Conjugates of membrane translocating agents and pharmaceutically active agents
a technology of membrane translocation agent and conjugate, applied in the field of peptides, can solve the problems of adverse effects, patient discomfort, and studies that do not address the use of membrane translocation peptides, and achieve the effects of preventing pathological disorders, diagnosing pathological disorders, and preventing pathological disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Peptide Synthesis
[0152] The membrane translocating peptides ZElan094, 204N and 204 and the targeting peptides HAX42, PAX2, P31 and Sni34 (U.S. patent application Ser. Nos. 09 / 079,819, 09 / 079,723 and 09 / 079,678) were synthesized chemically using a fmoc synthesis protocol (Anaspec, Inc., San Jose, Calif.). A dansyl group was added at the N-terminus of each sequence in order to enable the detection of the peptide with anti-dansyl antibody (Table 1).
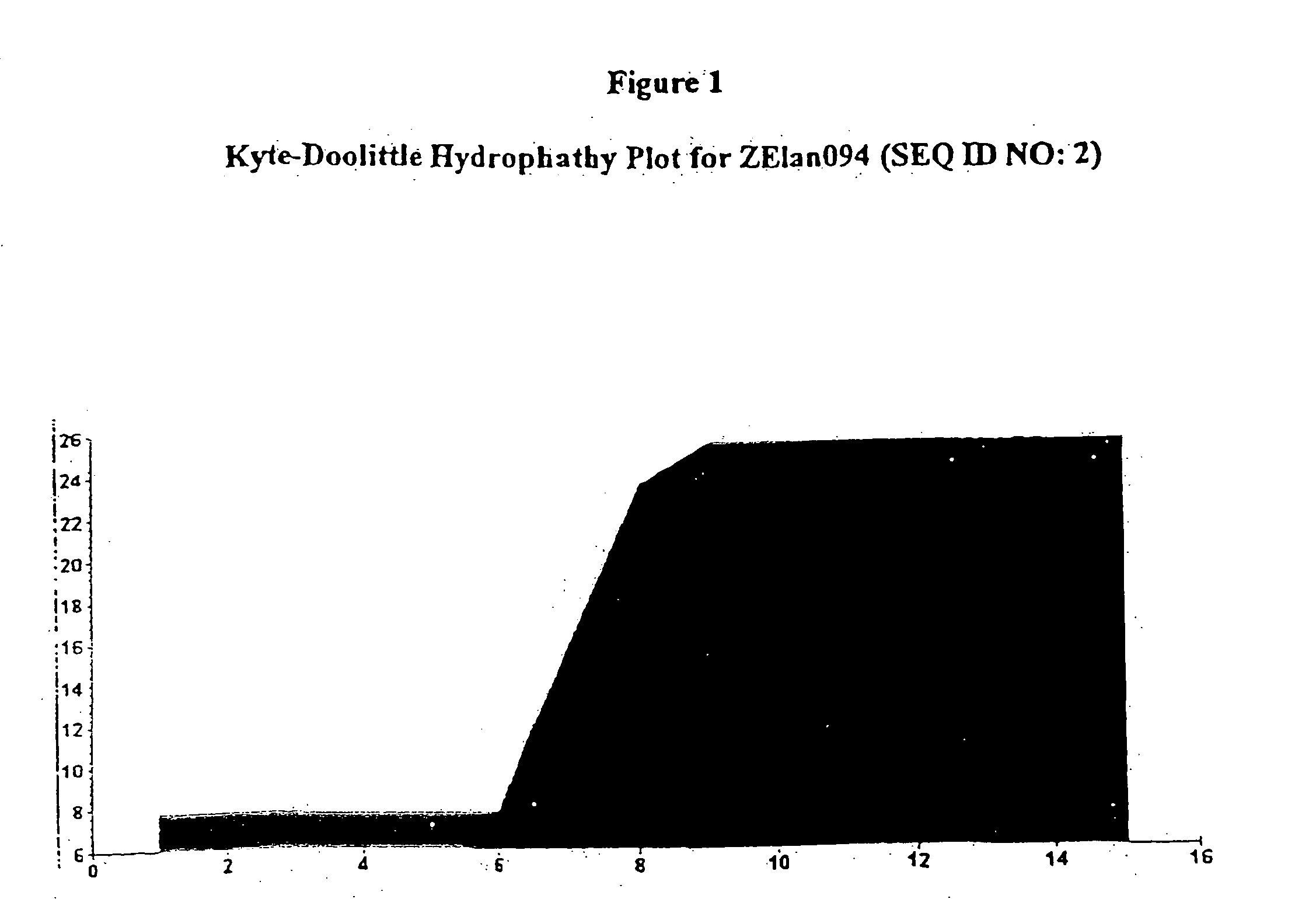
[0153] The physical characteristics of Zelan094 (SEQ ID NO:2) are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3Physical characteristics of ZElan 094 (SEQ ID NO: 2)Mass (M+H+):1838.03Solubility1 mg / ml waterAppearancewhite powderHPLC purity>95%Kyle-Doolittle Hydropathy Plot
example 2
Preparation of MTLP-Active Particle Complexes and of Targeting Peptide-Active Particle Complexes
[0154] Active particles were prepared from a polymer using a coacervation method. Preferably, particle size is between about 5 nm and 750 μm, more preferably between about 10 nm and 500 μm and most preferably between about 50 nm and 800 nm. MTLPs or targeting peptides were complexed to the particles using various methods known to those skilled in the art.
