Non-woven fabric comprising staple fibers and an absorbent article using the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
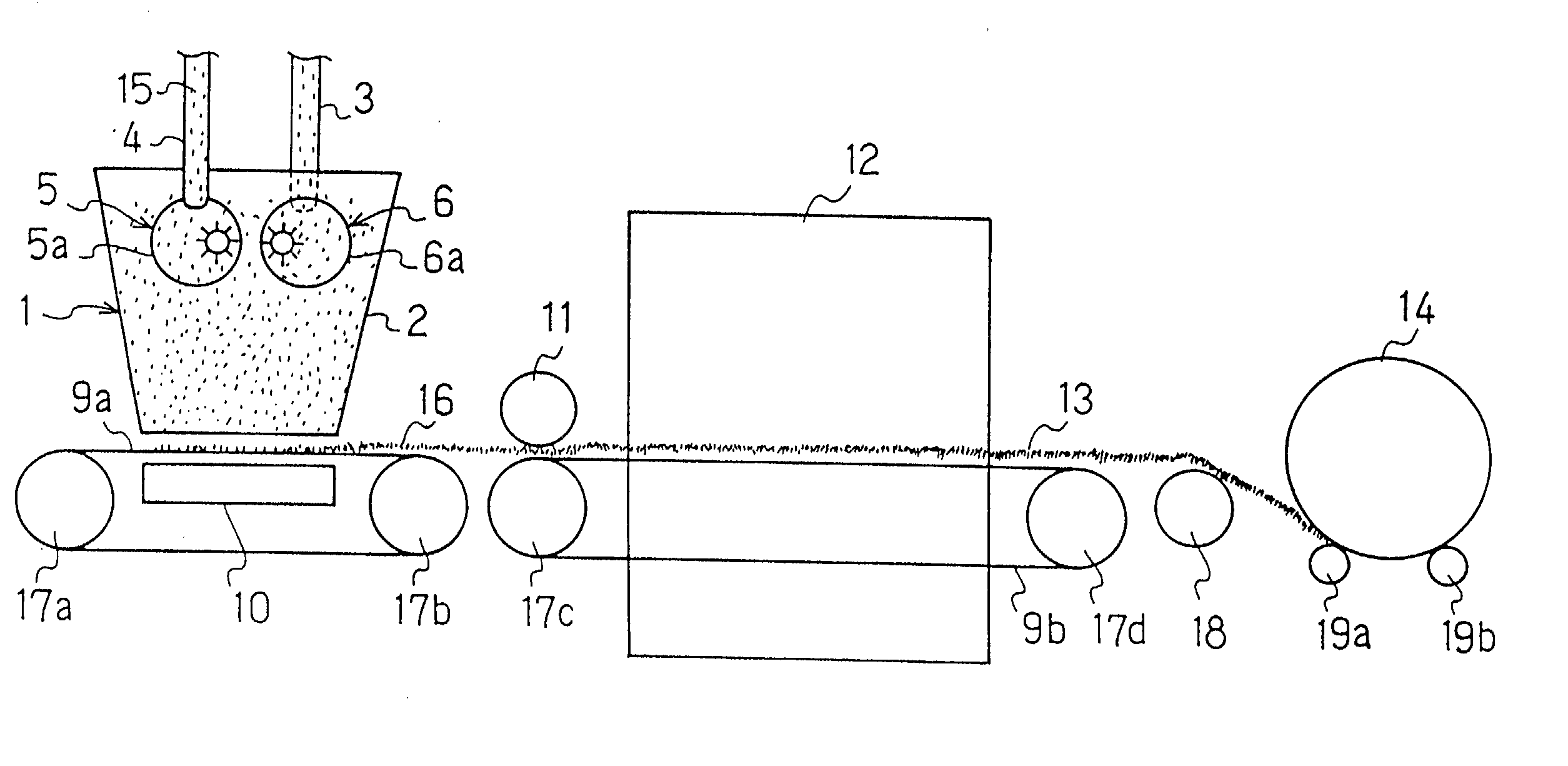
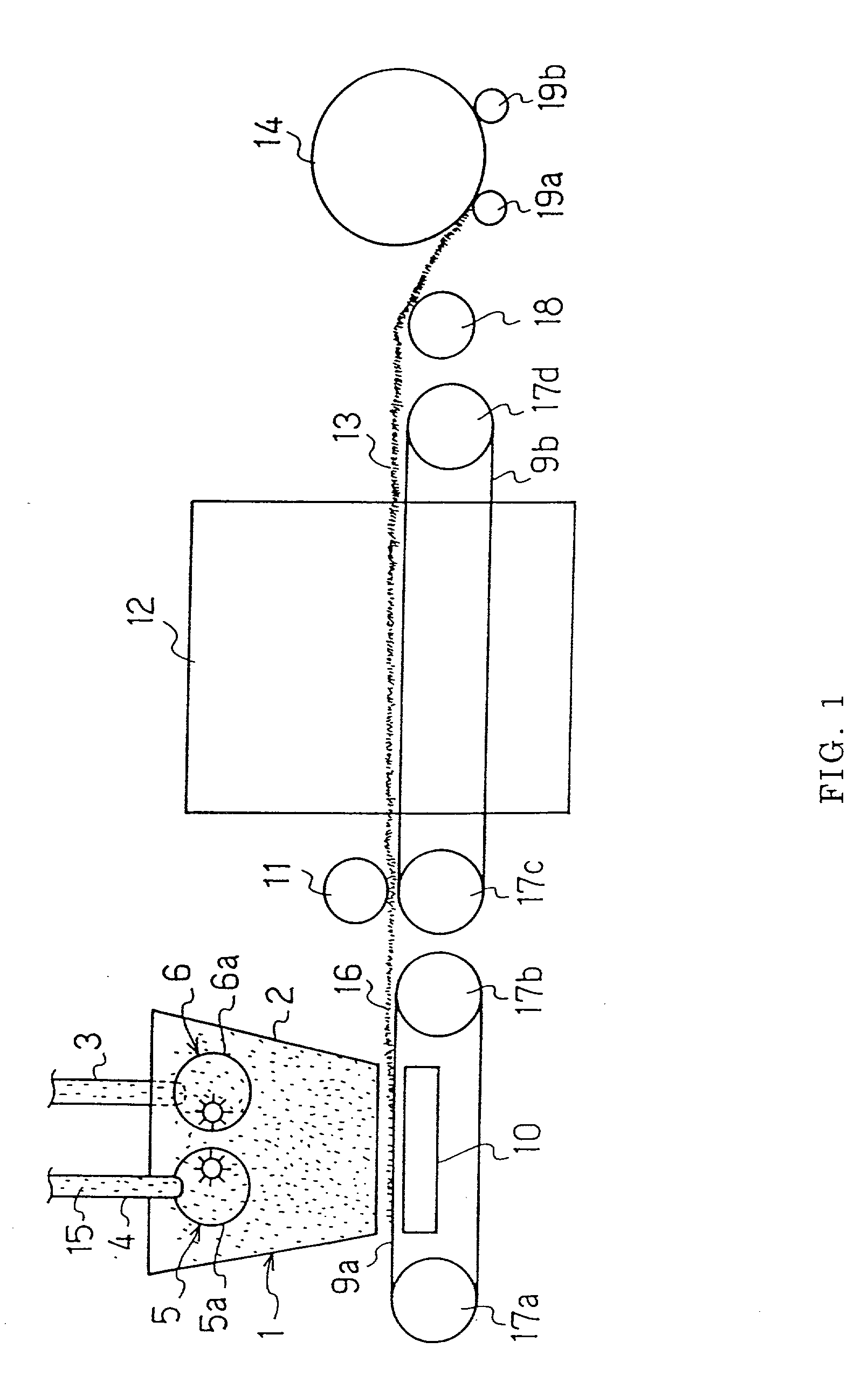
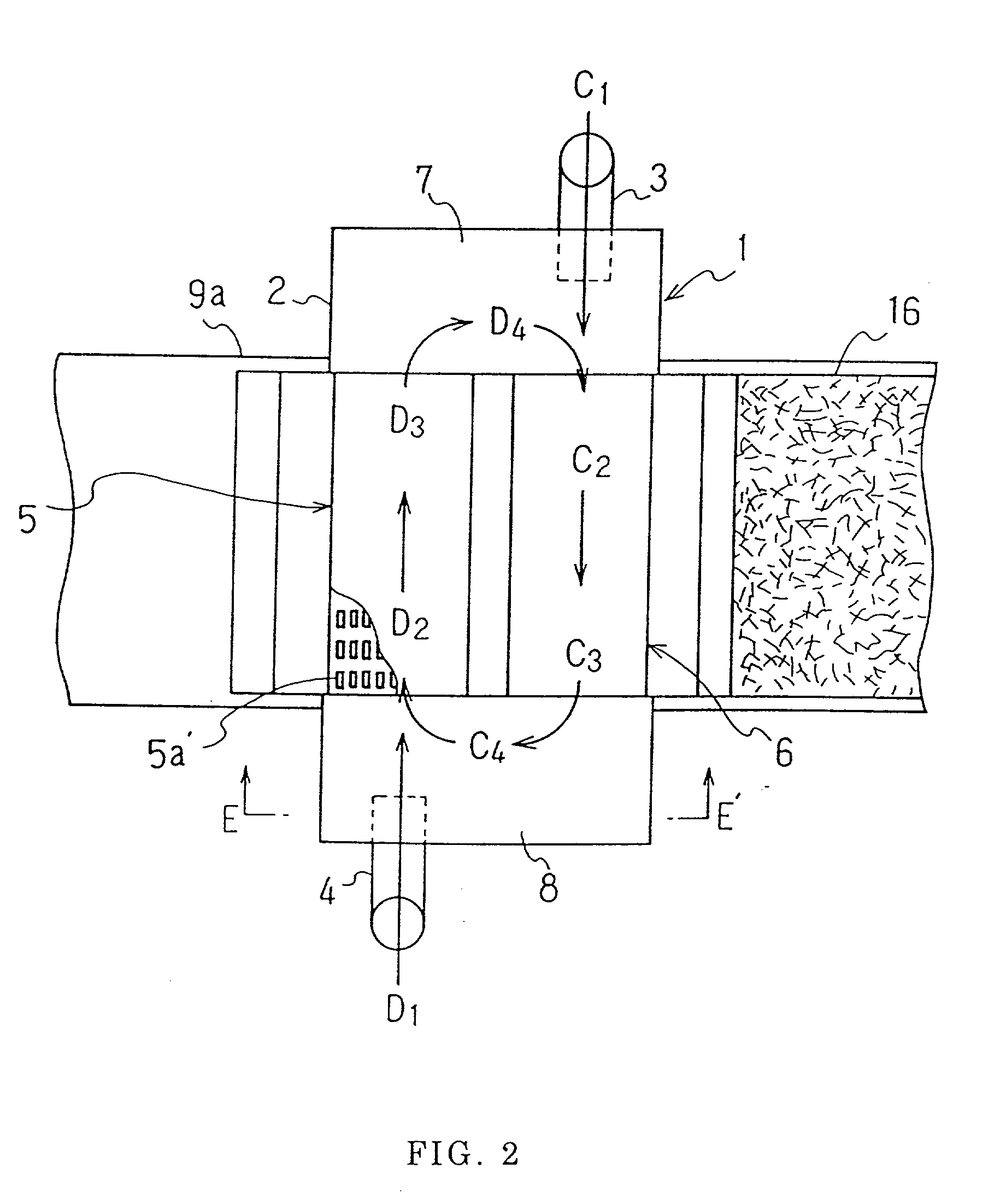
[0076] A method for producing thermal adhesive staple fibers:
[0077] High crystalline polypropylene having MFR (melt flow rate) of 11 g per 10 minutes (the conditions 14 specified in JIS K7210) as a core component and high density polyethylene having MI (melt index) of 16.5 g per 10 minutes (the conditions 4 specified in JIS K7210) were spun out of an eccentric core and sheath type spinneret having 621 holes at the discharging ratio of high crystalline