Drug-containing nanoparticle, process for producing the same and parenterally administered preparation from the nanoparticle
A drug-loading nanometer and nanoparticle technology, which is applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, nanomedicine, nanotechnology, etc., can solve problems such as failure to achieve practical application, unsatisfactory drug absorption or local irritation, etc. To achieve the effect of good bioavailability, high absorption, good sustained release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1: Preparation of Secondary Nanoparticles - Effect of Surfactants
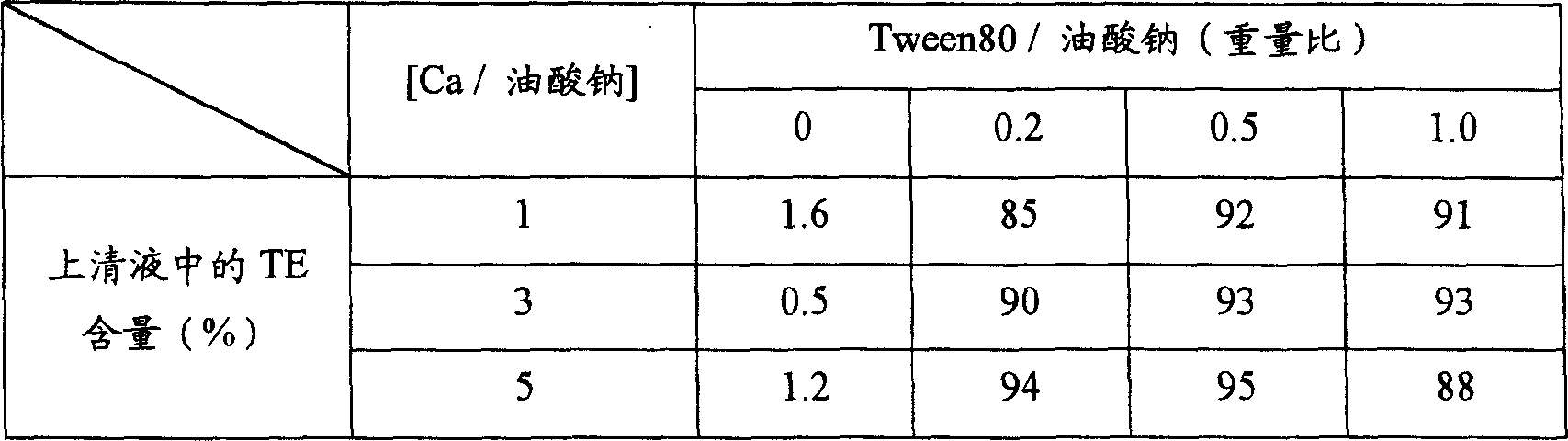
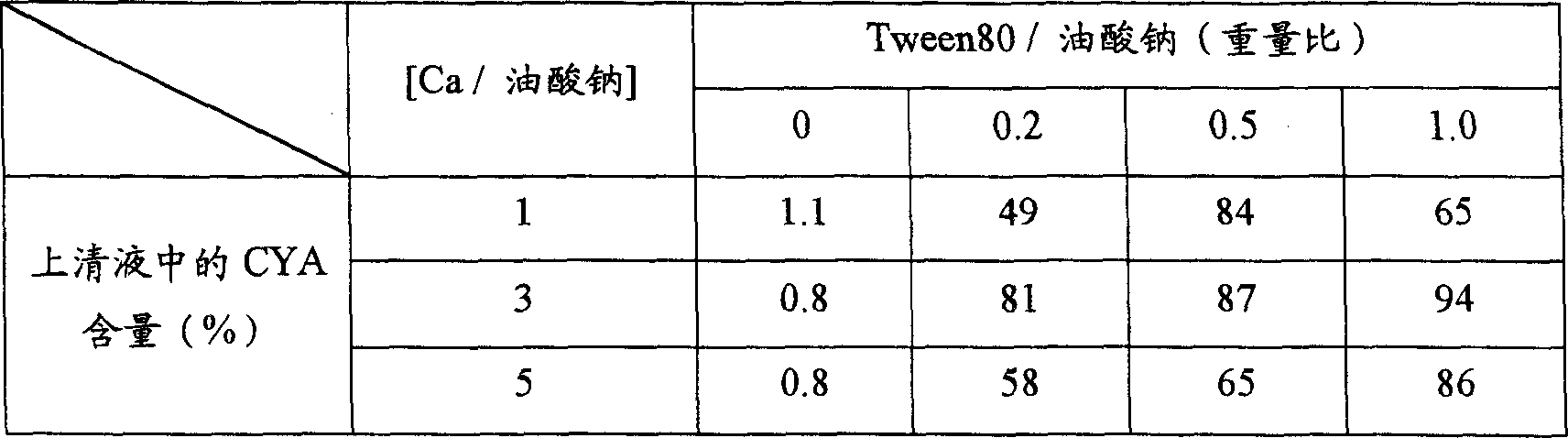
[0076] Add 10 mg of sodium oleate to 0.1 mL of water and dissolve it completely with a bath ultrasonic generator to form micelles. After that, 1 mg of testosterone enanthate or 1 mg of cyclosporine A dissolved in prescribed amounts of Tween80 and ethanol were mixed into the above solution, and the mixture was homogenized for 10 minutes with an ultrasonic generator. Then, by adding a prescribed amount of calcium chloride aqueous solution thereto and stirring for 30 minutes, secondary nanoparticles containing testosterone enanthate or cyclosporine A were prepared. The drug-containing solution thus prepared was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the contents of testosterone enanthate and cyclosporin A in the supernatant were quantified by HPLC. The results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0077] The effect of the amount (weight ratio) of calcium and Tween on the formation of micropa...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2: Preparation of Secondary Nanoparticles
[0085] Add 10 mg of sodium oleate to 0.1 mL of water and dissolve it completely with a bath ultrasonic generator to form micelles. Thereafter, 1 mg of betamethasone valerate dissolved in prescribed amounts of Tween 80 and ethanol was mixed into the above solution, and ultrasonic waves were irradiated for 10 minutes. Then, secondary nanoparticles containing betamethasone valerate were prepared by adding 33 μL of 1 M calcium chloride aqueous solution thereto and stirring for 30 minutes. The drug-containing solution thus prepared was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the content of betamethasone valerate in the supernatant was quantified by HPLC. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0086] Particle Formation of Betamethasone Valerate (BV)
[0087] [table 3]
[0088]
Embodiment 3
[0089] Embodiment 3: the relation of surfactant and particle size
[0090] Mix a predetermined amount of lipid-PEG (phosphatidylethanolamine-PEG (MW: 2000), manufactured by NOF) or Tween80 into 10 mg of sodium oleate, mix well with an ultrasonic generator, and then add 33 μL of 1M chlorine Calcium chloride aqueous solution, measure its particle size. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0091] The Effect of Surfactant Amount on the Particle Size of Surfactant / Oleic Acid Microparticles
[0092] [Table 4]
[0093]
[0094] ND: not determined
[0095] From the results shown in Table 4, it can be clearly seen that the greater the amount of surfactant used, the larger its particle size, and if the amount is too small, it will also aggregate or form large particles, and there is a mixing ratio that forms the smallest particle size.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com