Defined three dimensional microenvironment for cell culture
a three-dimensional microenvironment and cell culture technology, applied in cell culture active agents, embryonic cells, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems of batch-to-batch or lot, experimental variability, inherent heterogeneity, etc., to improve colony shape, increase the surface density of phsrn-rgdsp, and improve the effect of colony siz
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Electrospinnable Biofunctional Composition to Engineer an Extracellular Microenvironment
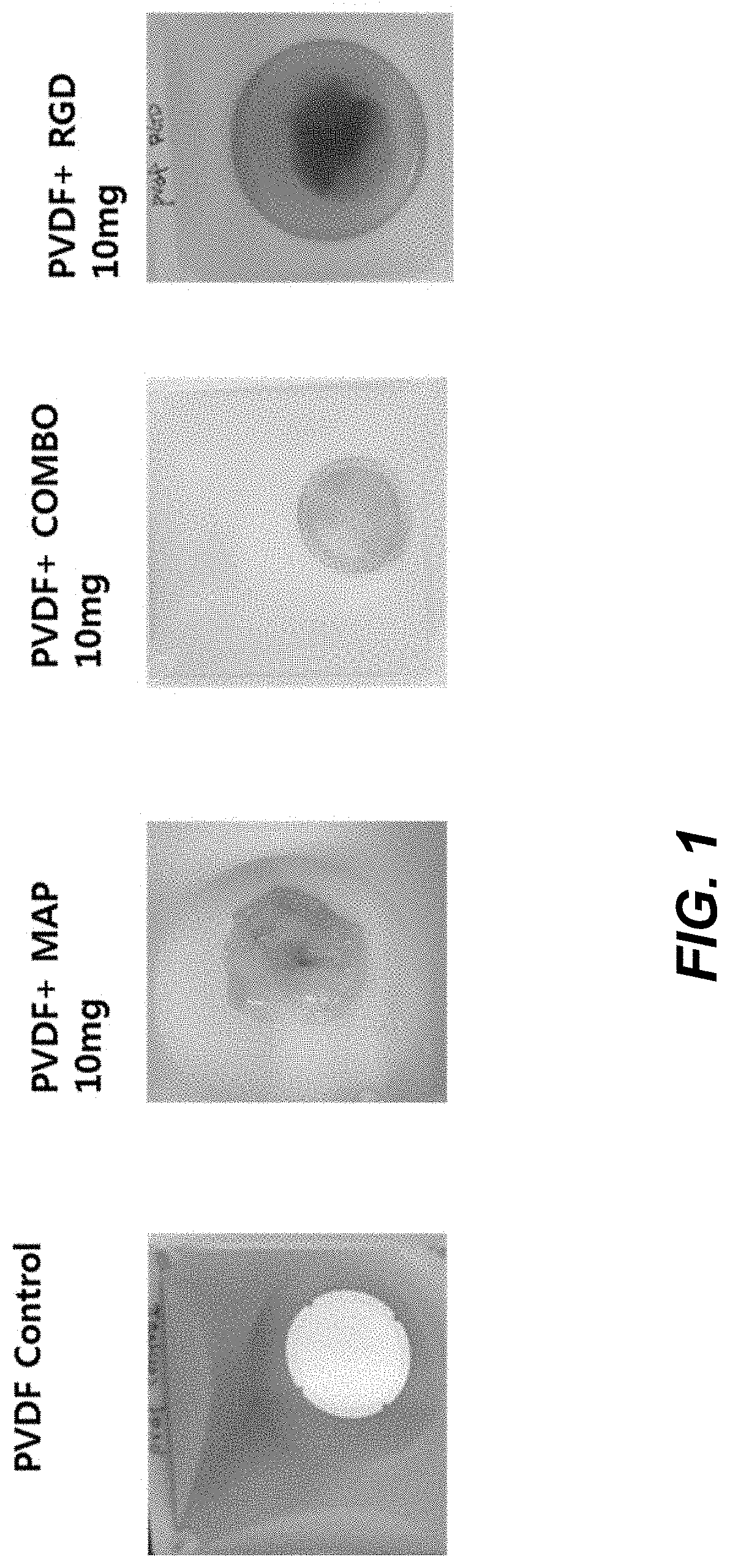
[0128]PVDF with an average molecular weight of 200 kDa from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, USA), PAN with an average molecular weight of 200 kDa, PES with an average molecular weight of 200 kDa purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, USA), PLA with an average molecular weight of 200 kDa purchased from Sigma Aldrich were dissolved in DMAc to prepare 20 wt % solution. MAPTrix™ ECM (no peptide motif, PHSRN-RGDSP (SEQ ID NO:17) (combo) containing, and RGD motif containing) purchased from Kollodis BioSciences (North Augusta, S.C., USA) was dissolved in an aqueous solution composed of distilled water and DMAc. Each polymer solution was mixed well together with MAPTrix™ ECM solution by vortexing it for 10 minutes to make homogeneous 18 wt % solution.
