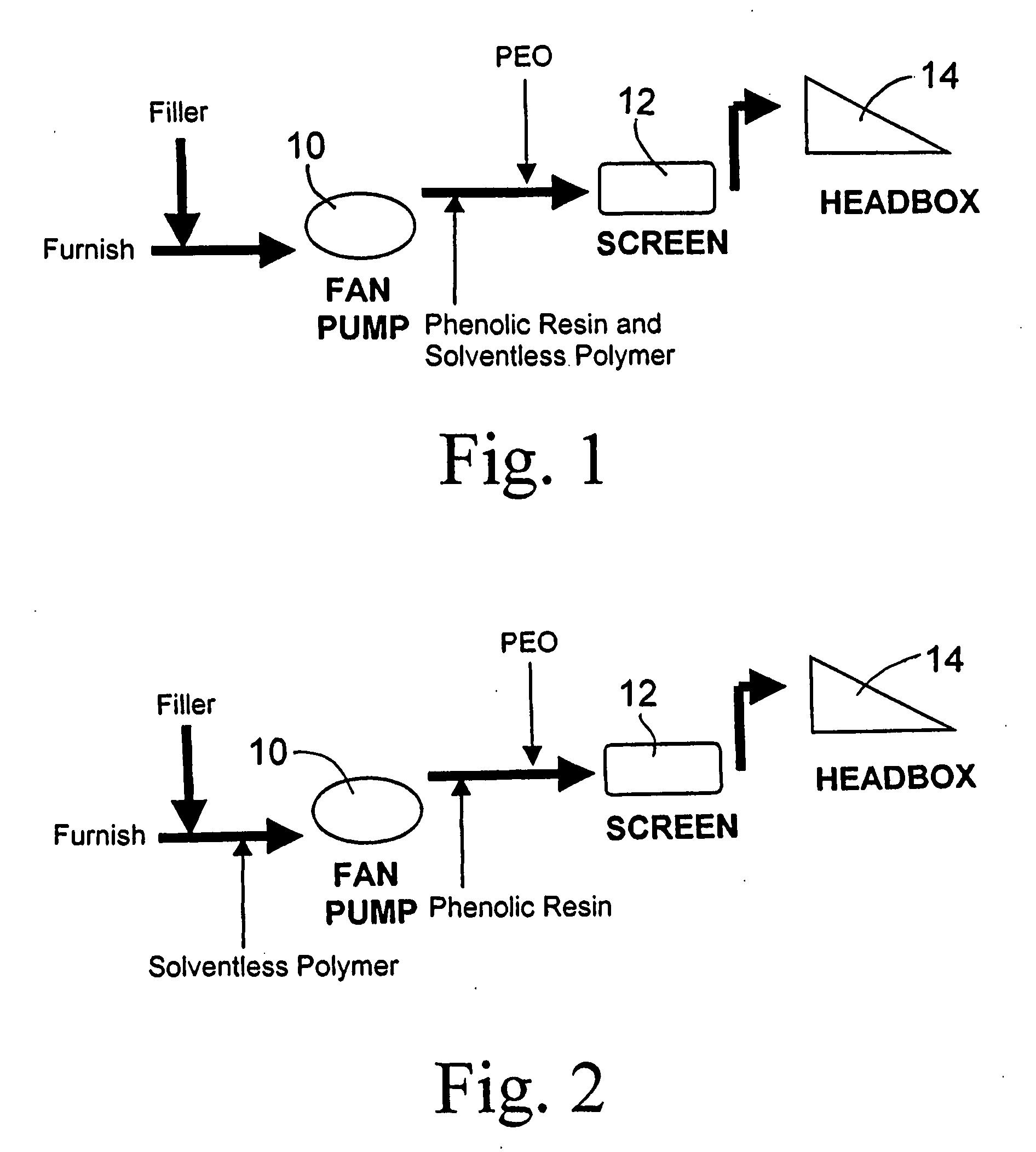
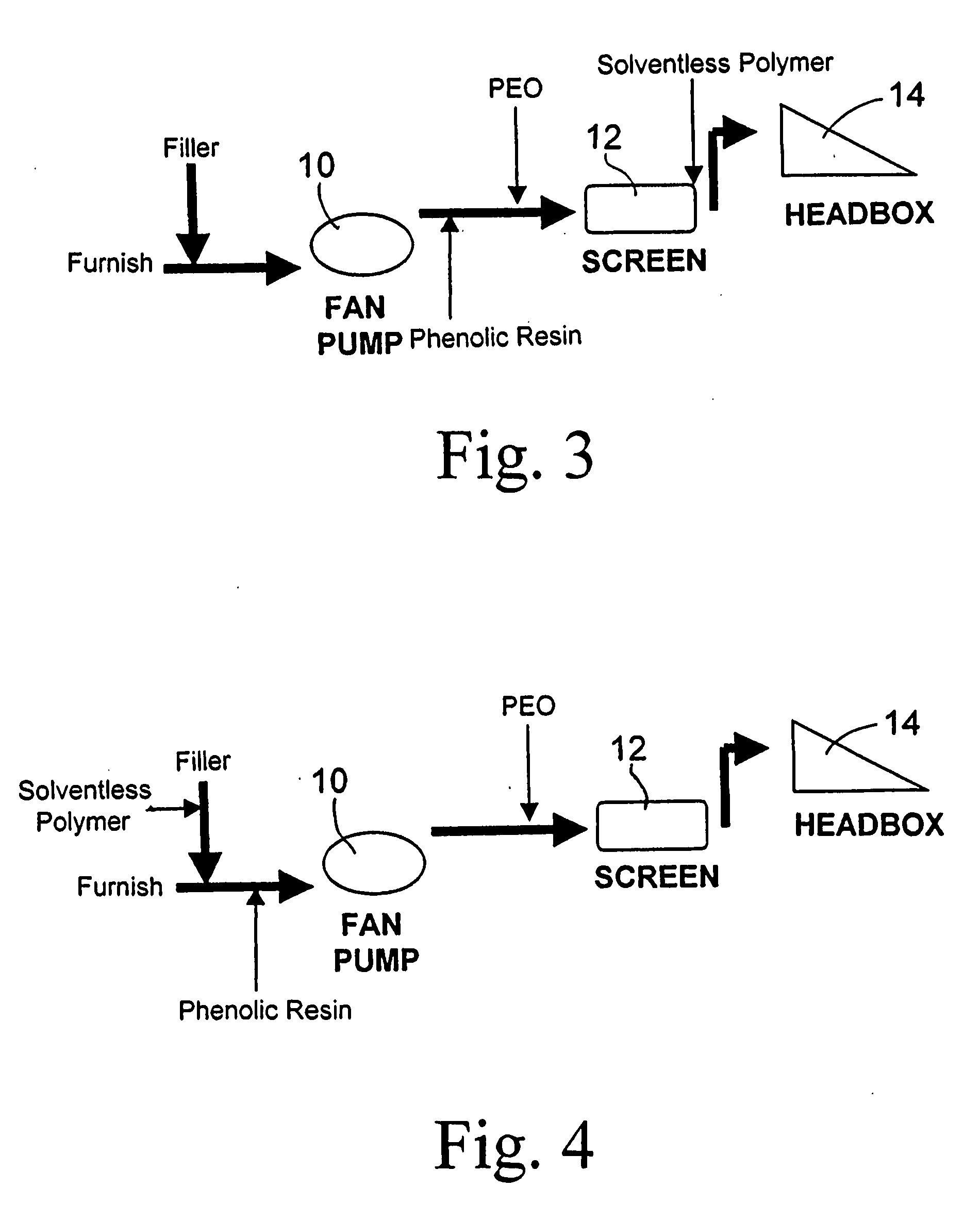
Papermaking furnish comprising solventless cationic polymer retention aid combined with phenolic resin and polyethylene oxide
a technology of phenolic resin and phenolic resin, which is applied in the field of papermaking furnish, can solve the problems of reducing performance, adverse effects of dissolved and colloidal contaminants, and the inability of phenolic resin/peo retention and drainage system to be adopted in mills producing grades, etc., to achieve better fines/filler retention, improve the dispersion of filler, and improve the speed of sheet drainage and machine speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0044] A 1.06% cellulosic fibre slurry consisting of 50% TMP (thermo mechanical pulp-hydrosulfonate bleached), 20% DIP (de-inked pulp) and 30% broke was taken from a newsprint mill. The slurry had a clay filler content of 20%. The pH of the slurry was set at 4.5.
[0045] For retention and turbidity tests a Dynamic drainage jar (DDJ) was used with a baffled cylinder and the speed of the stirrer was set at 550 rpm. A 500 ml sample was used for testing. FPR indicates the first pass retention.
[0046] For drainage, formation, and retention (with pad formation) tests a Dynamic Drainage Analyzer (DDA) was used with a baffled cylinder and the speed of the stirrer was set at 1000 rpm. A 800 ml sample was used for testing. The vacuum was set at 500 mBar.
[0047] Tables 1 and 2 below show the results when conventional phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide retention system is compared to phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide-solventless cationic polymer flocculant retention system. ...
example 2
[0049] A 0.992% cellulose fibre slurry consisting of 10% Kraft and 90% TMP (thermo mechanical pulp-hydrosulfite bleached) was taken from a specialty newsprint mill. The slurry had a clay filler content of 10%. The pH of the slurry was set at 6.0