[0155] The following is a general method for preparation of coacervated particles.
[0156] Phase A A polymer agent, a surface-active agent, a surface-stabilizing agent, a surface-modifying agent or a surfactant is dissolved in water (A). Preferably the agent is a polyvinyl alcohol (herein after “PVA”) or a derivative thereof having a % hydrolysis of about 50-100 and a molecular weight range of about 500-500,000 kDa. More preferably the agent is a PVA having a % hydrolysis of 80-100 and a molecular weight range of about 10,000-150,000 kD...
example 3
Bovine Insulin Loaded-MTLP Coated Nanoparticles—MTLP Added in the Final Wash
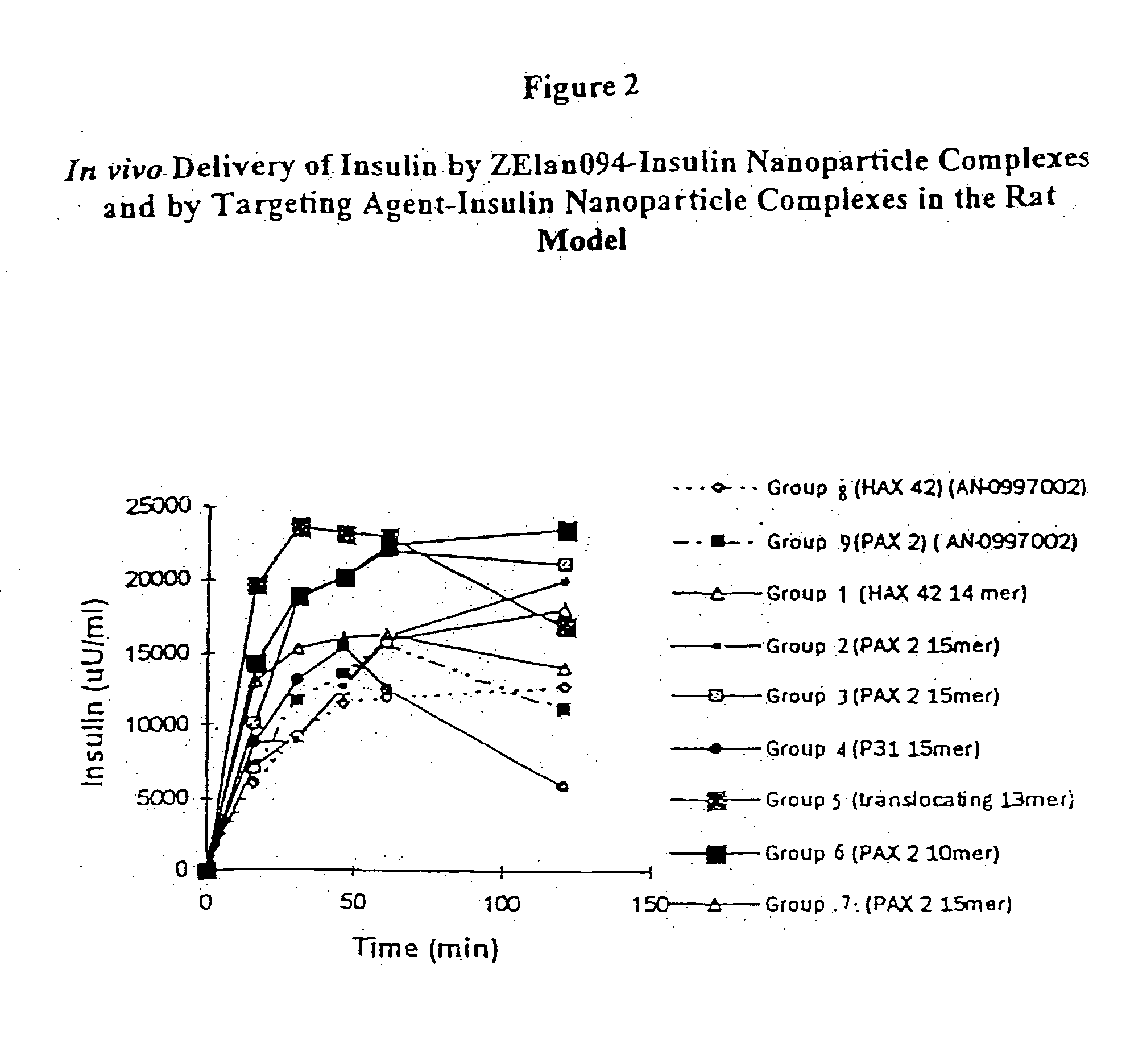
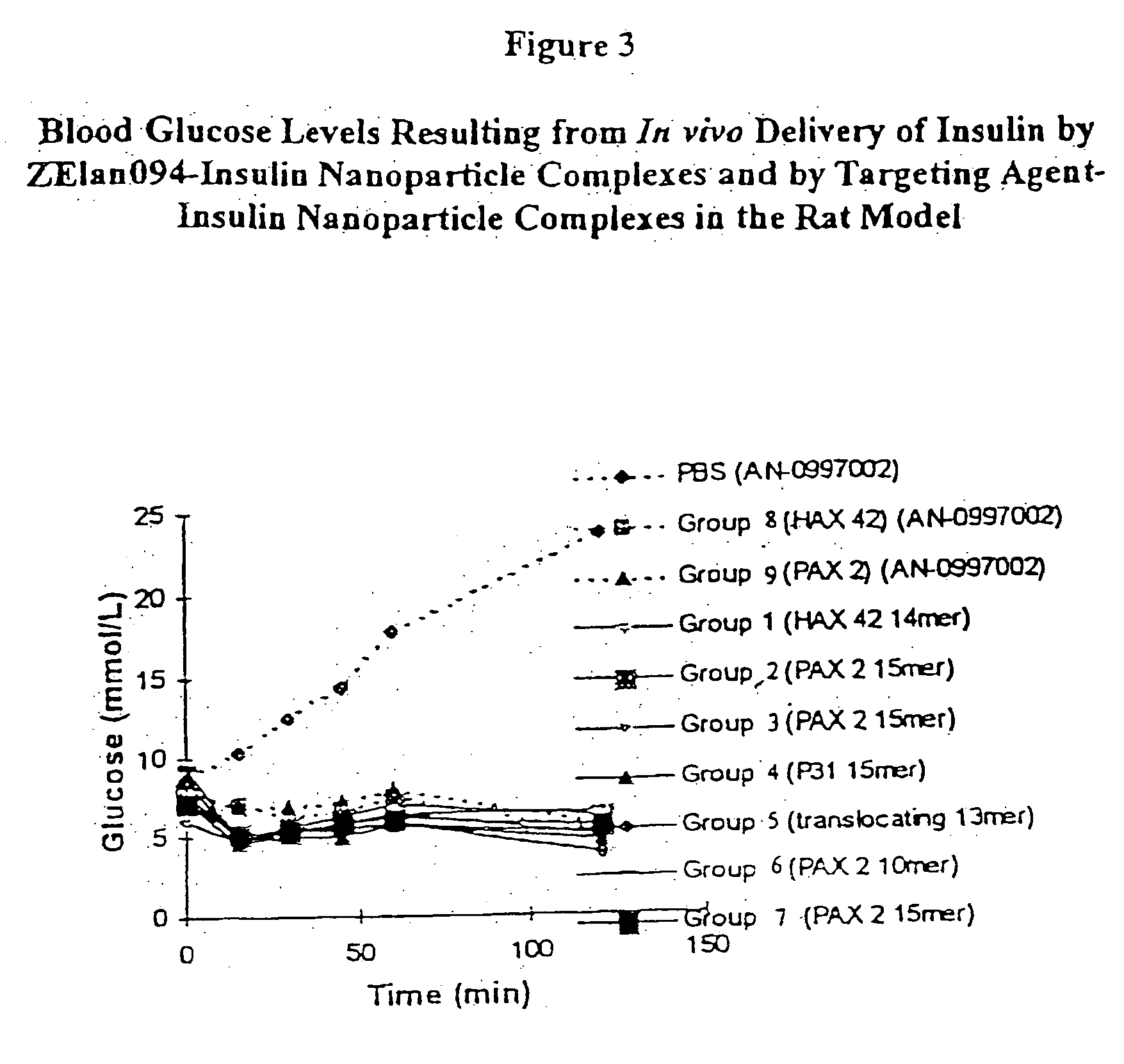
[0163] Fast acting bovine insulin (28.1 IU / mg) was incorporated into polylactide-co-glycolide (PLGA, Boehringer Ingelheim, Indianapolis, Ind.) at a theoretical loading of 300 IU of insulin / 210 mg of nanoparticles and the nanoparticles were coated with the dansylated ZElan094 (SEQ ID NO: 2).
COMPONENTAMOUNTPLGA RG504H (Lot # 250583)2gAcetone45mlsEthanol5mlsPVA (5% w / v) (13-23 kDa, 98% hydrolysis)400mlsBovine Insulin (Lot # 86HO674)100mgZElan094 (SEQ. ID NO: 2)10 mg / 50 ml dH20
Preparation: [0164] 1. Water was heated to near boiling, PVA was added to 5% w / v and the solution was stirred until cool (phase A). [0165] 2. Acetone and ethanol were mixed to form the organic phase (phase B). [0166] 3. PLGA was added to the acetone and ethanol (step 2) and dissolved by stirring (phase B). [0167] 4. An IKA™ reactor vessel was set at 25° C. Phase A (step 1) was added into the reactor vessel and stirred at 400 rpm. [016...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com