Methods for detecting, diagnosing and treating human renal cell carcinoma
a human renal cell carcinoma and gene expression technology, applied in the field of cancer research, can solve the problems incurable renal cell carcinoma, and largely ineffective existing systemic therapies in affecting disease response or patient survival, so as to improve the survival rate of renal cell carcinoma, cure, or stabilize the disease, and prevent or treat renal cell carcinoma.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Tissue Banking
[0054] Renal tissue (normal and tumor) was transported to a sterile hood on ice and under sterile conditions. Tissue was dissected under the direction of a pathologist. The tissue was frozen in liquid nitrogen for isolation of RNA, DNA, and protein or processed to establish primary cell cultures. The tissue was fixed in formalin for immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization and RNAlater (Ambion) for RNA isolation. Primary normal renal epithelial (NRE) cell cultures were established using standard collagenase / Dnase techniques to digest tissue and isolate single cells. NREs were easily isolated and grew well in culture for up to 10 passages. These cells were further analyzed for homogeneity with regard to epithelial population using appropriate immunohistochemical markers such as vimentin, cytokeratin, and megalin.
example 2
Genomic Gene Array and Microarray Data Analysis
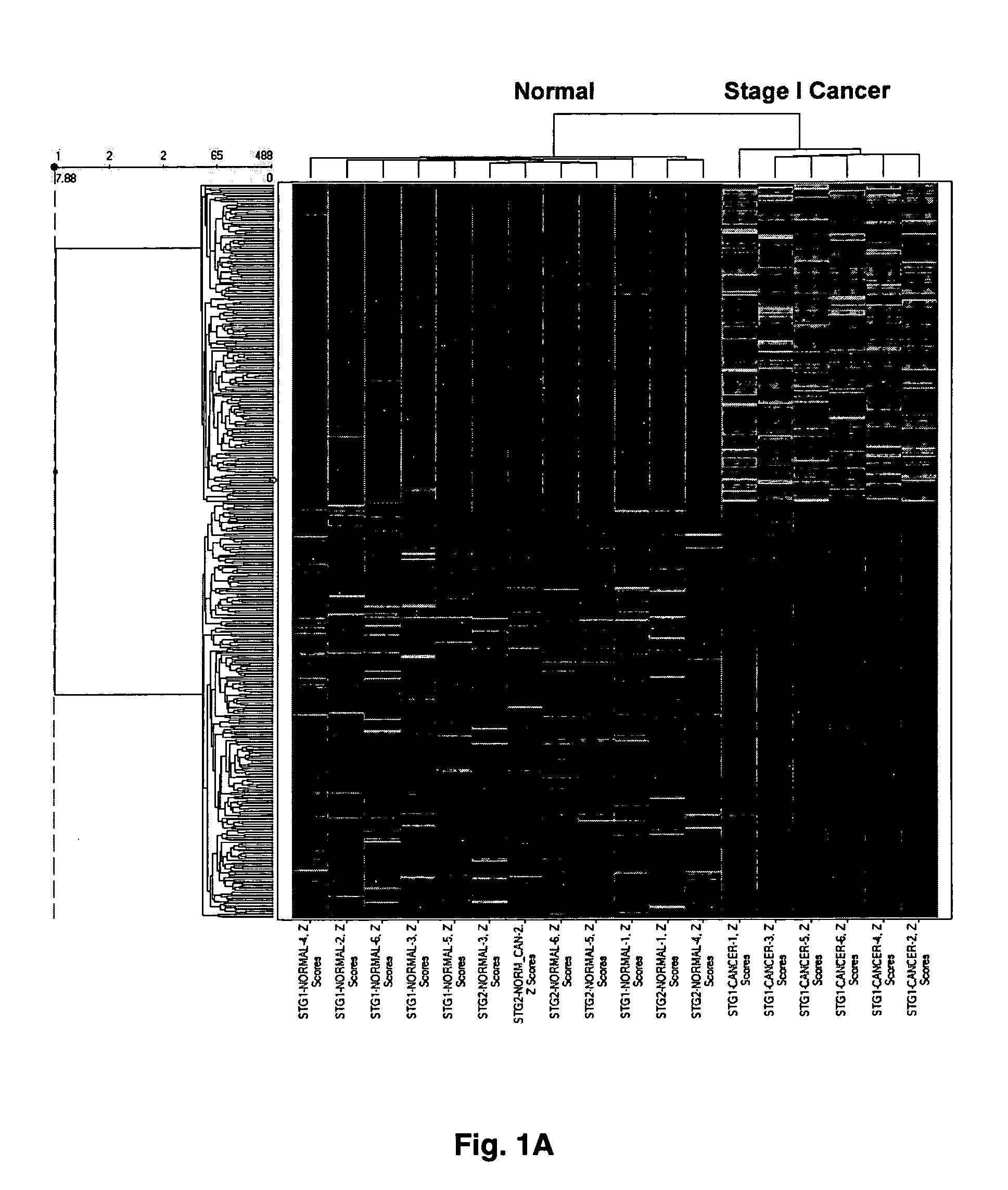
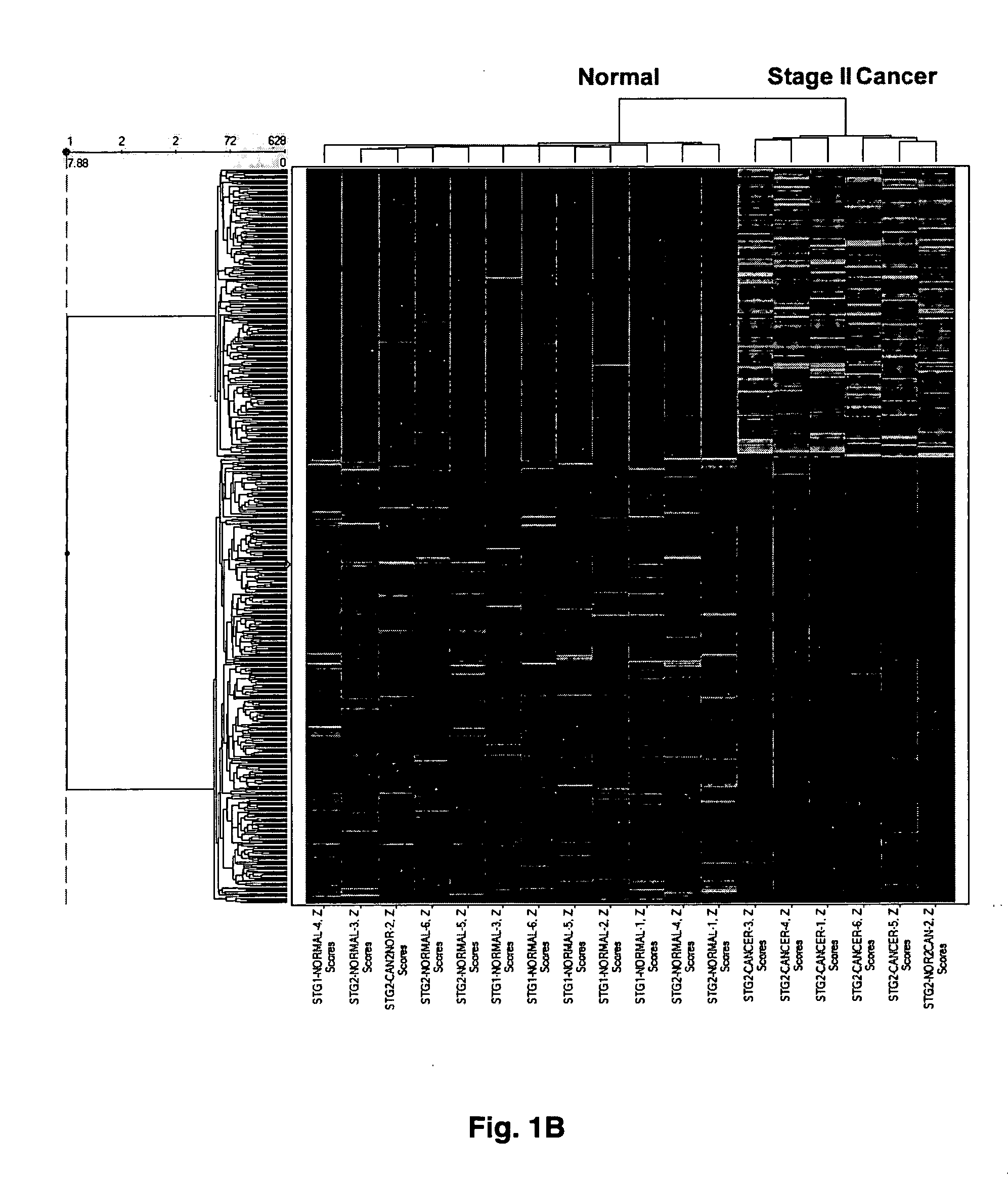
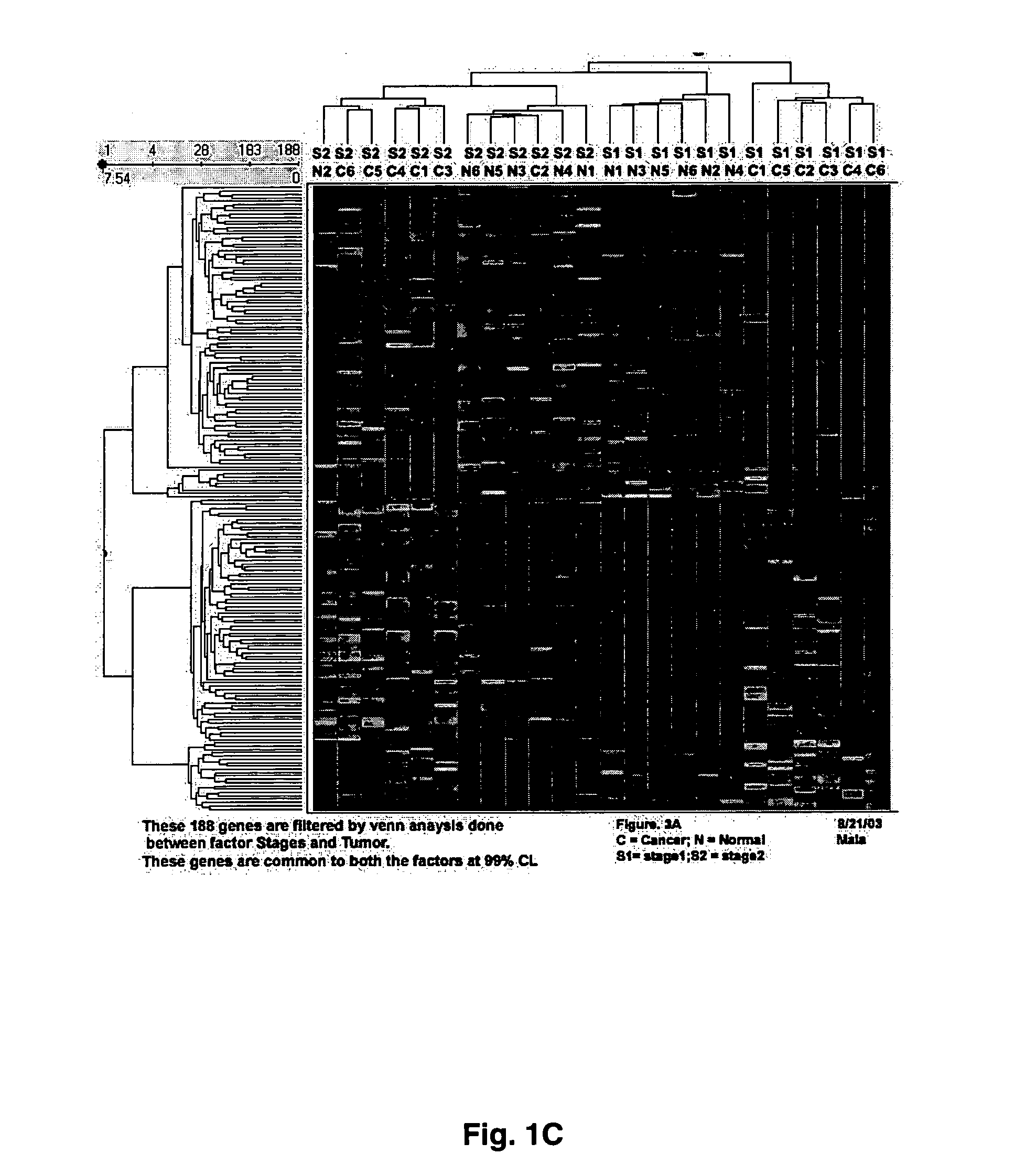
[0055] Gene expression profiling was performed using Affymetrix HU95A oligonucleotide gene arrays (>12,600 genes) or HG-U133 A&B GeneChip® oligonucleotide microarrays (33,000+ probe sets). Total RNA (Trizol®, Ambion) was extracted from patient-matched normal renal cortex and tumor tissue from patients diagnosed with local disease confined to the kidney. Alternatively, the investigators analyzed metastatic disease defined by lesions in lymph nodes, adrenal, or other organs. Data were analyzed by a combination of two-dimensional ANOVA, Affymetrix MAS5.0®, and hierarchical cluster analysis using Spotfire®. Procedure that were used to identify altered expression of large sets of genes, as well as other issues concerning microarray analyses can be found in a recent review article by Copland et al. (2003).
example 3
Real-Time PCR
[0056] Applied Biosystems' assays-by-design or assays-on-demand 20X assay mix of primers and TaqMan® MGB probes (FAM® dye-labeled) for all target genes and predeveloped 18S rRNA (VIC® dye-labeled probe) TaqMan® assay reagent for internal control were used for real-time PCR measurements. These assays were designed to span exon-exon junctions so as not to detect genomic DNA and an primers and probes sequences were searched against the Celera database to confirm specificity. Validation experiments were performed to test the efficiency of the target amplification and the efficiency of the reference amplification. All absolute values of the slope of log input amount versus DCT is less than 0.1.
[0057] Separate tubes (singleplex) for one-step RT-PCR was performed with 50 ng RNA for both target genes and endogenous controls using TaqMan® one-step RT-PCR master mix reagent kit (Applied Biosystems). The cycling parameters for one-step RT-PCR were: reverse transcription 48° C. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| real time PCR | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com