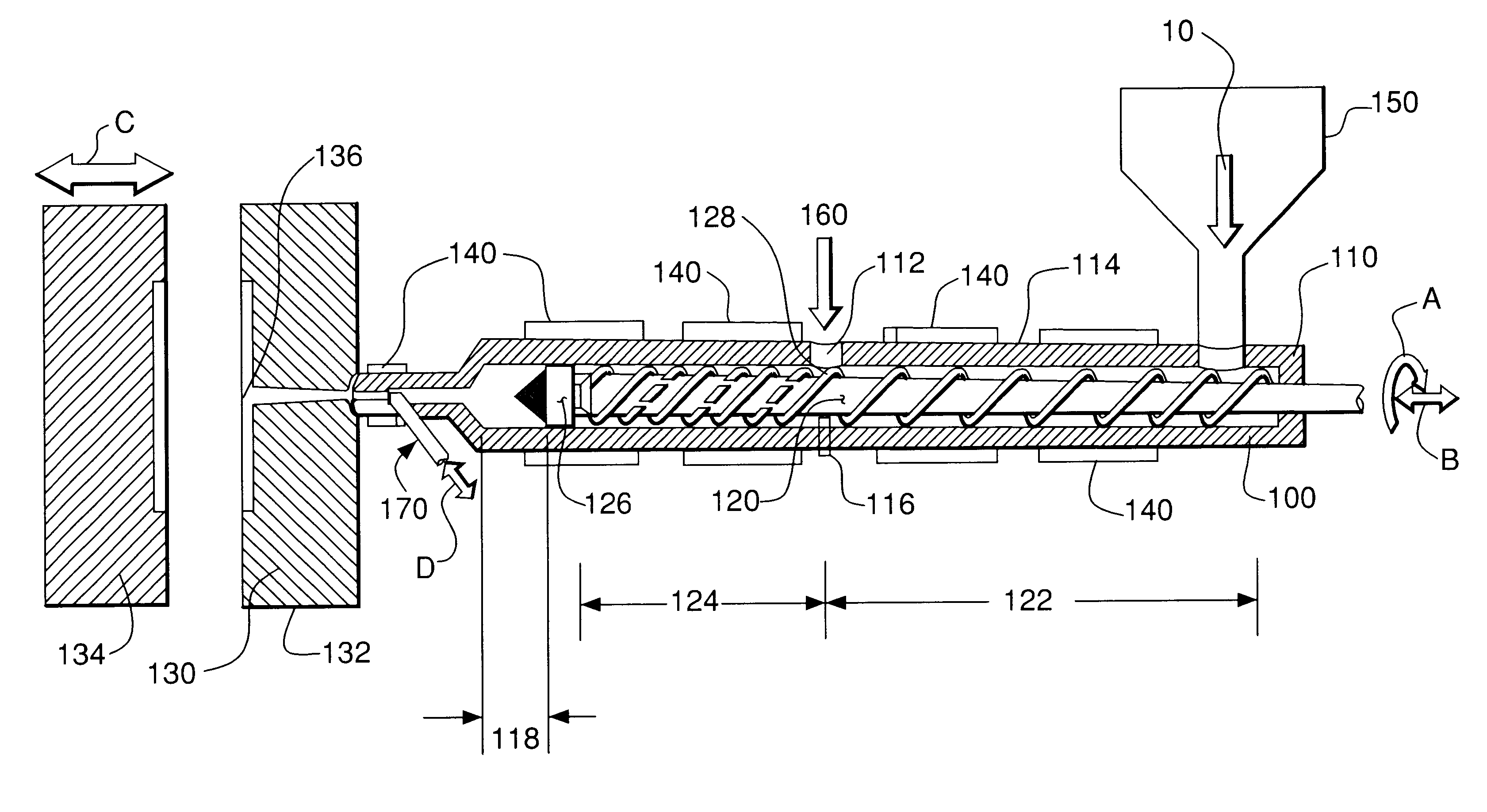
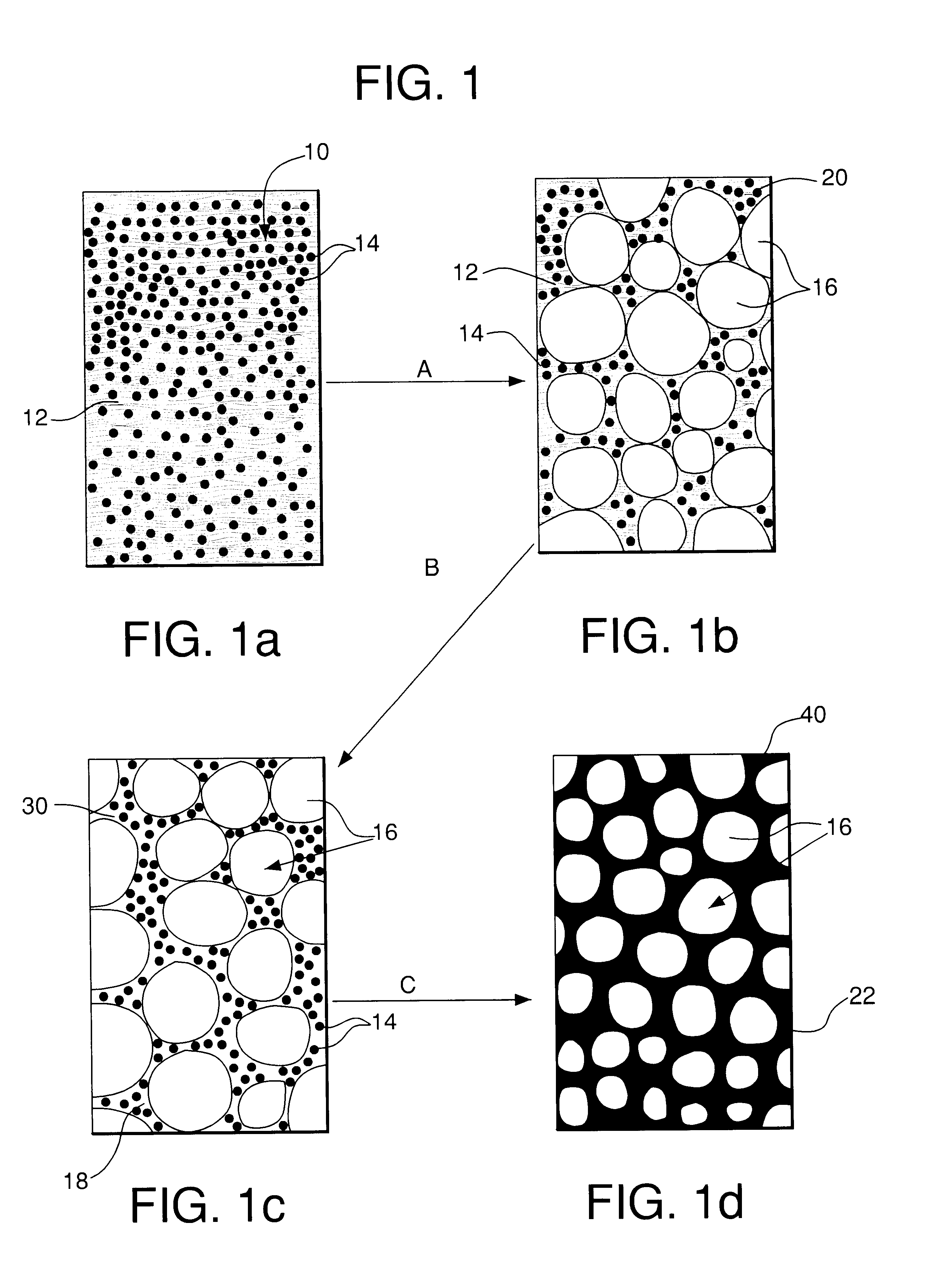
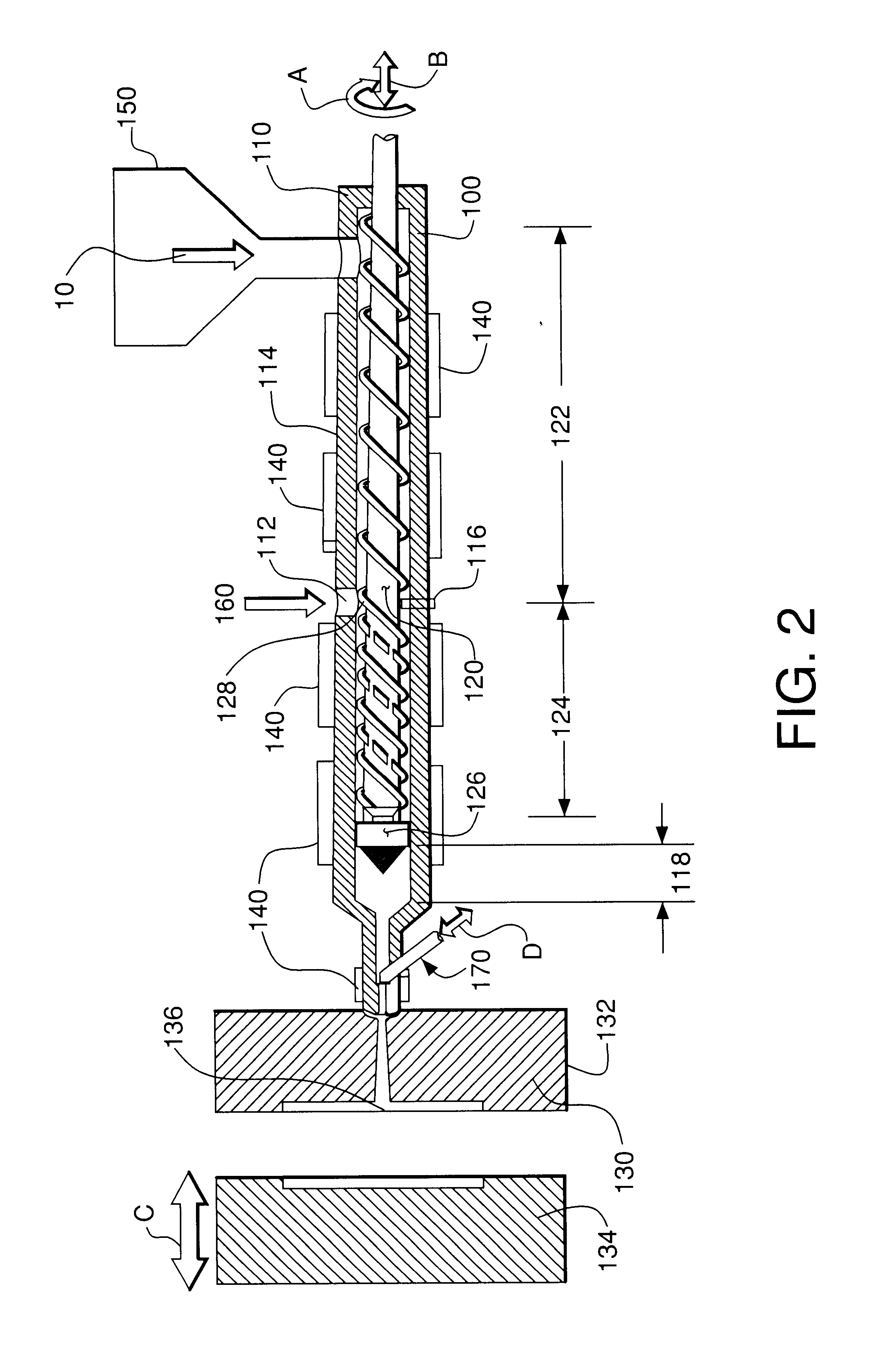
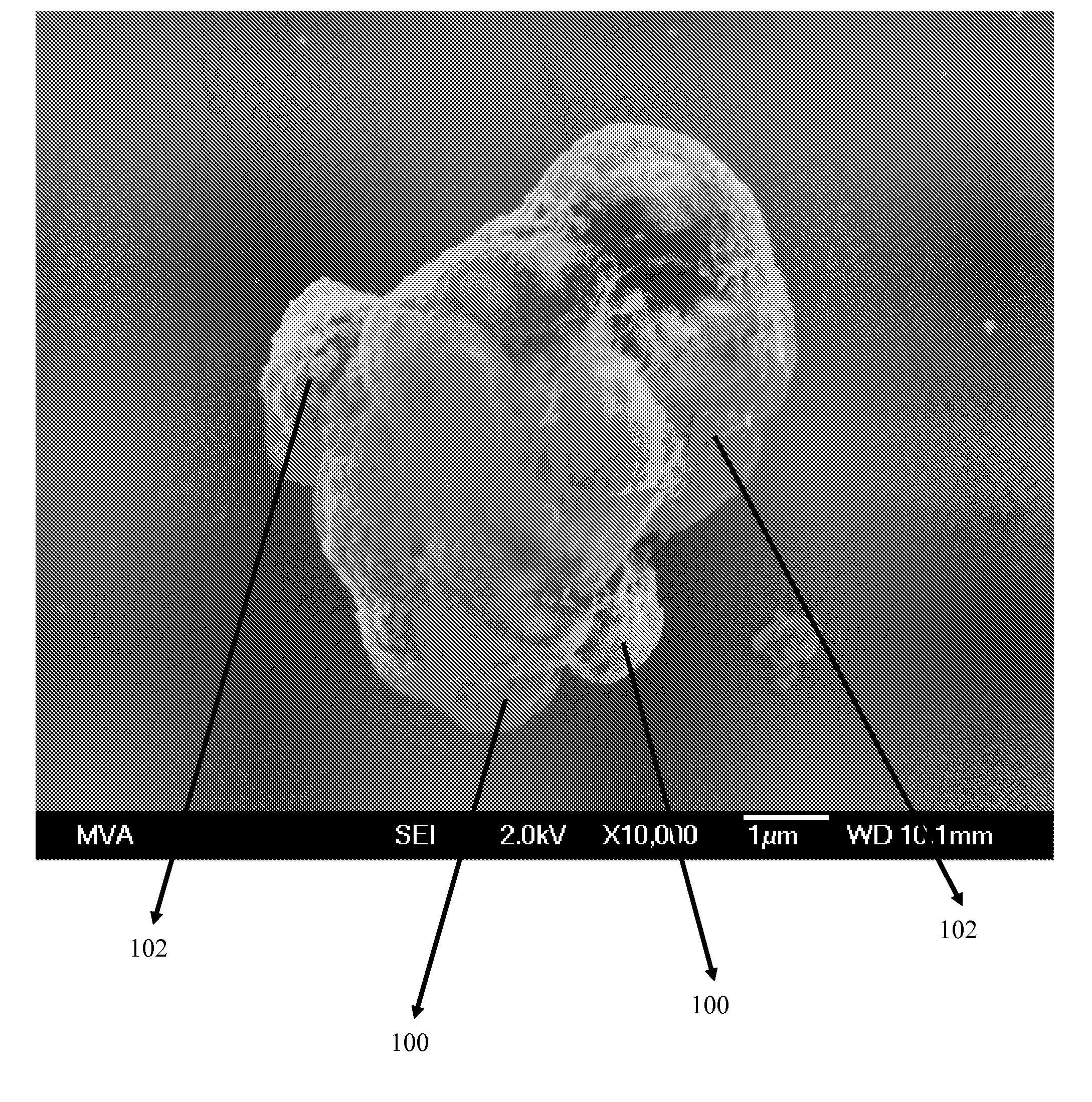
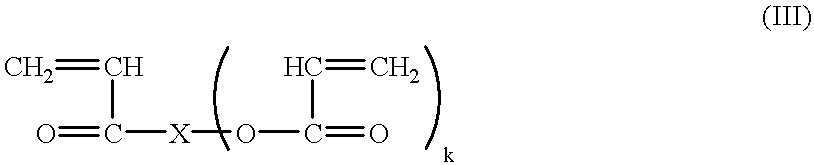Patents
Literature
201results about "Cork mechanical working" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and device for manufacturing three-dimensional bodies
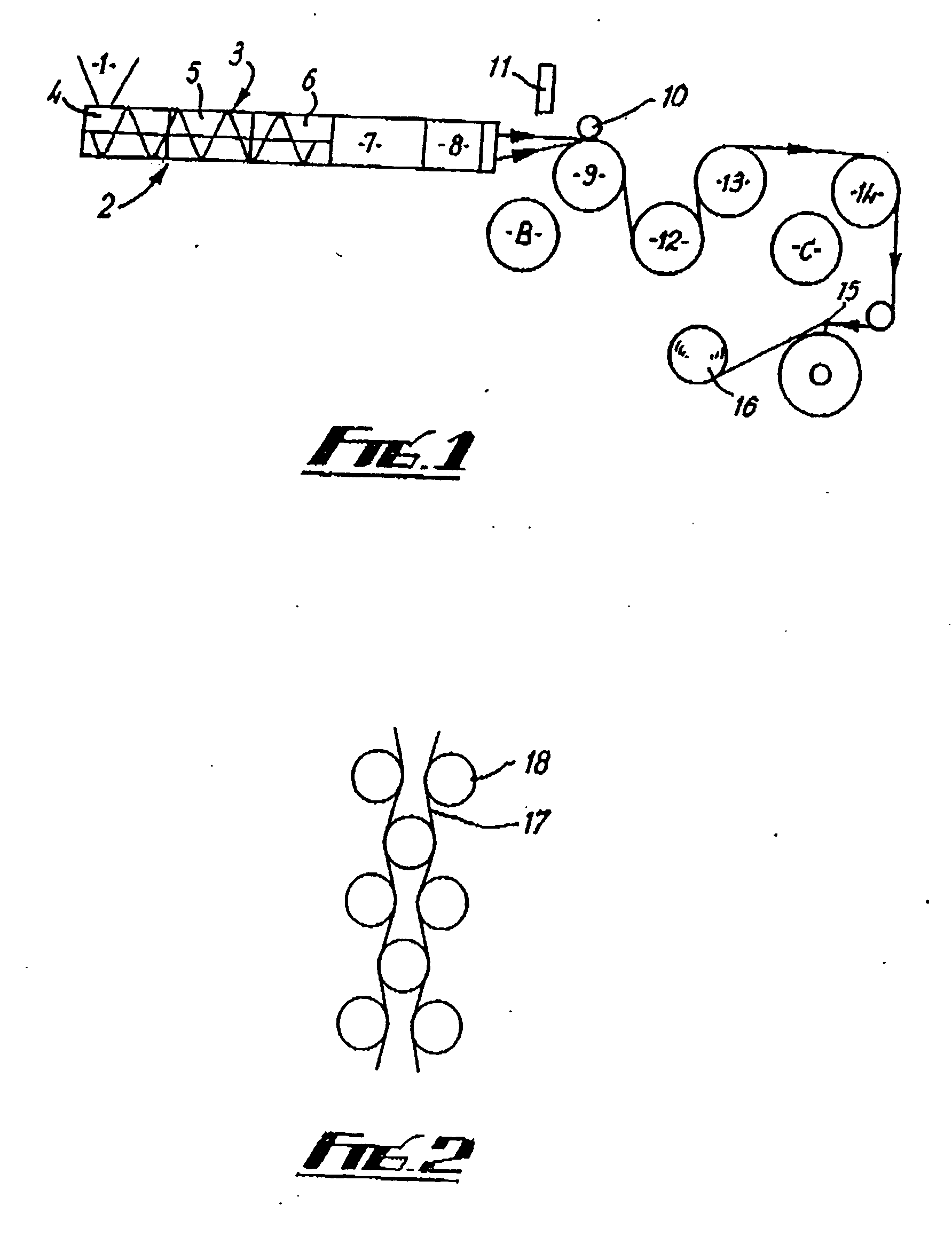
A method for producing three-dimensional bodies of a large number of mutually connected layers of a particle-shaped material such as a powder, and where the information of the appearance of each layer is achieved from a computer's CAD-unit or similar. An essentially even particle layer (7) of building material is applied on a support base (6) and on a masking device (9) is arranged a masking pattern in accordance with the information from the CAD-unit, which masking device is led over said particle layer and close to it. A radiation producer (8) is arranged or is led over the masking device (9), whereby the particles which are not covered by the masking pattern are exposed for radiation and thereby are attached to each other. The masking pattern is removed from the masking device and new sequences in accordance with the above are carried through until the three-dimensional body (19) is produced.