[0050] For drainage, formation, and retention (with pad formation) tests a Dynamic Drainage Analyzer (DDA) was used with a baffled cylinder and the speed of the stirrer was set at 1000 rpm. A 800 ml sample was used for testing. The vacuum was set at 500 mBar.
[0051] Table 3 below shows the results when conventional phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide retention system is compared to phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide-solventless, cationic polymer flocculant retention system.
TABLE 3DDA TESTINGNormalizedProductProductProductProductProductProductRetentionDrainageCostNameDose (g / t)NameDosage (g / t)NameDosage (g / t)(%)(sec)(0 to 100)Blank0000078.8783.930Solventless Polymer Flocculant added before Phenolic resin and PEOSolventles...
example 3
[0052] A 1.12% cellulose fibre slurry consisting of 5% Kraft, 70% TMP (thermo mechanical pulp-hydrosulfite bleached) and 25% deinked pulp (DIP) was taken from a specialty newsprint mill using recycled fibres. The slurry had a clay filler content of 30%. The pH of the slurry was set at 6.2
[0053] For retention and turbidity tests a Dynamic drainage jar (DDJ) was used with a baffled cylinder and the speed of the stirrer was set at 550 rpm. A 500 ml sample was used for testing. FPR refers to the first pass retention and FPAR the first pass ash retention.
[0054] Table 4 below shows the results when conventional phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide retention system is compared to phenol formaldehyde resin-polyethylene oxide-solventless, cationic polymer flocculant retention system.
TABLE 4DDJ TESTINGNormalizedProductProductProductProductProductProductFPR / FPARTurbidityCostNameDose (g / t)NameDosage (g / t)NameDosage (g / t)(%)ntu(0 to 100)Blank0000035.6 / 45.486.10Solventless Polymer Flo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com