Methods for reducing the effects of stress on skin condition
A technology for skin inflammation and chronic stress, applied to skin diseases, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulas, etc., can solve problems such as poor knowledge of skin appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
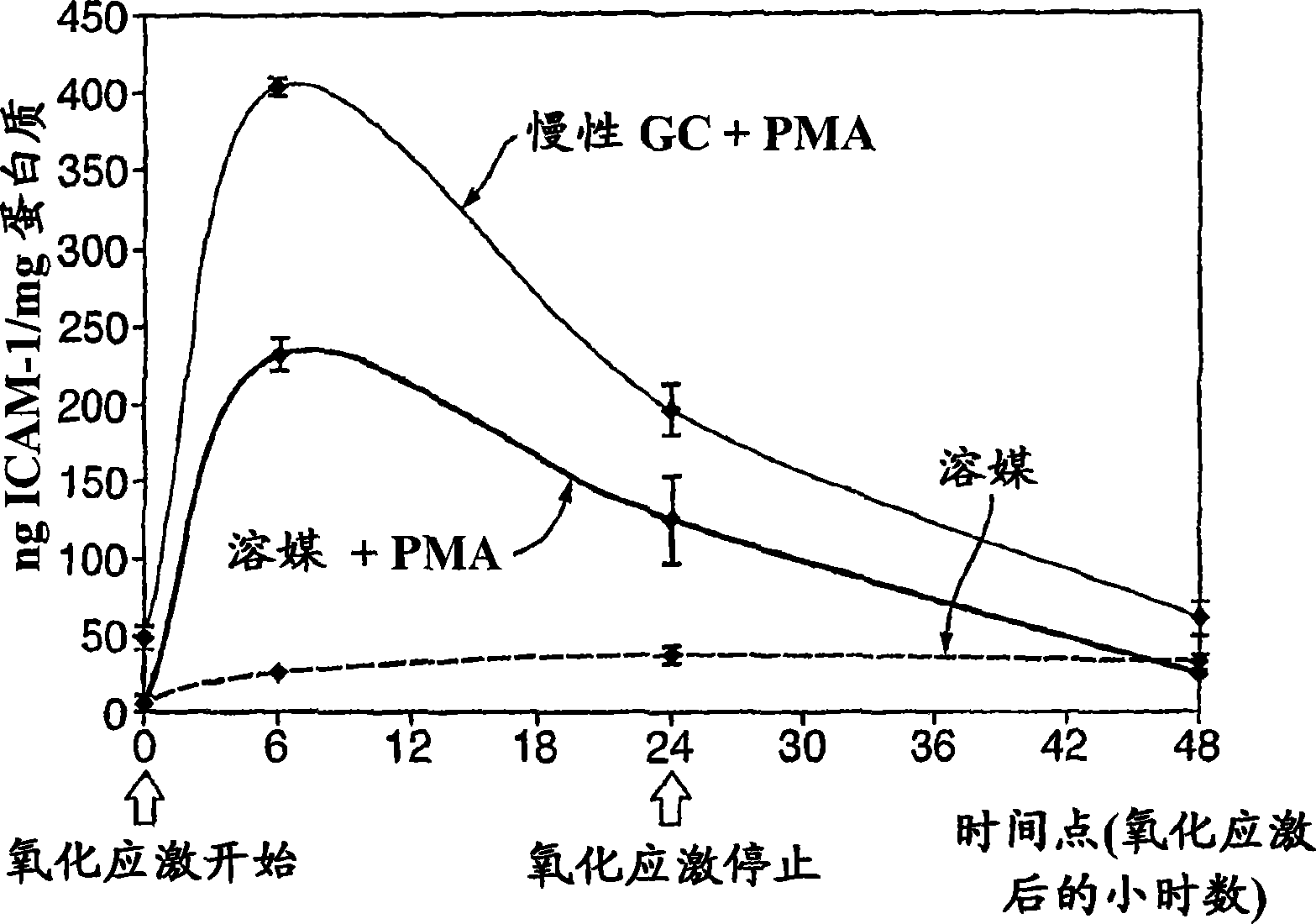
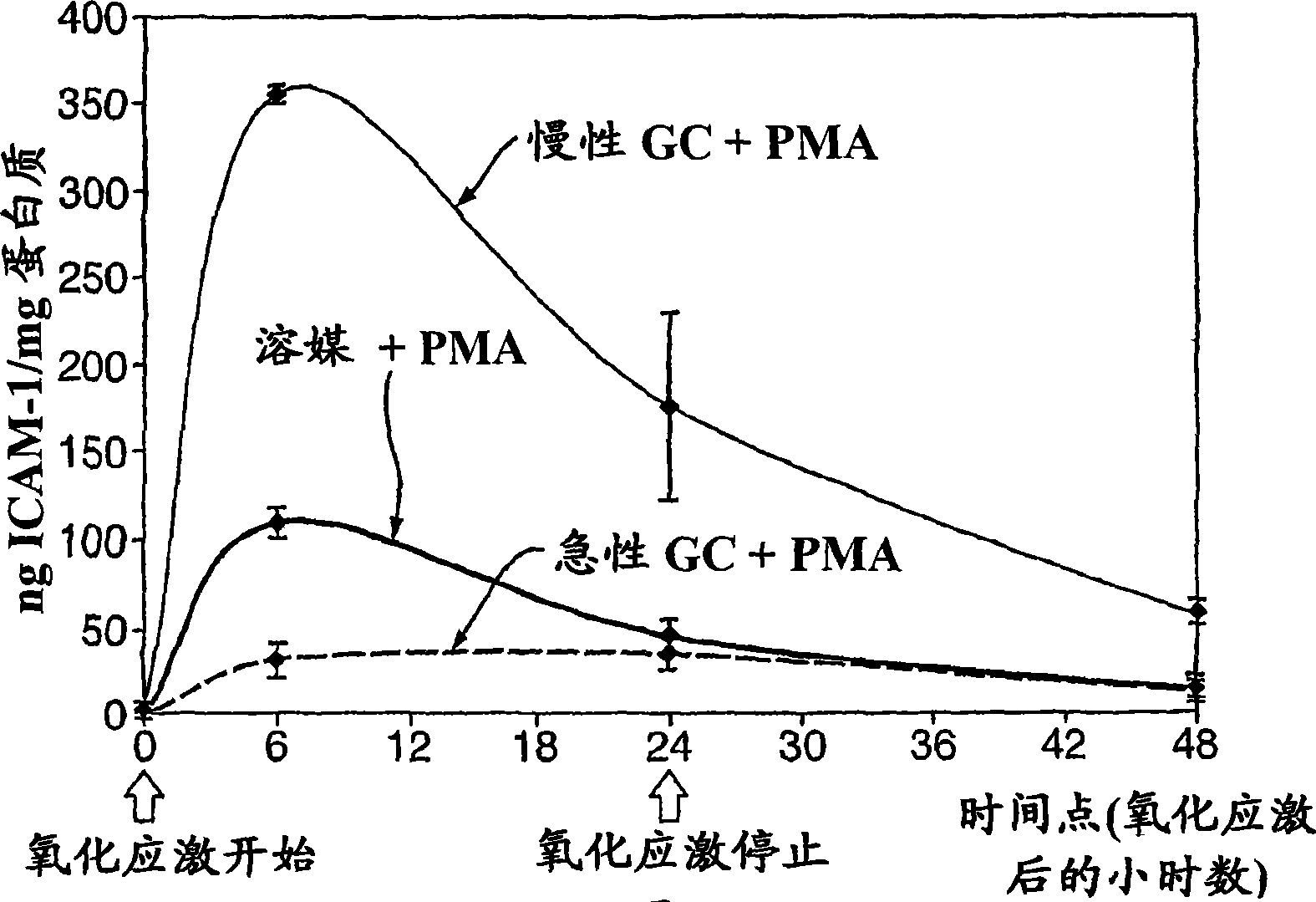
[0115] Example 1: Effects of Chronic Stress on the Inflammatory State of Endothelial Cells
[0116] Summary of Experimental Methods
[0117] An in vitro model has been developed to study the effect of chronic stress on the inflammatory state of endothelial cells.
[0118] a. Let the cells in 6 wells (9.5cm 2 ) plate growth.
[0119] b. Pretreatment with synthetic glucocorticoid (dexamethasone) was added every day for 5 days, so that the cells were subjected to "chronic stress".
[0120] c. At time point TO, harvest tissue culture supernatant and cell pellet.
[0121] d. Cells were subjected to oxidative stress with 1 [mu]M phorbol myristate acetate (PMA).
[0122] e. Tissue culture supernatants and cell pellets were harvested 6 hours, 24 hours and 48 hours after PMA treatment (T6, T24 and T48, respectively).
[0123] f. All tissue culture supernatants were assayed for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) to measure cytotoxicity and interleukin-6 synthesis.
[0124] g. All the cel...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Example 2: Effects of chronic stress on dermal matrix remodeling
[0176] The dermal matrix component of the skin is mainly composed of elastic fibers, collagen fibers, proteoglycans and other glycoproteins. This connective tissue complex acts as a scaffolding for the dermis to which cells, such as fibroblasts, can attach. The major protein component of such tissues is collagen, a fibrous protein of heterogeneous nature. Type I collagen is the predominant structural protein in the skin, and the appearance of aging skin is largely attributable to the breakdown of type I collagen. Normal fibril formation requires multiple post-translational modifications, including the proteolytic conversion of precursor procollagen to collagen. Therefore, the estimated amount of procollagen I can reflect the amount of collagen I molecules to be synthesized. Indeed, the histological features of damaged aged skin typically include flattened, hardened, disorganized bundles of collagen fi...