Owner:SPEED PART RP
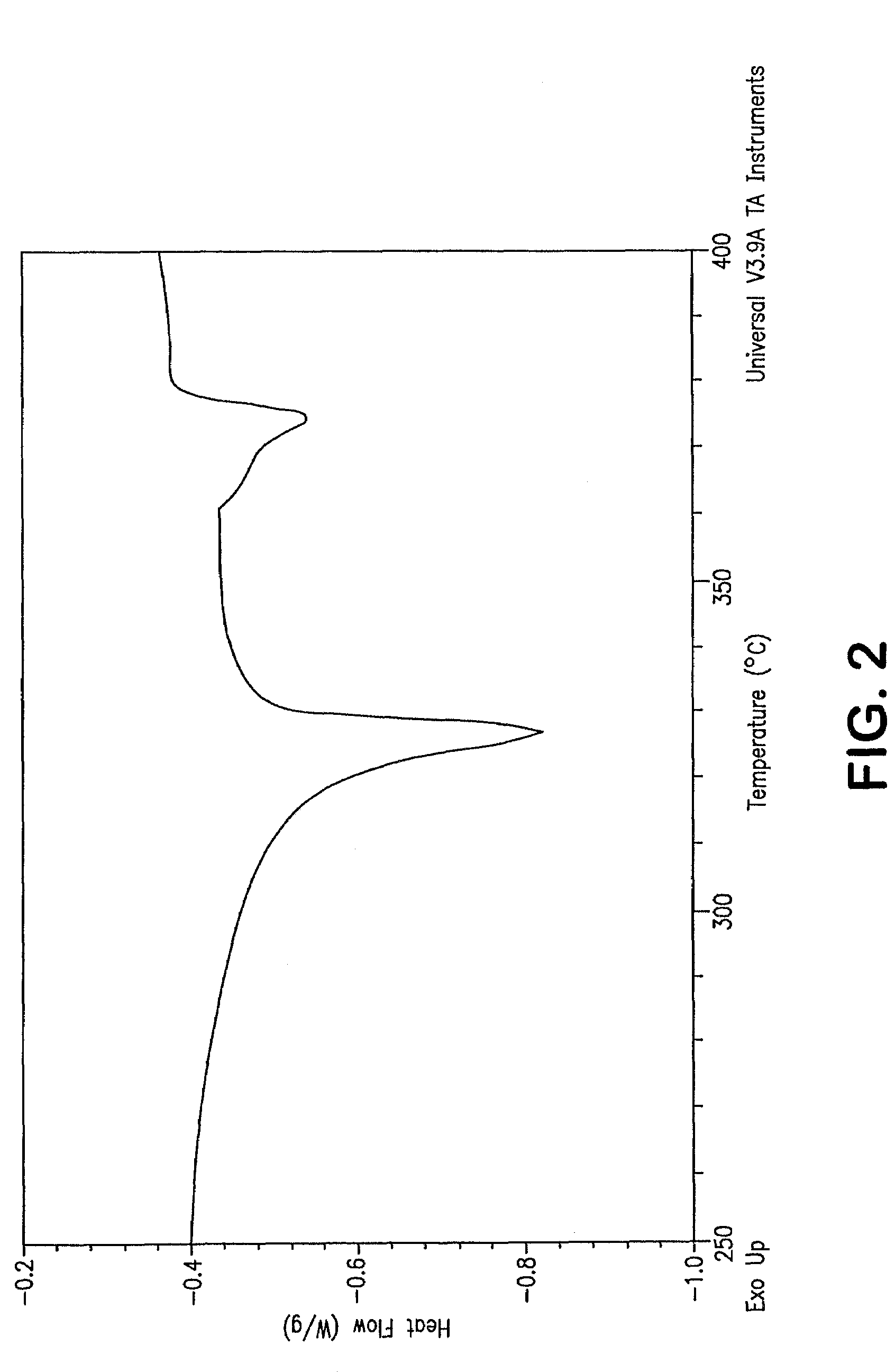
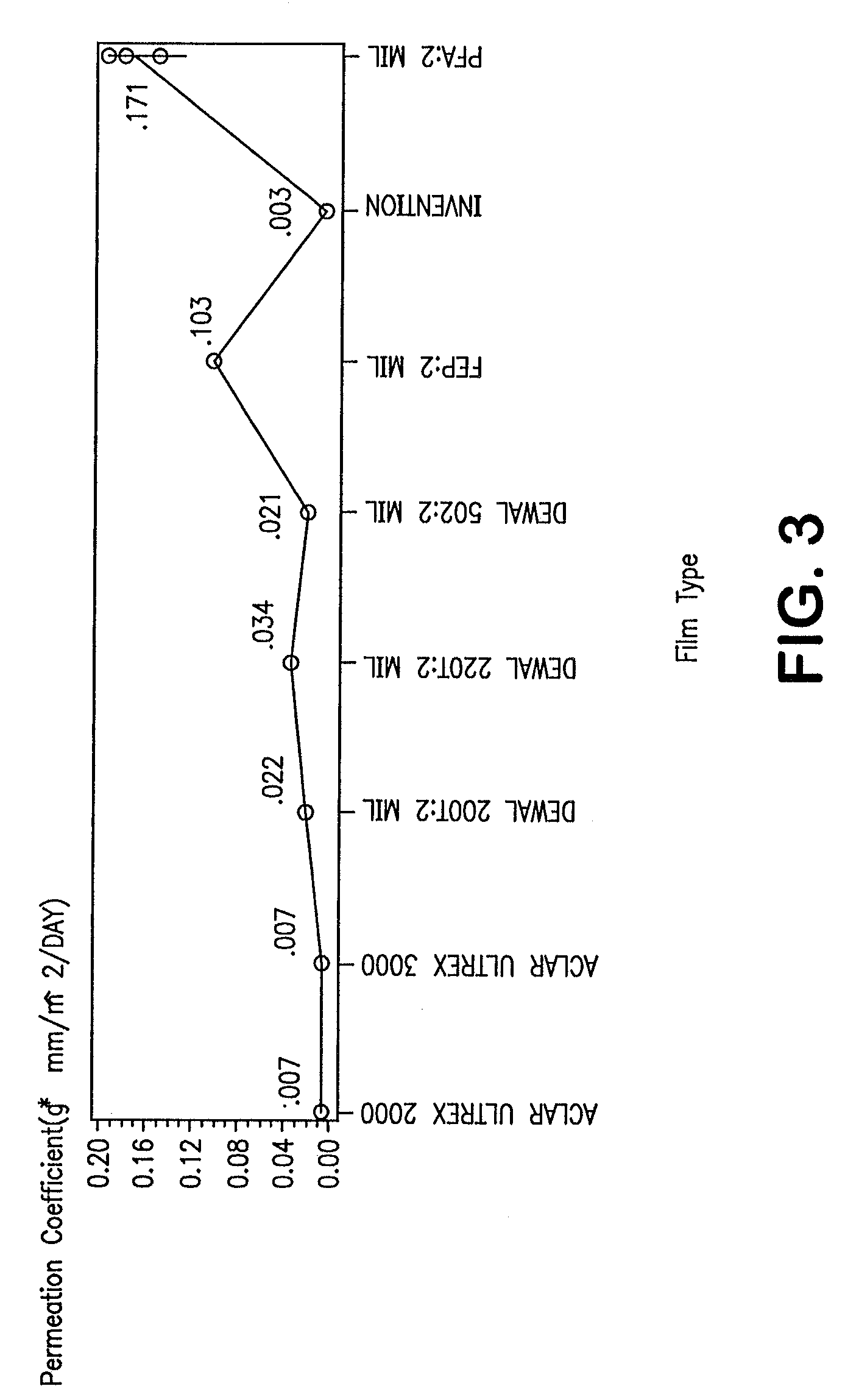
Fluoropolymer barrier material
InactiveUS7521010B2Improve barrier propertiesImprove permeabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceWater vapor permeability
A novel densified fluoropolymer article is described which has a water vapor permeation of about 0.015 g-mm / m2 / day or less, and preferably has a matrix tensile strength of at least 10,000 psi in two orthogonal directions. The articles are made by compressing expanded porous PTFE at pressures, temperatures and times which result in elimination of the pores, and subsequent stretching above the crystalline melt temperature.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Continuous manufacture of superabsorbent/ion exchange sheet material
InactiveUS20020007166A1Increase in sizeNon-fibrous pulp additionWood working apparatusPapermakingIon exchange
A continuous sheet having a combination of acidic and basic water-absorbing resin particles that are essentially not neutralized and can be continuously manufactured on conventional papermaking apparatus, using a wet, dry, or wet-dry process to manufacture a water-absorbent sheet-like substrate containing 50%-100% by weight of the combination of acidic and basic water-absorbent particles. The acidic and basic essentially unneutralized resins can be contained in the sheet material articles of the present invention as separate acidic and basic resin particles, or as multicomponent particles containing both the acidic and basic resins. The sheet materials can be manufactured having new and unexpected structural integrity, with little or no shakeout or loss of superabsorbent particles during or after manufacture while exhibiting exceptional water absorption and retention properties. The sheet materials have an ability to absorb liquids quickly, demonstrate good fluid permeability and conductivity into and through the resin particles, and have a high gel strength such that the hydrogel formed from the SAP particles resists deformation under an applied stress or pressure, when used alone or in a mixture with other water-absorbing resins.
Owner:BASF AG
Grip and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6226836B1Easy to manufactureIncreased durabilityTravelling carriersHoldersBiomedical engineering
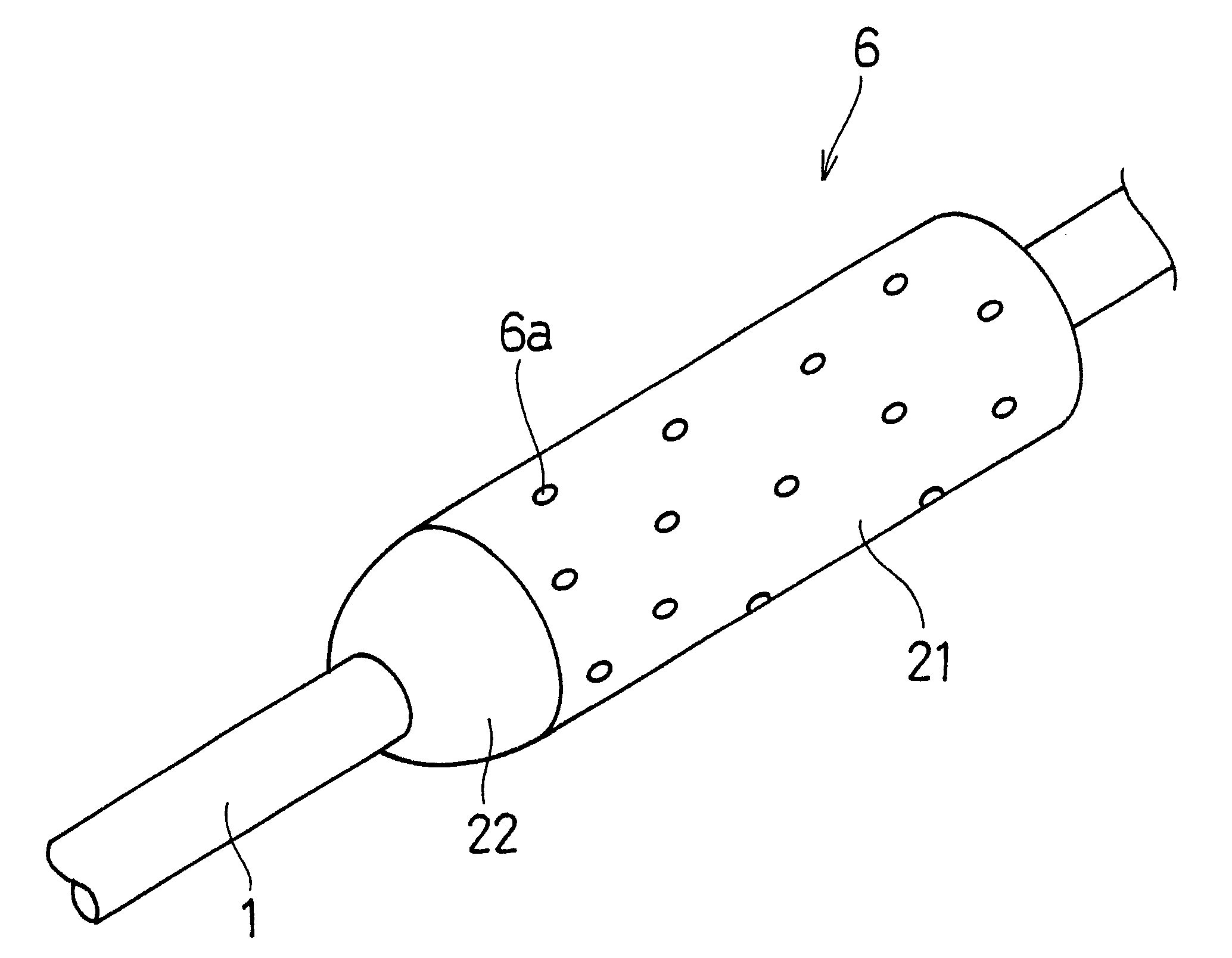
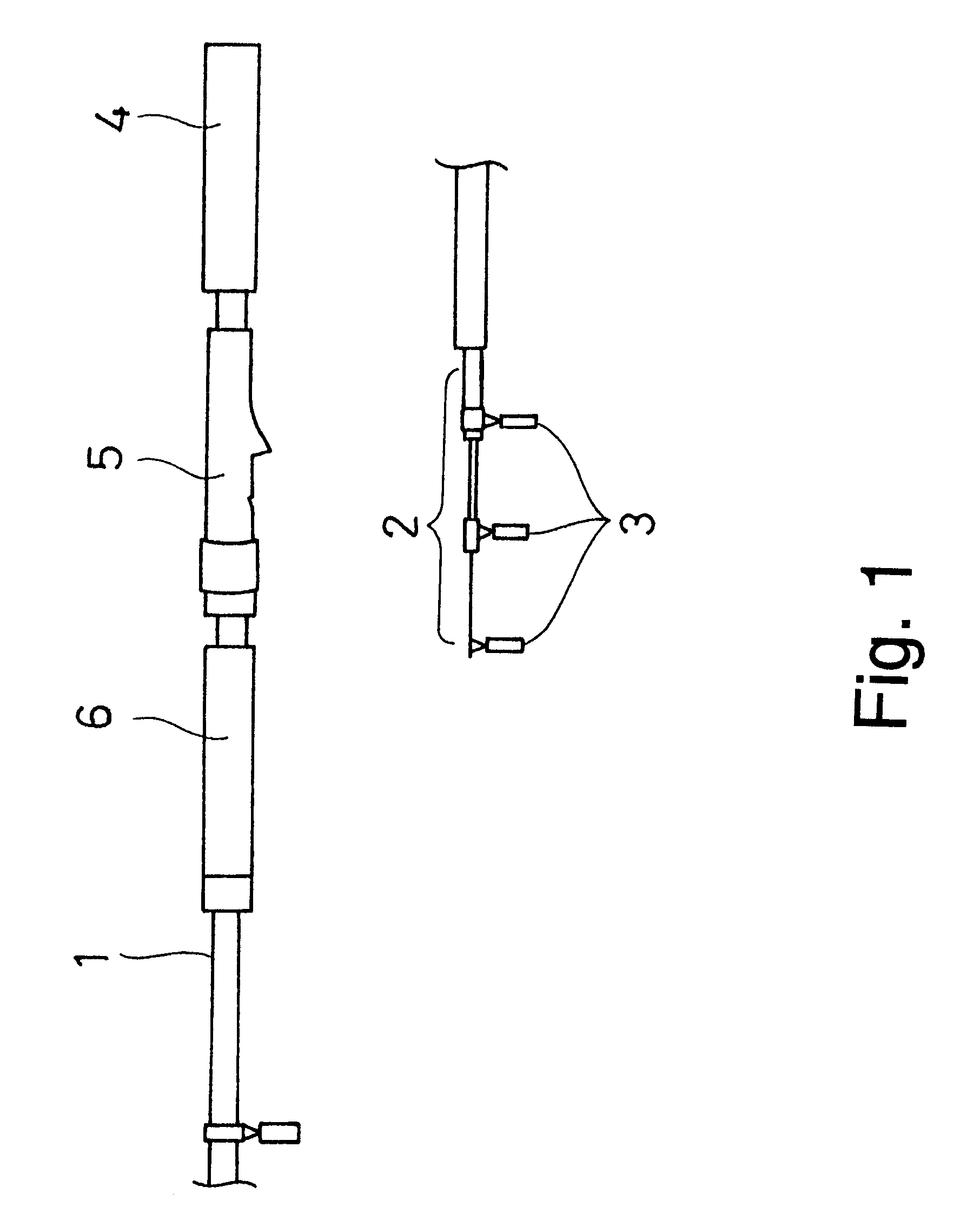
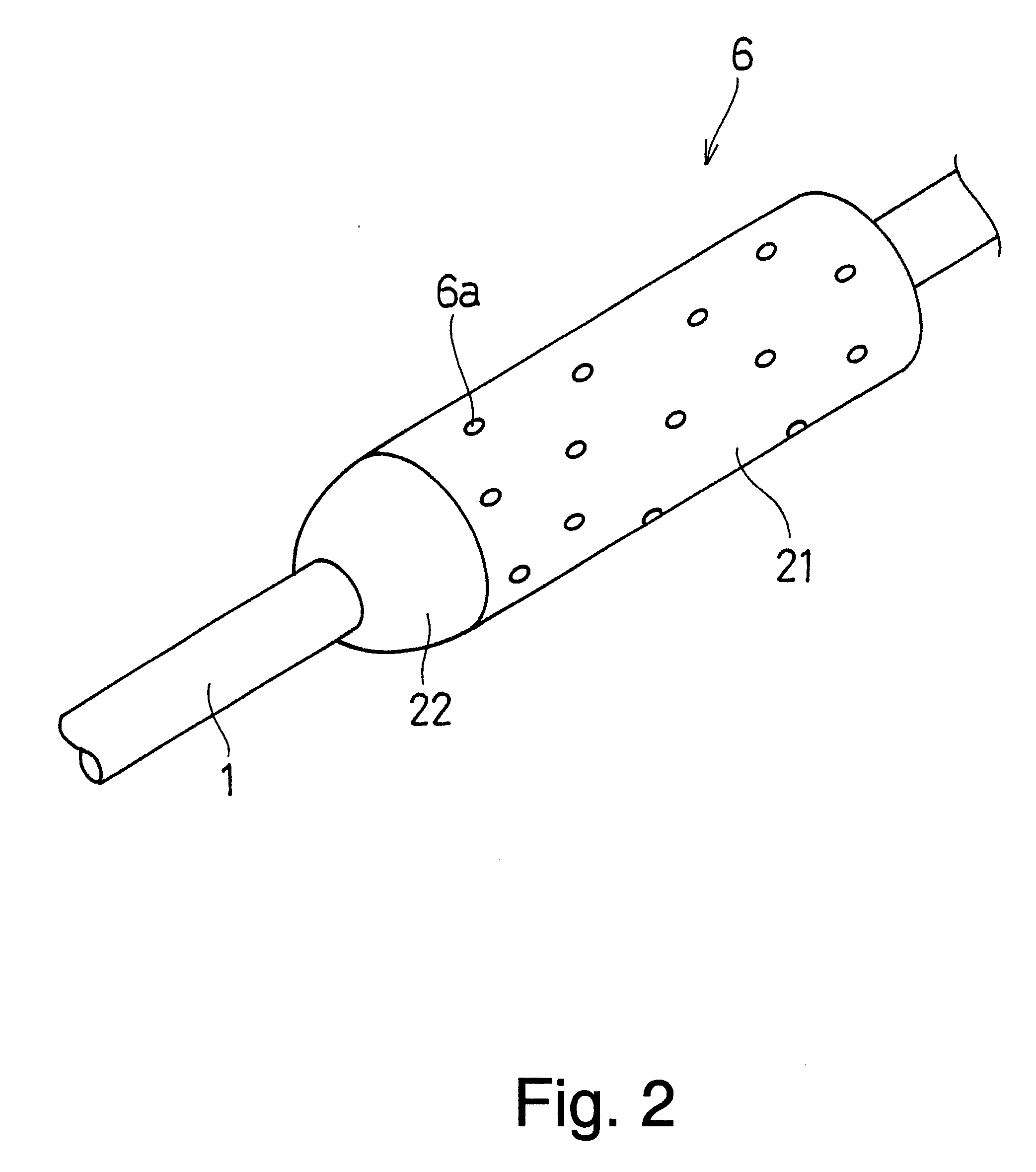
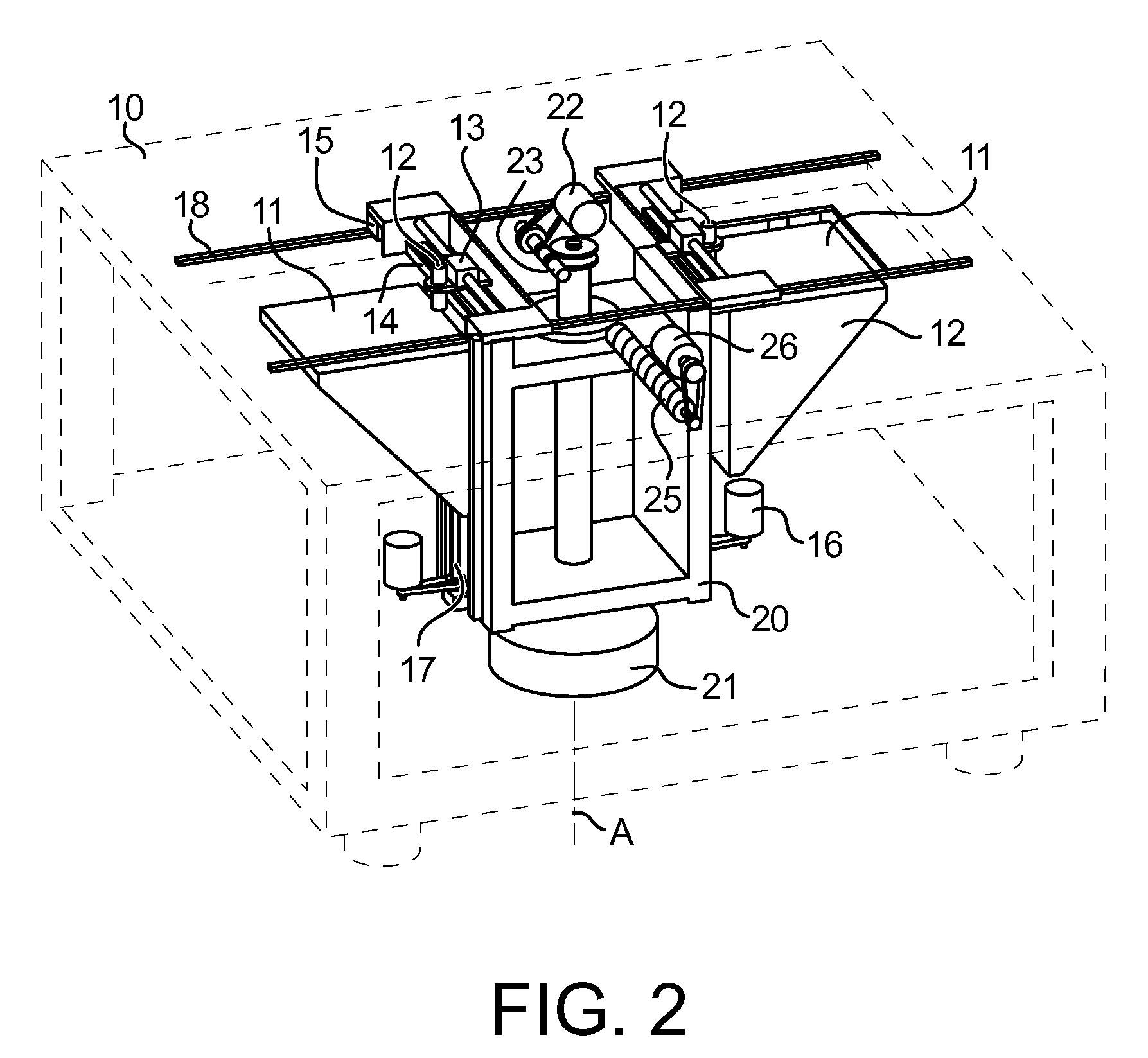
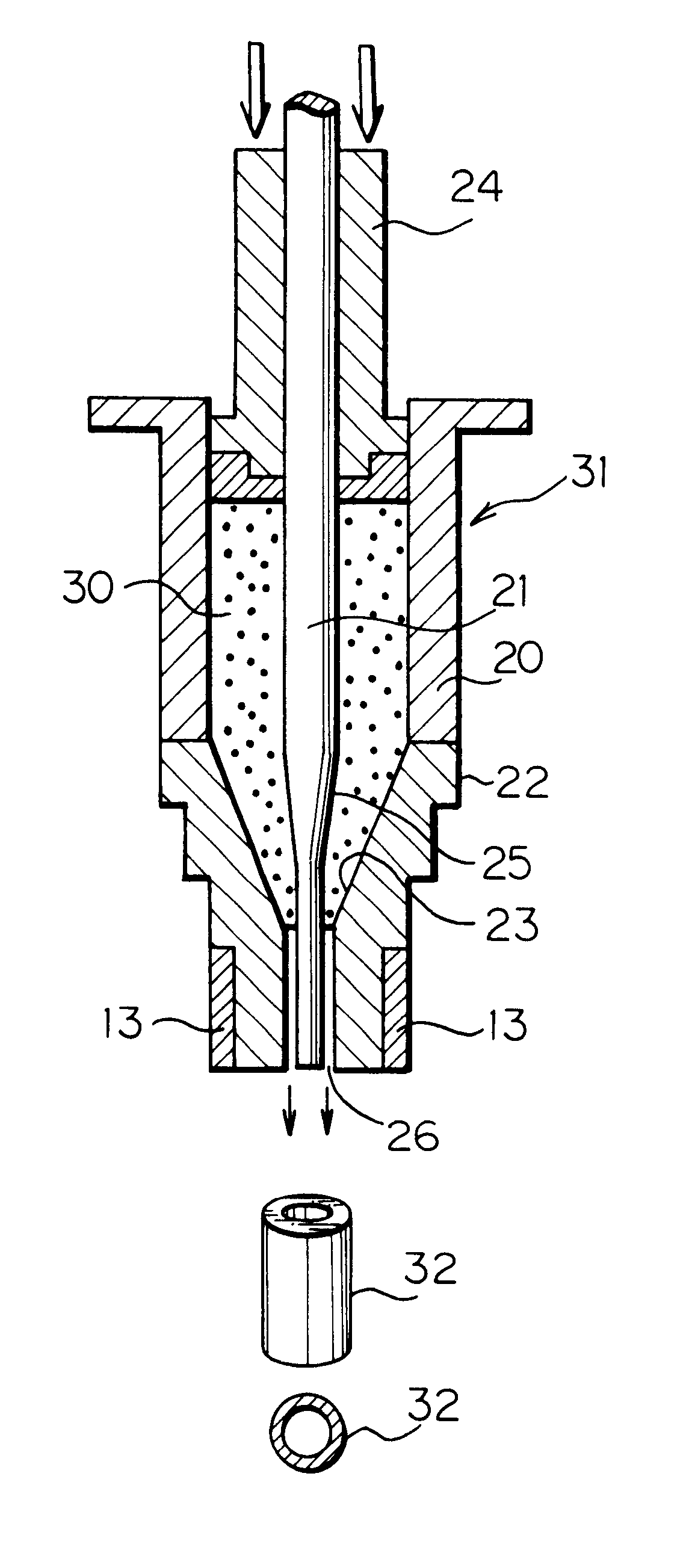
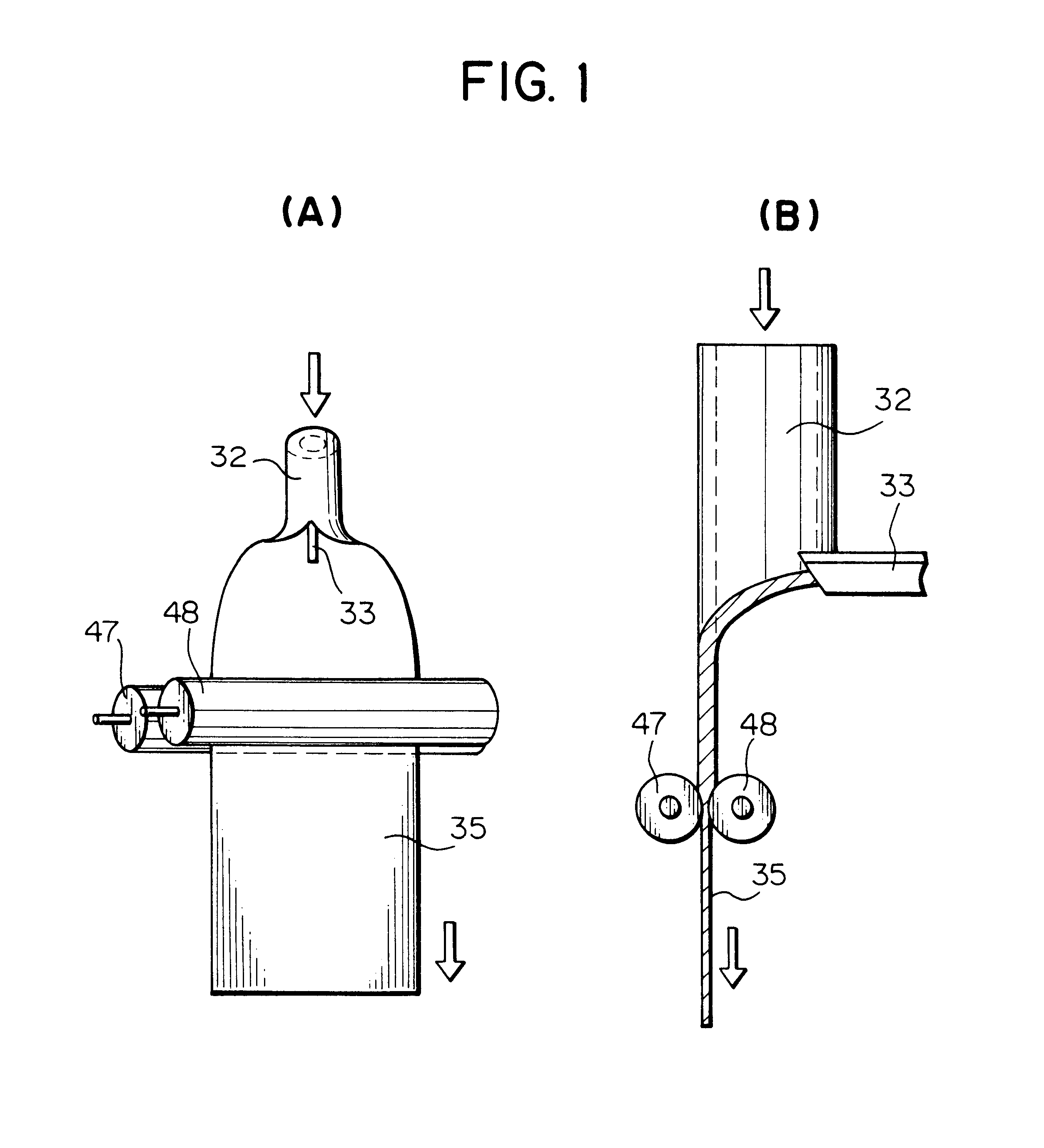
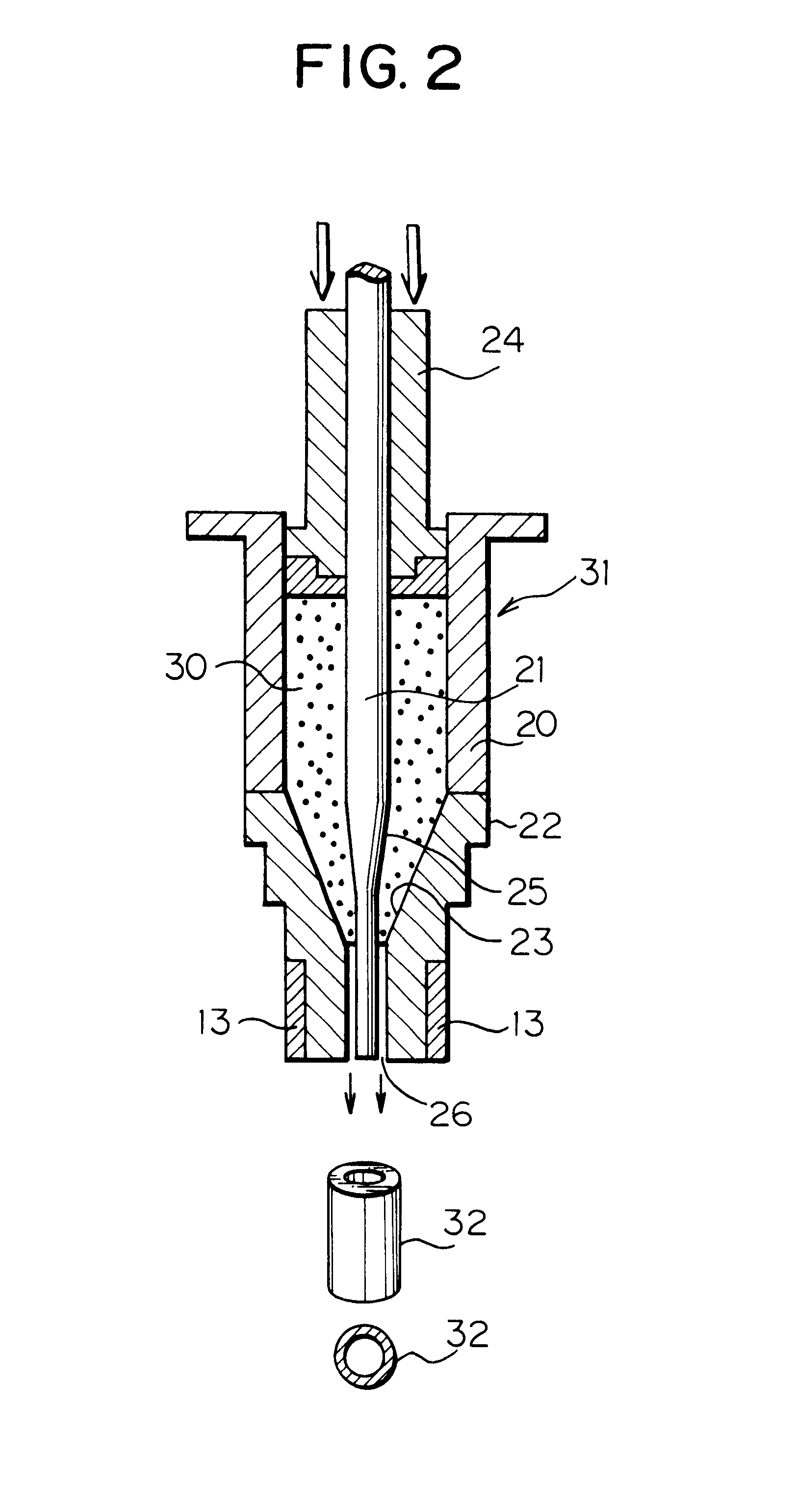
A cork grip includes a main part (21) that is formed of cork pieces each having a predetermined cylindrical shape that are punched out of a cork sheet formed of cork material stripped from a cork tree and pressed into the shape of a board. The cork sheet is punched into the cylindrical shapes in such a manner that pithy tissues (6a) of the cork intersect with the axial direction of the main part (21). The pithy tissues (6a) of the main part 21 are filled with a filling agent that includes a mixture of binder and cork powder.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Tobacco smoke filter for smoking device with porous mass of active particulate
