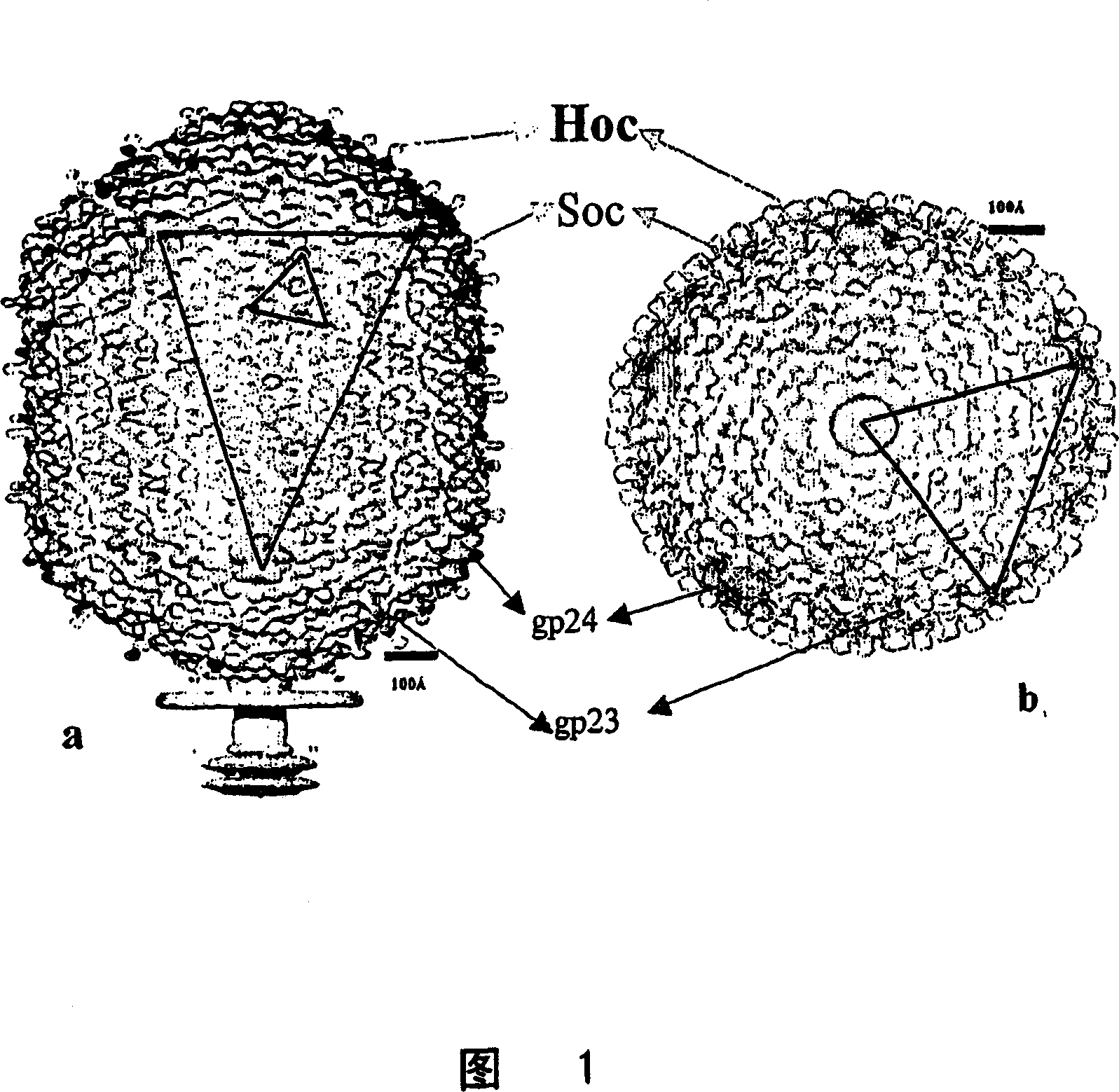
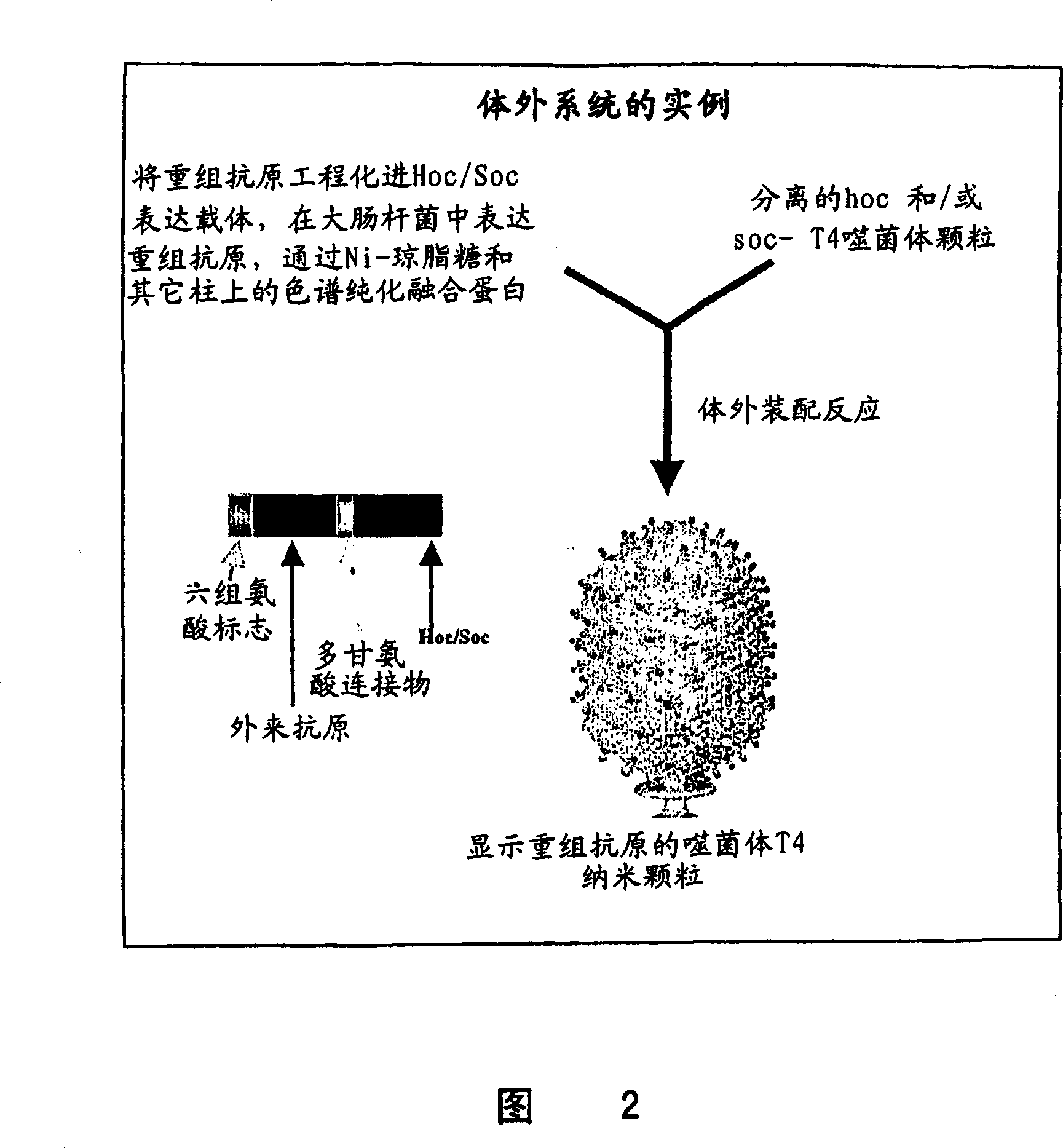
Methods and compositions comprising bacteriophage nanoparticles
A composition and phage technology, applied in the field of T4 phage, can solve problems such as inability to package DNA, difficulty in copy number, inability to use stimulation-strengthening strategies, etc., and achieve reliable production effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
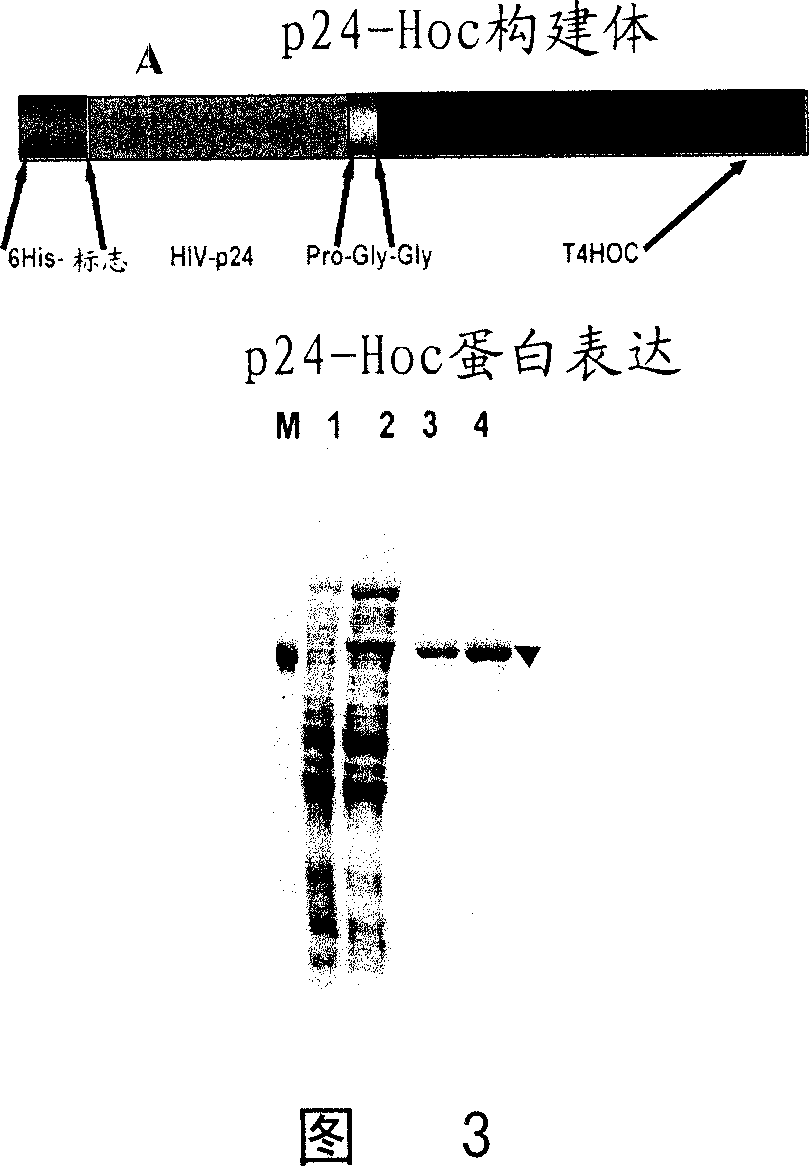
[0086] Construction, overexpression and purification of p24-Hoc
[0087] A DNA fragment corresponding to the full-length p24 polypeptide (225 amino acids, 24 kDa) was ligated to the 5'-end of the hoc gene via the DNA sequence encoding the pro-gly-gly linker sequence. As mentioned above, p24 is the large capsid subunit of the HIV capsid, which encloses 2 molecules of the HIV genome and other protein (e.g., reverse transcriptase, integrase) and nucleic acid (e.g., tryptophan tRNA primer) components, It is necessary for infection. This can be achieved through the SOE strategy disclosed by Kuebler and Rao, 1998. In-frame insertion of the construct into the BamHI site of the T7 expression vector pET15b (Novagen Inc. Madison, WI, USA) resulted in the insertion of a 26 amino acid sequence consisting of a hexahistidine tag to the N-terminus of the p24-Hoc protein sequence. Binding (Fig. 3(A)). Induced by IPTG, the expressed 66kDa HexaHis-p24-Hoc fusion protein accounted for about 1...
Embodiment 2
[0089] In vitro assembly of T4 nanoparticles
[0090] To assemble or "load" recombinant antigen onto the surface of T4 phage particles, approximately 2x10 10 Sucrose gradient - purified HOC - soc - T4 nanoparticles with TMG buffer (50mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH7.0, 75mM NaCl and 1mMMgSO 4 ) with increasing amounts of purified HIV-p24-Hoc and incubated at 37° C. for about 60 min. Then, the resulting T4 nanoparticles were precipitated at 14,000 rpm for 60 min, and the unbound supernatant fraction was discarded. Wash the pellet twice with excess buffer to remove any unbound or non-specifically captured protein. All samples, starting material, unbound and bound fractions, and controls were analyzed by 4-20% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and stained with Coomassie blue. Referring to Figure 4, the ratio of HIV-p24-Hoc and Hoc binding sites is indicated at the top of the figure. Lanes are as follows: St, starting p24-Hoc; Su, p24-Hoc in...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Specificity and stability of in vitro assembly systems
[0093] p24-Hoc and hoc - soc - The binding interactions between T4 nanoparticles are highly specific. Figure 5 illustrates this specificity. Using the experimental design of Example 2, T4 nanoparticles were incubated with p24 alone (lanes 2-4) or a mixture of p24 and p24-Hoc (lanes 5-7). When compared to control phage (lane 1, C-Ph), p24 bound to particles only when fused to Hoc (lanes 5-7). Note that no significant p24 binding occurs. The position of p24-Hoc is marked with an arrow. These results indicate that fusion to the Hoc polypeptide or a fragment thereof is required for binding to T4 particles. Neither the control proteins BSA (66 kDa) nor anthrax PA (89 kDa) showed significant binding to T4 particles (data not shown).
[0094] The stability of the interaction between displayed p24-Hoc and T4 phage particles was assessed by treating p24-T4 nanoparticles with pH 2.0 buffer or 6M urea, and whether eit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com