Thin layer semi-conductor structure comprising a heat distribution layer
a thin layer, semi-conductor technology, applied in the direction of transistors, electric devices, solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, need to resort to non-standard micro-electronic equipment, and the drawback of silica, so as to reduce the thickness of the first substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
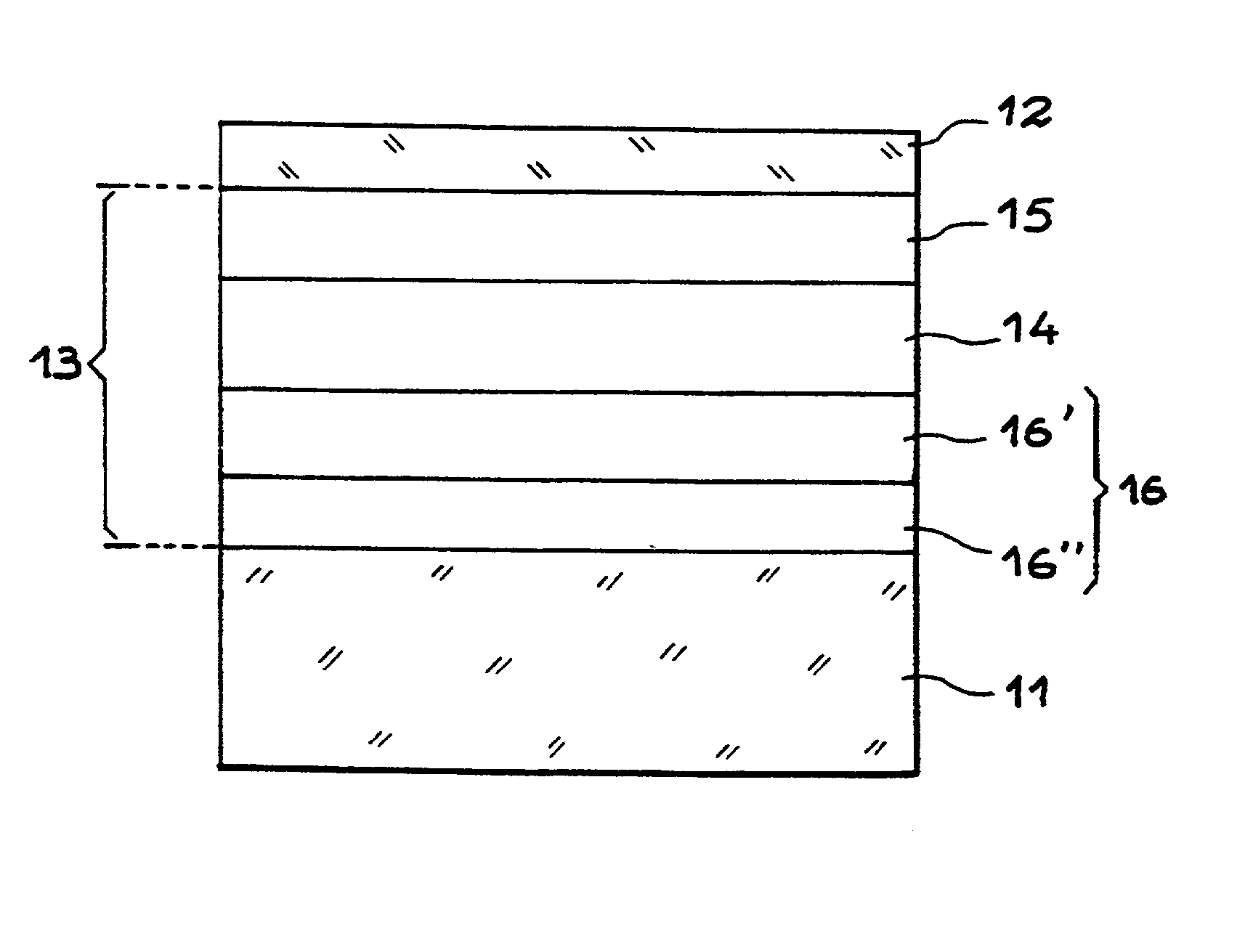
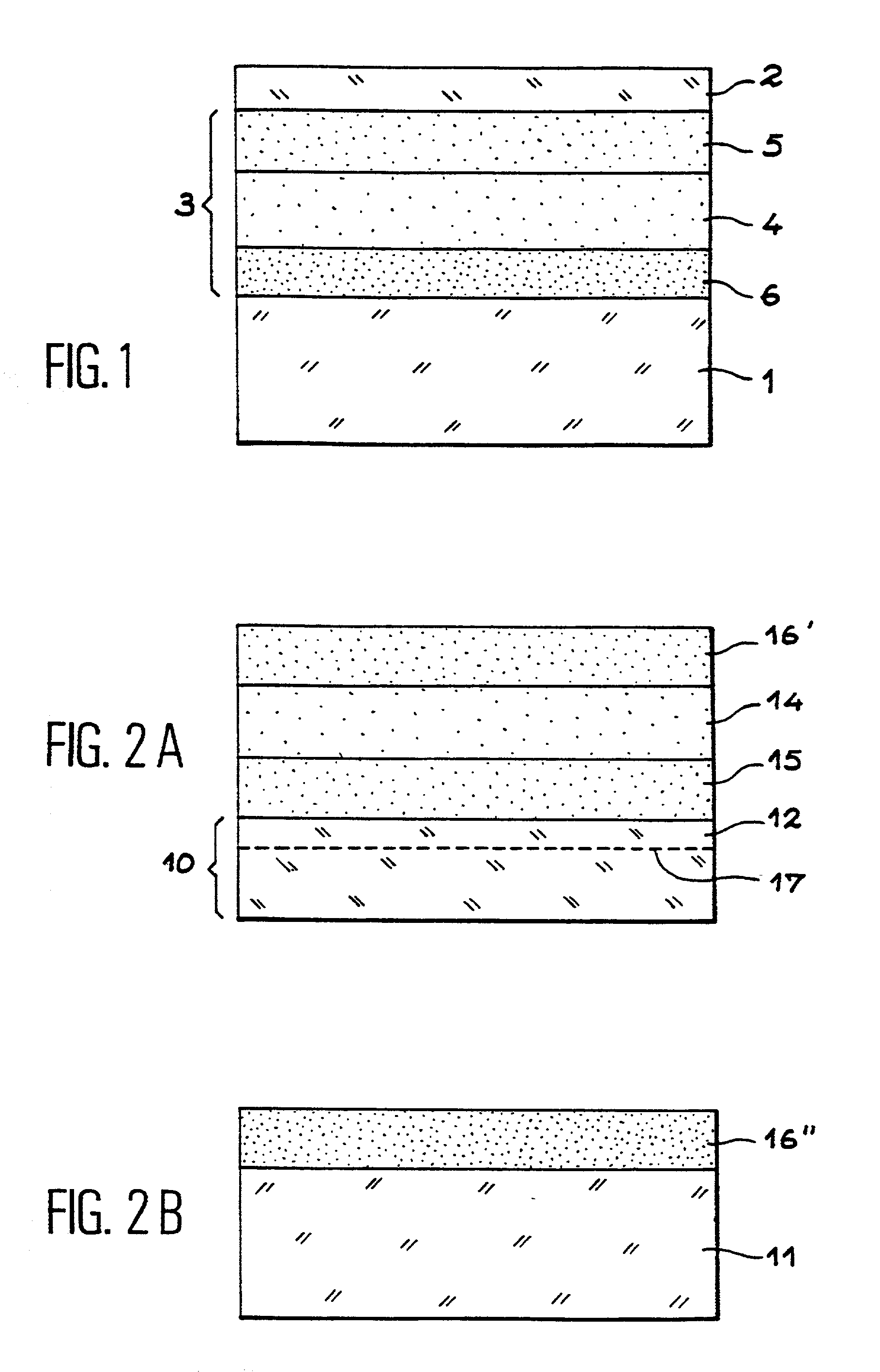
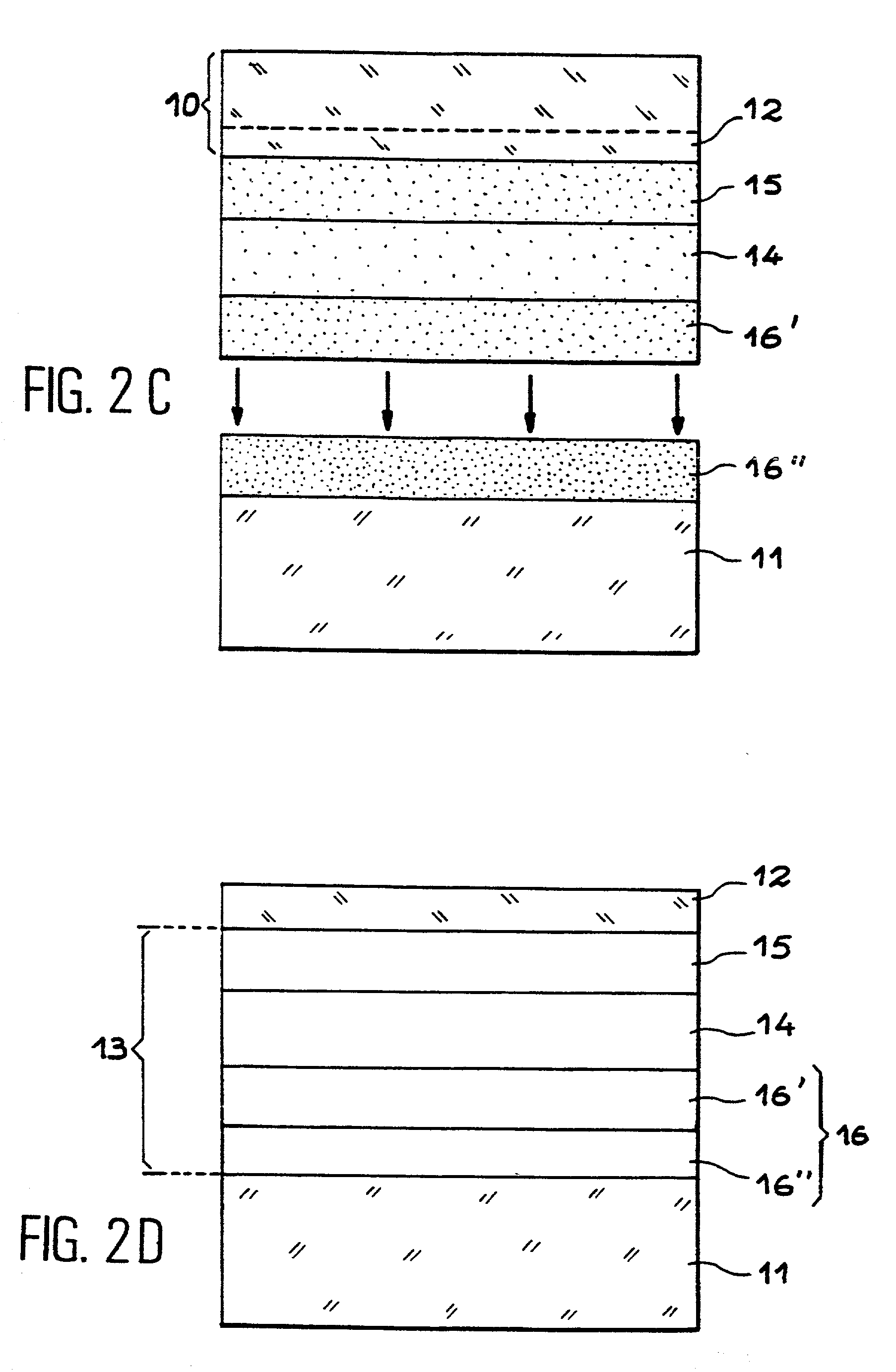
[0032] FIG. 1 shows a first example of a semi-conductor structure according to the invention. This structure comprises a support substrate 1 for example of silicon, a surface layer 2 of silicon and an intermediate zone 3. The intermediate zone 3 comprises at least one layer 4 of good thermal conductivity, an insulating layer 5 conferring good electrical quality of interface with the semi-conductor surface layer 2 and an insulating layer 6, being able to be of low thermal conductivity, adhering to the support substrate 1.
[0033] In the case of an SOI structure implementing the molecular adhesion process, the layer 6 may in particular be made of silica. This layer 6 may of course be a multi-layer.
[0034] When the layer 4 of good thermal conductivity makes it possible to have directly a good electrical interface with the surface layer of silicon 2, the layer 5 may be omitted.
[0035] The structure according to the invention makes it possible to retain the materials and thicknesses allowing...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thicknesses | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thicknesses | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com