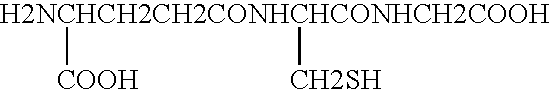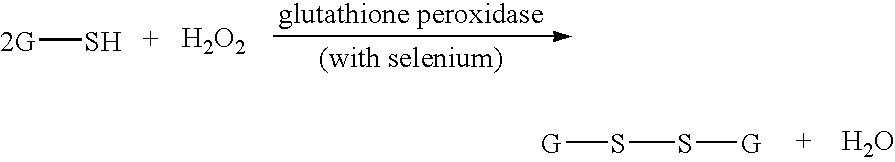Methods of assessing the need for and the effectiveness of therapy with antioxidants
a technology of antioxidants and need, applied in the field of need and effectiveness assessment of therapy with antioxidants, can solve the problems of limiting the patient's exposure to the drug, difficult to establish a cause and effect relationship between free radical-generating agents or conditions and disease pathology, and various treatment strategies with anti-oxidants are difficult to monitor, so as to increase glutathione synthesis or re-synthesis, and measure the utilization efficiency of anti-oxidants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Assessment of the Effects of IMMUNE FORMULATION 100™ or 200™ on Adriamycin Induced Oxidative Stress Levels in Rats
[0264] Adriamycin, while being an effective anti-cancer agent in humans, is known to induce nephropathy in a rat model (Zima, T. et al (1998), Nephrol. Dial. Transplant, 13: 1975-1979). Its deleterious effects on the kidney are believed to be due in part on the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) following its metabolism in vivo. Thus, the administration of adriamycin in a rat model provides an opportunity to study the effects of this compound on the generation of reactive oxygen species by measuring the by-products of such ROS, such as urinary lipid peroxides and pyroglutamic acid, as well as plasma glutathione. Furthermore, one can also use this model to look at the effects of this toxic compound on kidney damage, and on numbers of immune cell populations and on natural killer cell activity. In addition, this model provides an opportunity to assess the need fo...
example 2
IMMUNE FORMULATION 100™ Tablet Formulation
[0277]
Ingredients:Whey (PROLIANT ™ 8010 or 8200)1 gmColostrum1 gmSelenium methionine5 μg
[0278] Blend the ingredients together and pass through a 60 mesh screen and tumble until the components are thoroughly mixed. Compress using a 7 / 16 inch standard concave punch.
example 3
IMMUNE FORMULATION 100™ Powder Formulation
[0279]
Ingredients:Whey (Proliant ™ 8010 or 8200)75 gmColostrum25 mgSelenium methionine15 μg
[0280] Thoroughly mix the ingredients in a blender and pass through a 80 mesh screen.
[0281] This powder may be used for mixing with animal feeds, frostings, fruit spreads and beverages to be pasteurized.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com