polypropylene to high density polyethylene of 5:5 and at the discharging volume of 450 g / min, and then taken up at the speed of 592 m / min to produce 11 denier unstretched fibers. When spinning was conducted, fibers were cooled by air cooling just below the spinneret, and then finishing agent comprising lauryl phosphate potassium salt as a main component was applied by using a contact roll.
[0078] This unstretched fiber was stretched between the first roll and the second roll to produce a stretched fiber having the fineness of 3 denier a...
example 3
[0082] The non-woven fabric was produced under the same conditions as Example 2 except that the fiber length of the conjugated fiber was made to be 10 mm.
[0083] As to the physical properties, the resultant non-woven fabric had a basis weight of 25 g / m.sup.2, a thickness of 4.4 mm, specific volume of 176 cm.sup.3 / g, and the number of the fiber lumps of 1.9 lumps per 20 g. The results are shown in Table 1.
example 4
[0084] The non-woven fabric was produced under the same conditions as Example 2 except that the fiber length of the conjugated fiber was made to be 15 mm.
[0085] As to the physical properties, the resultant non-woven fabric had a basis weight of 25 g / m.sup.2, a thickness of 4.25 mm, specific volume of 170 cm.sup.3 / g, and the number of the fiber lumps of 3.8 lumps per 20 g. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com