Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
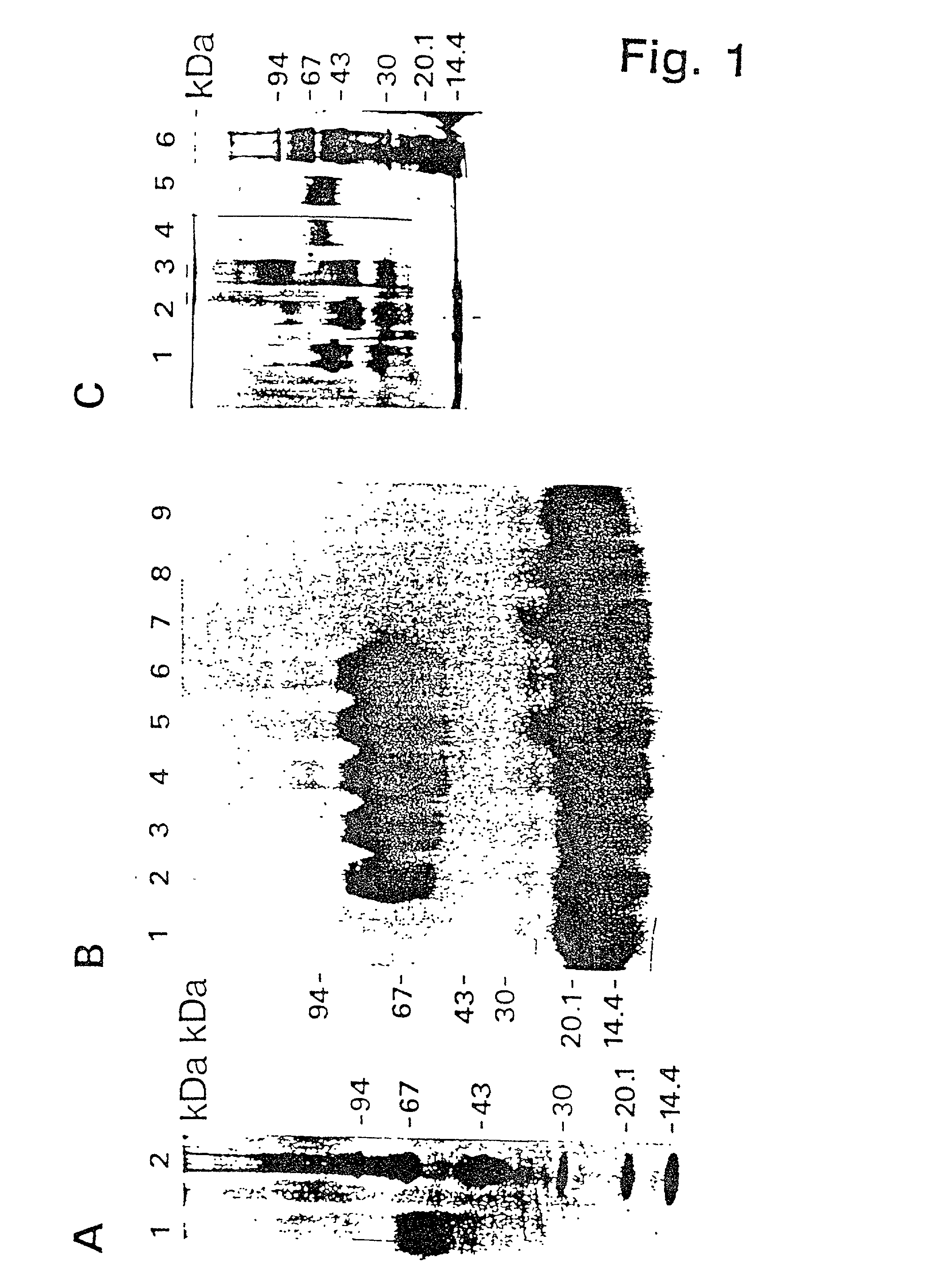
[0264] Purification and Characterization of u-PAR
[0265] Materials and Methods
[0266] SDS-PAGE.
[0267] When not stated otherwise, SDS-PAGE was performed according to Laemmli, U. K., "Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4", Nature 227: 680-682, 1970, using 6-16% gradient slab gels. Pretreatment of samples under nonreducing conditions was performed without boiling. When reducing conditions were used, the samples were boiled for 5 minutes in the presence of 20 mM DTT.
[0268] Phast-gel SDS-PACE was performed on a Phast gel apparatus (Pharmacia), using ready-made 10-15% gradient gels. Electrophoresis was performed according to the recommendations of the manufacturer. Silver staining was performed according to Heukeshoven and Dernick, 1988.
