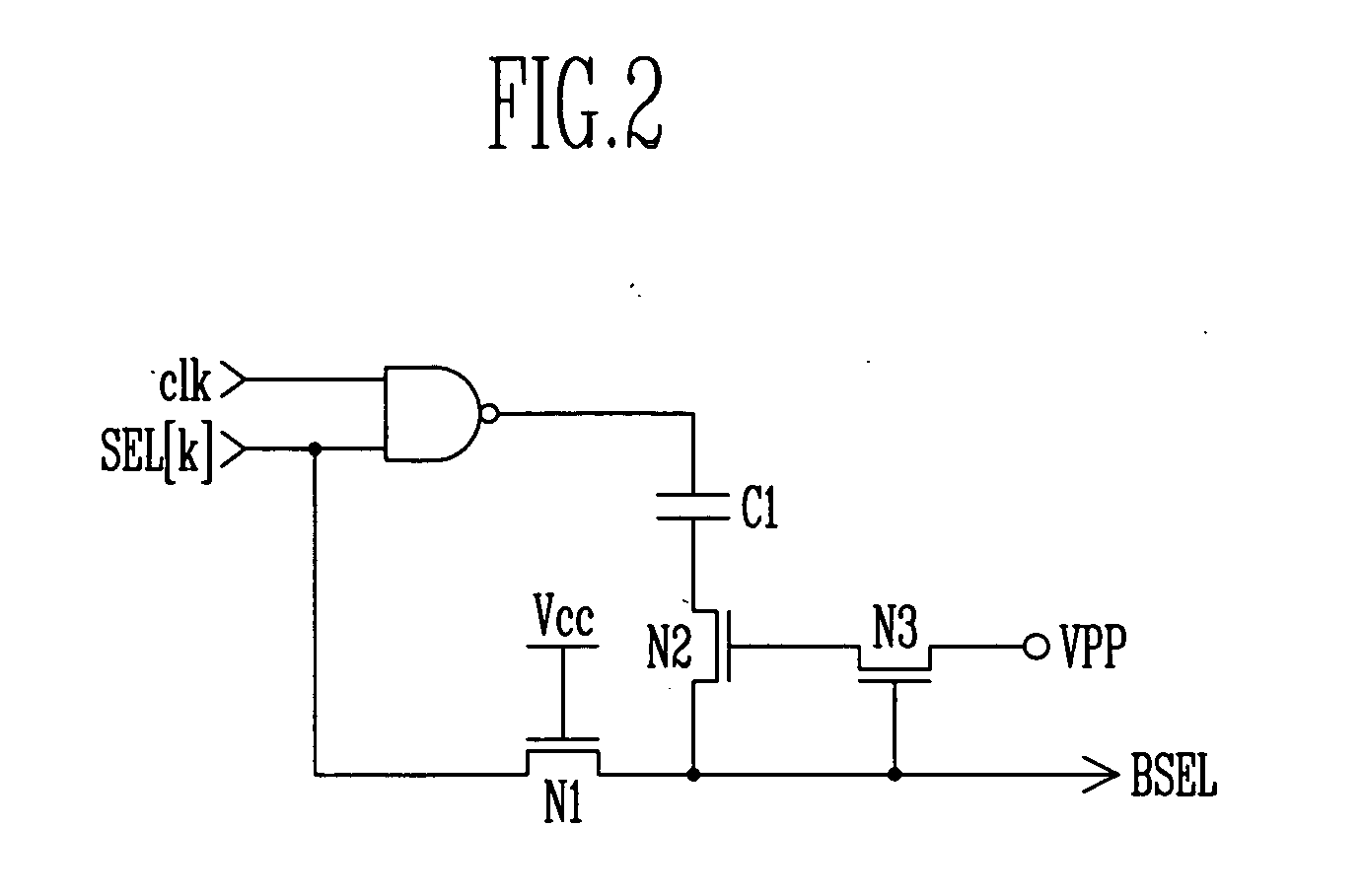
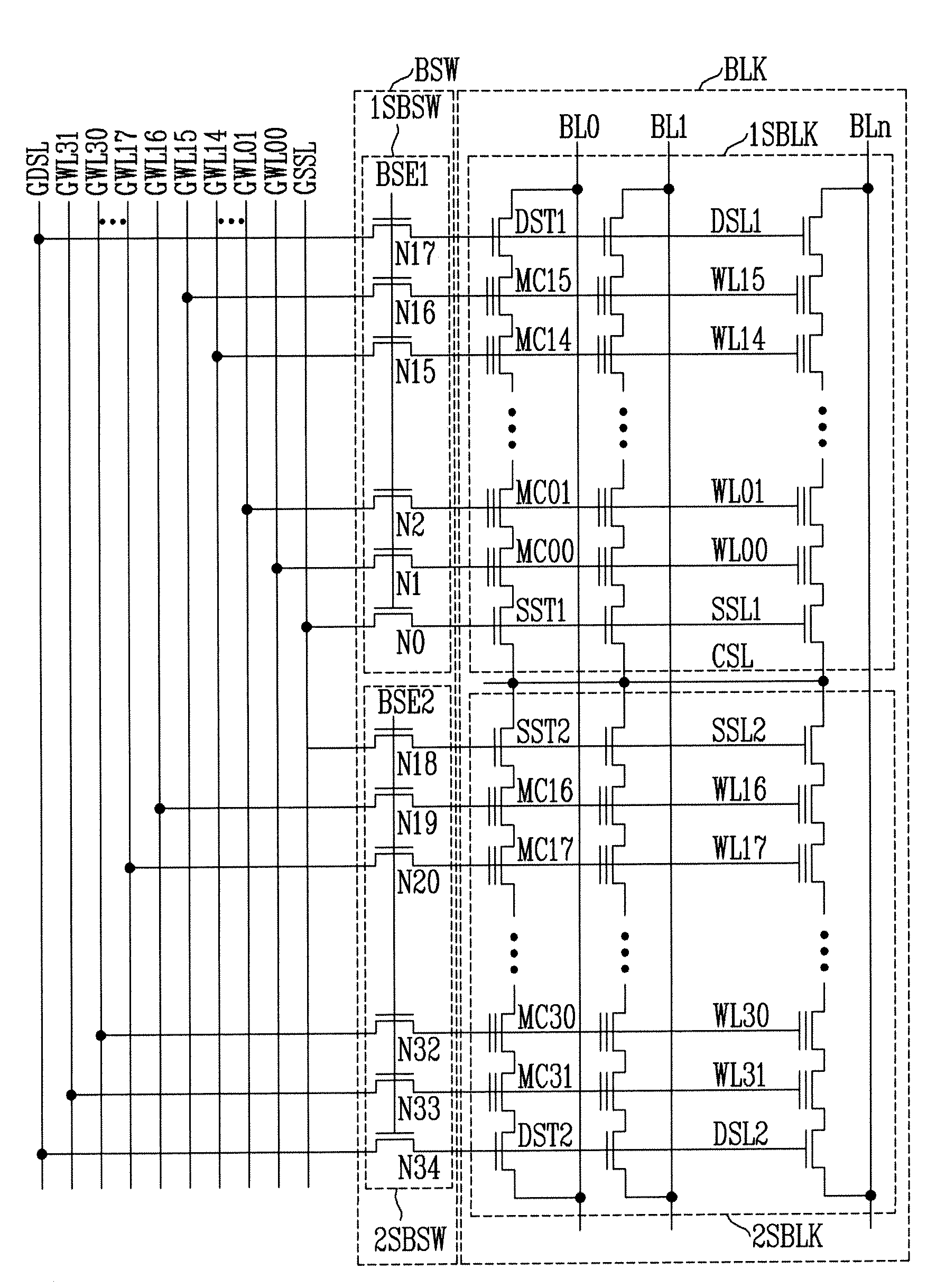
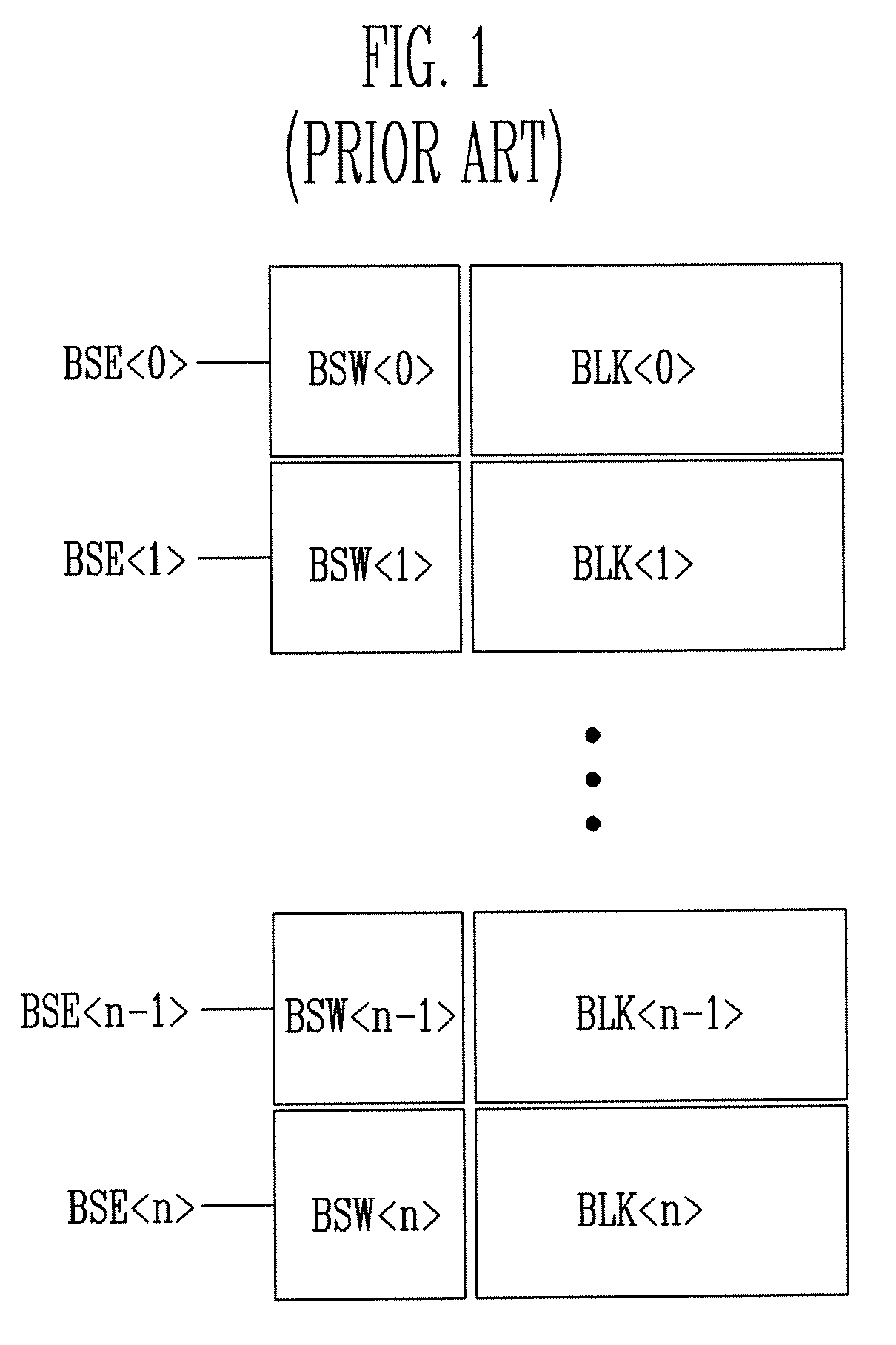
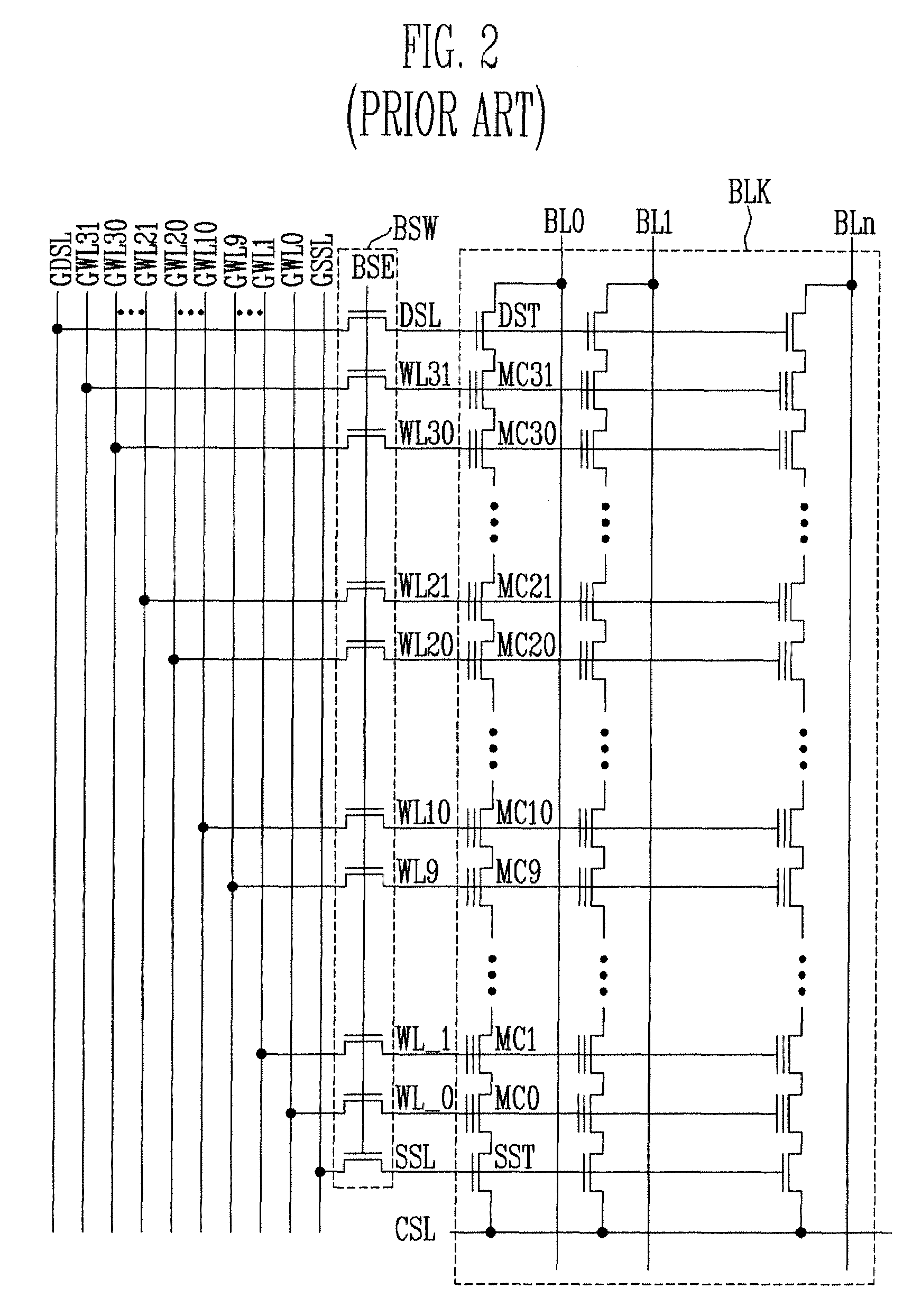
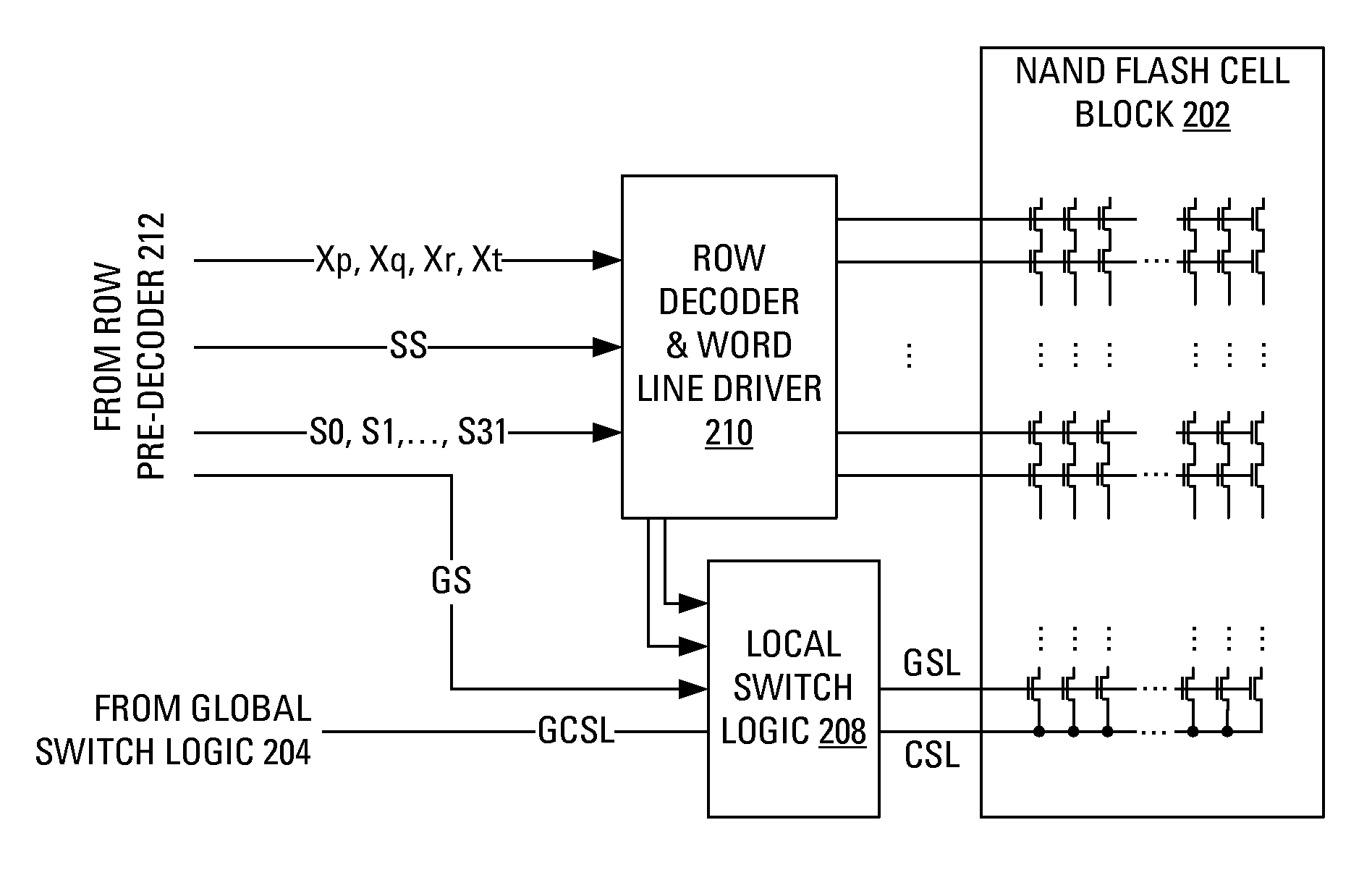
