High shrinkage side by side type composite filament and a method for manufactruing the same
a composite filament and high shrinkage technology, applied in the direction of weaving, yarn, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of difficult synthetic fibers, reduced crimping properties, complicated process, etc., and achieve excellent shrinkage, fine denier filament, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
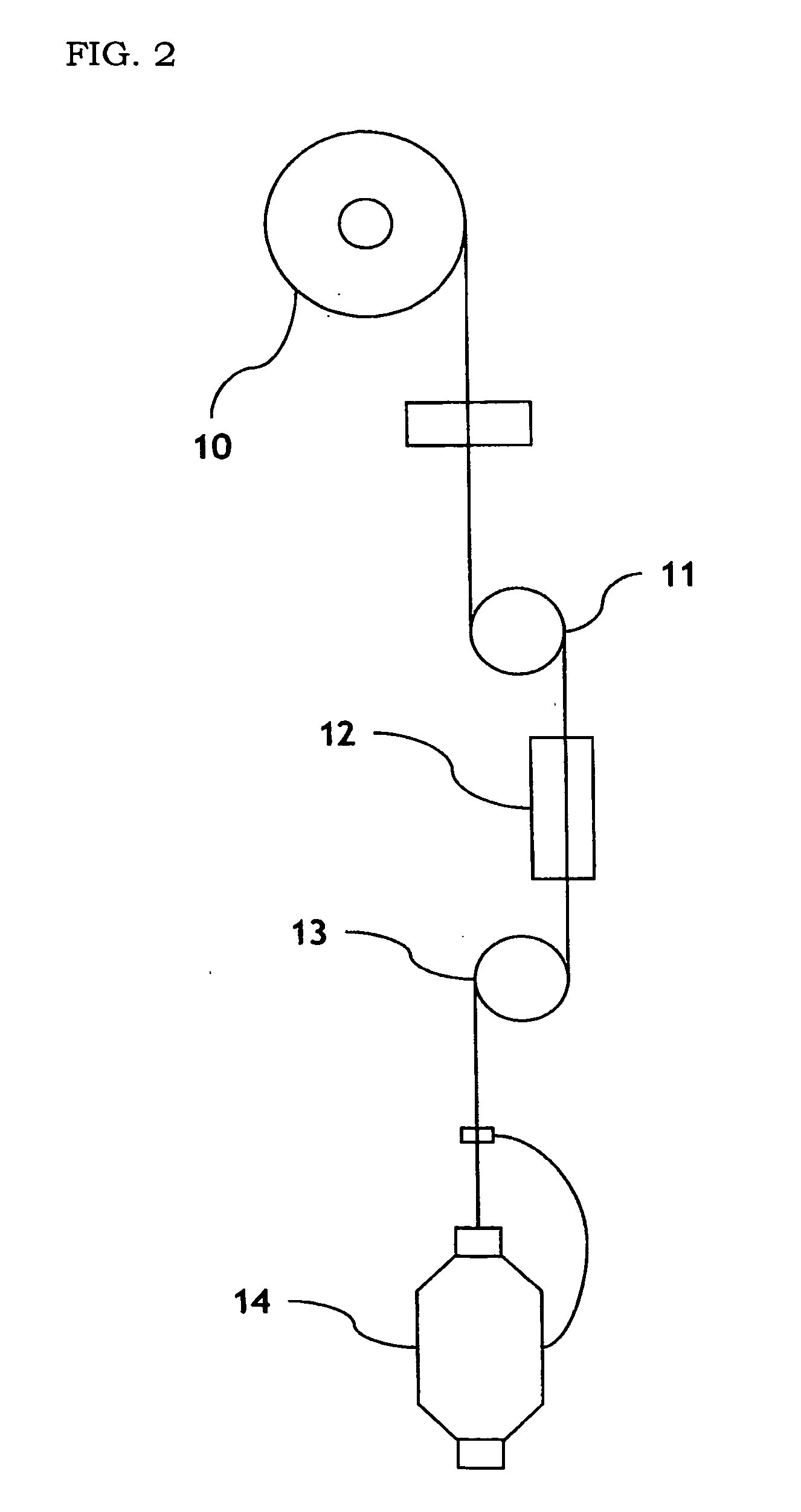
[0071] A polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 15,000 and a polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 25,000 are conjugated-spun in side by side type at a speed of 3,000 m / min at a temperature of 285° C. The resulting material is drawn and heat-treated at a draw speed of 650 m / min and at a drawn ratio of 1.68 in a drawing and heat treatment process as shown in FIG. 2, to prepare a side-by-side type conjugate (composite) filament having 100 deniers / 24 filaments. The drawing and heat-treatment temperature (hot plate temperature) is set to 132° C. so that the composite filament can satisfy the following physical properties.
[0072] Maximum thermal stress per denier: 0.21 g / denier
[0073] Temperature exhibiting maximum thermal stress (Tmax): 155° C.