A tobacco smoking device comprises a porous mass of active particles adapted to enhance a tobacco smoke flowing over said active particles and binder particles. The active particles comprises about 1-99% weight of the porous mass, and the binder particles comprises about 1-99% weight of said porous mass. The active particles and said binder particles are bound together at randomly distributed points throughout the porous mass. The active particles have a greater particle size than the binder particles.
Owner:ACETATE INT LLC
Electrospinning of PTFE with high viscosity materials
An improved process for forming a PTFE mat is described. The process includes providing a dispersion with PTFE, a fiberizing polymer and a solvent wherein said dispersion has a viscosity of at least 50,000 cP. An apparatus is provided which comprises a charge source and a target a distance from the charge source. A voltage source is provided which creates a first charge at the charge source and an opposing charge at the target. The dispersion is electrostatically charged by contact with the charge source. The electrostatically charged dispersion is collected on the target to form a mat precursor which is heated to remove the solvent and the fiberizing polymer thereby forming the PTFE mat.
Owner:ZEUS COMPANY INC
Medical device formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin
Medical devices having at least a component, such as a catheter balloon, stent cover and vascular graft, formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, such as ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The device component is formed from ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene that has been processed so that it is microporous and has an oriented node and fibril structure. The device component expands compliantly at low strains and are substantially less compliant at higher strains. The invention also comprises methods for making such medical devices, including the steps of compacting a polyethylene powder and deforming it to impart the oriented structure.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Continuous manufacture of superabsorbent/ion exchange sheet material
A continuous sheet having a combination of acidic and basic water-absorbing resin particles that are essentially not neutralized and can be continuously manufactured on conventional papermaking apparatus, using a wet, dry, or wet-dry process to manufacture a water-absorbent sheet-like substrate containing 50%-100% by weight of the combination of acidic and basic water-absorbent particles. The acidic and basic essentially unneutralized resins can be contained in the sheet material articles of the present invention as separate acidic and basic resin particles, or as multicomponent particles containing both the acidic and basic resins. The sheet materials can be manufactured having new and unexpected structural integrity, with little or no shakeout or loss of superabsorbent particles during or after manufacture while exhibiting exceptional water absorption and retention properties.
