TNF-derived peptides for use in treating oedema
a peptide and oedema technology, applied in the field of tnf-derived peptides for use in treating oedema, can solve the problems that potentially toxic molecule and pleiotropic molecule cannot be used to treat oedema, and achieve the effect of increasing ion permeability and similar potencies in induction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0024] Material and Methods
[0025] Animals, cells and reagents. Male CBA / J or C57BL / 6 mice, as well as male TNFR 1 / 2.sup.0 / 0 C57BL / 6 mice deficient in TNF receptors (Bruce et al., 1996 ) provided by H. Bluethmann, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Basel, Switzerland, were used at the age of 8-10 weeks. Their care was in accordance with institutional guidelines. Lung microvascular endothelial cells were isolated from CBA / J mice and characterized as described (Jackson et al., 1990) using magnetic beads (Dynabeads M-450, Dynal, Oslo, Norway), covalently bound to a purified rat-anti-mouse PECAM-1 monoclonal antibody (donated by B. Imhof, University of Geneva). Microvascular lung endothelial cells were resuspended in DMEM containing 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U / ml penicillin, 10 mg / ml streptomycin, 20% FCS, 40 U / ml heparin and 100 mg / ml endothelial cell growth supplement (Brunschwig Chemie, Basel, Switzerland). For patch clamp experiments, cells were plated onto 35.times.10 mm easy grip Petri dishes (Beck...
example 1.1
Effect of TNF on Membrane Conductance in Murine Cells
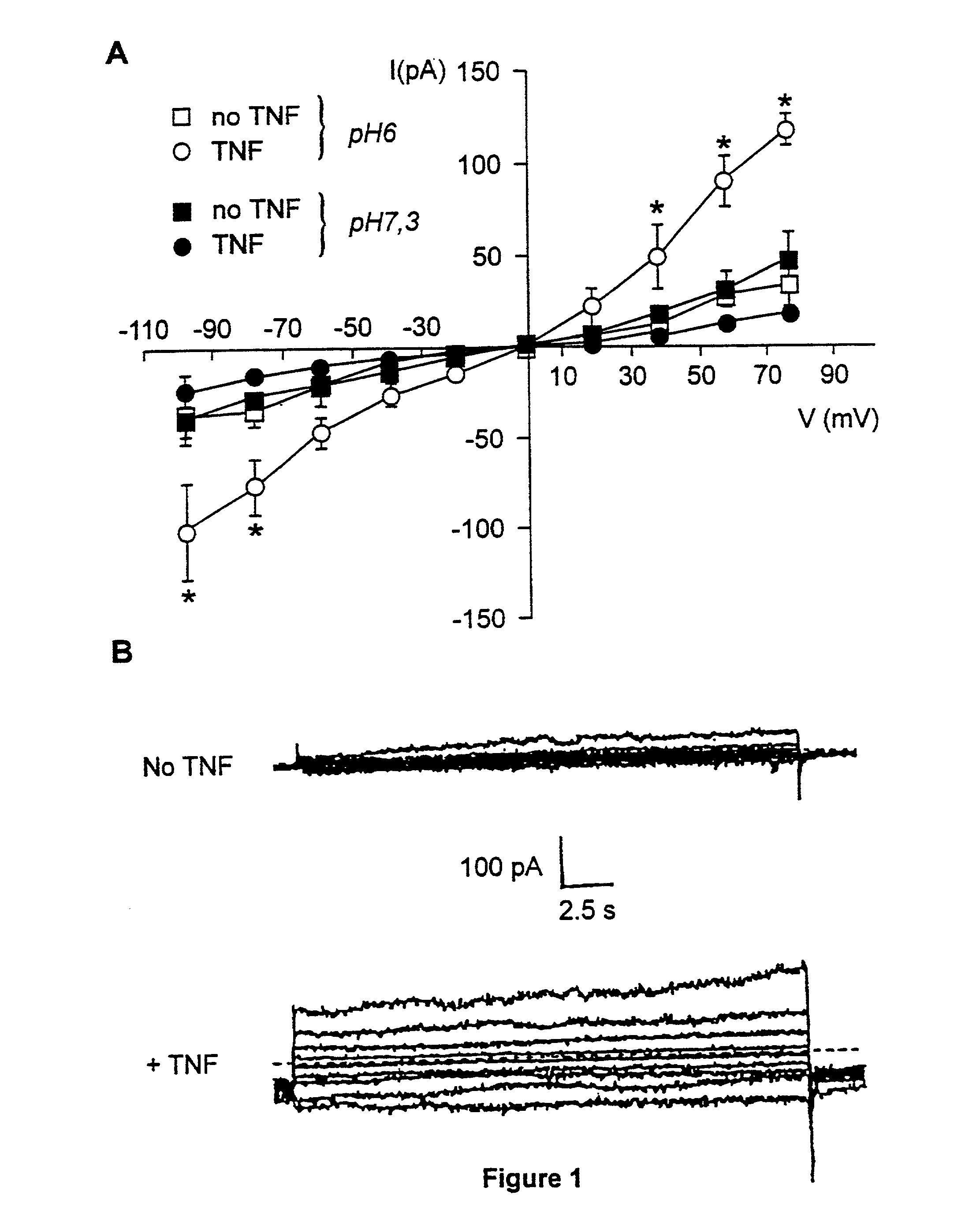
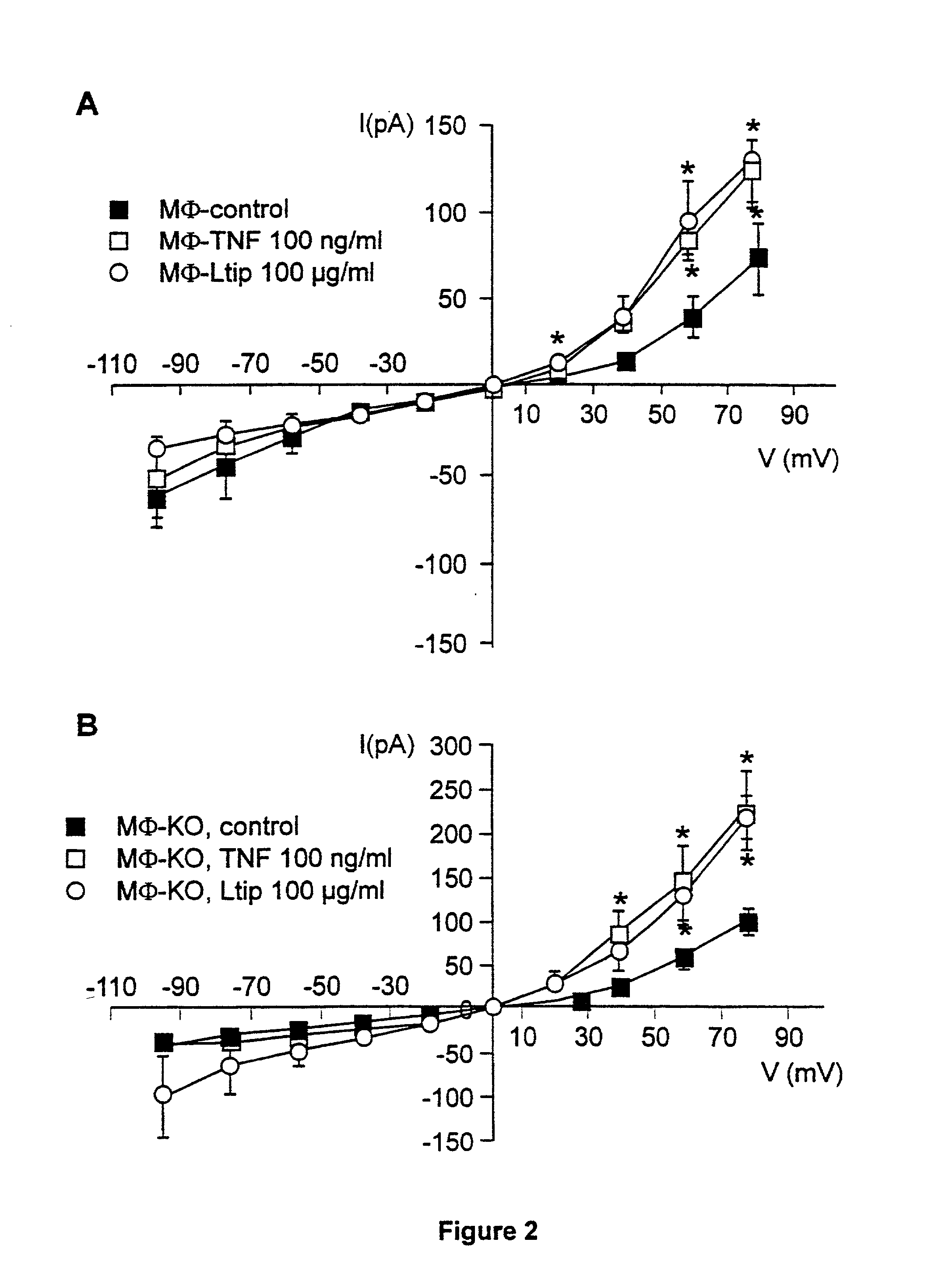
[0034] We first investigated whether TNF modified the whole cell current in primary murine cells. A 30 min preincubation of resident peritoneal macrophages and lung microvascular endothelial cells with 100 ng / ml of TNF resulted in a significant increase in outward and, to a lesser extent, inward current in the case of microvascular endothelial cells, as measured by means of whole-cell patch clamp, as compared to cells unexposed to TNF (endothelial cells, FIG. 1A; and macrophages, FIG. 2). A reduction in preincubation time (down to 5 min) or in dose of TNF (down to 10 ng / ml) gave similar results (data not shown). This effect required acidic preincubation conditions, since it did not occur when the preincubation was performed at pH 7.3 (FIG. 1). The conductance induced by TNF was voltage-independent and showed a reversal potential of about 0 mV in the case of endothelial cells. In order to investigate whether the ion current increas...