[0074] Temperature area exhibiting 95% of maximum thermal stress (Tmax, 95%): 122 to 228° C.
[0075] Next, a five-harness satin with a warp density of 190 yarns / inch and a weft...
example 2
[0076] A polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 12,000 and a polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 25,000 are conjugated-spun in side by side type at a speed of 3,000 m / min at a temperature of 285° C. The resulting material is drawn and heat-treated at a draw speed of 650 m / min and at a drawn ratio of 1.68 in a drawing and heat treatment process as shown in FIG. 2, to prepare a side-by-side type conjugate filament having 100 deniers / 24 filaments. The drawing and heat-treatment temperature (hot plate temperature) is set to 140° C. so that the composite filament can satisfy the following physical properties.
[0077] Maximum thermal stress per denier: 0.31 g / denier
[0078] Temperature exhibiting maximum thermal stress (Tmax): 165° C.
[0079] Temperature area exhibiting 95% of maximum thermal stress (Tmax, 95%): 122 to 228° C.
[0080] Next, a five-harness satin with a warp density of 190 yarns / inch and a weft density of ...
example 3
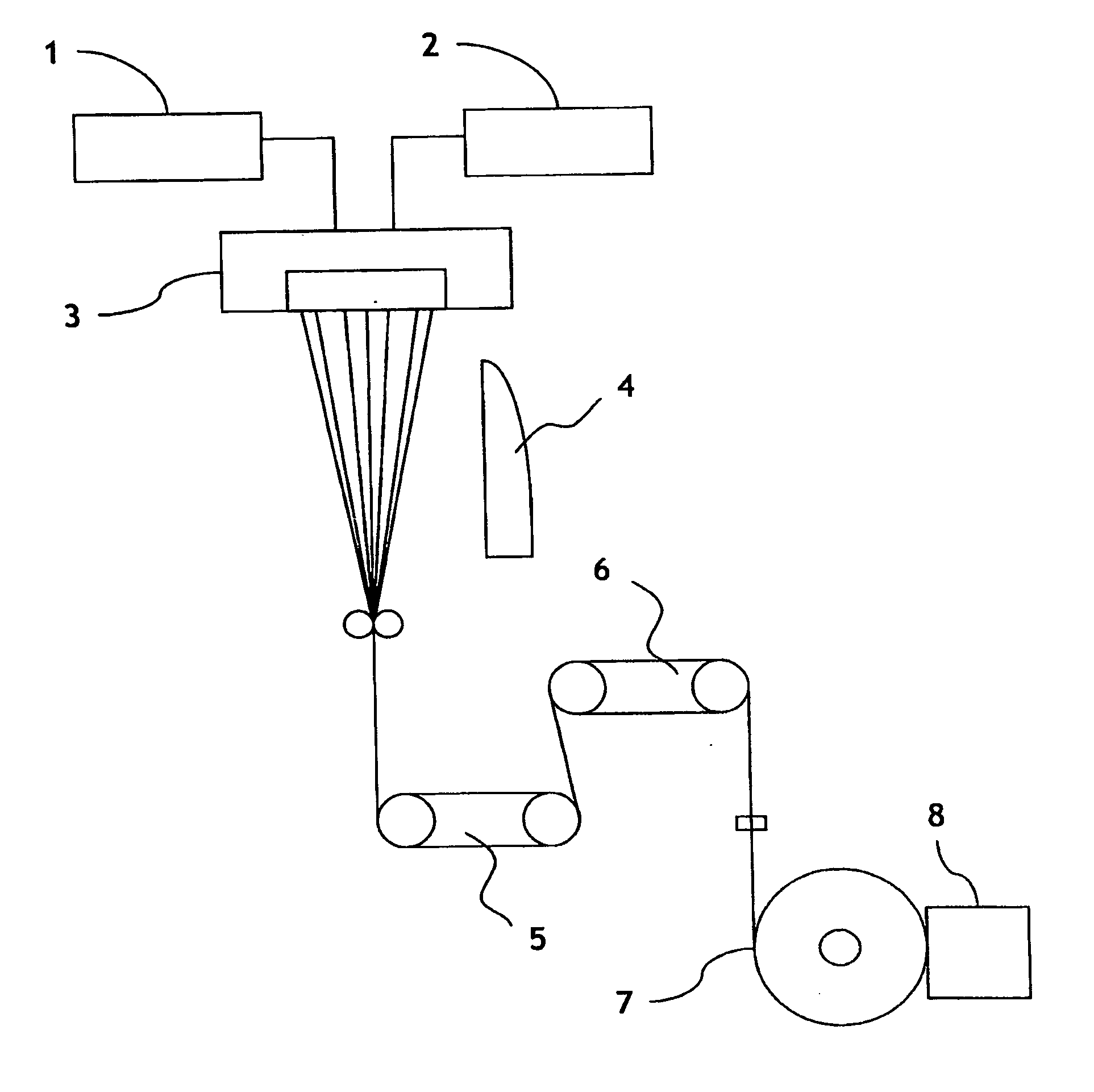
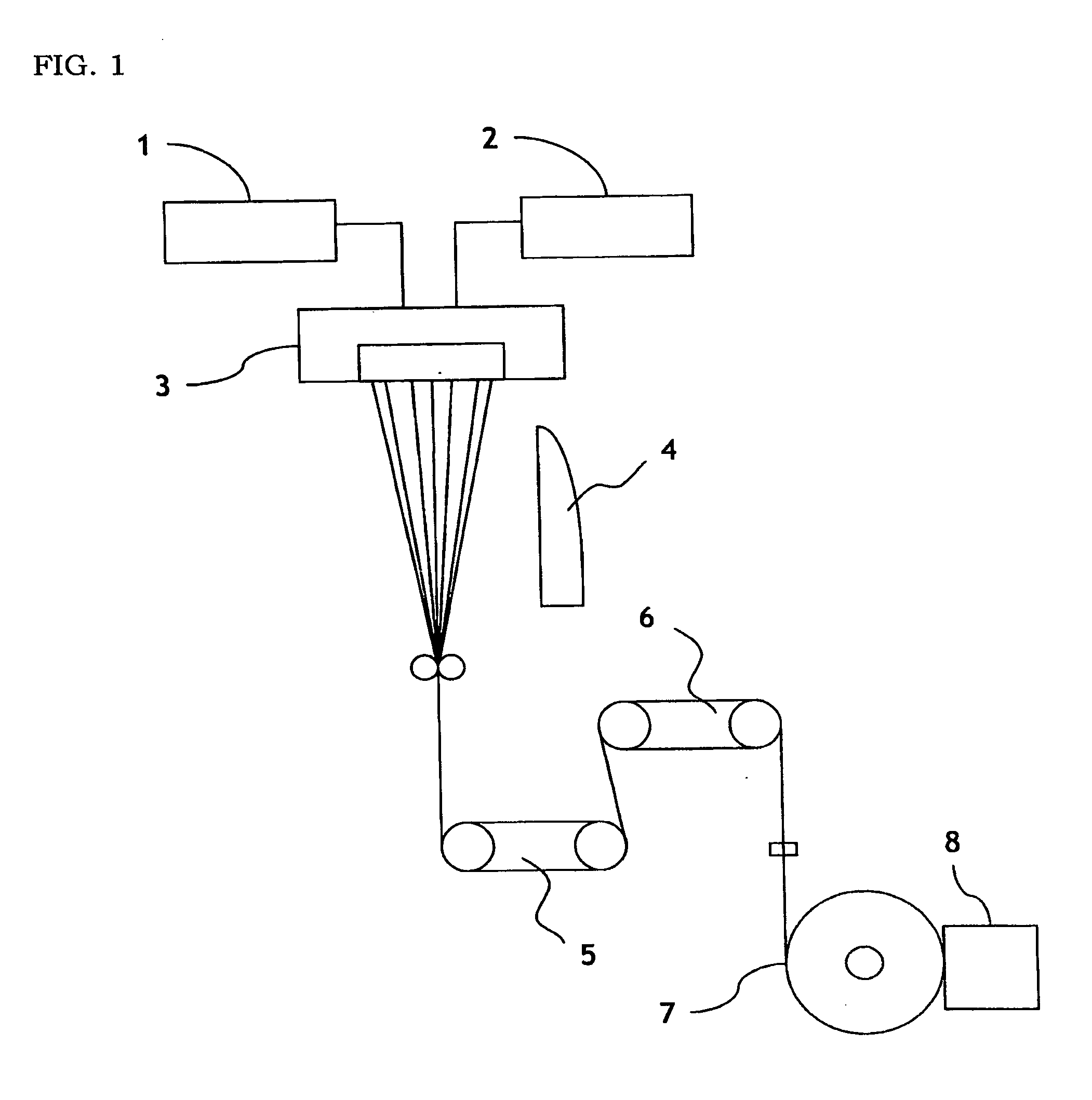
[0081] A polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 16,000 and a polyethylene terephthalate with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 28,000 are conjugated-spun in side by side type at a temperature of 290° C. The resulting material is drawn and heat-treated in a continuous drawing and baking process as shown in FIG. 1, to prepare a side-by-side type conjugate filament having 100 deniers / 24 filaments. The temperature of a first Godet roller is set to 82° C. and the speed thereof is set to 1,800 m / min. The speed of a second Godet roller is set to 4,815 m / min, the speed of a take-up roller is set to 4,800 m / min, and the temperature of the second Godet roller is set to 163° C., so that the conjugate filament can satisfy the following physical properties.
[0082] Maximum thermal stress per denier: 0.16 g / denier
[0083] Temperature exhibiting maximum thermal stress (Tmax): 175° C.
[0084] Temperature area exhibiting 95% of maximum thermal stress (Tmax, 95...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com