[0269] Tricine-SDS-PAGE of samples to be electroblotted for amino acid analysis or NH.sub.2-terminal amino-acid sequencing was performed in a Mini Protean II apparatus (BioRad) according to Schagger and von Jago...
example 2
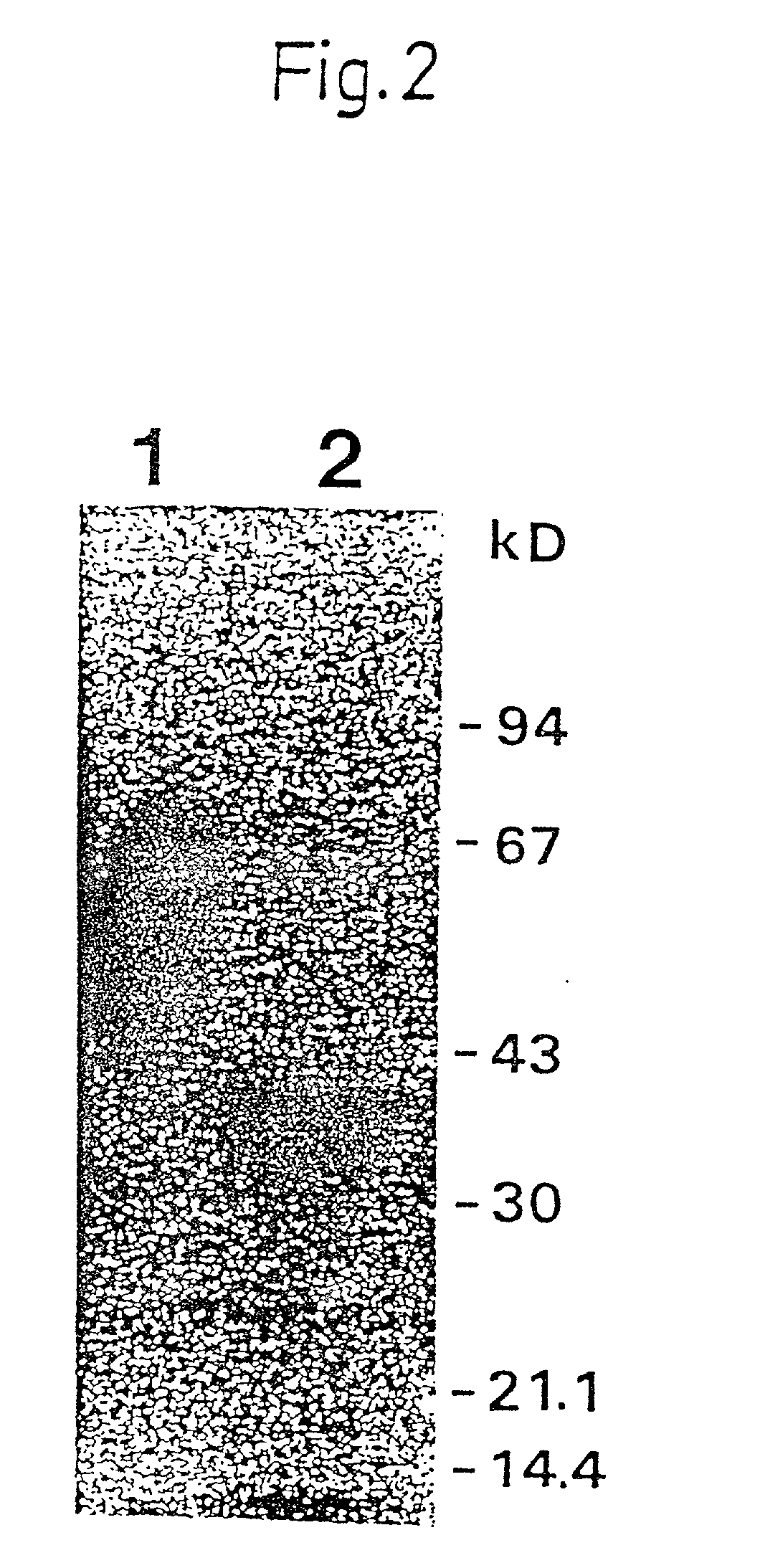
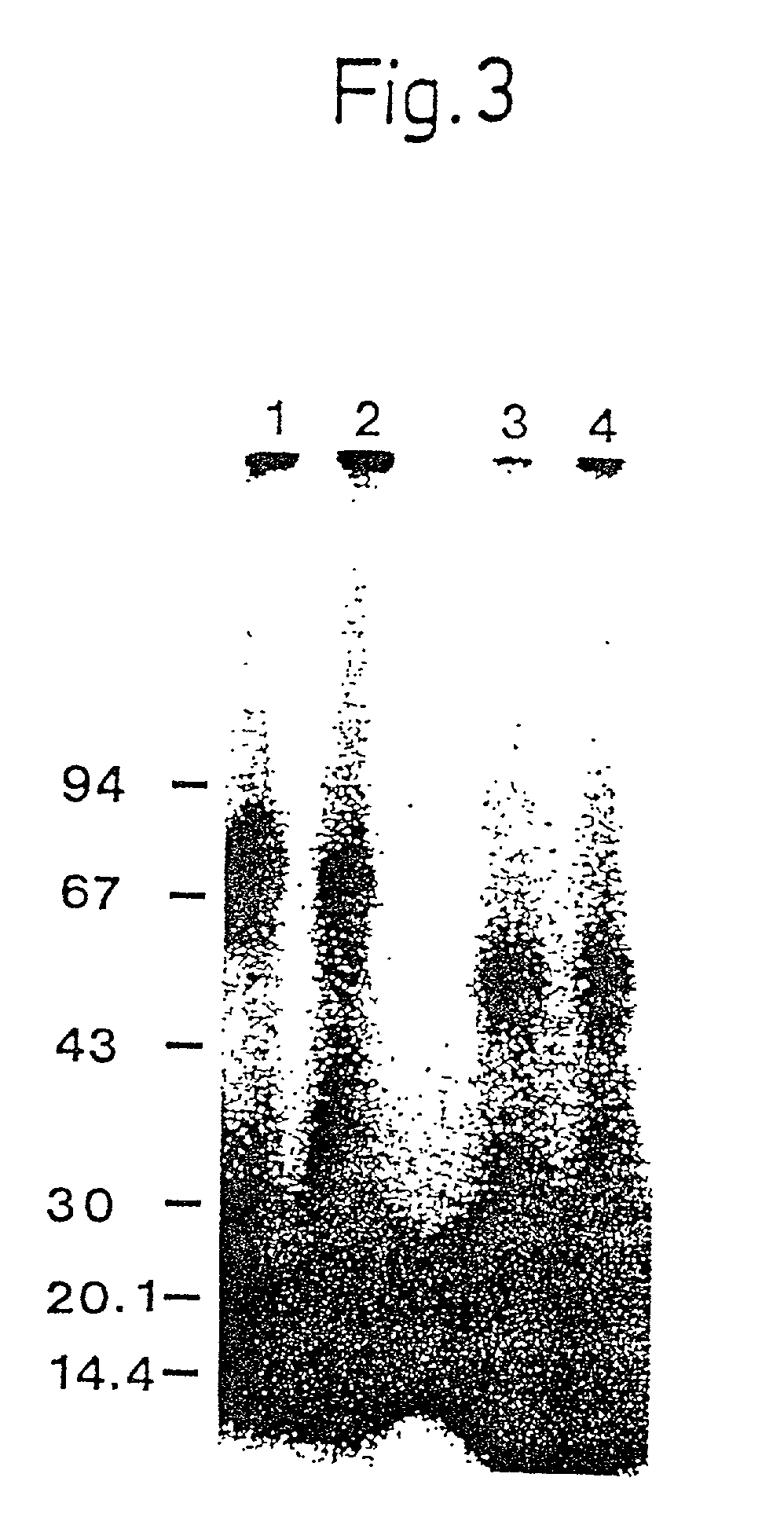
[0333] Isolation and Identification of the Ligand Binding Domain of u-PAR
[0334] Methods
[0335] Enzymatic Degradation:
[0336] Affinity purified u-PAR was dialyzed against 0.1% acetic acid and lyophilized as described in Example 1. The freeze-dried material was redissolved it incubation buffer (0.05 M Tris / HCl, 0.05% CRAPS, pH 8.1) to yield a protein concentration of approx 25 .mu.g / ml. 9 .mu.l samples of this u-PAR solution were treated with chymotrypsin (Worthington; final concentrations ranging from 8-200 ng / ml), by addition of 1 .mu.l of the appropriate stock solution of the enzyme, dissolved in incubation buffer. The samples were incubated for 16 h at 37.degree. C. after which the degradation was stopped by addition of 0.5 .mu.l of 20 mM phenylmethylsulfonylfluoride, dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide. The samples were stored at -80.degree. C. until analysis.
[0337] Analysis:
[0338] Direct electrophoretic analysis was performed by Tricine SDS-PAGE (see example 1) on a 10% T, 3% C gel aft...
example 3
[0350] Cloning of u-PAR
[0351] cDNA Libraries Used
[0352] A human cDNA library was used made from SV 40 transformed human GM637 fibroblasts in a plasmid vector based on pBR322 (carrying an ampicillin resistance gene) (Okayama H, Berg P, "High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA", Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 161-170, 1982). The library was kindly donated by Dr. Okayama. This library was selected on the basis of the known high number of u-PAR in GM637 cells (Blasi, unpublished).
[0353] The plasmid vector (FIG. 8) uses the SV 40 promoter and has high expression in various eukaryotic cells, but very low or no expression in prokaryotes.
[0354] Screening Procedures
[0355] The library was screened with synthetic oligonucleotide probes made on the basis of amino acid sequence data from purified receptor protein (Tables 4-5). The melting temperatures were calculated from Lathe, J. Mol. Biol. 183: 1-12, 1985. The equation used was modified from:
t.sub.m-16.6 logM+0.41(% G+C)+81.5
[0356] in which M is the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com