Owner:BASF SE
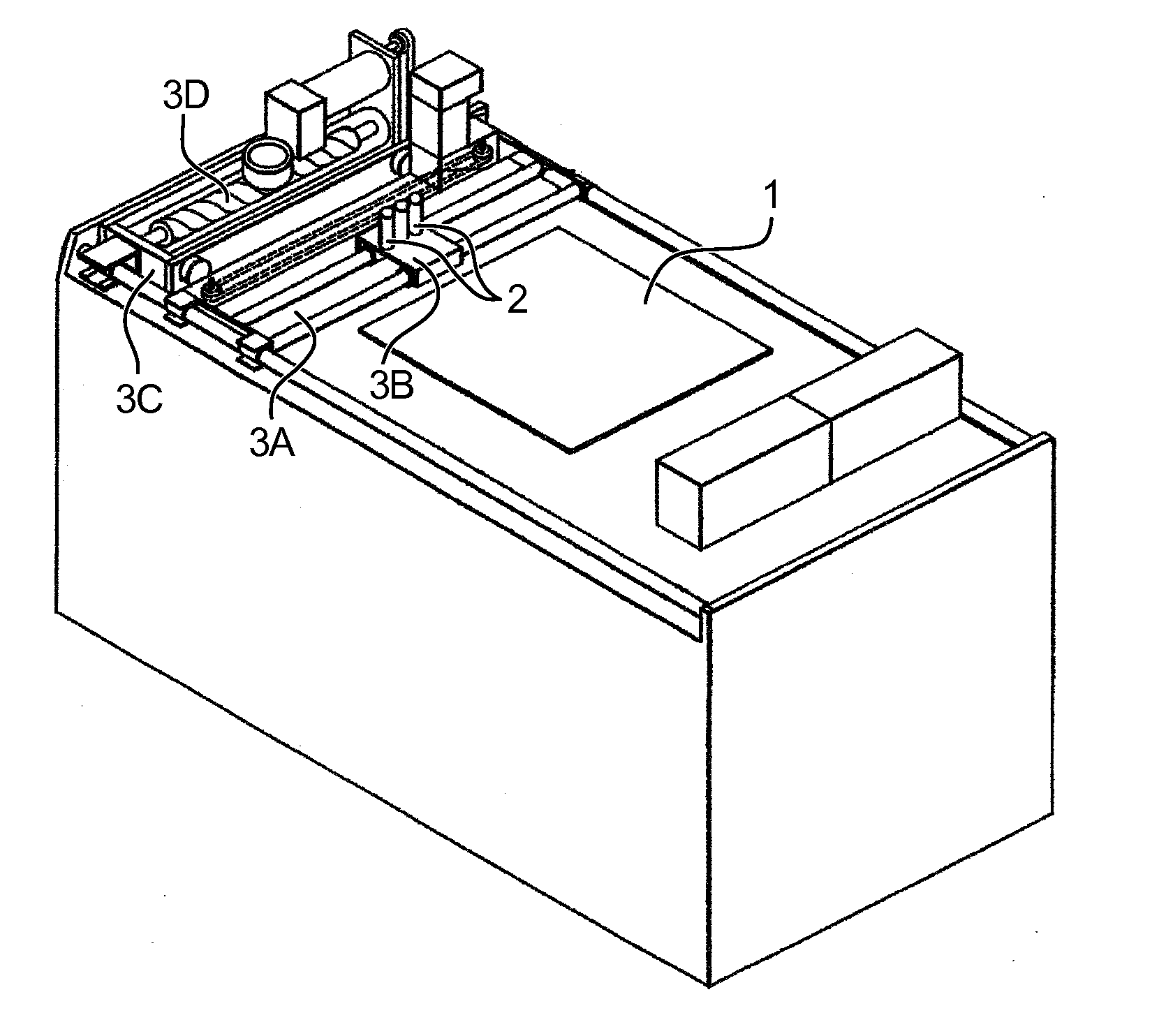
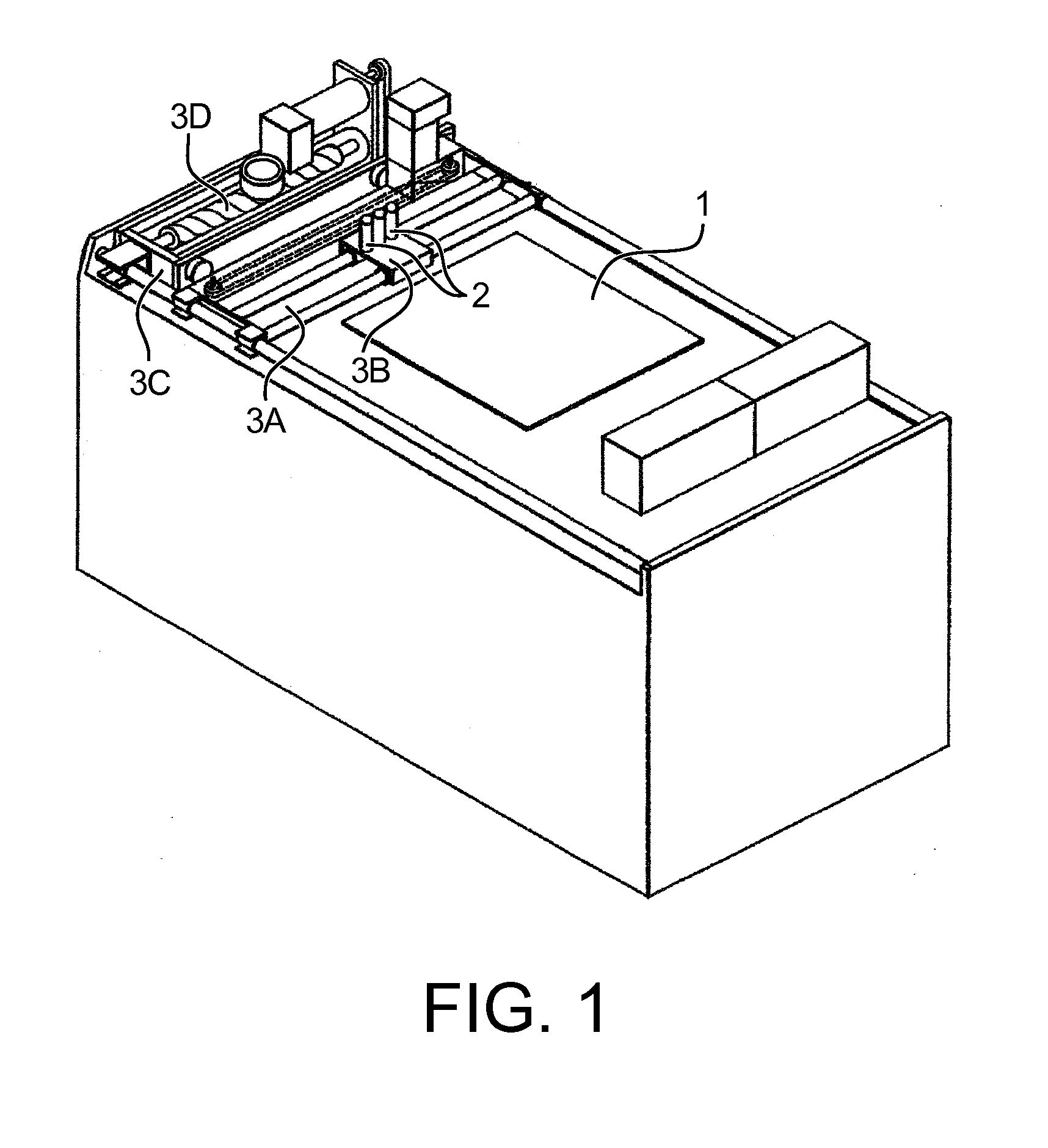
Method and machine for producing three-dimensional objects by means of successive layer deposition
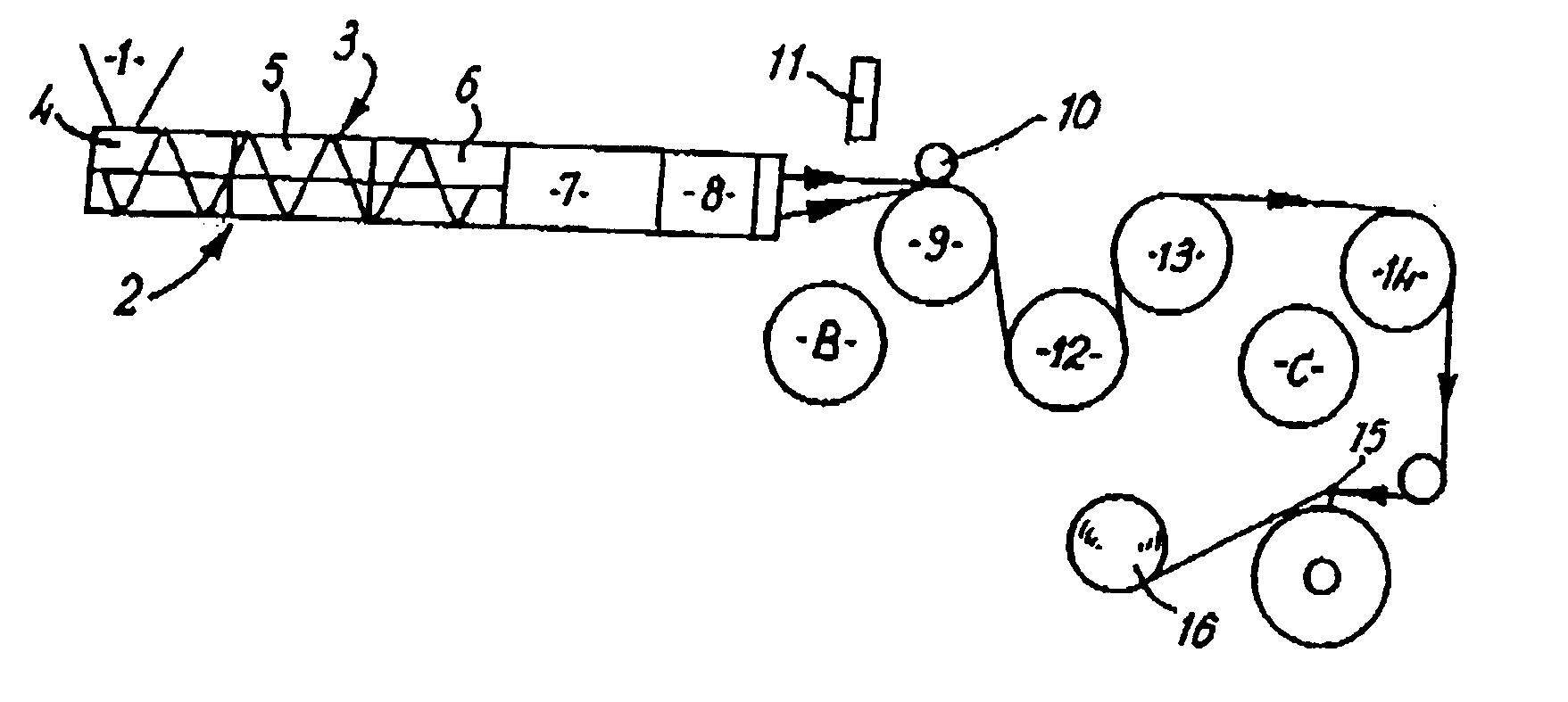
Inventive machine allowing the simultaneous fabrication of several objects by a method of “rapid prototyping” type, by depositing a succession of layers of heat-fusible fluid.It chiefly comprises a crossbar (20) carrying two platforms (11) on each of which an object is fabricated by deposition. Two fixed work stations are arranged diametrically opposite each other so that the jet (12) of each of these fixed stations can perform a depositing operation at the same time as the other jet (12). After each deposit, the crossbar is rotated 180° to alternate the depositing operations of the two different materials.Particular application to prototyping jewellery models.
Owner:MARSAC NICOLAS
Manufacturing method of a highly conductive polytetrafluoroethylene sheet
InactiveUS6270707B1Electrode manufacturing processesActive material electrodesTetrafluoroethyleneMaterials science
This invention concerns a method of manufacturing a highly conductive polytetrafluoroethylene sheet; a method of manufacturing a highly conductive unsintered polytetrafluoroethylene sheet: and a method of manufacturing a highly conductive sintered sheet. In the first method, a paste of polytetrafluoroethylene powder admixed with conductive substance and extrusion lubricant is extruded to preform an unsintered tube-like material, and at least one place on the circumference of this extruded material, the material is cut open longitudinally and the resulting sheet is calendered if necessary. The second method includes a sintering process for the sheet. This invention also concerns a highly conductive polytetrafluoroethylene sheet having a wide-width and long-length, which is obtained by the above-mentioned method. This sheet is not less than 170 mm in width and has variance of volume resistivity (conductivity) in the longitudinal direction, 10% or less, preferably 7% or less in the cross direction. This invention can provide a highly conductive wide-type PTFE sheet whose conductivity in the longitudinal direction is nearly uniform in the cross direction.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Polymeric resin bonded magnets
Briefly, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a process for making a magnetic composite which comprises providing a polymeric resin and a magnetic powder, the magnetic powder having a mean particle size with a value for standard deviation that is less than the value for the mean particle size of the said magnetic powder, the said magnetic composite being made by mixing said magnetic powder with said polymeric resin and molding the said mixture into a desired shape and a size and said magnetic composite having a magnetic permeability between 30 and 50. In another embodiment the present invention is a composition for a magnetic composite comprising a polymeric resin and a magnetic powder, the said powder having a mean particle size with a value of standard deviation that is less than the value of the mean particle size of the magnetic powder, wherein said magnetic composite has a magnetic permeability between about 30 and about 50.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Electrospinning of PTFE with high viscosity materials
An improved process for forming a PTFE mat is described. The process includes providing a dispersion with PTFE, a fiberizing polymer and a solvent wherein said dispersion has a viscosity of at least 50,000 cP. An apparatus is provided which comprises a charge source and a target a distance from the charge source. A voltage source is provided which creates a first charge at the charge source and an opposing charge at the target. The dispersion is electrostatically charged by contact with the charge source. The electrostatically charged dispersion is collected on the target to form a mat precursor which is heated to remove the solvent and the fiberizing polymer thereby forming the PTFE mat.
