Universal amplification of fragmented RNA
a technology of rna and amplification method, which is applied in the field of universal amplification of rna, can solve the problems of ineffective step, insufficient material for analysis without prior amplification of rna, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the sensitivity of rt-pcr and improving the sensitivity of rna analysis methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific embodiments
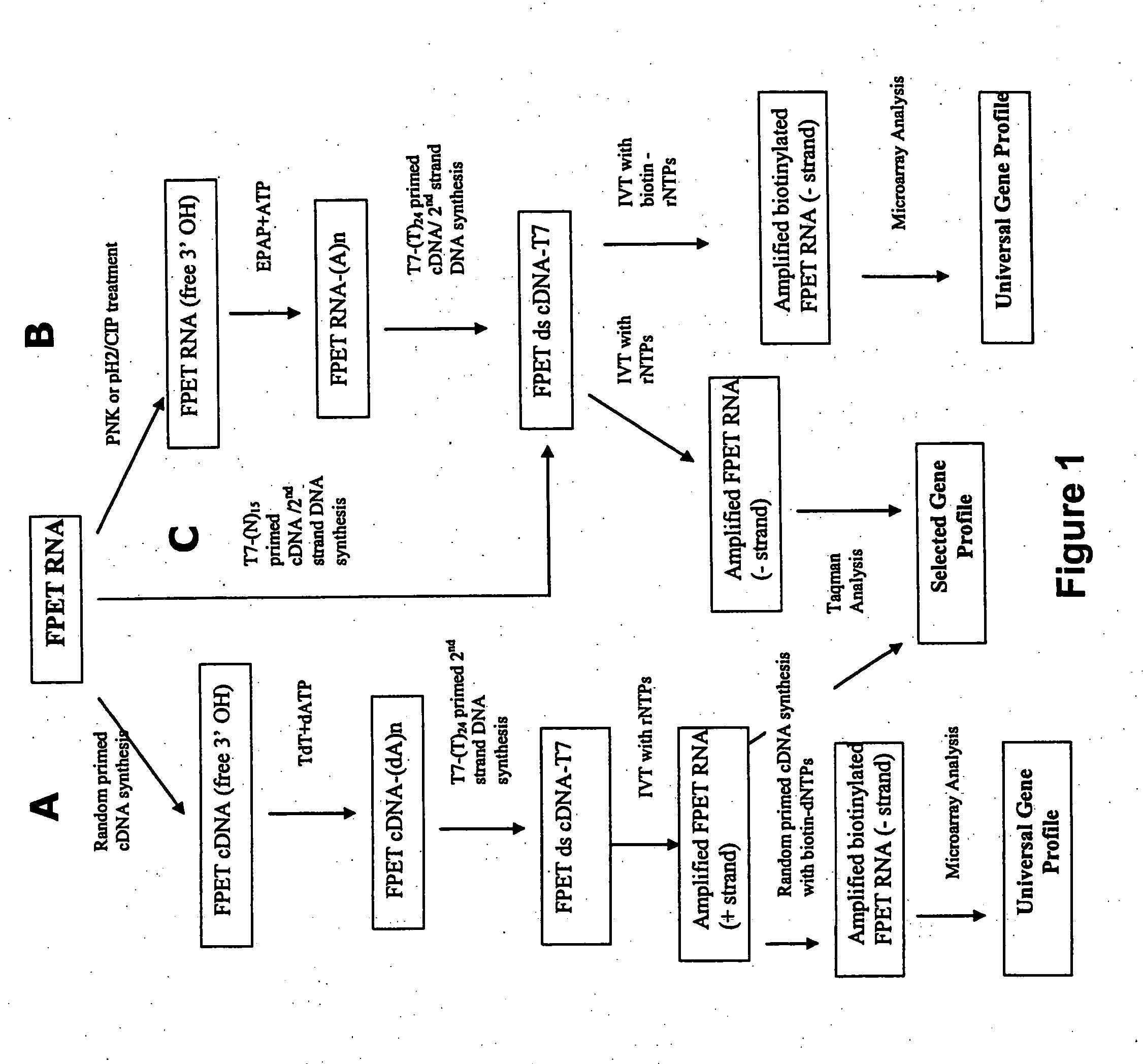
[0094] Three representative protocols (A, B and C) of the invention are illustrated in FIG. 1. Processes A and B start with FPET RNA and involve 1) direct or indirect unblocking of the 3′ OH on the terminal nucleotide, 2) poly A tailing of the 3′end, 3) poly dT-primed double-strand cDNA synthesis with the incorporation of a T7 RNA polymerase promoter, and 4) RNA amplification by in vitro transcription.
[0095] Process C (central arrow in the diagram) starts with FPET RNA and involves 1) T7-(N)15 primed double-stranded cDNA synthesis with the incorporation of a T7 RNA polymerase promoter, and 2) RNA amplification by in vitro transcription.