example 1.2
The Tip Domain of TNF Mediates its Membrane Conductance Increasing Effect
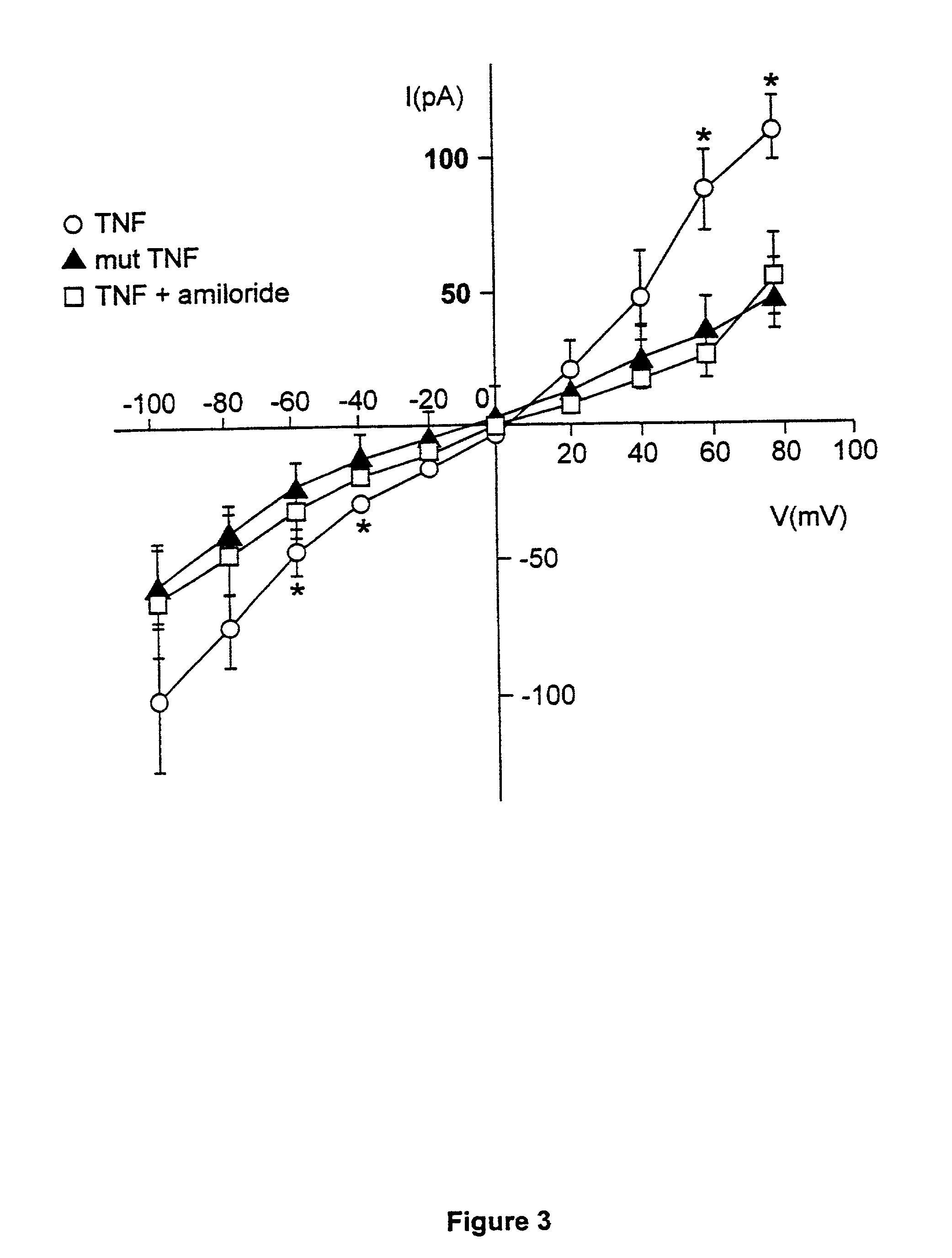
[0036] Since the tip domain of TNF seemed to be critical for its activation of ion permeability, we next tested whether a peptide mimicking this region was sufficient for increasing membrane conductance, as observed with native TNF. Treatment of endothelial cells and macrophages with the 17 amino acid (aa) circularized long tip peptide (Ltip peptide), that mimics the lectin-like domain of TNF, resulted at acidic pH in increased outward, and inward currents in the case of microvascular endothelial cells. In contrast to TNF, the effect persisted at neutral pH, although less pronounced (FIGS. 2A and 4A). Similarly to TNF, the effect was blocked by 100 .mu.M amiloride (FIG. 4B). A mutant (T104A-E106A-E109A) 17 aa circularized peptide (mutTip peptide) and a 17 aa circularized peptide containing the same aa as Ltip peptide in a random sequence (scramblTip peptide) were inactive with regard to the ion channel activity...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| slit widths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com