Owner:ZEUS COMPANY INC
Auxetic filamentary materials
InactiveUS20050159066A1Improve energy absorptionFibre pulloutWood working apparatusCork mechanical workingPolymer sciencePolymer
An auxetic material, which has a negative Poisson ratio so that it has the property of expanding or contracting transversely to a direction in which it is extended or compressed, is made in filamentary or fibrous form. A suitable process involves cohering and extruding heated polymer powder so that the cohesion and extrusion is effected with spinning to produce auxetic filaments. Typically the powder is heated to a temperature sufficient to allow some degree of surface melting yet not high enough to enable bulk melting.
Owner:AUXETIC TECH
Sintered polymeric materials and applications thereof
ActiveUS8141717B2Advantageous chemical and mechanical propertyIncrease flexibilitySemi-permeable membranesLaboratory glasswaresElastomerPolymer science
The present invention provides sintered polymeric materials and methods of making the same which are useful in a variety of applications. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a sintered polymeric material comprising at least one plastic and at least one elastomer.
Owner:POREX CORP
Auxetic filamentary materials
InactiveUS7247265B2Improve propertiesIncrease resistanceWood working apparatusCork mechanical workingPolymer sciencePolymer
An auxetic material, which has a negative Poisson ratio so that it has the property of expanding or contracting transversely to a direction in which it is extended or compressed, is made in filamentary or fibrous form. A suitable process involves cohering and extruding heated polymer powder so that the cohesion and extrusion is effected with spinning to produce auxetic filaments. Typically the powder is heated to a temperature sufficient to allow some degree of surface melting yet not high enough to enable bulk melting.
Owner:AUXETIC TECH
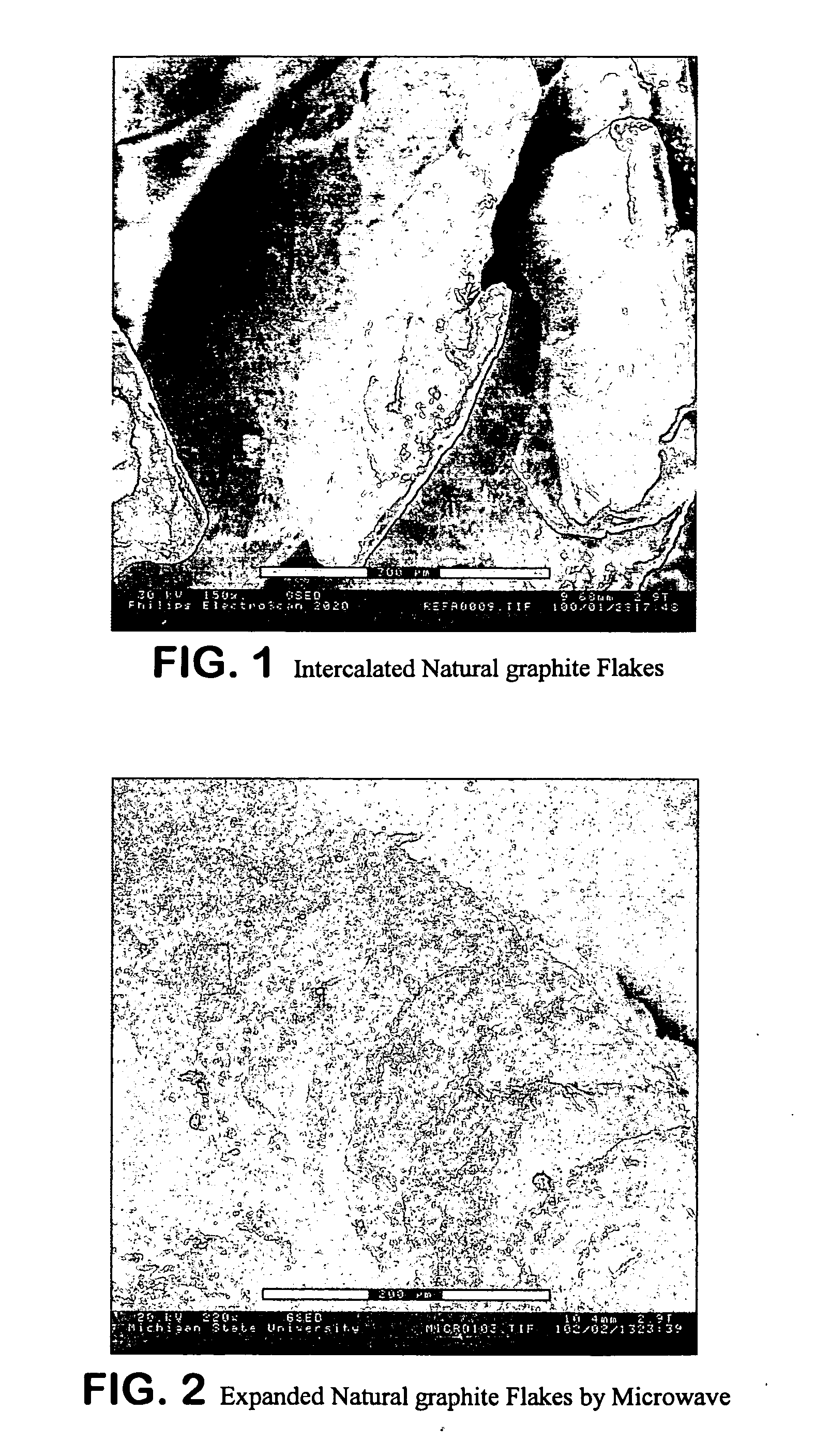
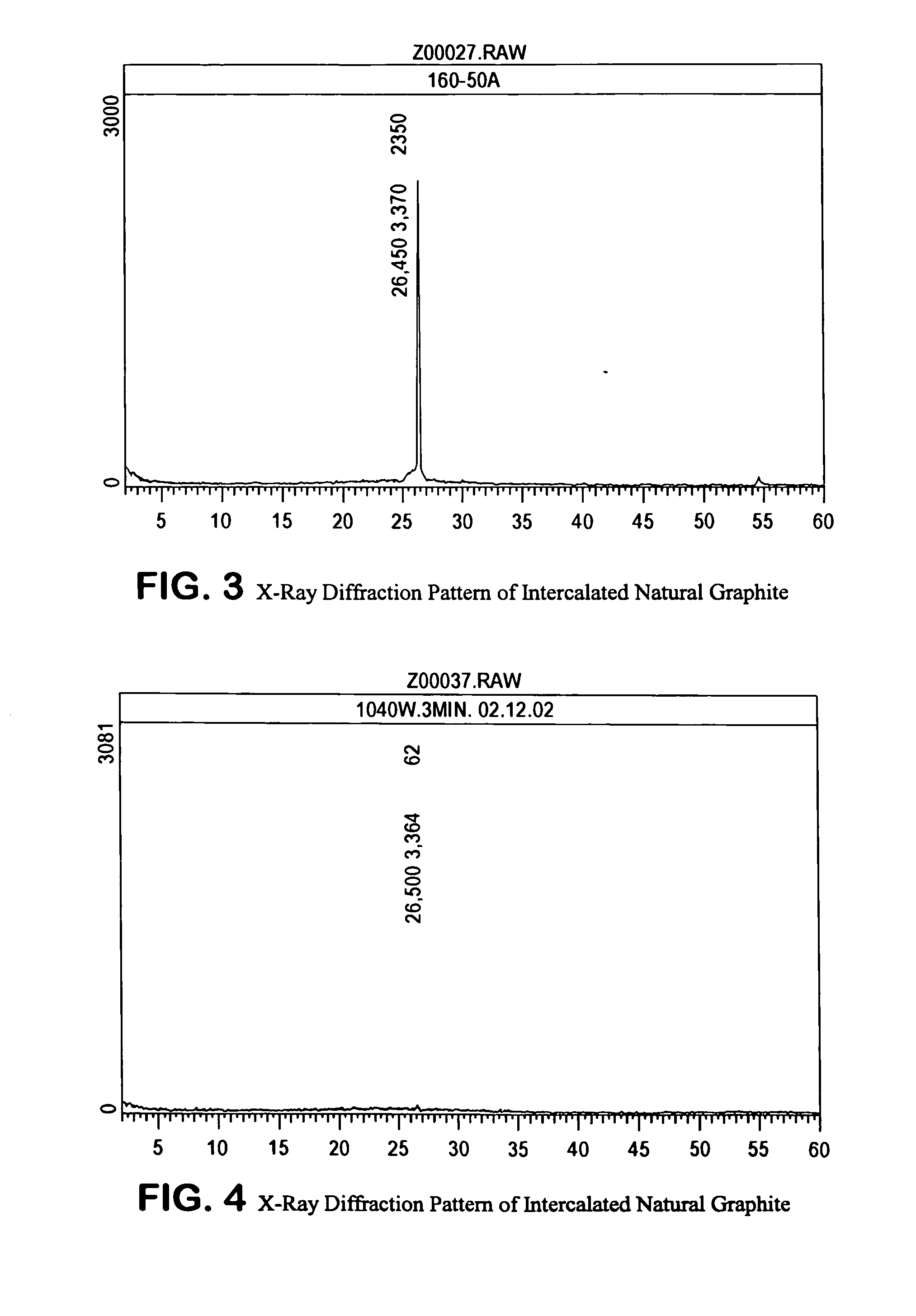
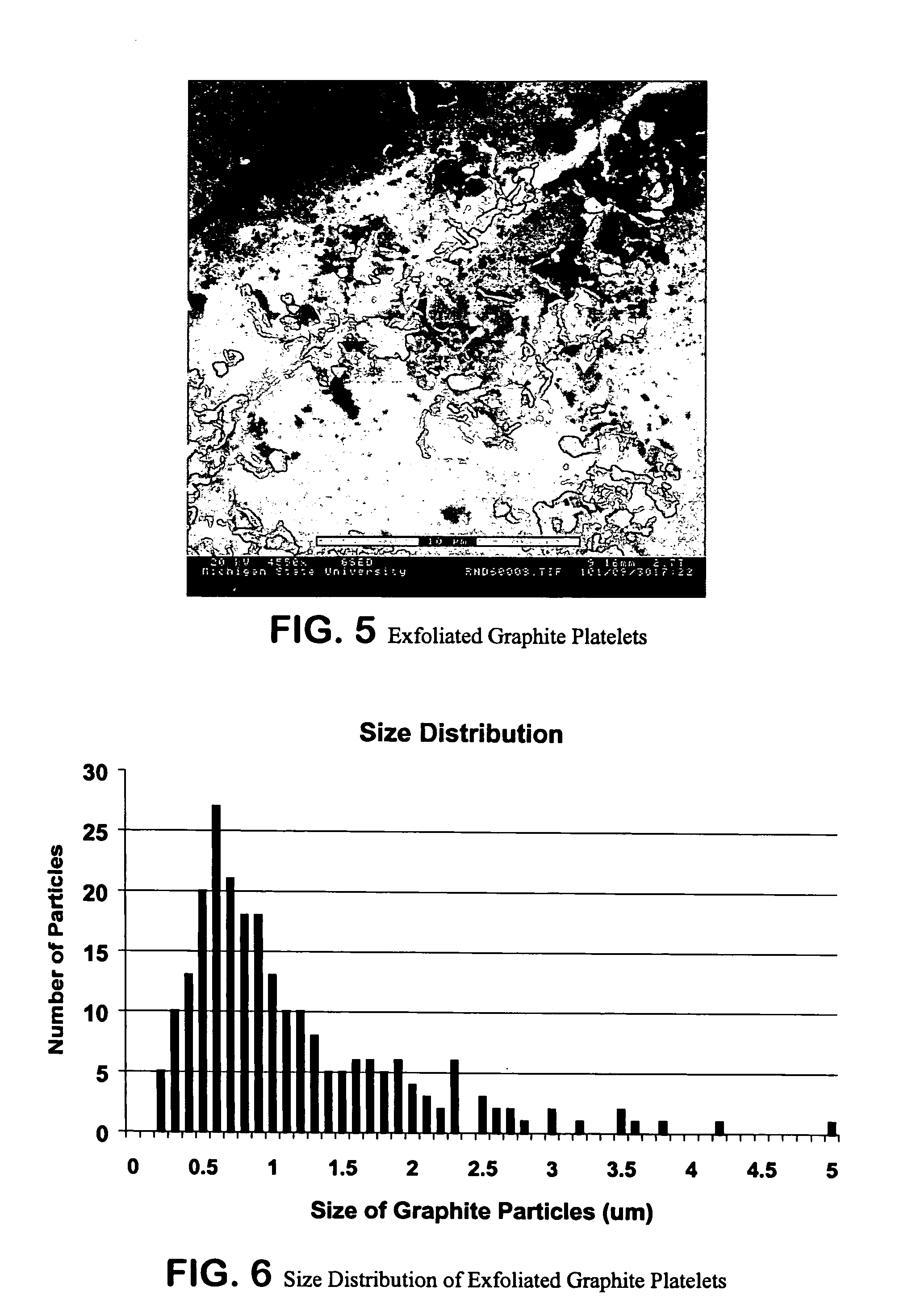
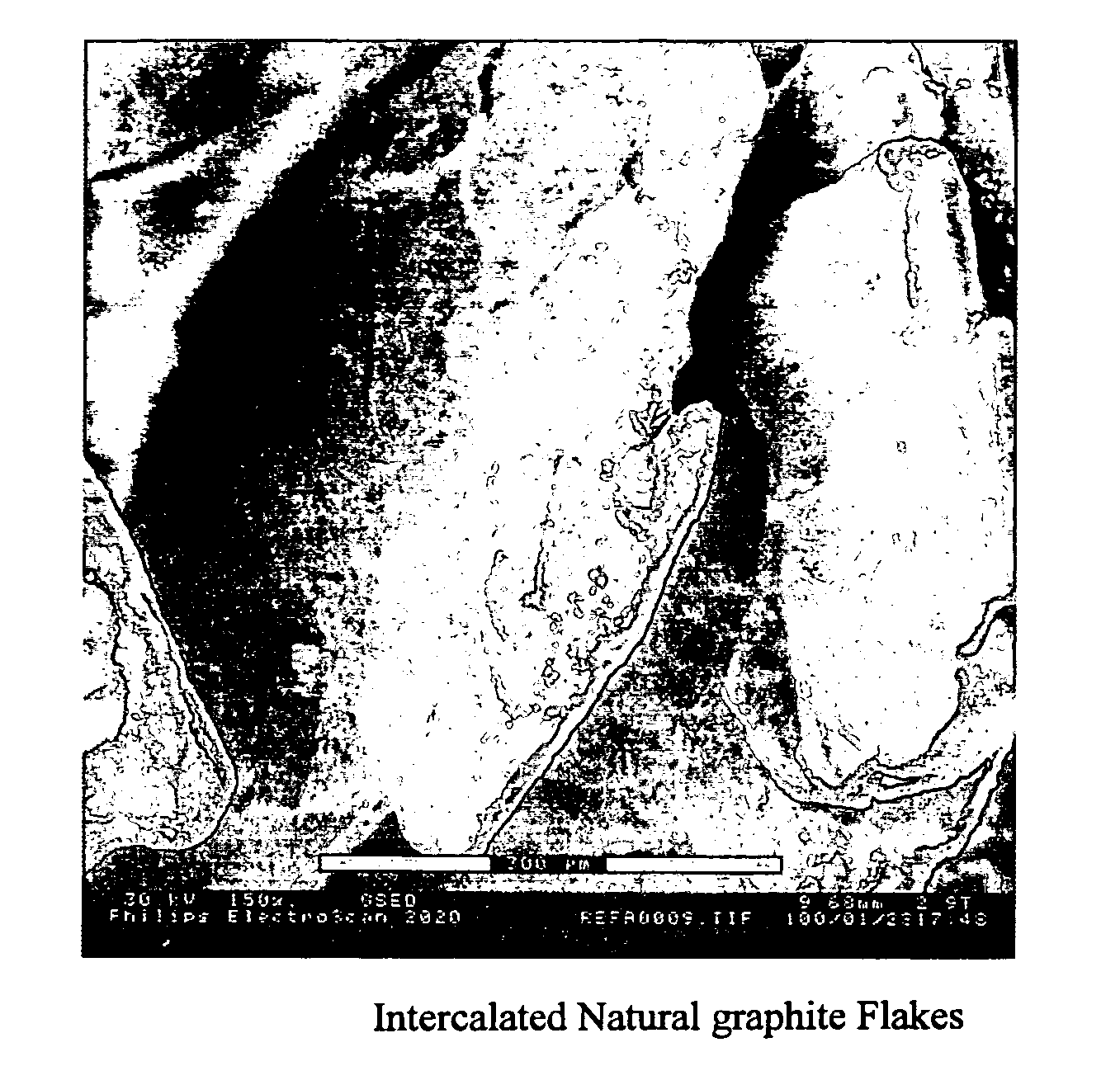
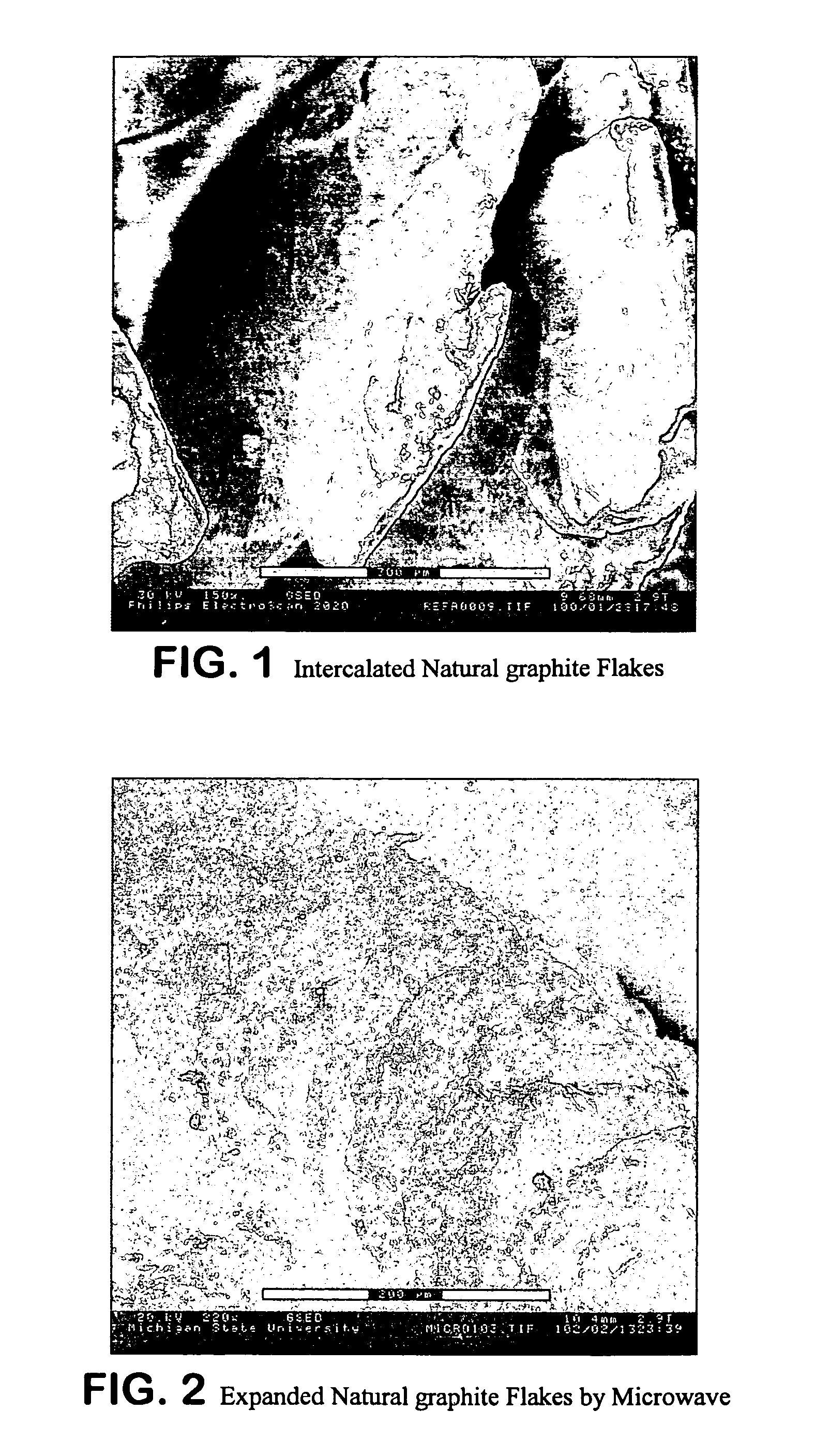
Expanded graphite and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS20060148966A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove thermal conductivityLayered productsConductive materialFuel cellsGraphite
Graphite nanoplatelets of expanded graphite and composites and products produced therefrom are described. The preferred method of expanding the graphite is by microwaves or other radiofrequency wave treatment of intercalated graphite. The expanded graphite is preferably then crushed to nanometer (substantially all 200 microns or less). The expanded graphite is used in polymer composites. The expanded graphite is particularly useful for batteries, anodes and fuel cells.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
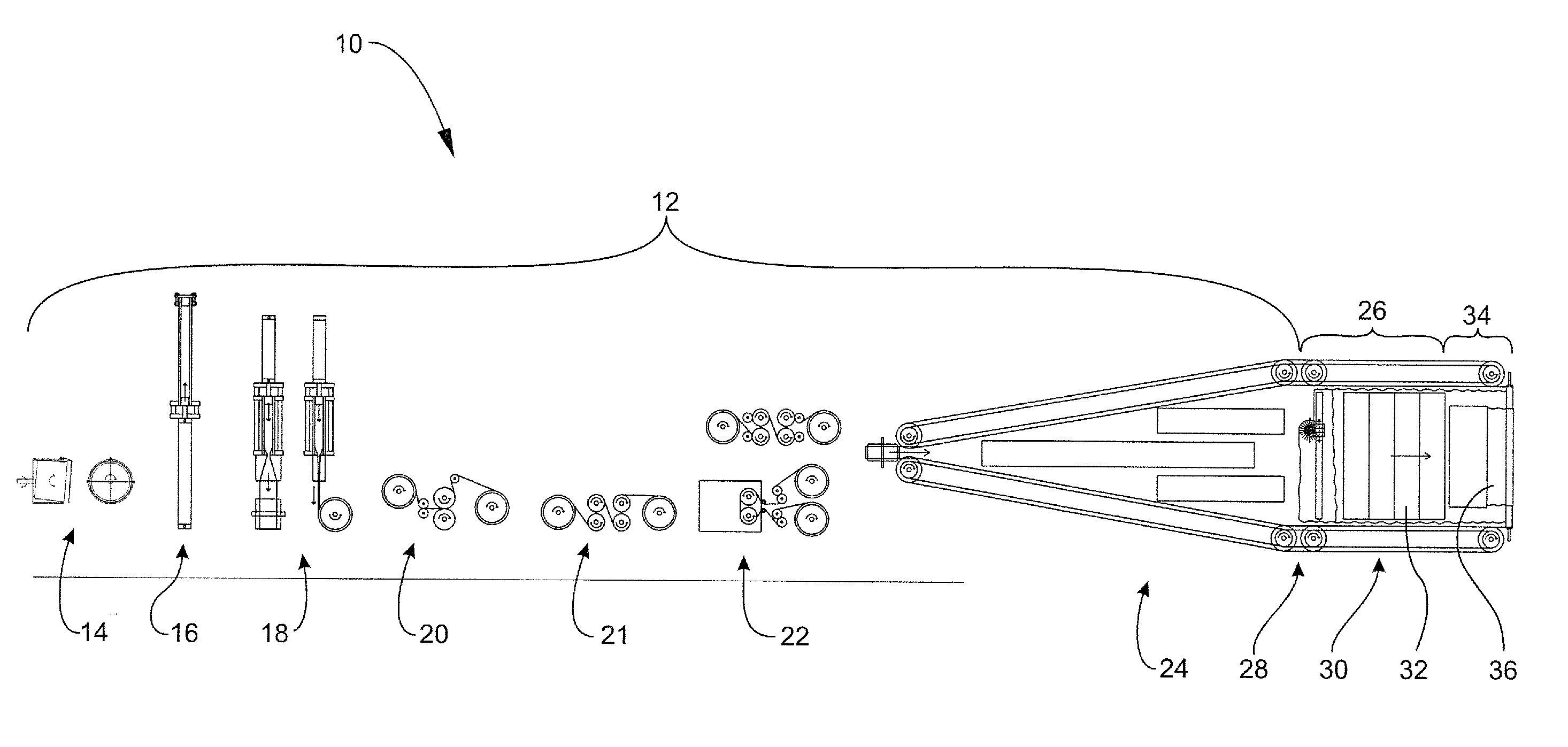
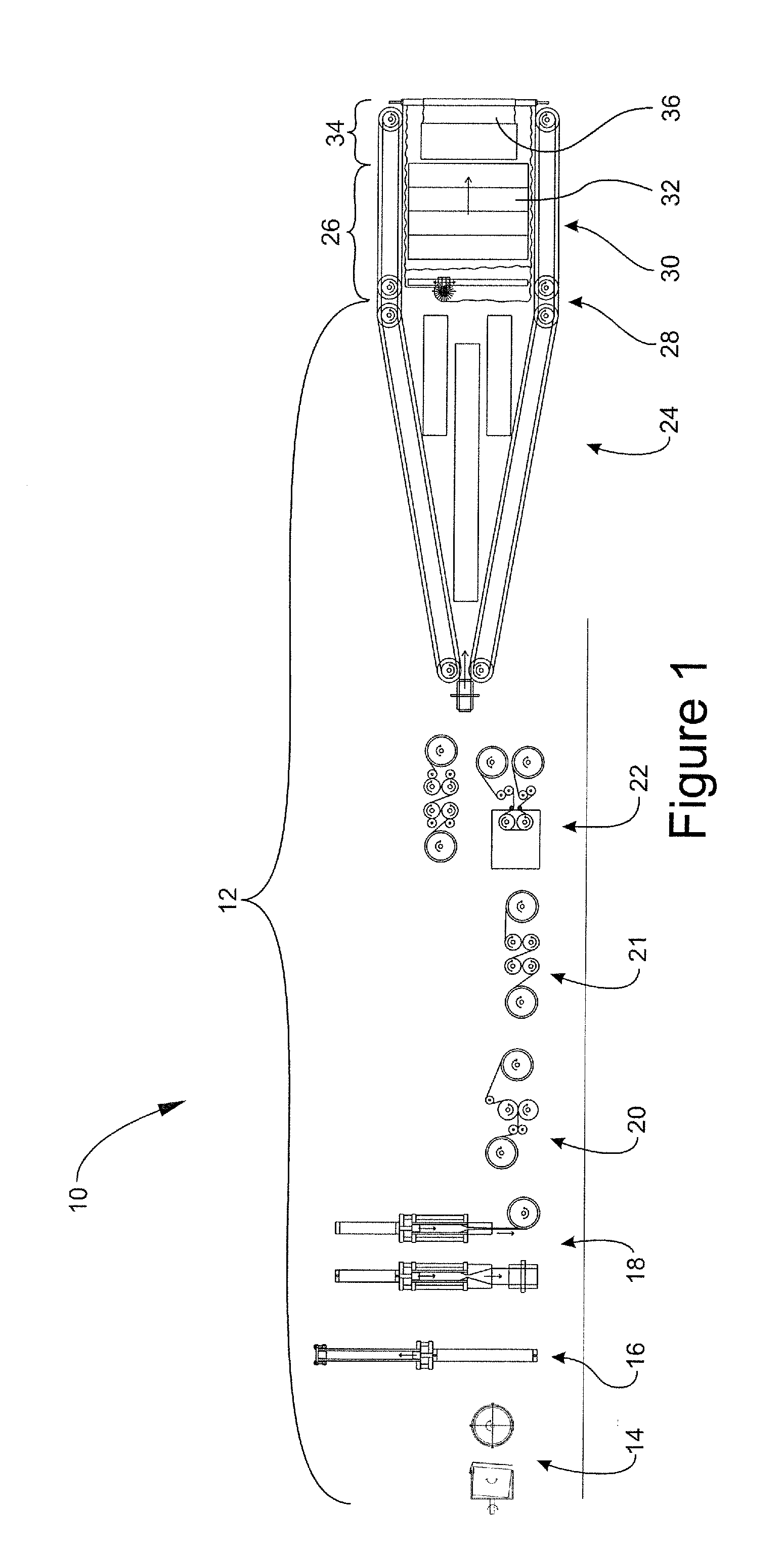
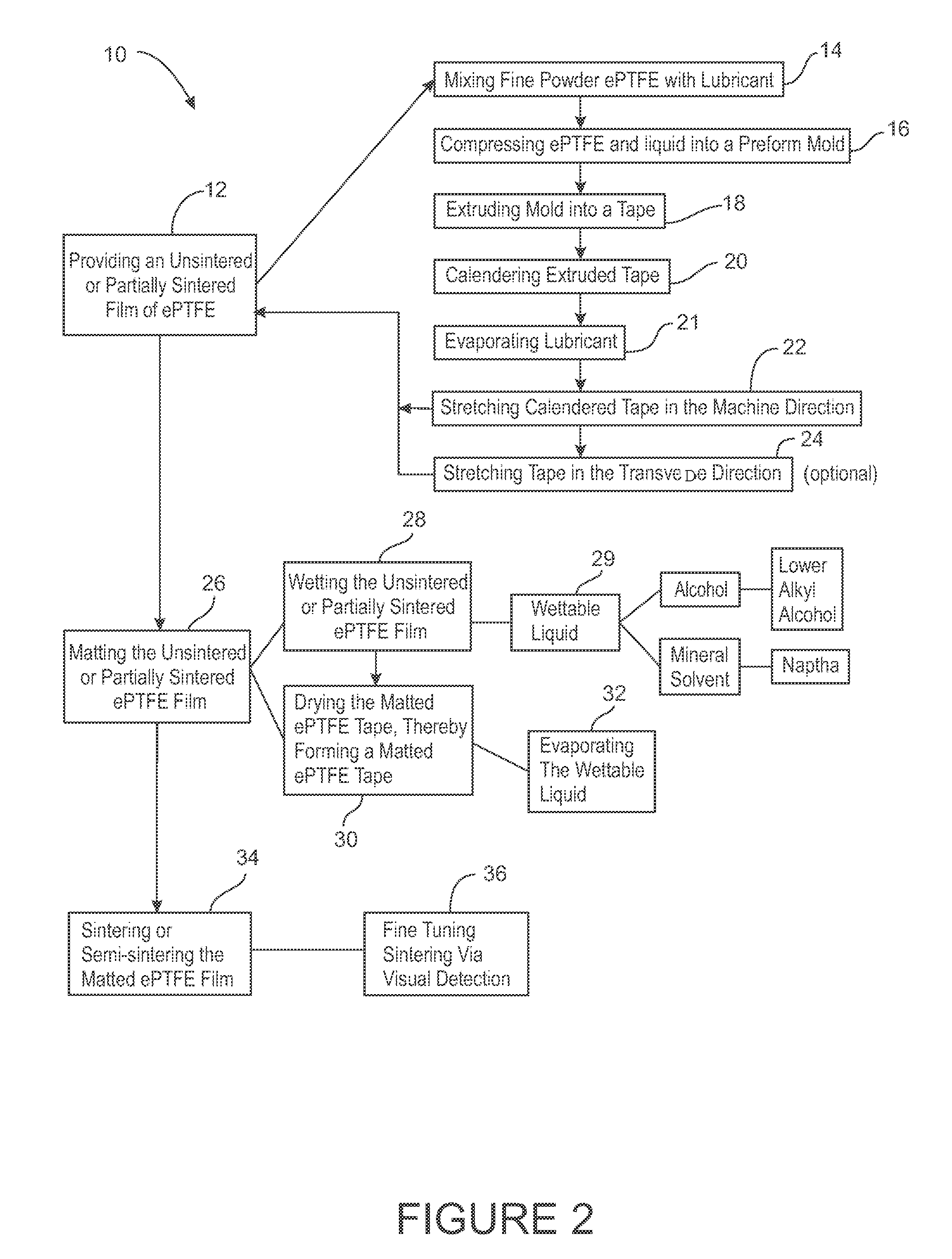
Thin wall expandable polymer tubes having improved axial and radial strength, and a method of manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20120201988A1Final product manufactureCeramic shaping apparatusUltimate tensile strengthPolymer
A method for making a thin walled ePTFE tube having improved axial and radial strength includes the steps of: providing an unsintered or partially sintered ePTFE membrane; wrapping the ePTFE membrane around a mandrel or form tool to form an ePTFE tube; matting the ePTFE tube; immediately thereafter, sintering the matted ePTFE tube; removing the sintered ePTFE tube from the mandrel or form tool; stretching the sintered ePTFE tube in the axial direction; stretching the ePTFE tube in the radial direction over a second mandrel that is greater in diameter than the reduced axially stretched diameter, but less than the first mandrel diameter; overwrapping the second mandrel with a second ePTFE membrane; matting the ePTFE tube; immediately thereafter, sintering the matted ePTFE tube; and removing the sintered ePTFE tube from the second mandrel or form tool.