[0096] Specifically, Protocol A involves a random primed (hexamers) cDNA synthesis that generates cDNA with a free 3′ OH on the terminal nucleotide of the FPET cDNA. The FPET cDNA is then tailed with Terminal Transferase (TdT) and dATP. The poly dA-tailed cDNA is then converted to double-stranded DNA with DNA polymerase I (Klenow) and T7-(dT)24 prim...
reference example 1
[0111] In Example 1 below, the following methods were used.
FPET RNA Extraction Procedure
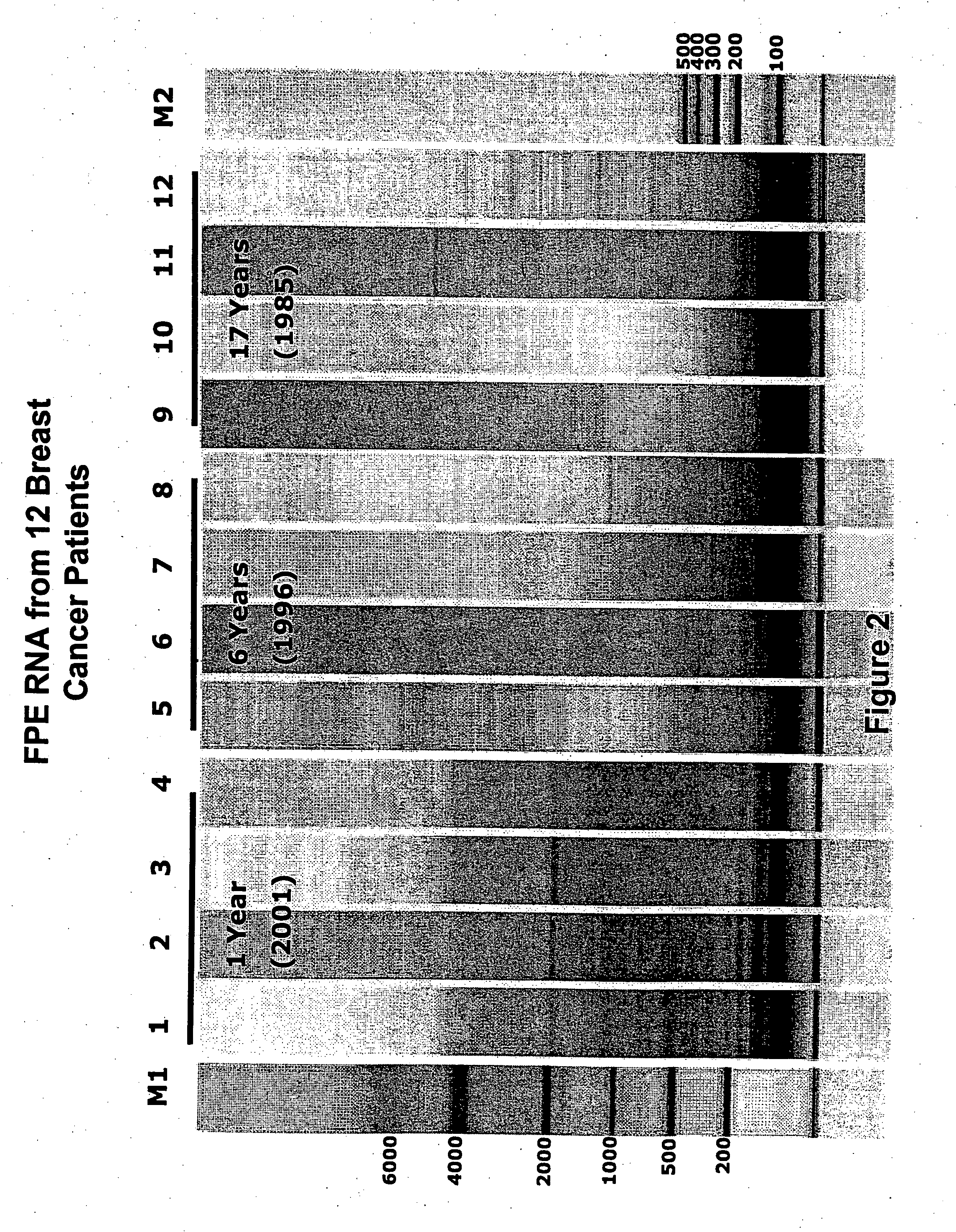
[0112] RNA was extracted from 3-10 μm sections (for each patient). Paraffin was removed by xylene extraction followed by ethanol wash. RNA was isolated from sectioned tissue blocks using the MasterPure™ Purification kit (Epicentre Technologies, Madison, Wis.) and included a DNase I step. FPET RNA was further purified by filtration through a CHROMA SPIN™ DEPC-H20 30 column as described by suppliers (Clontech, Palo Alto). Briefly, 30 μl of 50-300 ng / μl FPET RNA was loaded onto a column (pre-spun at 2500 rpm (664×g) for 5 min. in a 5417 C eppendorf centrifuge), spun through the column (same conditions as the pre-spin) and stored at −80° C. FIG. 2 shows an example of RNA isolated from formalin fixed, paraffin embedded (FPE) breast cancer samples that were archived from 1 to 17 years.