Embodiment 3
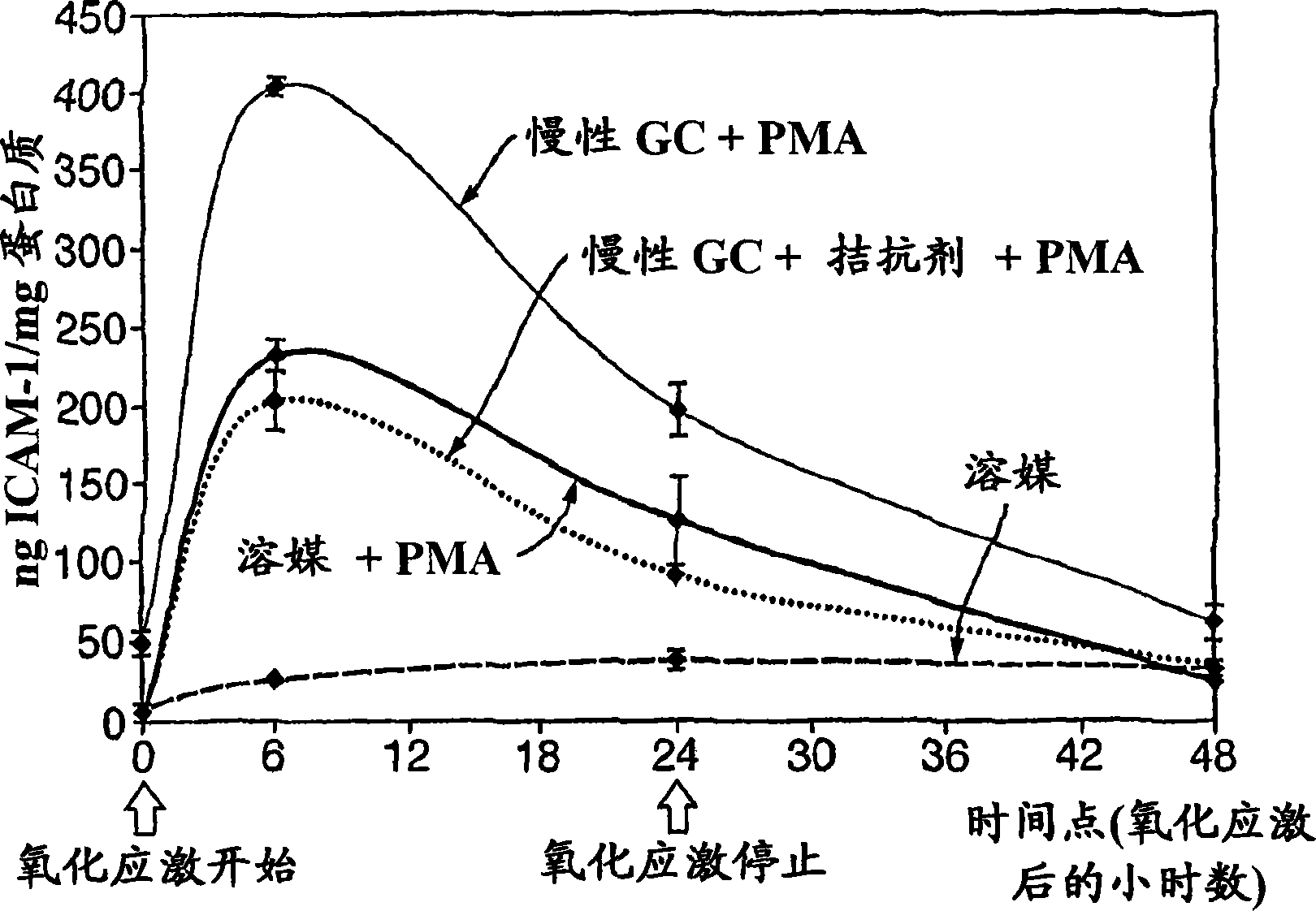
[0213] Example 3: Identification of drugs that inhibit glucocorticoid-mediated effects on skin cells-inflammation
[0214] Materials and Methods
[0215] The same method as described in Example 1 was used, except that various test drugs were added to the cells during pretreatment (see Table 1).
[0216] drug
source
22-OH-cholesterol
Ciglitazone
bisabolic acid
Ginsenoside Rb1
Ginsenoside Rc
Kyolic brand garlic
Pycnogenol (pycnogenol)
WY14643
Sigma H9384
Aldrich 74264
Sigma C0625
Calbiochem 230950
C. Rawlins, Unilever Research
Colworth (method below)
Sigma C7727
Sigma G3381
Sigma G0777
Sigma G0902
Quest Vitamins Ltd, Birmingham, UK
Sigma M2147
Sigma O9381
Nature's Aid, Preston, UK
Sigma R5010
A&E Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com