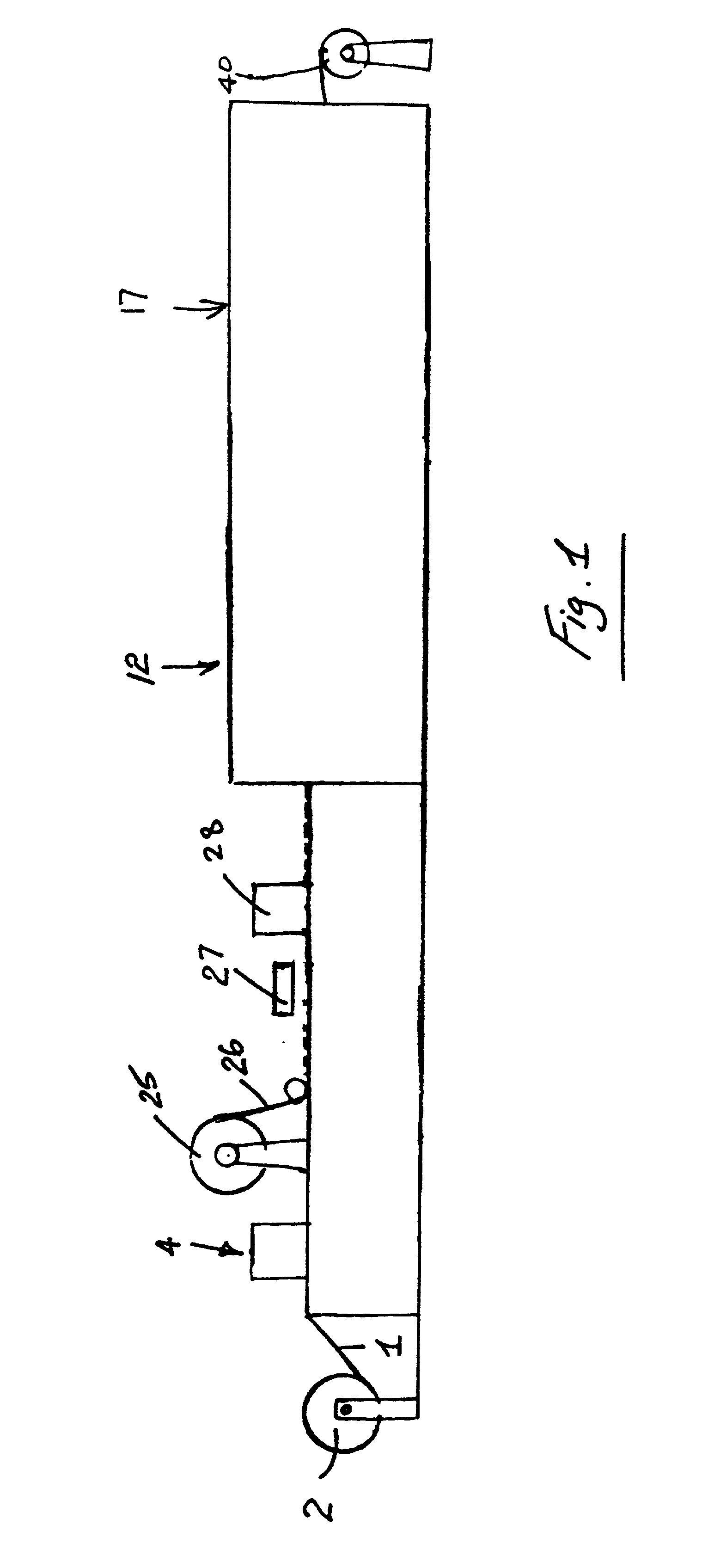
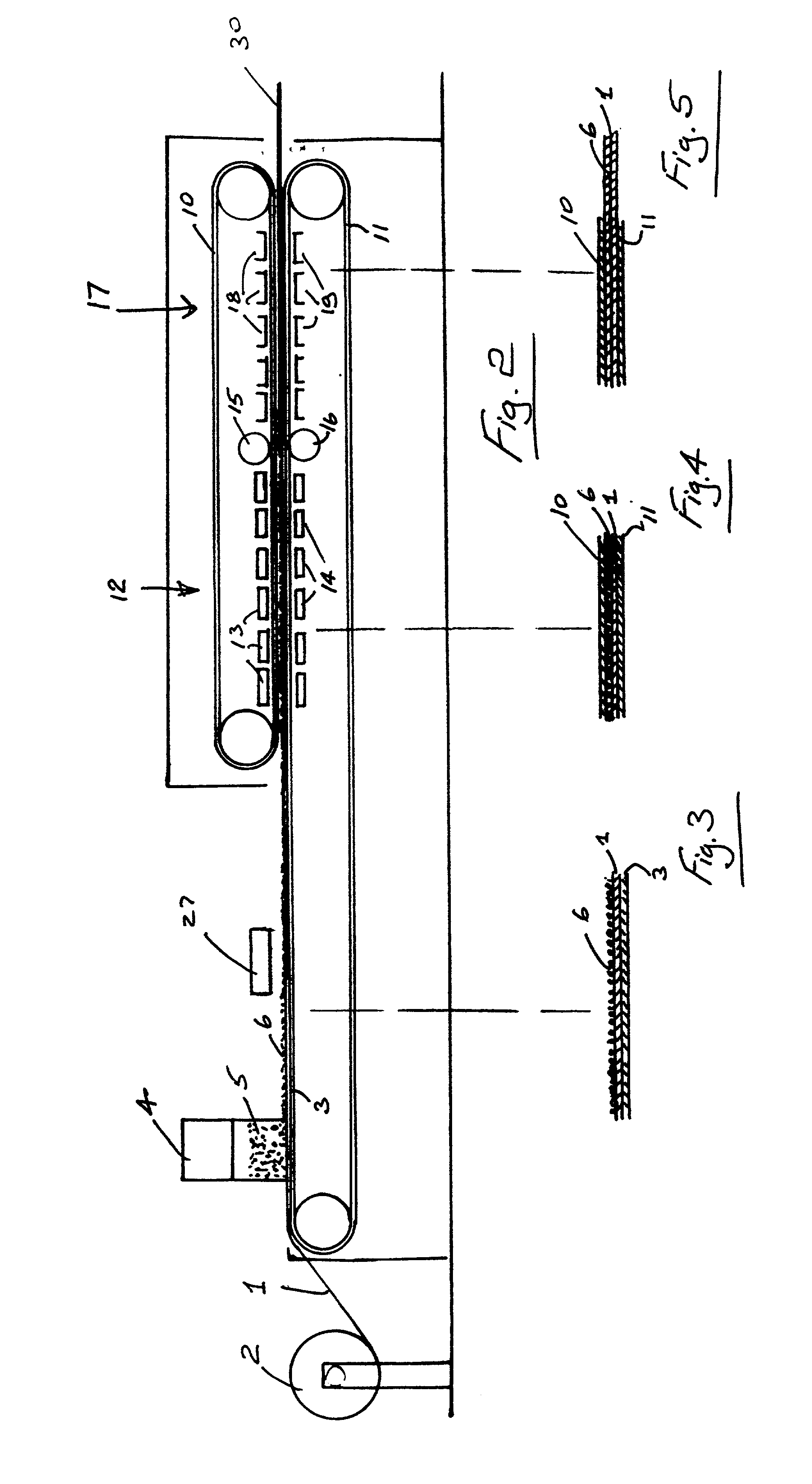
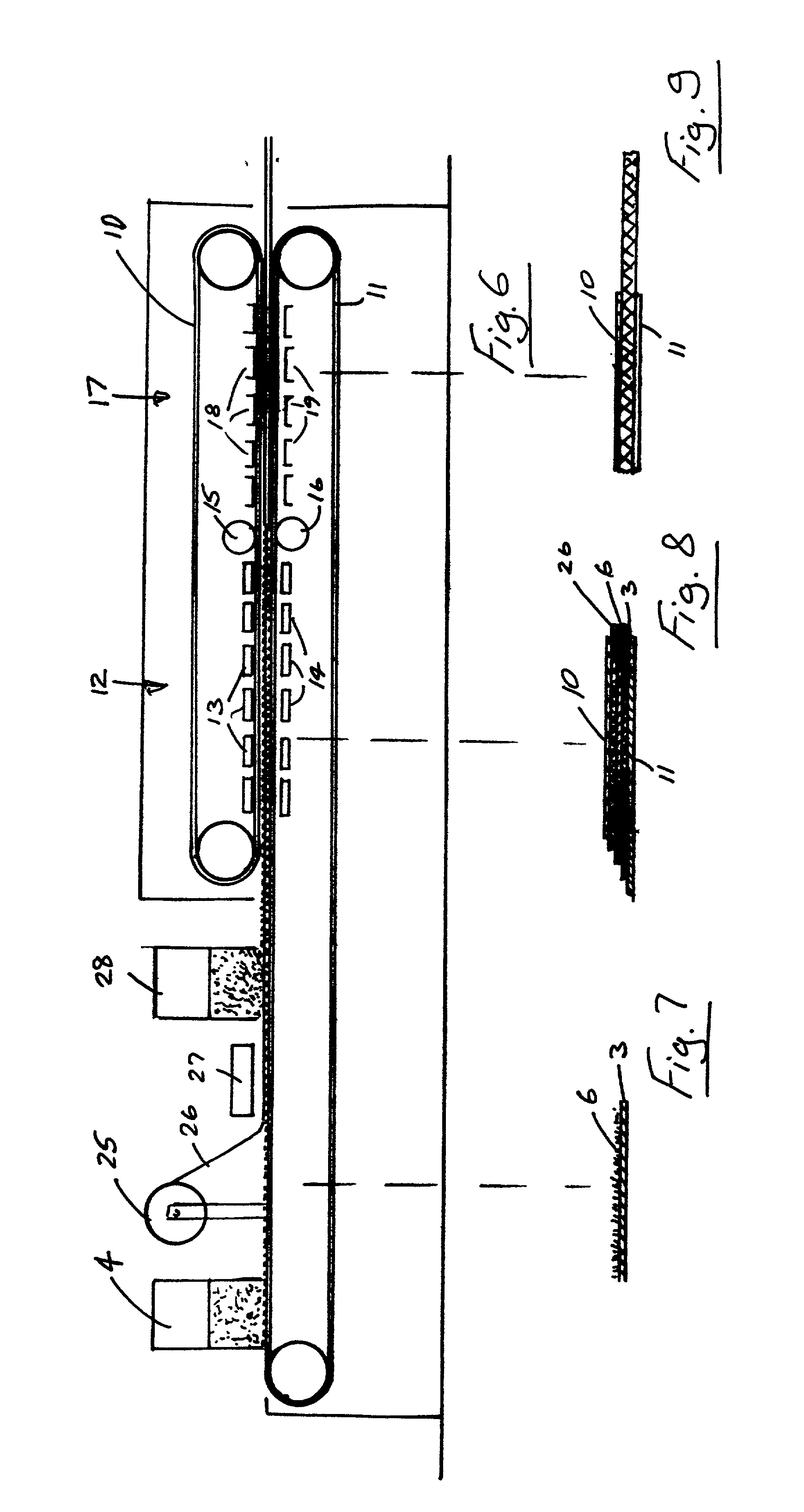
Method for manufacturing a floor covering
a manufacturing method and technology for floor coverings, applied in the direction of cork mechanical work, mechanical apparatus, non-woven fabrics, etc., to achieve the effects of easy control, controlled scattering, and high processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0086] A foamed basecoat material may be applied to a saturated substrate using the following basecoat dry blend formulation:
2 Parts by Weight Suspension Grade PVC 95-100 Dispersion Grade PVC 0-5 Di-2-Ethyl Hexyl Phthalate 20-50 Butyl Benzyl Phthalate 20-50 Calcium Carbonate Filler 20-80 Barium / Zinc Stabiliser 1.5-3.5 Blowing Agent Mixture 2-4 (Azodicarbonamide / Zinc Oxide) Titanium dioxide 6-10
[0087] The foamable basecoat material is scattered onto the saturated substrate at a single scattering station at a rate of from 250-450 g / m.sup.2 and further processed as described above in Example 1.
[0088] It will be appreciated that the method is applicable to producing non directional homogeneous floor covering materials.
[0089] It will also be appreciated that while the invention has been described particularly in relation to PVC material it may also be applied to any suitable thermoplastics materials which are substantially free of PVC.
[0090] Many variations on the specific embodiments of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermoplastic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com