Positive Control Complementary RNA (cRNA) Synthesis
[0113] Small RNA fragments complementary to amplicons for the ...
example 1
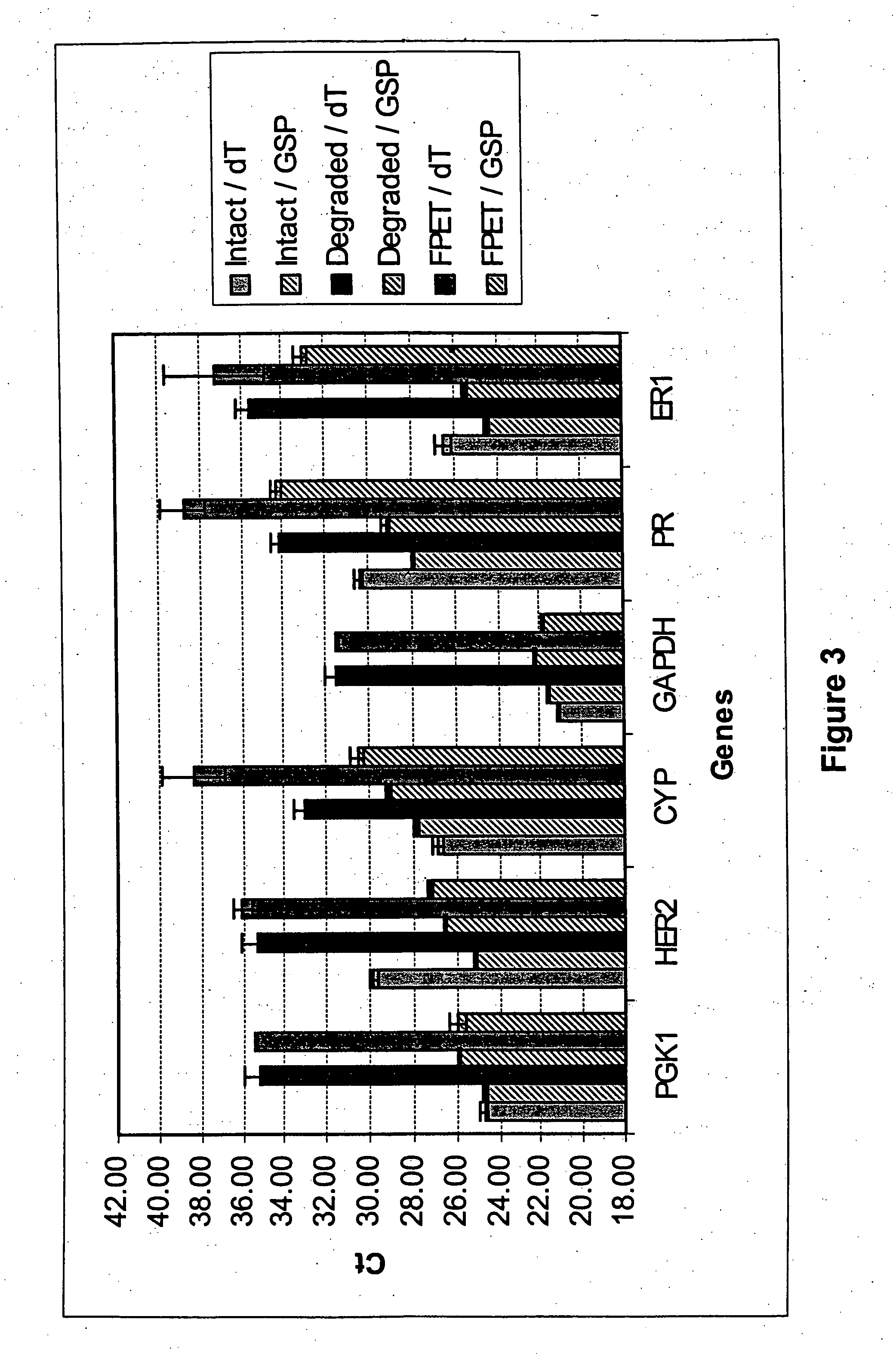
[0124] RNA was treated with polynucleotide kinase (PNK) or calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), enzymes with 2′-3′ cyclic phosphatase activity and 3′ phosphatase activity, respectively. Capillary electrophoretic [Agilent 2100] analysis of the treated FPET RNA suggested that treatment of the FPET RNA with PNK or CIP removed the blocking phosphates, as judged by a subtle decrease in the mobility of the enzyme-treated RNA relative to that of the untreated RNA (FIG. 6A). Decreased electrophoretic mobility was expected because removal of the charged phosphate group would have decreased the charge / mass ratio of the FPET RNA.
[0125] If the blocking phosphates from the 3′ end of the FPET RNAs were effectively removed, then polyadenylation of the RNA should be possible. Treatment of FPET RNA with PNK followed by EPAP treatment (+PNK / +EPAP) resulted in a significant decrease in electrophoretic mobility of the FPET RNA (FIG. 6B). To confirm that the mobility shift was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com