Owner:PHILLIPS SCI
Process for forming microporous metal parts
InactiveUS6759004B1Reduces and eliminates interstitial poreMetal-working apparatusCork mechanical workingMetalMaterials science
A metal injection-molding feedstock is heated and plasticized. Supercritical carbon dioxide is injected into the feedstock to form micropores when the pressure is reduced and a parts mold is filled. The micropores are retained when the green parts are debindered and sintered.
Owner:SOUTHCO
Composite PTFE Materials and Applications Thereof
The present invention provides sintered composite polymeric materials and methods of making and using the same. The sintered composite polymeric materials are made by sintering composite particles comprising a polytetrafluoroethylene component and a carbonaceous component, wherein the carbonaceous component is dispersed throughout the polytetrafluoroethylene component.
Owner:POREX CORP
Tobacco smoke filter for smoking device with porous mass of active particulate
A tobacco smoking device comprises a porous mass of active particles adapted to enhance a tobacco smoke flowing over said active particles and binder particles. The active particles comprises about 1-99% weight of the porous mass, and the binder particles comprises about 1-99% weight of said porous mass. The active particles and said binder particles are bound together at randomly distributed points throughout the porous mass. The active particles have a greater particle size than the binder particles.
Owner:ACETATE INT LLC
Porous barrier media comprising color change indicators
ActiveUS20080199363A1Rapid responseAvoid aspirationRecord information storageAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor changesChemistry
Owner:POREX CORP
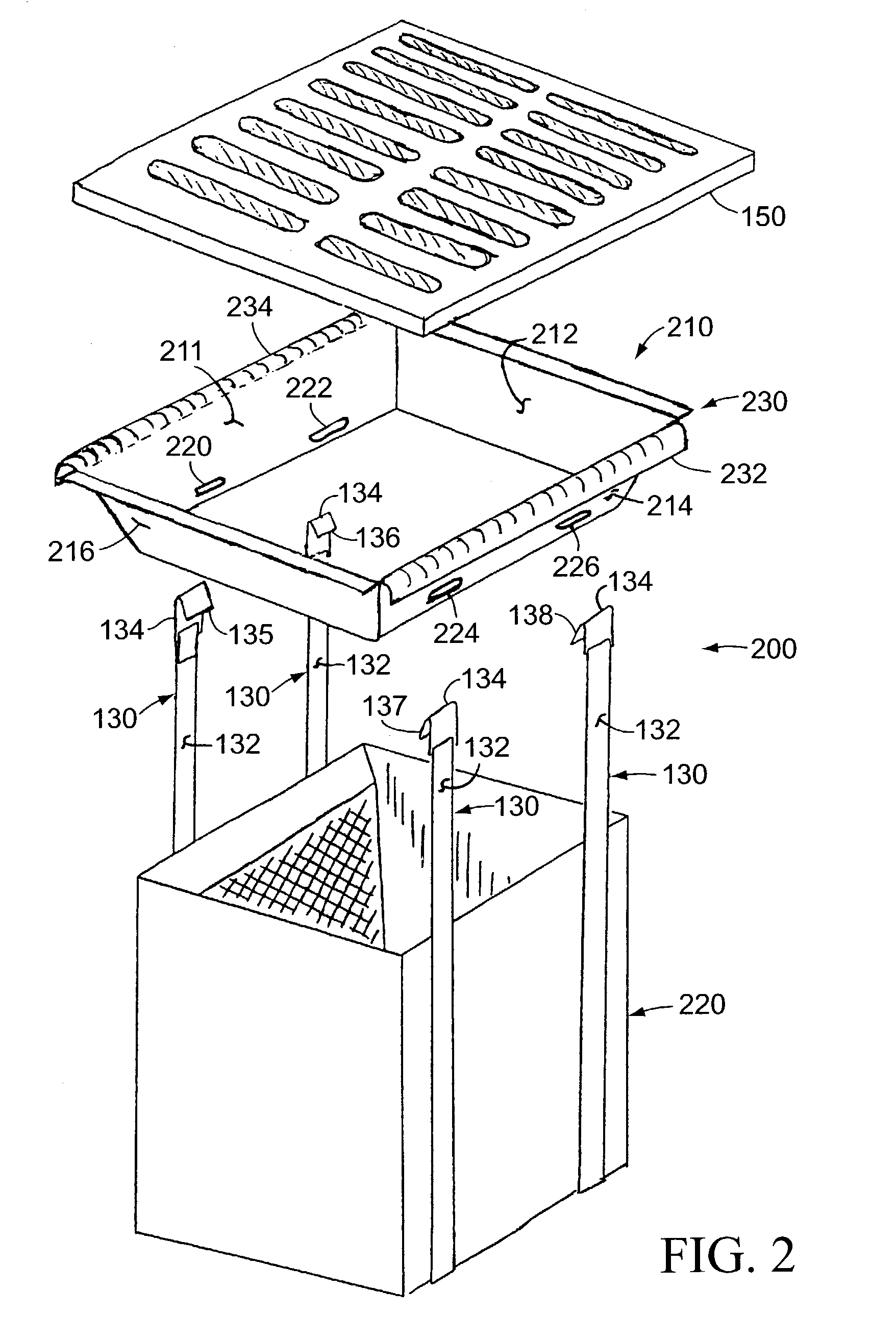
Method of making and using a filter in the form of a block of agglomerated copolymer fragments
InactiveUS7094338B2Easy to useCork mechanical workingLoose filtering material filtersFilter systemEngineering
One of the exemplary filter systems described includes a bracket and a filter module that can be suspended from the bracket by a plurality of flexible supports. The bracket can support the filter system beneath the grate of a storm drain without the need for the filter system to be attached to the grate. The grate can be lifted out of the storm drain separately from the filter unit, which allows the filter system to be lifted without the added weight of the grate. When the grate has been lifted out of the way, a suitable fastener structure can be attached to the bracket of the filter system to make the use of mechanical lifting devices more convenient. The bracket can be manufactured to known dimensions, or it can be offered from among a set of brackets that are pre-configured for known storm drain dimensions or as a standard bracket that can be modified to fit the dimensions of a particular storm drain.
Owner:ABTECH IND +1
Method and machine for producing three-dimensional objects by means of successive layer deposition
Inventive machine allowing the simultaneous fabrication of several objects by a method of “rapid prototyping” type, by depositing a succession of layers of heat-fusible fluid.It chiefly comprises a crossbar (20) carrying two platforms (11) on each of which an object is fabricated by deposition. Two fixed work stations are arranged diametrically opposite each other so that the jet (12) of each of these fixed stations can perform a depositing operation at the same time as the other jet (12). After each deposit, the crossbar is rotated 180° to alternate the depositing operations of the two different materials.Particular application to prototyping jewellery models.
Owner:MARSAC NICOLAS
Method for making dimensionally stable composite products from lignocelluloses
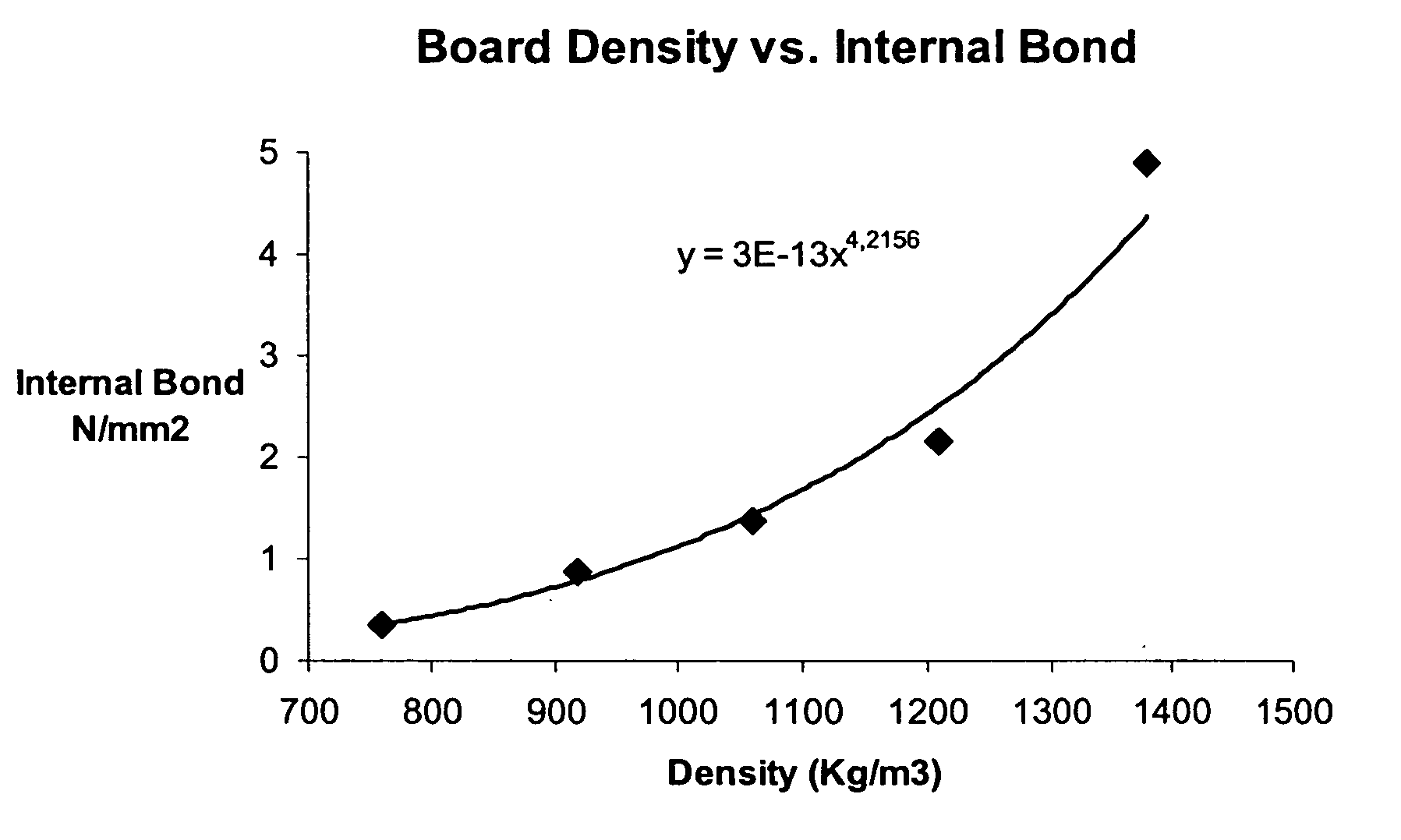
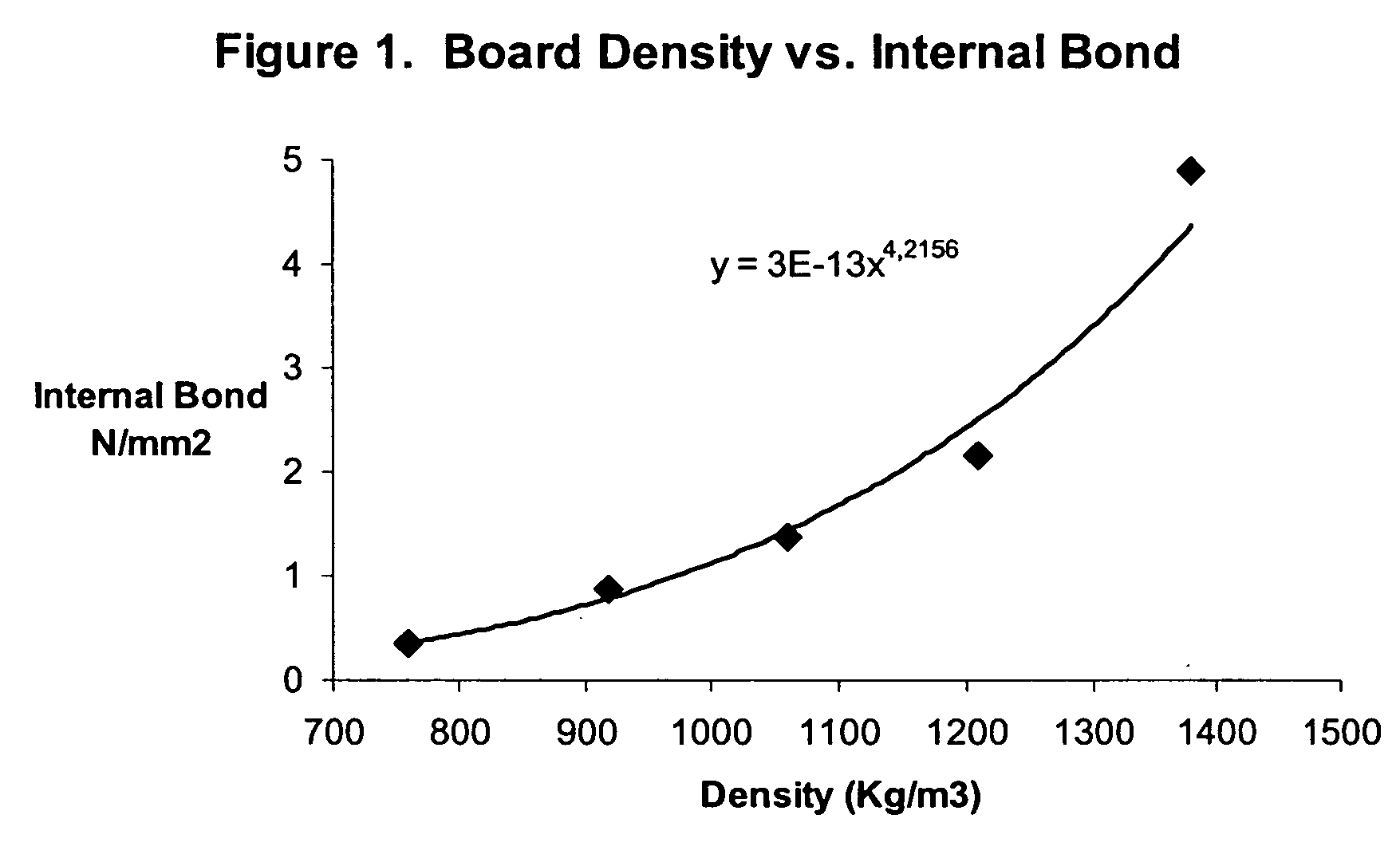
InactiveUS20060091577A1Good physical propertiesImprove water resistanceCeramic shaping apparatusCork mechanical workingHigh densityDecomposition
This invention relates to a process for making dimensionally stable reconstituted composite products from lignocellulosic material. By treating lignocellulose with high pressure steam to decompose and hydrolyse the hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin fractions of the lignocellulose and using those decomposition products as both a bonding and bulking agent, it converts, under heat and pressure in a moulding operation, the treated lignocellulose into moulded composite products such as panel boards and moulded articles. The composite products thus produced possess good physical and mechanical properties. Specifically, the dimensional stability in terms of the thickness swelling and linear expansion of panel boards such as fibreboards and particleboard, can be minimized to very low levels when the panel boards are made in high density. The adhesive bond developed from thermosetting of the decomposition products of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin is strong and stable, and resistant to boiling water and acid hydrolysis, and is free of formaldehyde emissions. Thus, the reconstituted panel boards and moulded products are suitable for exterior and particularly for indoor applications. The absence of free formaldehyde emissions makes the product very suitable for interior applications. The manufacturing cost for the reconstituted products is significantly lower in comparison to the conventional process because expensive synthetic resin is not used.
Owner:SHEN KUO C +1
Expanded graphite and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS7550529B2Improve mechanical propertiesImprove thermal conductivityLayered productsConductive materialFuel cellsGraphite
Graphite nanoplatelets of expanded graphite and composites and products produced therefrom are described. The preferred method of expanding the graphite is by microwaves or other radiofrequency wave treatment of intercalated graphite. The expanded graphite is preferably then crushed to nanometer (substantially all 200 microns or less). The expanded graphite is used in polymer composites. The expanded graphite is particularly useful for batteries, anodes and fuel cells.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
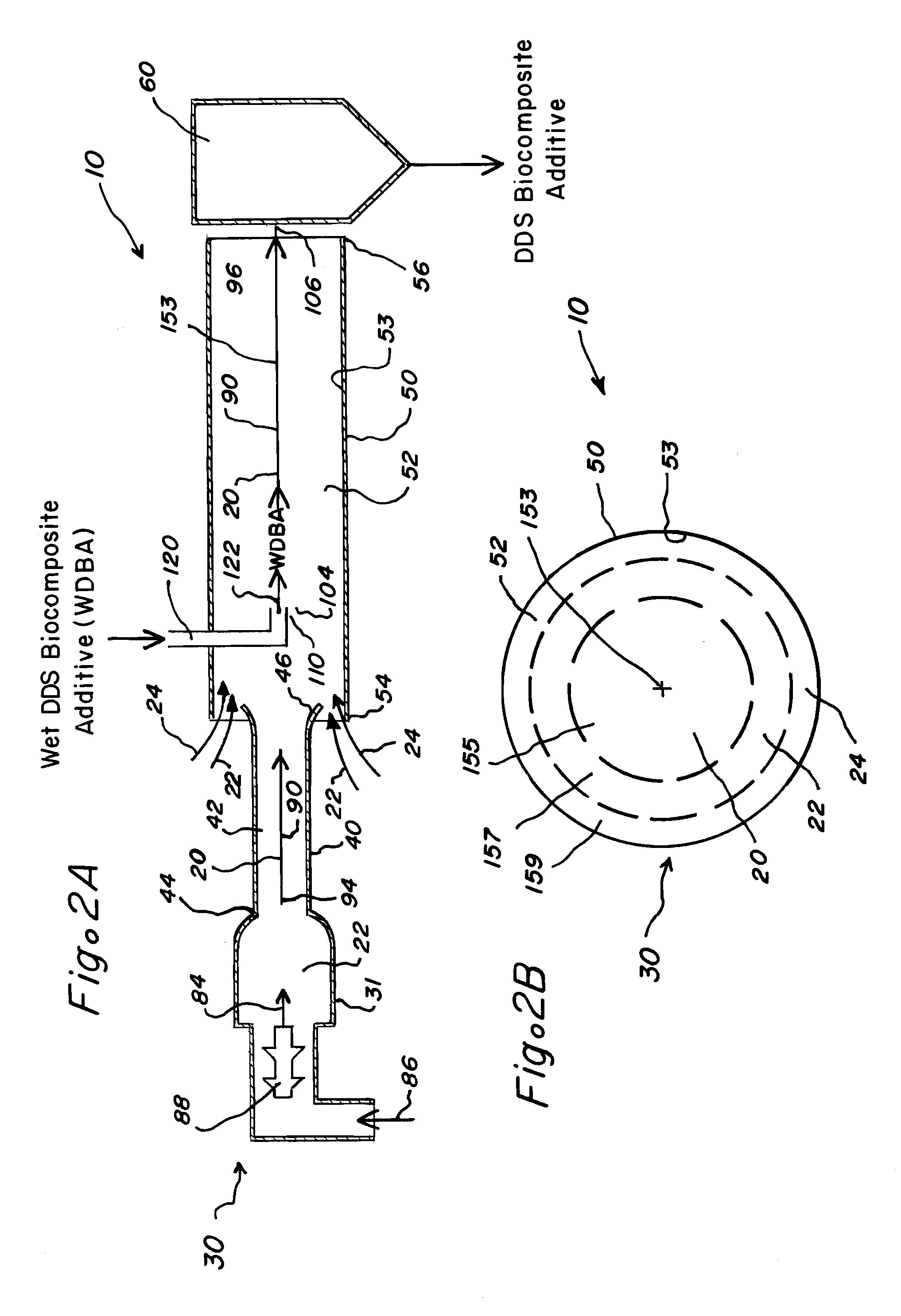
Multifunctional biocomposite additive compositions and methods
Biocomposite compositions and compositions, which include dried distillers solubles, and which can be used in making biocomposite compositions are described. Methods for preparing the compositions are also described.