[0129]The electrospinnable (e-spin) solution was placed in a plastic syringe fitted with a 27 G needle. A syringe pump (KD Scientific, USA) was u...
example 2
Preparation of Nanofiber Having Different Diameter
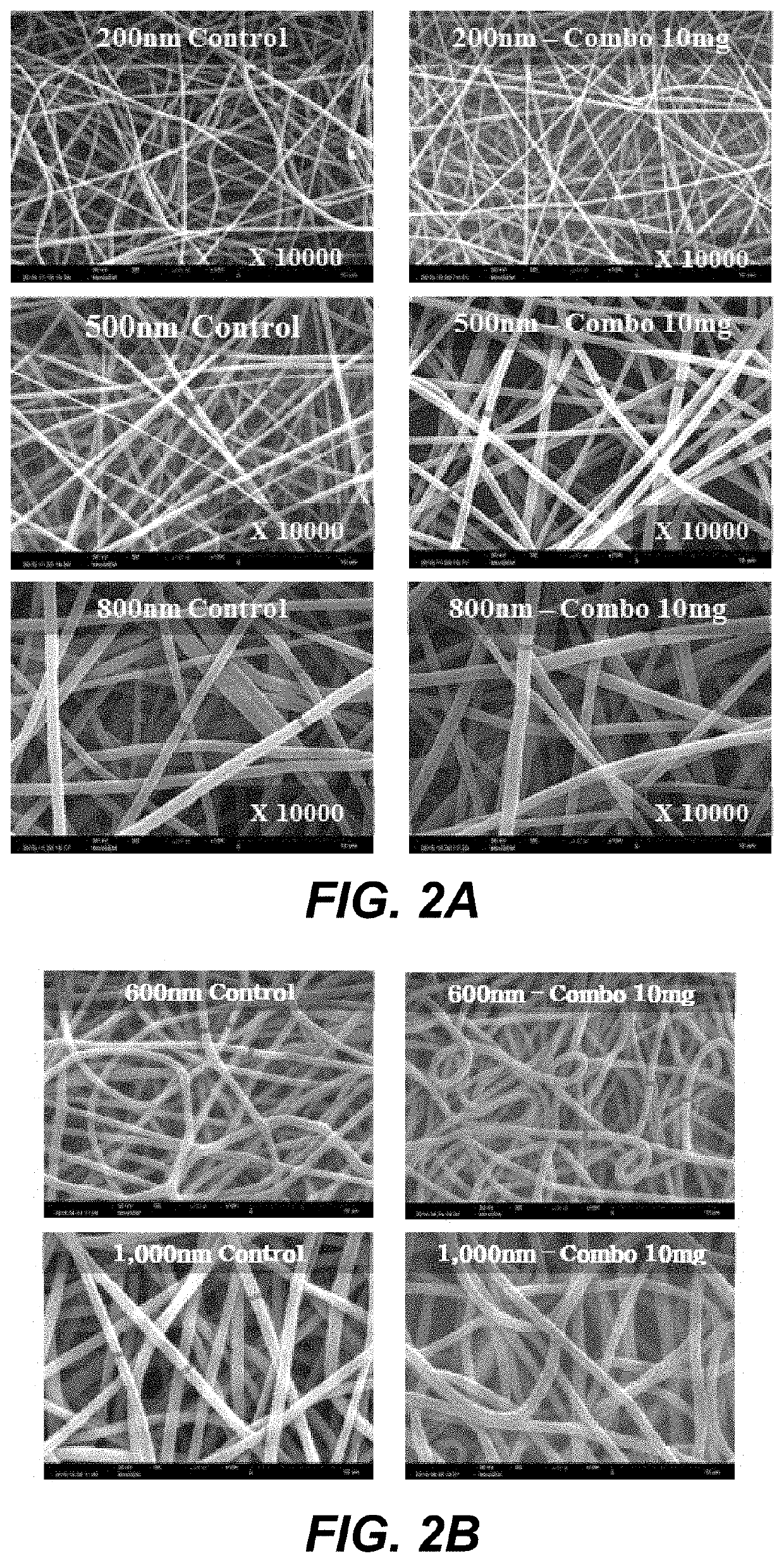
[0136]Each Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF)-Kynar 761(Homopolymer, Mw: 400,000-500,000), and Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVdF)-Solef 21216(Co-polymer, Mw: 600,000) or Polyacrylonitril-Pulver (Co-PAN, Mw: 85,000) was dissolved in DMAC and blended. The blending ration of homopolymer to copolymer were 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, 1:5, 1:6, 1:7, 1:8, 1:9. Nanofibers having different diameter were formed by the same procedure mentioned in EXAMPLE 1.
[0137]The diameter of each nanofiber sheet is measured by observation using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), a thin gold layer was deposited on the surface of each nanofiber sheet. FIG. 2A shows nanofiber sheets having a diameter of 200, 500, and 800 nm, respectively. FIG. 2B shows nanofiber sheets having a diameter of 600 and 1,000 nm, respectively.
example 3
Preparation of Nanofiber Having Particles
[0138]MAPTrix™ ECM based particles were formed by reaction of the carboxyl group of MAPTrix™ activated by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimides / N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (EDC / s-NHS) on the C-terminus with the amino groups of the MAPTrix™.
[0139]1-Ethyl-3-[3-Dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) solution is prepared by dissolving 10 mg of EDC in 1 ml of sodium bicarbonate buffer (10 mM, pH 6.5). 5 mg of solid sulfo-N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (S—NHS) is added to the EDC solution. The EDC / S—NHS solution is added to the nanofiber surface to activate carboxyl group of MAPTrix™ surfaced on the nanofiber sheet for 30 minutes. After the C-terminus activation, 0.1 mg of MAPTrix™ having PHSRN-RGDSP (SEQ ID NO:17) motif dissolved in 1 mL distilled water was added to the nanofiber surface. Crosslinking is carried out at ambient temperature for 30 minutes to get crosslinked MAPTrix™ particle presenting PHSRN-RGDSP (SEQ ID NO:17) on ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com