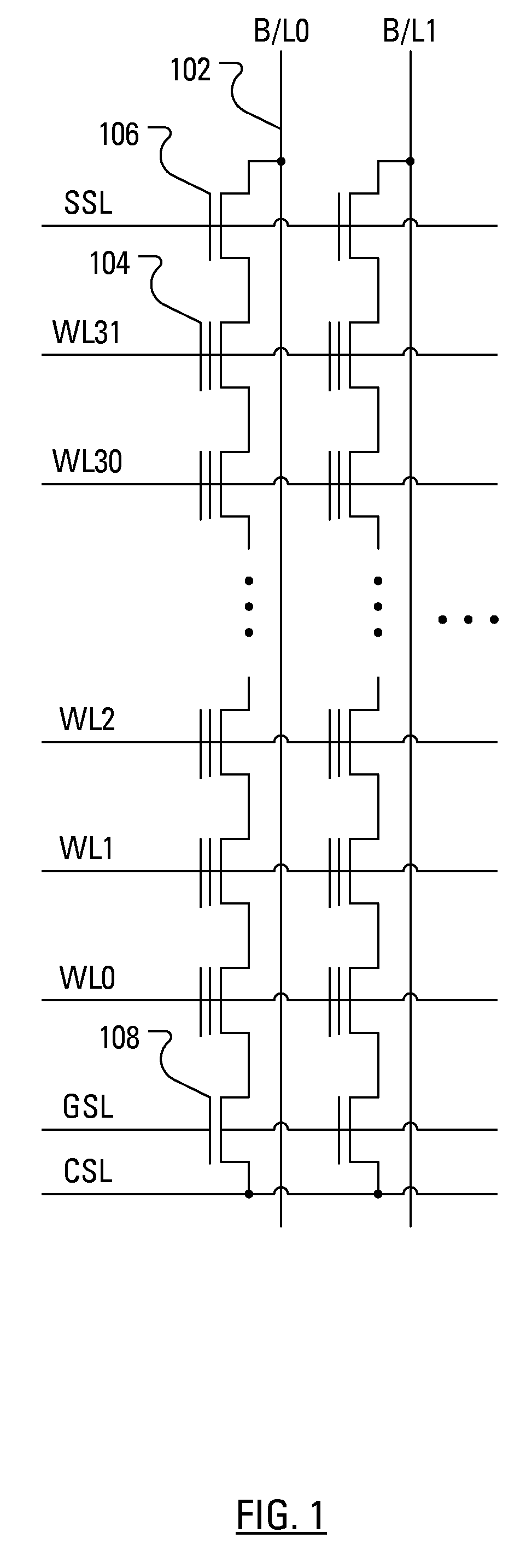
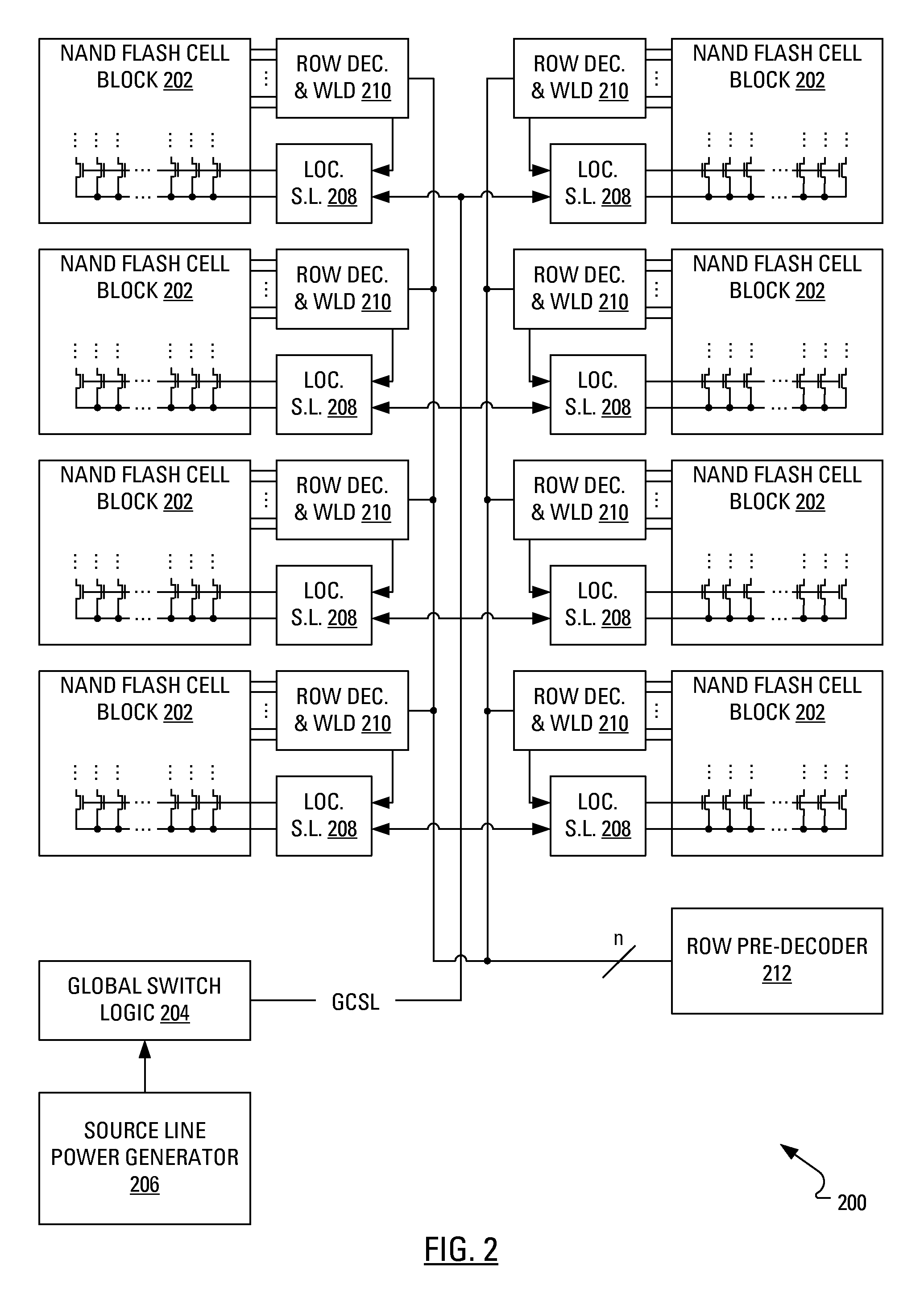
Hierarchical common source line structure in NAND flash memory
Each memory cell string in a generic NAND flash cell block connects to a Common Source Line (CLS). A value for applying to the CSL is centrally generated and distributed to a local switch logic unit corresponding to each NAND flash cell block. For source-line page programming, the distribution line may be called a Global Common Source Line (GCSL). In an array of NAND flash cell blocks, only one NAND flash cell block is selected at a time for programming. To reduce power consumption, only the selected NAND flash cell block receives a value on the CSL that is indicative of the value on the GCSL. Additionally, the CSLs of non-selected NAND flash cell blocks may be disabled through an active connection to ground.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com