Owner:GENAREX FD LLC
Production of particle board from agricultural waste
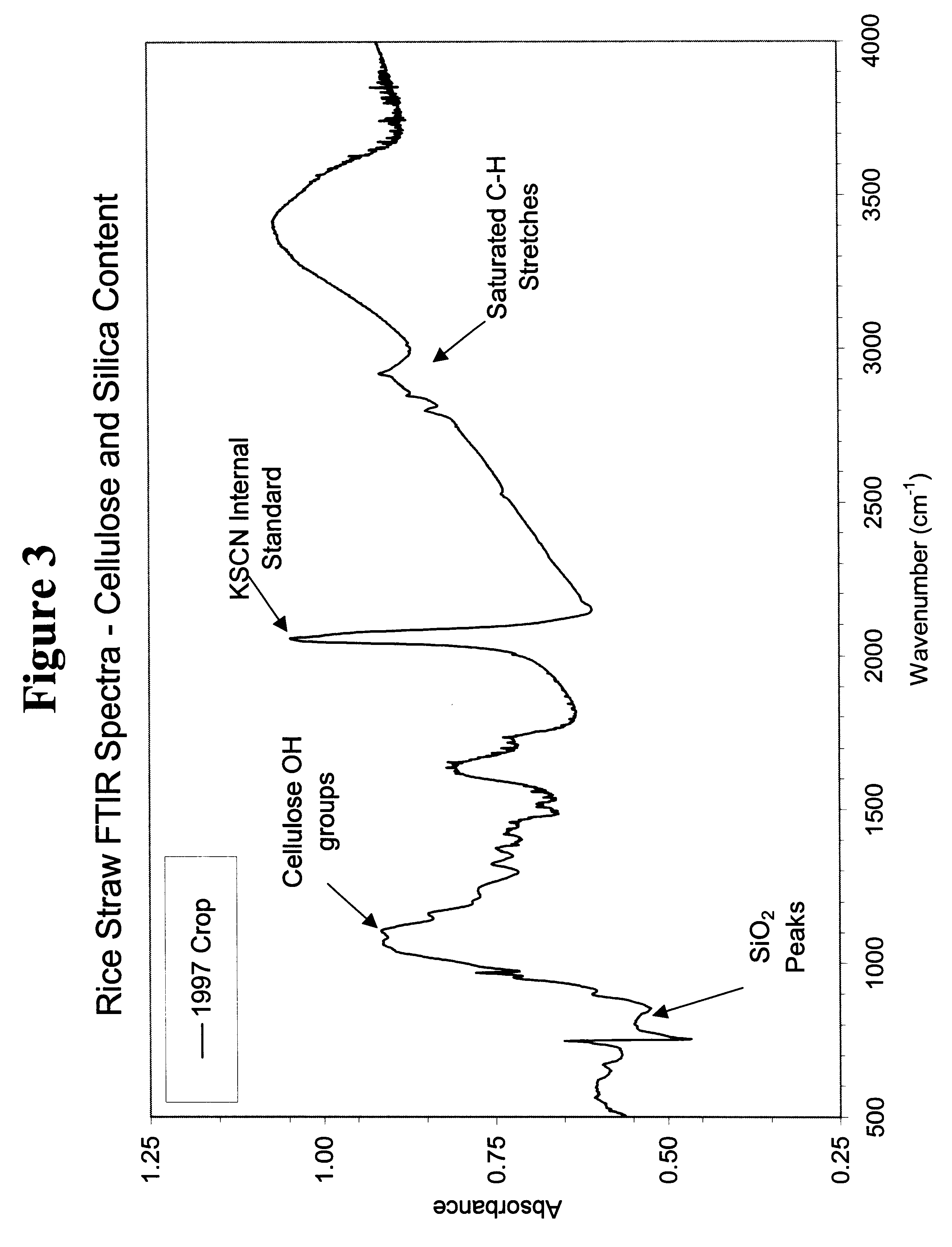
The present invention describes a process of using agricultural biomass to make particle or fiberboards. The preferred biomass is selected with high cellulose and hemicellulose concentration and low silica content. The process utilizes short refining time and low steam pressure.
Owner:AGFIBER IP LLC
Method for making ePTFE and structure containing such ePTFE. such as a vascular graft
InactiveUS20060147665A1Facilitates subsequent radial expansionImprove the immunityStentsSynthetic resin layered productsMicro structureFiber
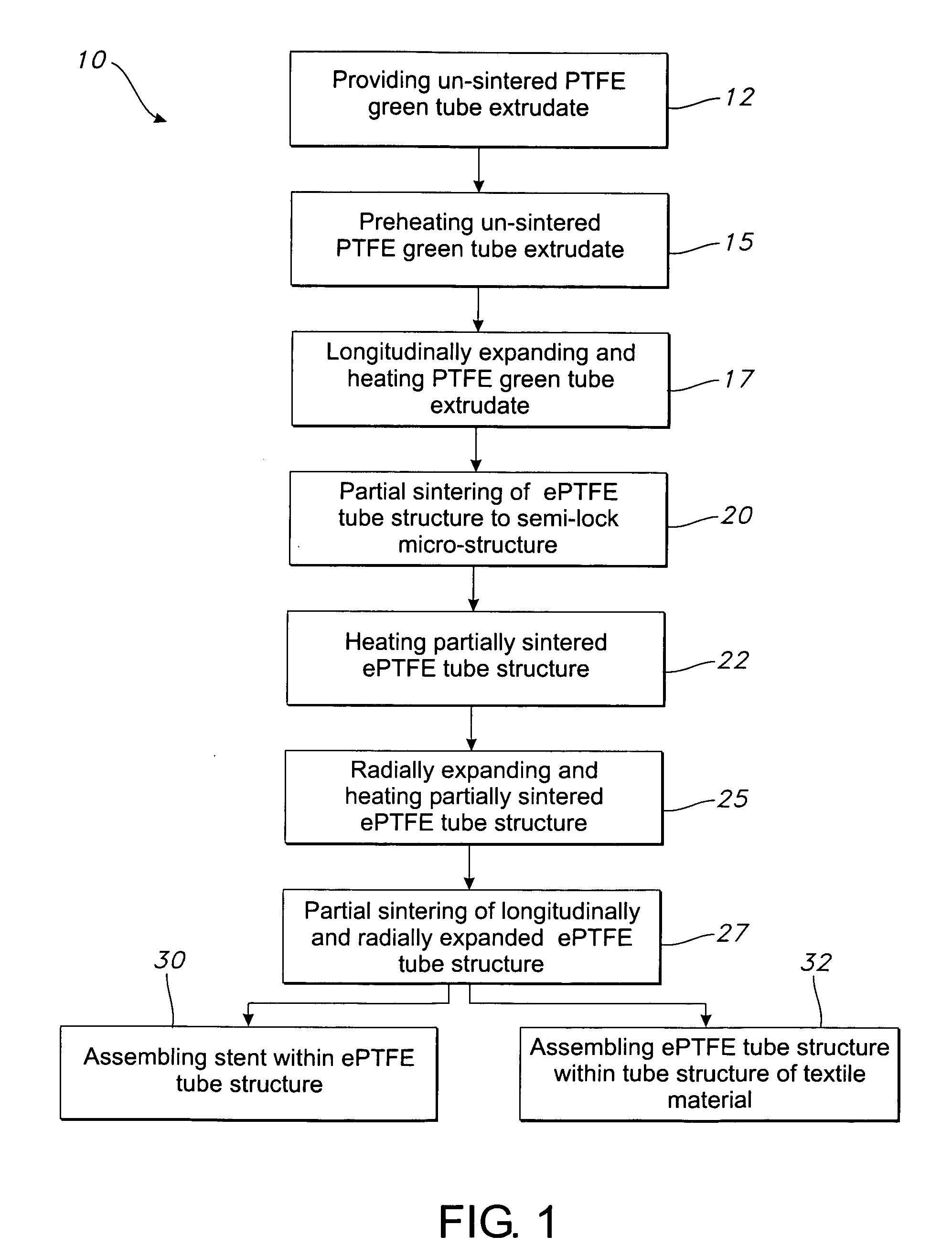
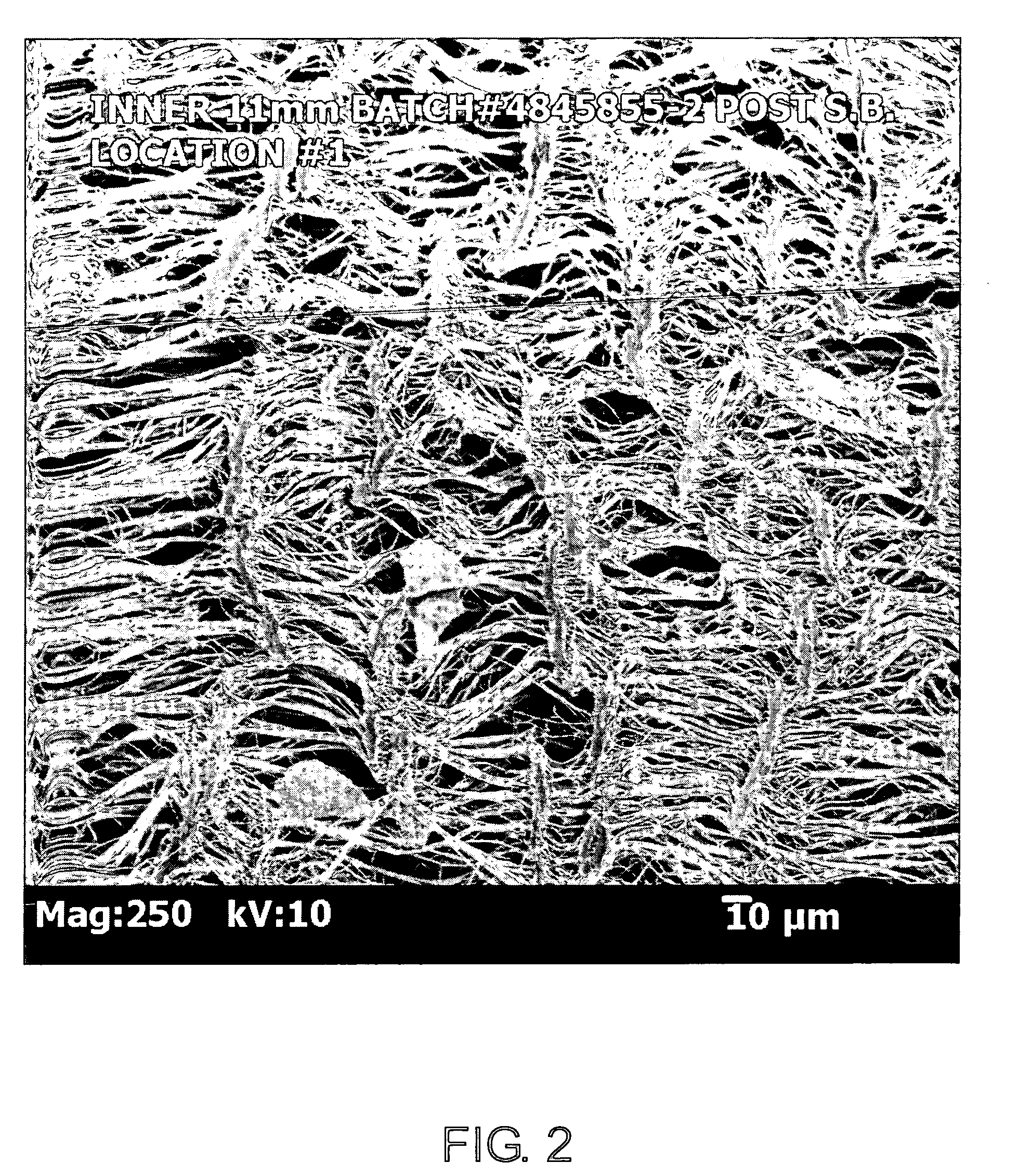
A method for making a vascular graft includes providing a PTFE green tube extrudate which is un-sintered, and then initially expanding the un-sintered extrudate to produce an initial node and fibril micro-structure therein. This is followed by heating the extrudate to raise the temperature thereof for a time period of sufficient duration such that the extrudate is partially sintered. The partially sintered extrudate is subsequently expanded to make the vascular graft. The subsequent expansion produces a subsequent node and fibril micro-structure in the vascular graft. An alternative method for making a vascular graft includes providing a PTFE green tube extrudate which is un-sintered, longitudinally expanding the un-sintered extrudate to form an ePTFE tube structure, and radially expanding the un-sintered ePTFE tube structure. ePTFE made according to the method is fabricated into various structures, such as tube structures, filament structures, and sheet structures.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Porous barrier media comprising color change indicators
ActiveUS8187534B2Rapid responseAvoid aspirationRecord information storageAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor changesChemistry
Owner:POREX CORP
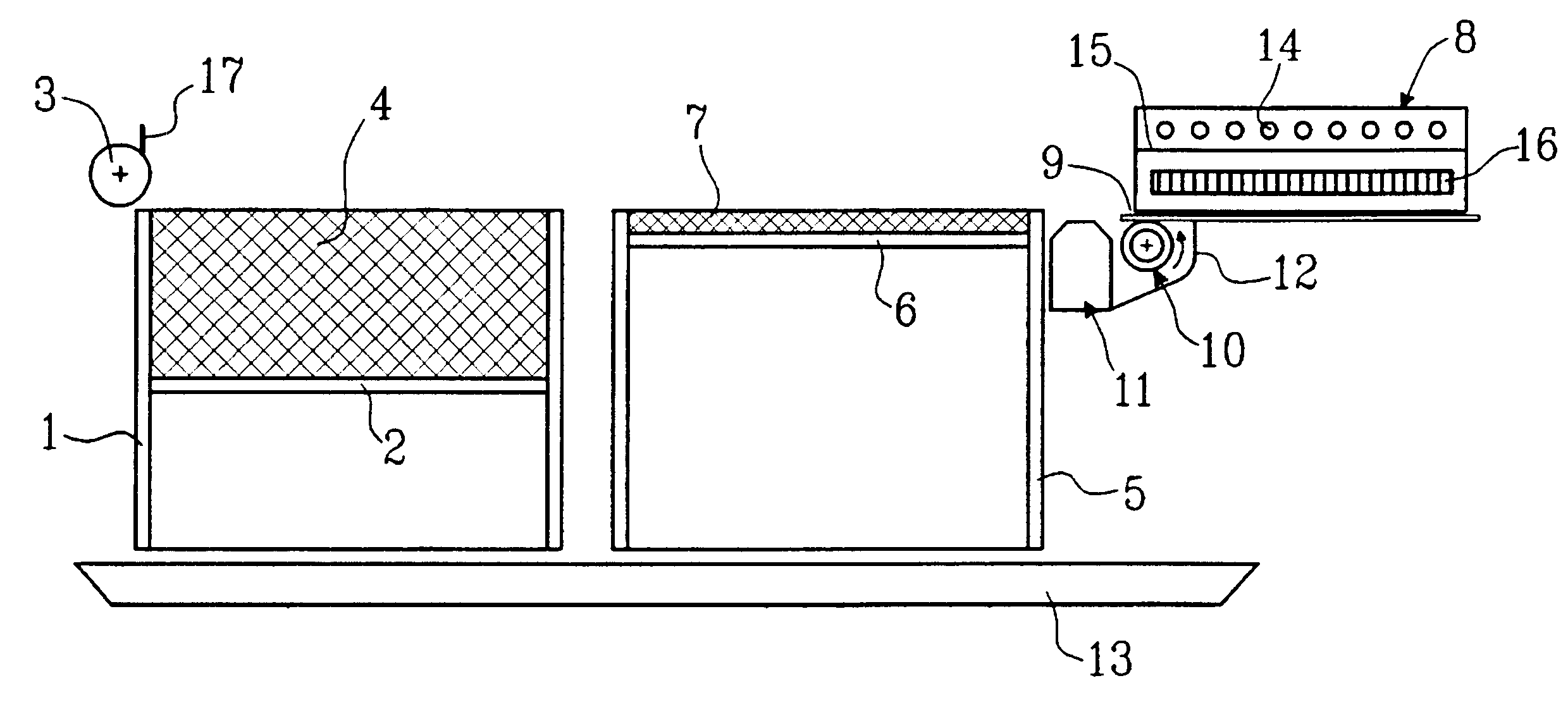
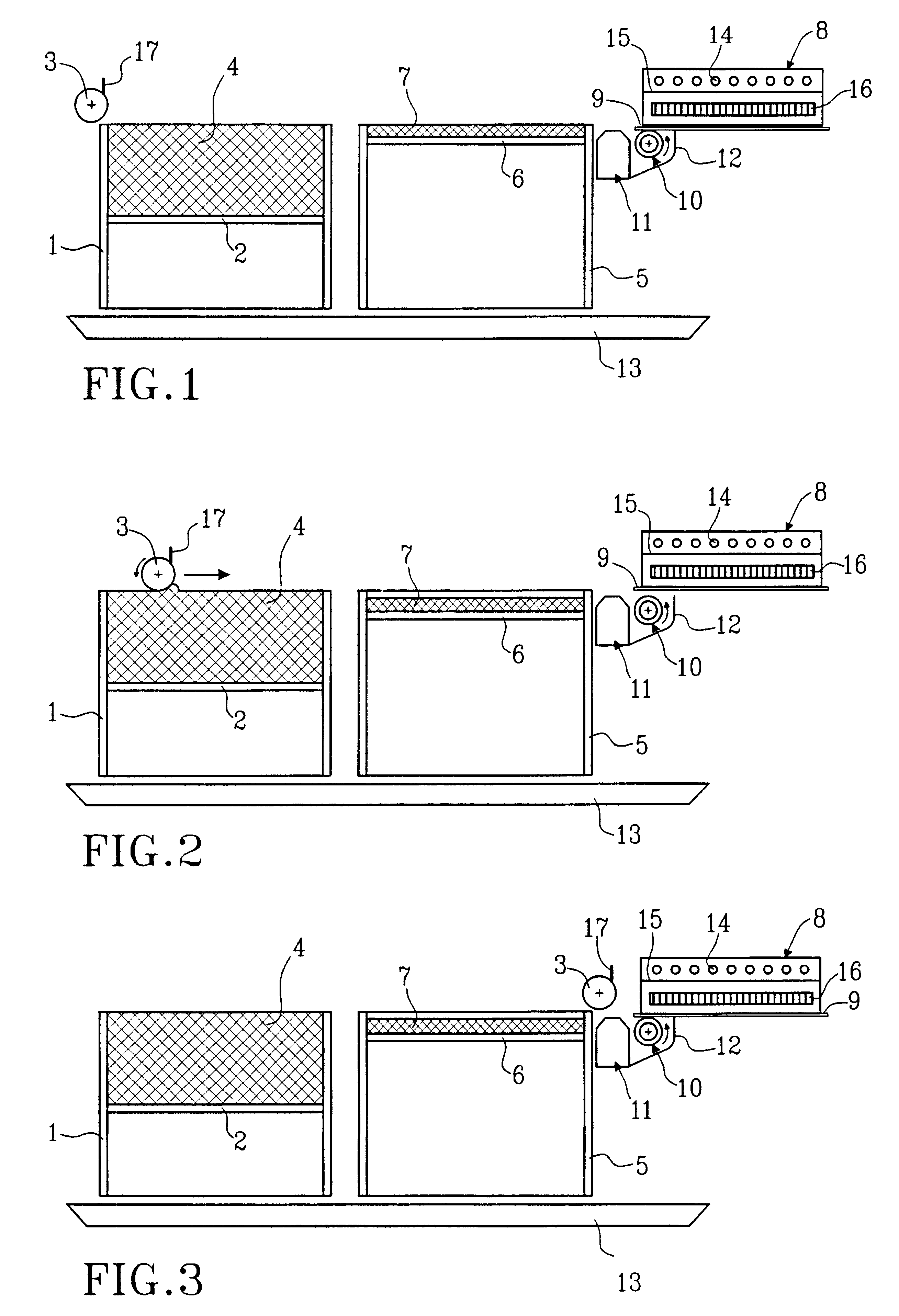
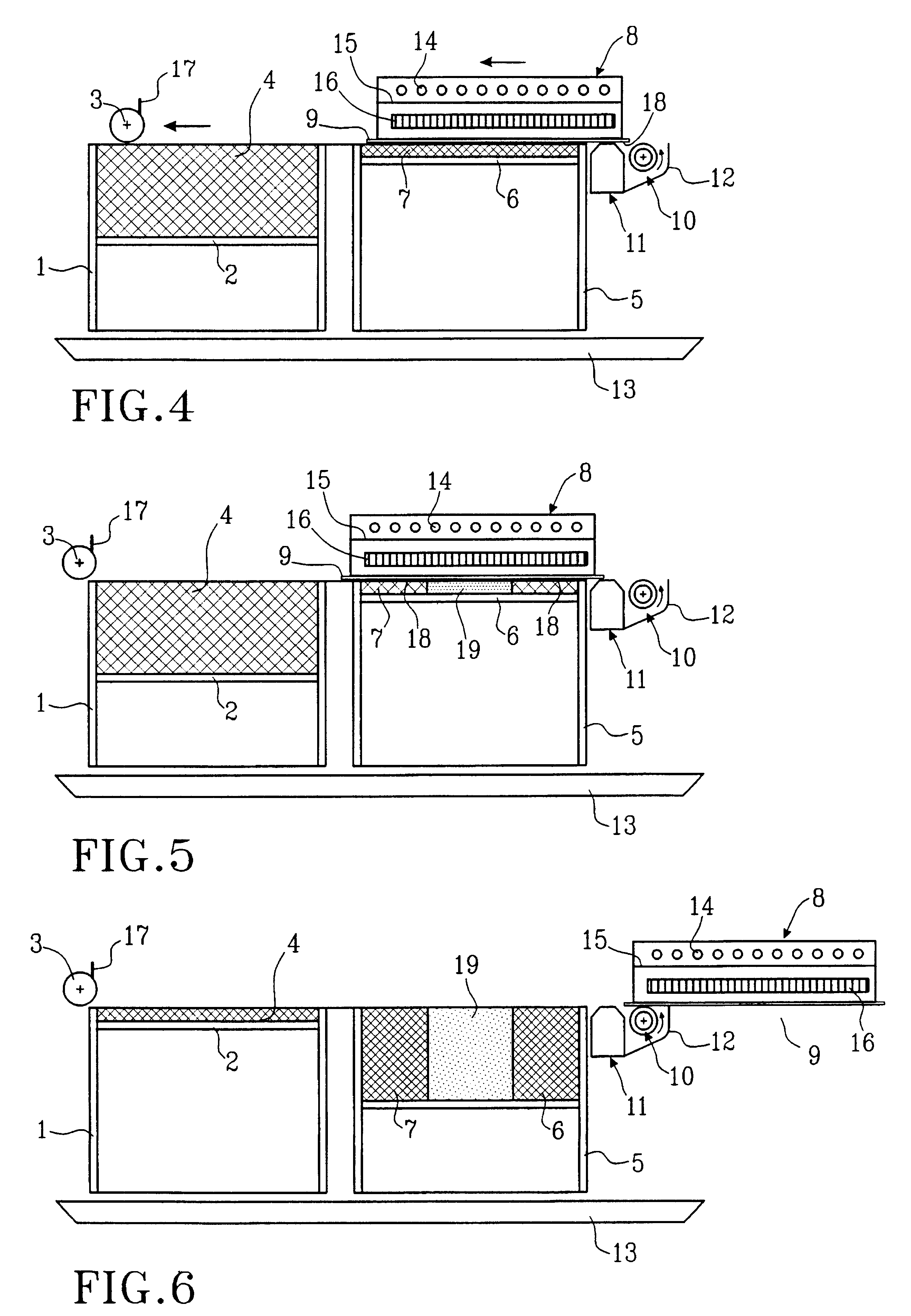
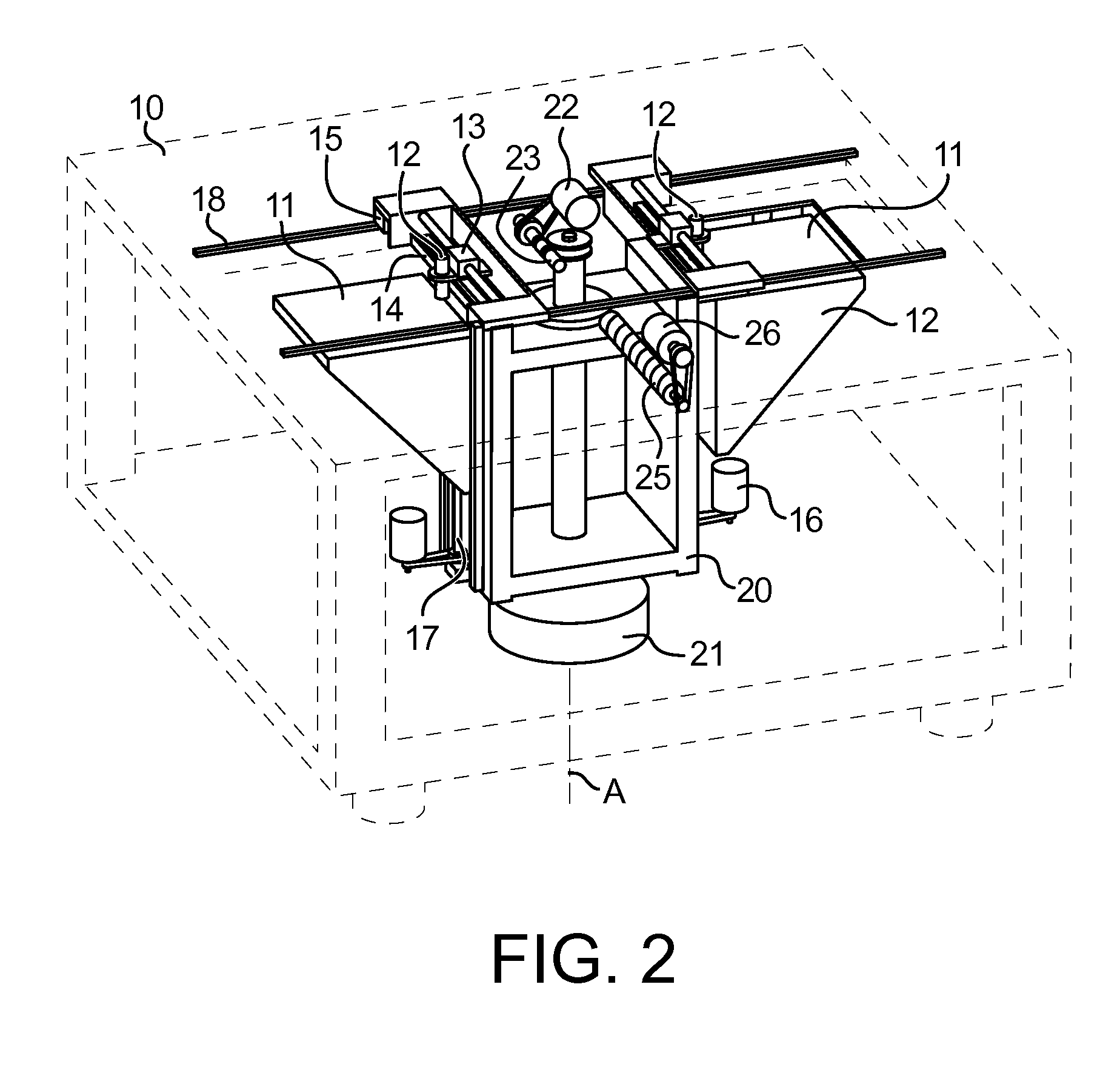
Process and device for producing solid bodies by sequential layer buildup
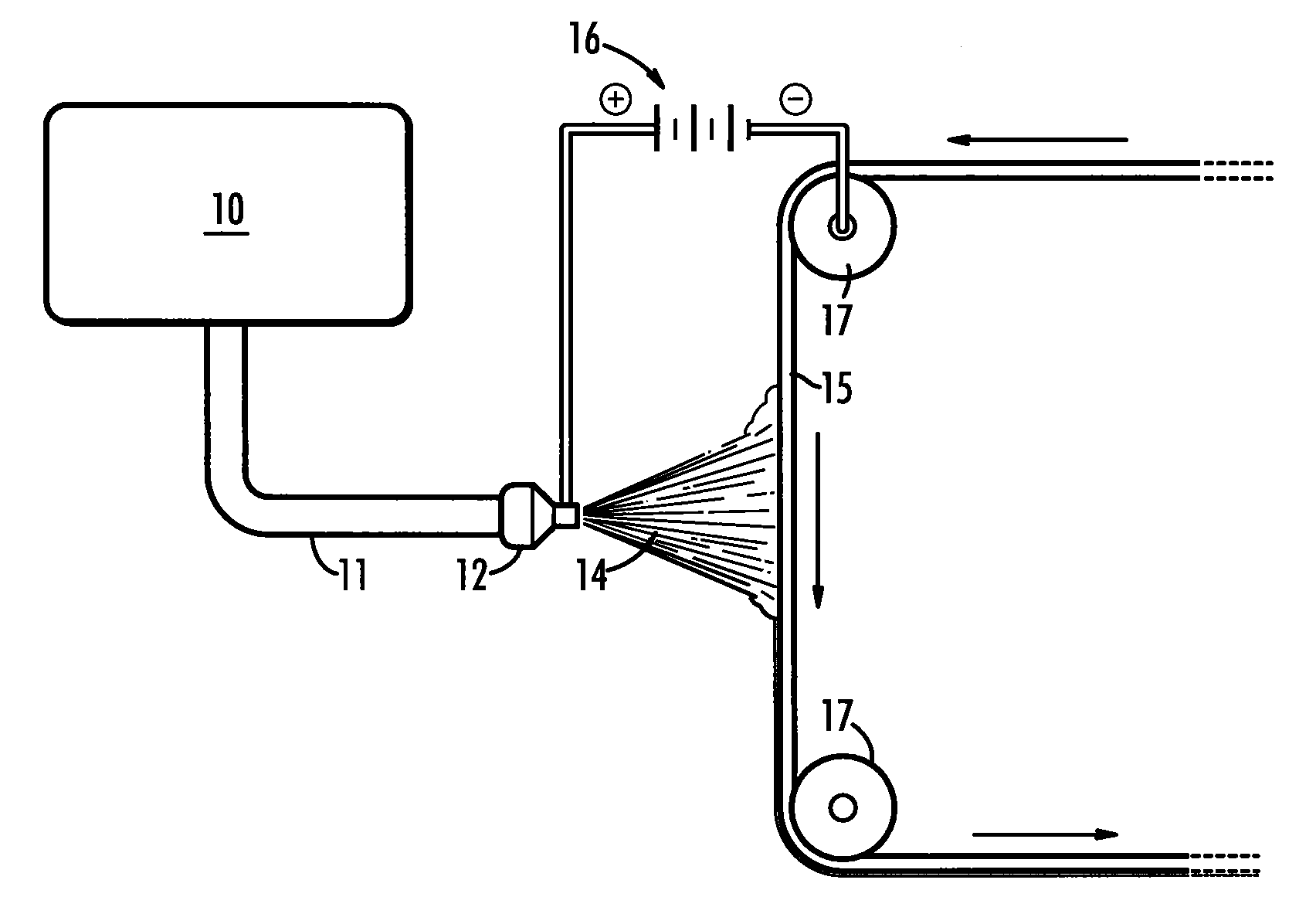
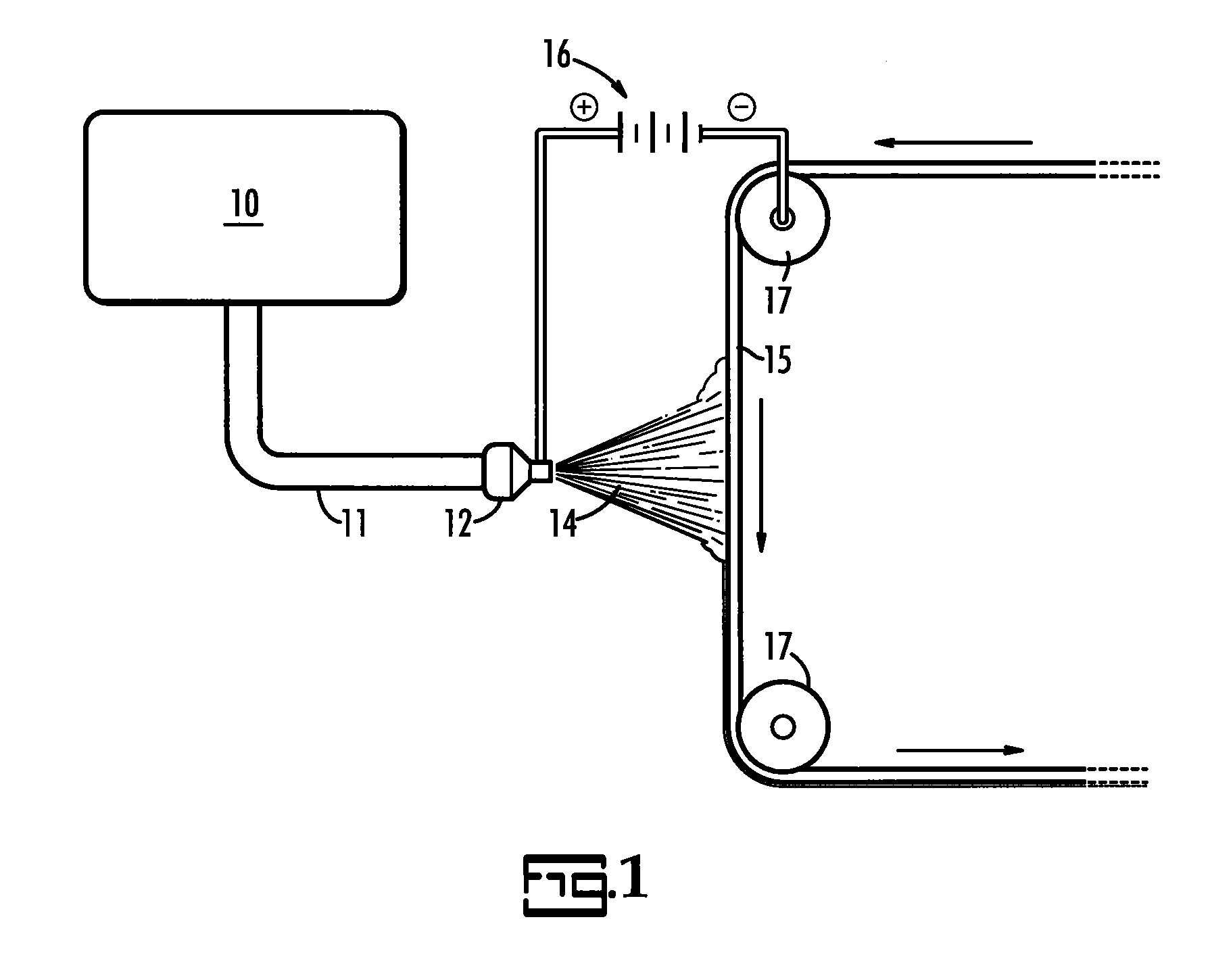
ActiveUS7285234B2Mechanical working/deformationCork mechanical workingBiological activationRapid prototyping
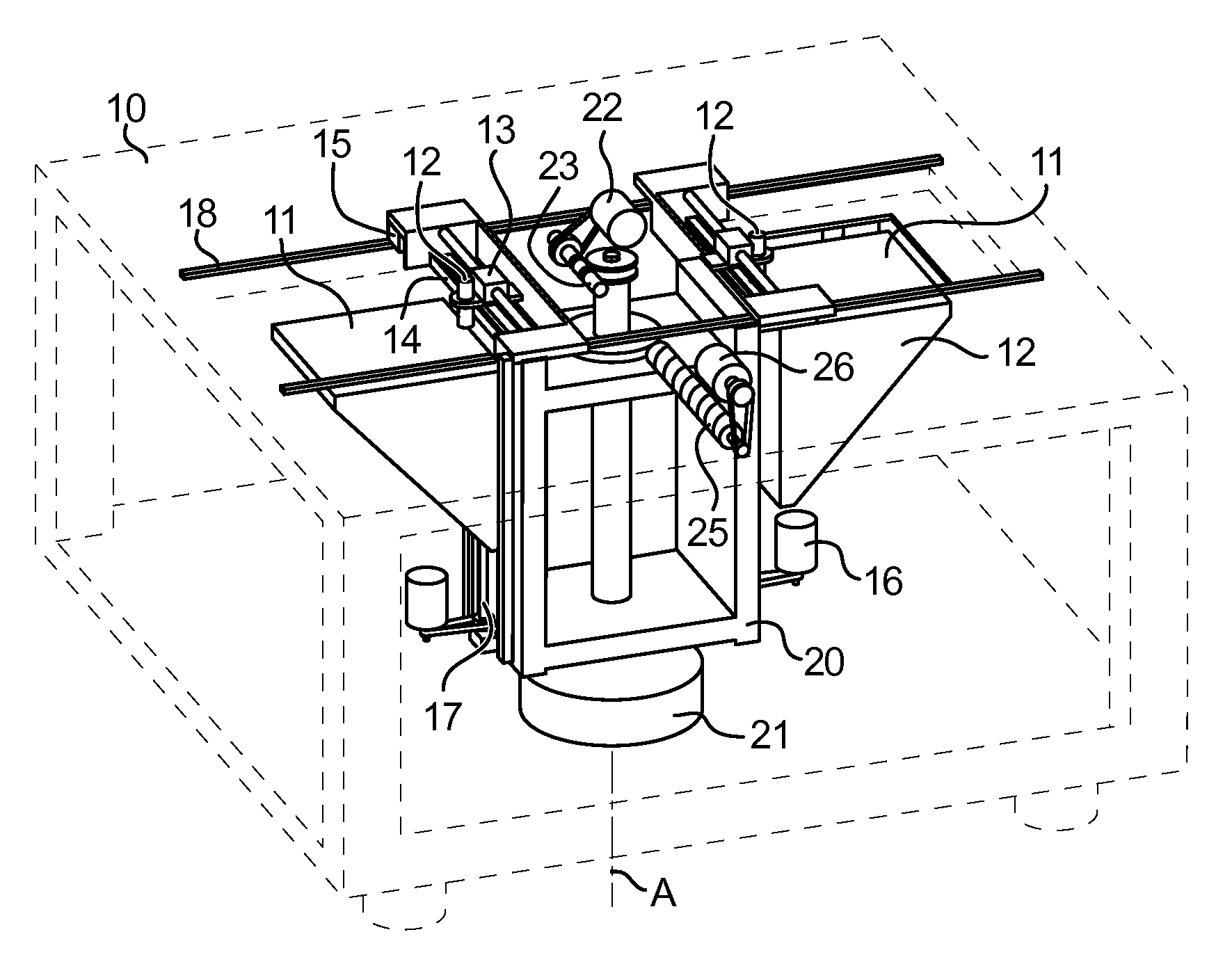
Process for layer-wise production of a three dimensional body (generative rapid prototyping), in particular by 3D binder printer, including a multiple succession of the steps of depositing a powder particle layer, activating in defined areas an adhesive present on the powder particles and / or in the powder particle coating, as well as adhering the powder particles to each other and to the layer thereunder, wherein the powder particle layer is electrically discharged by ionized particles and brushed flat by means of an electrically insulated blade prior to activation of the adhesive material, and the invention further concerns a device adapted for application of thin powder particle layers, including at least one ionizing device.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com